Bored piles are often used for a strong and functional foundation. This is a type of pile foundation, when concrete is poured into a hole made in the ground, in which a reinforcing frame is placed. On loose soils, special formwork or casing are used for strengthening. This technology is suitable for the construction of country houses and industrial facilities. It is used for work in urban areas, where vibration is contraindicated for surrounding buildings.
Description and Application
The technology of a bored foundation made of piles with a connecting grillage is described in the construction rules SP 50-102-2003. Several basic techniques for constructing bored foundations:
- Using a continuous auger (CSA) with simultaneous supply of concrete mixture from the bottom to the top of the well through a process valve.
- Protection against destruction of the walls of a hole in the ground by creating back pressure of bentonite solution.
- The use of casing pipes loaded and retrieved using vibratory hammers or a “dreiteller” (rotating loader).
According to each of the technologies, concrete is fed into the well, with reinforcement pre-installed in it, and set directly in the soil. On loose, moving, wet soils, in private construction, casing pipes are required to hold the concrete in the well. After the concrete mixture has hardened, the pipes are carefully removed or left as permanent formwork.
Bored piles are used when it is difficult to use other types of pile foundations:
- in the city, where noise from driving can have a negative impact on surrounding residents;
- on swampy, soft soils, when it is necessary to get to hard layers;
- when constructing structures on sites with a steep slope;
- in industrial construction.
A bored foundation must be made with a grillage, which is a frame made of reinforced concrete monolith connecting the pile heads. This is done to evenly distribute pressure on each element of the base. The result is a strong strip foundation with bored piles, which can be used on difficult soils.
Scope of foundation
The pile-grillage foundation is suitable for brick, frame, wooden and block houses.
It is advisable to install such foundations in areas with heaving, peaty and floating soils, in places with complex terrain, high groundwater levels, and in areas with increased seismic activity.
In addition, bored piles with monolithic grillages are erected:
- in conditions of dense urban development, when it is impossible to make driven piles due to dynamic and static effects on nearby buildings;
- during the construction of massive industrial structures;
- for wooden buildings or structures made using frame technology.
Piles are installed strictly vertically along the perimeter of buildings in corners, places where walls intersect, along the perimeter of external and internal load-bearing walls.
The distance between structures depends on the total mass of the object and is determined by calculations.
The grillage is mounted horizontally. It combines piles into a single structure and redistributes the loads from the structure to the ground.
The number of foundation piles is determined by design calculations.
It is advisable to install pile foundations with a grillage on complex terrain, with weak, heaving or deeply frozen soils.
Classification
The bored foundation is classified depending on the manufacturing technology. On clayey and other dense soils, the NPSH (continuous hollow auger) technique is used. The auger is a hollow pipe closed with a check valve that prevents the excavated soil from entering it. A strong spiral is attached to the pipe, lifting the soil to the surface like a classic drill. When the required depth is reached, concrete is fed into the pipe cavity under high pressure. It opens the valve, gradually filling the well as the auger rises upward. To make the bored pile stronger, a reinforcing frame is introduced into the concrete using a powerful vibrator. After pouring, the pile is left until the solution reaches the required strength.
The second technique is the installation of bored piles with a casing; this technology is used on unstable soils. The pipe protects wells from collapse when a reinforcing structure is introduced into it or excess pressure is applied to the poured solution. To do this, a well is drilled along the diameter of the pipe, which is placed into it by rotation, pressing, or simply installed there. After this, the drill is removed from the ground, and reinforcement is installed in the well so that a protective layer of concrete of about 60 mm is formed. Then the solution is poured with simultaneous compaction, and the casing is gradually removed from the well.
Concrete laying
Schematic representation of the constituent elements of a bored base.
After the drilling process is completed, the formwork and frame are constructed, the concrete mixture can be poured. Concrete is laid in layers with gradual compaction - bayoneting. Only a “heavy” solution is suitable for this. This term implies the use of the following "heavy" aggregates:
- quartz sand;
- crushed stone/gravel (hard rocks).
Concreting of each bored pile is carried out continuously. This means that the time interval between laying each layer should not exceed 1 hour. The process of complete setting of concrete is completed after 28 days, after which the resulting foundation structure can be loaded.
Features of the technology
In construction, bored foundations are becoming increasingly popular. This is explained by the advantages of this technology, which allows the construction of structures on almost any soil. Features of bored piles include:
- Wide range of application, possibility of use on both dense and unstable soils (heaving or loose soils, near water bodies).
- Fast construction of the foundation. Technology using bored piles makes it possible to complete all work faster than pouring a strip base or Swedish slab.
- Built in compliance with all standards, the foundation on bored piles will last at least 150 years.
- Simplicity of design due to the relatively small volume of excavation work; it is enough to drill wells.
- The ability to independently select the diameter and height of the supports, the type of reinforcement, depending on the properties of the soil and the design features of the building.
- Increased load-bearing capacity. Such a foundation can support the weight of multi-story, industrial buildings, and massive reinforced concrete structures.
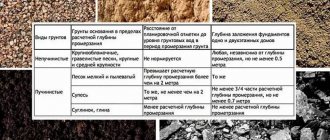
The diameter of the pile is selected in accordance with the current SNiP after geodetic surveys, taking into account climatic and geological features. Directly during design, the mass of the building, the number of supports are calculated and the type of soil is determined. Information on the bearing capacity of bored piles on different soils can be found in the table:
Bored foundation technology has disadvantages, which include:
- use of heavy equipment for drilling, installation of casing pipes, reinforcement at large construction sites;
- relative complexity of technological processes;
- the need for calculations.
Application of bored technology in private construction
Scheme for constructing a foundation using TISE technology
The technology for constructing bored structures is simple and suitable for constructing a foundation with your own hands. The construction industry has at its disposal various types of drills for wells with different sections. Their use helps to drill wells up to several meters deep.
The diameters of the piles can also be different: from 15 to 40 cm. The so-called TISE technology involves the use of a special drill, with which you can drill wells 20 cm in diameter with an expansion at the base (up to 40 or 60 cm). Thus, an increase in the support area is achieved, which does not allow heaving to push the pile out.
There are also special mechanisms (hole drills, motorized drills, etc.) that can significantly facilitate the installation of supports.
Construction of a bored foundation
This type of foundation is used not only in industrial, but also in private construction. Building a foundation on bored piles requires special equipment, but it is faster and cheaper than pouring the popular strip foundation. An important feature of a bored foundation is the possibility of its independent construction using hand-held or motorized drills.
Before starting work, you need to prepare the tools and materials:
- tape measure, a roll of cord, a set of pegs and a hammer for marking;
- drill for wells - manual, electrically driven or with an internal combustion engine;
- formwork made of roofing felt, plastic, reinforced concrete or asbestos cement, so that they can be left in the well; for industrial construction, removable casing pipes will be needed;
- reinforcement for supports and grillage;
- tools for preparing concrete mortar, cement, crushed stone, sand.
Necessary calculations
In order to correctly calculate the number of bored piles, it is necessary to determine the total mass of the building (weight of walls, floor slabs, communications, furniture, etc.). Considering that the piles are made of M300 concrete, with standard reinforcement, the load-bearing capacity of one bored pile can be found in the table:
| Pile diameter, mm | Support area, cm² | Load capacity, kg | Volume of concrete, m³ | Number of vertical bars of reinforcement, pcs. | Reinforcement consumption, linear m |
| 150 | 177 | 1062 | 0,0354 | 3 | 7 |
| 200 | 314 | 1884 | 0,0628 | 4 | 9 |
| 250 | 491 | 2946 | 0,0982 | 4 | 10 |
| 300 | 707 | 4242 | 0,1414 | 6 | 14 |
| 400 | 1256 | 7536 | 0,2512 | 8 | 18 |
Using portable drills, you can prepare wells with a diameter of up to 200 mm, which is why they are most often used in private construction.
To calculate the depth of the support, you need to find out the depth of soil freezing in the area and add 20 centimeters. For example, if freezing reaches 1.3 m, then bored piles are immersed to a depth of 1.5 m. On heaving, loose, swampy and mobile soils, additional research will be required, and when deepening it will be necessary to get to layers with hard rock.
To calculate the number of piles, you will need to divide the mass of the building by the load-bearing capacity of one support, and multiply the result obtained by an error factor of 1.2. It takes into account possible inaccuracies when determining the mass of the grillage, furniture, and snow load.
Preparation and marking
The foundation layout begins with a diagram of the pile field, which indicates the placement of bored supports. To do this, at the corners of the site, to make sure that it is rectangular, you need to measure the diagonals, they must be equal.
The first four bored piles are installed in the corners, the rest should be evenly distributed under the load-bearing walls. In the places where the wells will be made, pegs are driven in.
According to the technology, the distance between bored piles with a grillage should not exceed 2 m, but not less than 3 pile diameters, so as not to disturb the soil structure.
Installation
After the preparatory stages, you can begin installing bored piles with your own hands. Using a manual, mechanical or electric drill, we drill holes to a given depth, according to the markings.
Prefabricated reinforcement cages are lowered into the wells and casing pipes are installed. They can be made of metal, plastic, roofing felt, asbestos, reinforced concrete. In private construction, they serve as permanent formwork for future bored piles. The main condition is precise vertical installation in level.
The space between the casing pipes and the well is filled with soil, which is periodically compacted. In this case, it is necessary to control the verticality of the pipe. The height of the piles is checked with a hydraulic or laser level so that the piping is horizontal. If the pipes are higher, they are cut off, the reinforcement cage remains as the basis for tying the grillage together.
M300 grade concrete mortar is poured into the prepared formwork, which is compacted with a manual tamper or vibrator. The poured bored piles are left until the cement has completely set within 2-3 weeks.
Pouring the grillage
To achieve maximum strength, the bored foundation is connected with a grillage - a reinforced concrete strip or frame. It distributes pressure evenly on all piles. The construction of the grillage is similar to the construction technology of a standard strip foundation. The only difference is that its lower part is suspended, without resting or going deep into the ground. The basis of the grillage is the pile heads raised above the ground to the design height.
The width of the grillage is equal to the thickness of the load-bearing walls, the height for wooden and foam concrete walls is equal to the width. For stone and brick buildings - 50% more width. The grillage is poured in several stages:
- formwork is installed in the form of a box, in which holes are made for piles and future utilities;
- a monolithic grillage must be reinforced according to the requirements for reinforced concrete structures, the frame is connected to the protruding reinforcement of bored supports;
- a concrete mixture is poured into the formwork, which must set completely, then the formwork is dismantled;
- The surface is waterproofed with a roofing felt tape folded in two layers, or with coating compounds.
Bored or screw piles: which is better?
When building on subsiding, swampy and soft soils, both bored and screw foundations are used. It is difficult to unequivocally answer the question of what is best.
It is believed that screw piles are a more reliable structure that can withstand high design loads. Their installation is faster than the installation of bored piles; they are immediately ready to bear the full load, and no additional time is required for the solution to harden.
Bored piles.
Screw piles are subject to repair, but the process is considered simple. They can also be reused if necessary. But at the same time, they have a significant disadvantage compared to a bored foundation - they are more expensive.
Advice from professionals
Despite the fact that you can make a bored foundation yourself, during construction there are many aspects known only to experienced builders who share their experience. To avoid mistakes during construction, pay attention to the following points:
- carefully study the type of soil, for which it is better to perform geodetic reconnaissance, taking into account the information received when selecting the diameter and depth of installation of piles;
- for private construction, do not use supports with a diameter of more than 200 mm, since their installation will require special equipment, which will make the foundation more expensive;
- when pouring casing pipes, part of the reinforcement should protrude to the height of the future grillage to give it additional strength;
- the grillage can be poured only after the mortar in the bored piles has completely set;
- the distance between the bottom of the grillage and the ground surface should not be less than 150 mm so that it does not deform during swelling.
The construction of foundations from bored piles is a technology that is gaining popularity. It allows you to create a durable and inexpensive foundation for both private houses, light structures, and industrial buildings on any soil. The costs of constructing such a foundation are lower than those of constructing a classic strip foundation, buried below the freezing level of the soil, by an average of 40%. Strength and durability indicators remain comparable.
Partial and complete formwork construction
Arrangement of formwork for the bored base of the building
Next, the formwork is installed in the drilled well. But its function can be performed by the soil itself, if it is dense enough and does not crumble. Then only the upper part of the formwork structure is exposed to make pile caps.
So, the formwork can be the soil itself, drilled with a tip of 200-250 mm to 90 and up to 150 mm in depth, taking into account the condition of the soil. If, due to the characteristics of the soil, it has to be dug up, then metal or asbestos-cement pipes of the appropriate cross-section can be used as formwork. When constructing a bored foundation with your own hands, you can roll up the roofing material, turning it into something like a pipe.
In order to prevent the bored foundation from being squeezed out during seasonal swelling, its head, which is located half a meter (or more) below ground level, must be insulated with a galvanized steel roofing cover, several layers of film or roofing felt.
Experts call this cover a “shirt,” which is recommended to be made to cover the entire depth of the pile. The reasoning for performing this action is as follows. The rising soil “slides over or lifts the installed protection, leaving the base itself motionless.” In addition, the “jacket” prevents cement lait from flowing into the ground, and accordingly, the strength characteristics of concrete do not decrease.
Requirements for creating a high-quality grillage foundation
Since the main loads on the grillage are bending forces, one of the key points when creating a grillage foundation is reinforcement, which significantly increases the strength of the structure.
Reinforcement diagram Source stroidominvest.ru
The second significant point concerns the hardening time of the concrete structure - which is a whole month. The grillage will be able to withstand the proper loads only after the concrete has completely hardened.
Calculation
For high-quality installation, it is necessary to calculate the bored foundation. At a minimum, the following characteristics must be assessed:
- determine the type of soil, for construction purposes the typology is given in SNiP II-15-74;
- calculate the load, that is, calculate the mass that will put pressure on the base;
- select piles based on their load-bearing capacity and their number, while taking into account the maximum intersupport - 2 m;
- determining the amount of resources.
To select the desired type and design, it is advisable to consult professional designers.
Installation: step by step instructions
- At the initial stage, the construction site is cleared and the fertile layer of soil is removed. Compact the soil and mark out the pile field. The outlines of the future grillage are indicated using a cord and pegs.
- Then they begin drilling wells. To do this, use a hand drill. It is screwed into the ground strictly vertically. The wells should be 5-7 cm wider than the cross-section of the support.
- The bottom of the well is compacted and covered with a gravel-sand layer 10-25 cm thick.
- The casing is then lowered into the well. Typically, products made from asbestos cement, plastic, and metal are used. There are specialized casing pipes on the market that are equipped with connecting mechanisms for joining. After installation, the voids between the walls of the well and the pipe are tightly filled with soil.
- Then proceed to reinforcement. Usually a scheme of 4 or 6 rods is used. The diameter of the reinforcement cage should be 3-5 cm narrower than the cross-section of the pipe. The reinforcement is connected using wire and clamps. The length of the reinforcement cage should be 0.3 m longer than the casing pipe. The reinforcing skeleton is installed inside the pipe so that it does not touch its walls.
- After this, concrete is poured into the well through a special funnel. The brand of the mixture must be at least B-12.5. A funnel is necessary to avoid the formation of hollow balls inside the concrete. Pouring is carried out in a slow mode, layer by layer - 50 cm, each time compacting the poured layer with a deep vibrator.
- After pouring the piles, you must wait a week. This time is necessary for the concrete solution to consolidate inside the supports. Then you can install the grillage.
- The grillage is installed on a cushion of a mixture of gravel and sand 0.1-0.2 m thick.
- This layer is also covered with concrete preparation and then covered with waterproofing material. Roll waterproofing is usually used.
- Then they begin to install the formwork.
- The reinforcement is installed in the prepared form. The reinforcement frame is connected to rods protruding from the supports.
- The process of constructing a bored foundation with a grillage is completed by pouring concrete. The same class of mixture is used as for piles. Tamping with a deep vibrator is required. If the weather outside is dry and the air temperature is above 26 degrees, then the grillage must be periodically watered to protect the concrete from drying out and cracking. Polyethylene placed on top will also protect the foundation.
- The concrete curing period is 28 days. It is after this time that the foundation will gain its strength. It is strictly forbidden to start building walls before this date.
What is a grillage type pile foundation?
Such a foundation is a structure of piles buried in the ground below the freezing depth of the soil, and connected at the top using a metal or concrete strip (grillage). The supports can be combined by one common slab located at ground level or slightly above. The structure, built in accordance with all the rules, is reliable and has a long service life - several decades.
Concrete grillage Source domsdelat.ru
Here you can clearly see what a foundation grillage is - this is the entire upper part of any pile foundation, which is also called the “cap”. The purpose of the grillage is to evenly distribute the load from the load-bearing elements of the structure onto the piles and, accordingly, onto the ground.
There are several types of grillage:
- Made. It consists of separate elements, which are a structure of three piles reinforced with a welded frame. To install them, you will need a crane.
Prefabricated grillage from beams Source orchardo.ru
- Monolithic reinforced concrete. It is a solid plate or strip. Poured directly at the construction site.
Monolithic cast reinforced concrete grillage Source 24stroim-dom.by
- Prefabricated monolithic. An intermediate option, made from prefabricated parts, which in turn are assembled in a factory, and are already cemented in place using locks and key connections.