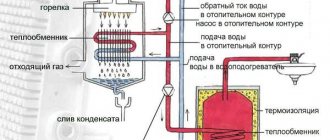
Hot water supply to a private home is an important engineering system, the arrangement of which always remains a pressing issue. This is a necessary condition in order to fill the house with coziness and make it comfortable for living. The installation of modern water heaters successfully solves the problems of hot water supply and heating in a private home, and for this it is no longer necessary to have powerful electrical wiring, gas or a chimney. All you need is to familiarize yourself with the operating principles of various systems, select a suitable scheme, and, if desired, you can carry out the installation yourself.
Factors affecting boiler operation
They are:
- Design. The equipment may have 1 or 2 circuits. It can be mounted on a wall or on the floor.
- Normative and actual efficiency.
- Proper heating arrangement. The power of the equipment is comparable to the area that needs to be heated.
- Technical conditions of the boiler.
- Gas quality.
Question about the design.
The device may have 1 or 2 circuits. The first option is complemented by an indirect heating boiler. The second one already has everything you need. And the key mode in it is the provision of hot water. When water is supplied, heating ends.
Models mounted on the wall have less power than those placed on the floor. And they can heat a maximum of 300 sq.m. If your living space is larger, you will need a floor-mounted unit.
P.2 efficiency factors.
The document for each boiler reflects the standard parameter: 92-95%. For condensation modifications it is approximately 108%. But the actual parameter is usually 9-10% lower. It decreases even more due to heat losses. Their list:
- Physical underburning. The reason is excess air in the apparatus when gas is burned, and the temperature of the exhaust gases. The larger they are, the more modest the efficiency of the boiler.
- Chemical underburning. What is important here is the volume of CO2 oxide produced when carbon is burned. Heat is lost through the walls of the apparatus.
Methods for increasing the actual efficiency of a boiler:
- Removing soot from pipelines.
- Elimination of scale from the water circuit.
- Limit chimney draft.
- Adjust the position of the blower door so that the coolant reaches its maximum temperature.
- Removing soot from the combustion compartment.
- Installation of a coaxial chimney.
P.3 Questions about heating. As already noted, the power of the device necessarily correlates with the heating area. A competent calculation is needed. The specifics of the structure and potential heat losses are taken into account. It is better to entrust the calculation to a professional.
If the house is built according to building codes, the formula works: 100 W per 1 sq.m. This results in a table like this:
| Area (sq.m.) | Power. | ||
| Minimum | Maximum | Minimum | Maximum |
| 60 | 200 | 25 | |
| 200 | 300 | 25 | 35 |
| 300 | 600 | 35 | 60 |
| 600 | 1200 | 60 | 100 |
It is better to purchase foreign-made boilers. Also in advanced versions there are many useful options that help you achieve the optimal mode. One way or another, the optimal power of the device is in the spectrum of 70-75% of the highest value.
The optimal operating mode of a gas boiler to save gas is achieved by eliminating clocking. That is, you need to set the gas supply to the lowest value. The attached instructions will help with this.
Adjustment
Automatic control is provided by the heating regulator.
It includes the following parts:
- Computing and matching panel.
- Actuating device on the water supply section.
- An actuator that performs the function of mixing liquid from the returned liquid (return).
- Boost pump and sensor on the water supply line.
- Three sensors (on the return line, on the street, inside the building). There may be several of them in the room.
The regulator closes the liquid supply, thereby increasing the value between return and supply to the value specified by the sensors.
To increase the flow, there is a boost pump and a corresponding command from the regulator. The incoming flow is controlled by a "cold bypass". That is, the temperature decreases. Some of the liquid that has circulated along the circuit is sent to the supply.
Sensors collect information and transmit it to control units, resulting in a redistribution of flows that provide a rigid temperature scheme for the heating system.
Sometimes, a computing device is used that combines hot water and heating regulators.
The hot water regulator has a simpler control scheme. The hot water sensor regulates the flow of water with a stable value of 50°C.
Advantages of the regulator:
- The temperature scheme is strictly maintained.
- Elimination of overheating of the liquid.
- Fuel and energy efficiency.
- The consumer, regardless of the distance, receives heat equally.
Heat exchanger features
Let's figure out why a heat exchanger is needed. In the device, two different media share thermal energy. Hot water in one container gives off its temperature to the cold liquid, which moves in another container. And the simplest example is a system of two steel pipes of different diameters.
Cold water moves less. A small section of this pipe is placed in another, larger diameter. The latter contains hot water. And after a short time, the temperatures of both liquids become equal.
In order for the process to proceed steadily and constantly, the water is forced to move (circulate). And giving the flows certain speeds allows you to minimize all heat losses. Moreover, only one energy source is used to heat two systems at once.
This arrangement significantly increases the autonomy of the home. And eliminating unnecessary equipment from operation allows you to be less dependent on network resources. Thereby reducing energy costs in the home.
Stainless steel heat exchanger Source s-ip.com.ua
The performance of the entire system is affected by:
- Device model (design).
- Temperature regime.
- State of the system.
The last point relates to the amount of heat loss. The surface of the pipes through which the liquid moves is responsible for this. If scale has formed on the walls, the heat transfer of the system is significantly reduced. The latter is also influenced by other factors, including simple fat deposits.
In the fight against losses, prevention of blockages and contamination comes first. The heating heat exchanger is equipped with filters that filter out foreign particles and suspension. Also, at certain intervals, the device must be completely cleaned of scale and other deposits. To do this, it is disassembled and washed using special means.
See also: Catalog of companies that specialize in engineering systems (heating, water supply, sewerage and others) and related work
Table with temperature graph
The operating mode of boilers depends on the environmental weather.
If we take various objects, for example, a factory building, a multi-storey building and a private house, they will all have an individual thermal diagram.
In the table we show the temperature diagram of the dependence of residential buildings on outside air:
| Outdoor temperature | Temperature of network water in the supply pipeline | Return water temperature |
| +10 | 70 | 55 |
| +9 | 70 | 54 |
| +8 | 70 | 53 |
| +7 | 70 | 52 |
| +6 | 70 | 51 |
| +5 | 70 | 50 |
| +4 | 70 | 49 |
| +3 | 70 | 48 |
| +2 | 70 | 47 |
| +1 | 70 | 46 |
| 70 | 45 | |
| -1 | 72 | 46 |
| -2 | 74 | 47 |
| -3 | 76 | 48 |
| -4 | 79 | 49 |
| -5 | 81 | 50 |
| -6 | 84 | 51 |
| -7 | 86 | 52 |
| -8 | 89 | 53 |
| -9 | 91 | 54 |
| -10 | 93 | 55 |
| -11 | 96 | 56 |
| -12 | 98 | 57 |
| -13 | 100 | 58 |
| -14 | 103 | 59 |
| -15 | 105 | 60 |
| -16 | 107 | 61 |
| -17 | 110 | 62 |
| -18 | 112 | 63 |
| -19 | 114 | 64 |
| -20 | 116 | 65 |
| -21 | 119 | 66 |
| -22 | 121 | 66 |
| -23 | 123 | 67 |
| -24 | 126 | 68 |
| -25 | 128 | 69 |
| -26 | 130 | 70 |
There are certain standards that must be observed in the creation of projects for heating networks and the transportation of hot water to the consumer, where the supply of water steam must be carried out at 400°C, at a pressure of 6.3 Bar. It is recommended that the heat supply from the source be released to the consumer with values of 90/70 °C or 115/70 °C.
Regulatory requirements must be met in compliance with the approved documentation with mandatory approval from the Ministry of Construction of the country.
Link to download the chart
- 110 - for industrial premises of categories B, D and D with emissions of flammable dust and aerosols;
- 130 - for industrial premises without the release of flammable dust and aerosols.
The maximum temperature, °C, of the heating surface should be taken as follows:
- c) for low-temperature panels for radiant heating of workplaces - 60.
- d) for high-temperature radiant heating devices - 250.
- e) for building structures with built-in heating elements:
- — 26 — for floors of rooms with constant occupancy;
- — 30 — for bypass paths, benches of swimming pools;
- — 31 — for floors of premises with temporary occupancy;
- - 28, 30, 33, 36, 38 for ceilings with a room height not exceeding 2.8, 3.0, 3.5, 4 and 6 m, respectively.
Risers and liners
Risers are responsible for the vertical distribution of water in apartments located one above the other. The connections perform the function of distributing liquid through taps and other plumbing fixtures inside the apartment.
In apartments, serial (tee) wiring is traditionally used. The collector type is more material-intensive and requires hidden installation of connections, which greatly complicates their further maintenance.
DHW systems are divided into two types:
- centralized,
- local (decentralized).
In centralized systems, a heating installation in a central heating point (centralized heating point) can serve one or more buildings within a microdistrict or village. Centralized circuits are designed and installed with circulation pipelines for uninterrupted supply of hot water. Without them, in the absence of water supply in the supply pipelines, the water cools down, and the consumer is forced to drain it, which leads to excessive water consumption on the meter. In addition, heated towel rails are installed, which cannot work in the absence of circulation.
Decentralized (local) hot water supply is used in cases where the construction of a centralized scheme is not economically profitable: with a low density of heat loads in rural settlements, etc.
DHW schemes are:
- With a dead-end pipeline, where, with low consumption or no water withdrawal, the water quickly cools down. This scheme is used in low-rise residential buildings with a short network, bath and laundry plants.
- With circulation risers. Similar schemes are used in multi-storey residential buildings and hotel complexes.
What happens when hot water is turned on simultaneously at two points of intake
The scheme becomes more complicated if, while using hot water at one point of intake, it becomes necessary to turn it on at another point, for example: when the shower is turned on in the bathroom, it becomes necessary to wash your hands in the toilet washbasin. In this case:
- the rate of hot water use increases sharply, its consumption increases,
- weak pressure of hot water appears;
- the flow of cold water into the boiler increases,
- a drop in the temperature of the boiler heat exchanger leads to the fact that the water temperature at the first intake point ceases to be comfortable,
- a few seconds are required to turn on the boiler automation for heating,
- a few more seconds for both users at two points of collection to be able to use water at a comfortable temperature.
All this time, both users cannot fully use hot water. It arrives intermittently. The unproductive consumption of water, which goes uselessly into the sewer system, increases sharply.
What if one of the users turned off the water? In this case, the consumption of hot water drops sharply. A temperature jump occurs on the heater of a double-circuit gas boiler. As a result, the temperature of hot water increases sharply at the point of intake that continues to operate. The user cannot fully use the water; it goes down the drain until the automation on the boiler is activated and water at the required temperature begins to flow to the user in a stable manner.
Since such situations are repeated several times every day, the unproductive consumption of hot water increases every day. At the same time, we should not forget about the discomfort that users experience when the supply of hot water is unstable.
Where does hot water supply to a private home begin?
Before you begin installing hot water supply in a private home, you need to decide on some parameters of this system.
First of all, you need to figure out what kind of plumbing fixtures you will use, in what quantity and where you will place the equipment. As a rule, this is a sink, bathtub, shower cabin, washbasin, jacuzzi, bidet, etc.
After you have decided where you will place the plumbing, you need to allocate a place in a private house for installing water heating equipment. To do this, it is necessary to take into account the technical capabilities of the device. Experts recommend placing it at the same distance from hot water consumers.
Then the pipes and all related fittings are selected. As a rule, pipes with a diameter of 15 or 20 mm are suitable for internal wiring. For these purposes, galvanized or non-galvanized pipes are used, as well as products made of metal-plastic, polyethylene or polypropylene. Polypropylene pipes are the most popular. You will need a certain number of fittings, couplings and other elements that must be purchased in the required quantities in accordance with the wiring plan for the hot water supply system of a private home.
Next, you should select equipment for preparing hot water.
Today, there are a large number of companies that will quickly help solve the problem of providing hot water supply to a private home, and will also provide the equipment necessary for water purification. These procedures are mandatory, since in private houses, as a rule, the water sources are wells, artesian wells, etc., and the water in them, as a rule, has a composition that is far from ideal. Therefore, such water cannot be used not only for cooking, but also in hot water supply systems. This is due to the fact that it contains salts of calcium, magnesium and other elements, due to which the water becomes harder.
Read material on the topic: Communications in a private home
Heating system water temperature
- In the corner room +20°C;
- In the kitchen +18°C;
- In the bathroom +25°C;
- In corridors and stairwells +16°C;
- In the elevator +5°C;
- In the basement +4°C;
- In the attic +4°C.
It should be taken into account that these temperature standards refer to the heating season and do not apply to the rest of the time. Also, it will be useful information that hot water should be from +50°C to +70°C, according to SNiP-u 2.08.01.89 “Residential buildings”. There are several types of heating systems: Contents
- 1 With natural circulation
- 2 With forced circulation
- 3 Calculation of the optimal temperature of the heating device 3.1 Cast iron radiators
- 3.2 Aluminum radiators
- 3.3 Steel radiators
- 3.4 Warm floor
With natural circulation The coolant circulates without interruption.
Design and installation
Before concluding a contract, the company’s engineers visit the site and make the necessary measurements and studies. Based on them, an engineering project is made. It is a package of documents that includes:
- technological calculations
- graphic documents (diagrams and detailed drawings);
- specification of basic and consumable materials, as well as equipment;
- estimate documentation.
The work schedule and cost of turnkey water supply installation are determined. After agreeing on the project with the customer or his representative, work on the installation of pipelines and other equipment is carried out. Celsis installers comply with technological and sanitary standards and work carefully and quickly. Upon completion of installation work, appropriate tests are carried out and all elements are checked for leaks. At all stages of work, quality monitoring is carried out by process engineers.
High professionalism and modern technical equipment allow Celsis to maintain reasonable prices for installation of water supply and sewerage systems, even in times of crisis. We guarantee our work and do it conscientiously. The company has developed relationships with suppliers of quality equipment, so you will be offered an option that is best suited for your home. You can order installation services right now - our managers are always at your service.
Reviews about the company
Coordination of coolant and boiler temperatures
Regulators help coordinate the temperature of the coolant and the boiler.
These are devices that create automatic control and adjustment of return and supply temperatures. The return temperature depends on the amount of liquid passing through it. Regulators cover the liquid supply and increase the difference between the return and supply to the level required, and the necessary indicators are installed on the sensor.
If the flow needs to be increased, a boost pump can be added to the network, which is controlled by a regulator. To reduce the heating of the supply, a “cold start” is used: that part of the liquid that has passed through the network is again transported from the return to the inlet.
The regulator redistributes the supply and return flows according to the data collected by the sensor, and ensures strict temperature standards for the heating network.
Use a recirculation pump
The best option is that the water heater is located in close proximity to the hot water intake points. The closer it is, the faster the hot water enters the tap, the more efficiently it is used. If this option for installing a water heater is not possible, then it is recommended to install a recirculation pump.
The pump is installed in the section between the water heater and the hot water intake points, ensuring the slow movement of hot water through the pipes. In addition, if you install a heated towel rail in this section, it will perform its direct function at any time of the year, regardless of the operation of the heating circuit of the boiler.
What is the difference between heating flow and return?
And so, let’s summarize the differences between supply and return in heating:
- Supply – coolant that flows through water pipes from a heat source. This could be an individual boiler or central heating of the house.
- Return water is water that, having passed through all the heating radiators, goes back to the heat source. Therefore, at the input of the system there is supply, and at the output there is return.
- It also differs in temperature. The feed is hotter than the return.
- Installation method. The water conduit that is attached to the top of the battery is the supply; the one that connects to the bottom is the return line.
After installing the heating system, it is necessary to adjust the temperature regime. This procedure must be carried out in accordance with existing standards.
Requirements for coolant temperature are set out in regulatory documents that establish the design, installation and use of engineering systems of residential and public buildings. They are described in the State Building Codes and Rules:
- DBN (V. 2.5-39 Heat networks);
- SNiP 2.04.05 “Heating, ventilation and air conditioning.”
For the calculated supply water temperature, the figure is taken that is equal to the water temperature at the outlet of the boiler, according to its passport data.
For individual heating, deciding what the coolant temperature should be should take into account the following factors:
- The beginning and end of the heating season based on the average daily outdoor temperature of +8 °C for 3 days;
- The average temperature inside heated premises of housing, communal and public importance should be 20 °C, and for industrial buildings 16 °C;
- The average design temperature must comply with the requirements of DBN V.2.2-10, DBN V.2.2.-4, DSanPiN 5.5.2.008, SP No. 3231-85.
According to SNiP 2.04.05 “Heating, ventilation and air conditioning” (clause 3.20), the coolant limit values are as follows:
Depending on external factors, the water temperature in the heating system can be from 30 to 90 °C. When heated above 90 °C, dust and paintwork begin to decompose. For these reasons, sanitary standards prohibit greater heating.
To calculate optimal indicators, special graphs and tables can be used, which define standards depending on the season:
- With an average reading outside the window of 0 °C, the supply for radiators with different wiring is set at 40 to 45 °C, and the return temperature at 35 to 38 °C;
- At -20 °C, the supply is heated from 67 to 77 °C, and the return rate should be from 53 to 55 °C;
- At -40 °C outside the window, all heating devices are set to the maximum permissible values. On the supply side it is from 95 to 105 °C, and on the return side it is 70 °C.
What elements does the water supply scheme of an apartment building include?
The water metering unit, which organizes the supply of water to the house, is responsible for several functions:
- It takes into account the consumption of cold water supply, that is, it acts as a water meter;
- It can shut off the supply of cold water to the house in emergency situations or when it is necessary to repair components and parts, as well as to eliminate leaks;
- Serves as a filter for coarse water purification: any hot water supply scheme for an apartment building should contain such a mud filter.
The device itself consists of the following components:
- A set of shut-off valves (taps, valves and valves) at the inlet and outlet of the device. Standardly these are gate valves, ball valves, valves;
- Mechanical water meter, which is installed on one of the risers;
- Mud filter (filter for coarse water purification from large solid particles). This could be a metal mesh in the housing, or a container in which solid debris settles to the bottom;
- Pressure gauge or adapter for inserting a pressure gauge into a water supply circuit;
- Bypass (bypass from a section of pipe), which serves to turn off the water meter during repairs or for data verification. The bypass is equipped with shut-off valves in the form of a ball valve or valve.
Heating point
It is also an elevator unit that performs the following functions:
- Ensures full and continuous operation of the heating system in an apartment building, and also regulates its parameters;
- It delivers hot water to the house, that is, it provides hot water supply (hot water supply). The coolant itself in the heating system enters the hot water supply system of the apartment building directly from the centralized heating main;
- The heating point can switch the hot water supply between return and supply. This may be necessary during severe frosts, since at this time the temperature of the coolant on the supply pipe can rise to 130-1500C, and this despite the fact that the standard supply temperature should not exceed 750C.
The main element of a heating point is a water-jet elevator, where hot water from the working fluid supply pipeline circuit in the house is mixed in a mixing chamber with the return coolant by injection through a special nozzle. Thus, the elevator allows a larger volume of low-temperature coolant to pass through the heating circuit, and, since injection is carried out through a nozzle, the supply volume is small.
Adapters for connecting DHW can be inserted between the valves at the inlet of the route and the heating station - this is the most common connection scheme. The number of inserts is two or four (one or two each on the supply and return). Two inserts are typical for old houses; in new buildings, four adapters are practiced.
On the cold water supply route, a dead-end tie-in scheme with two connections is usually used: the water metering unit is connected to the bottling, and the bottling itself is connected to the risers through which pipes are routed to apartments. Water will move in such a cold water supply system only during disassembly, that is, when opening any mixers, taps, valves or valves.
Disadvantages of this connection:
- If there is no water supply to a particular riser for a long time, the water will remain cold for a long time when drained;
- Heated towel rails embedded in the DHW inlets from the boiler rooms, which simultaneously heat the bathroom or toilet, will only be hot when the DHW is drawn from a specific riser in the apartment. That is, they will almost always be cold, which will cause the appearance of moisture on the walls, mold or fungal diseases of the building materials of the room.
A heating station with four hot water connections in the house makes the circulation of hot water continuous, and this happens through two bottlings and risers connected to each other by jumpers.
Important: if mechanical water meters are installed on the hot water taps, then the water supply consumption will be taken into account without taking into account the water temperature, which is incorrect, since you will have to overpay for hot water that was not used.
Hot water supply can operate in three ways:
- From the supply pipe to the return pipe to the boiler room. Such a hot water system is effective only in the warm season when the heating system is turned off;
- From supply pipe to supply pipe. Such a connection will bring maximum benefits in the demi-season - autumn and spring, when the coolant temperature is low and far from maximum;
- From the return pipe to the return pipe. This DHW scheme is most efficient in extreme cold, when the temperature at the supply pipe rises to ≥ 750C.
For continuous movement of water, a pressure difference is required between the starting and ending points of insertion into one circuit, and this difference is ensured by limiting the flow. This limiter is a special retaining washer - a steel pancake with a hole in the middle. Thus, the water that is transported from the inlet to the elevator encounters an obstacle in the form of a washer body, and this obstacle is regulated by a rotation that opens or closes the retaining hole.
But too much restriction of the movement of water in the pipeline route will disrupt the operation of the heat station, so the retaining washer should have a diameter 1 mm larger than the diameter of the heat station nozzle. This size is calculated by representatives of the heat supplier so that the temperature at the return heating pipe of the elevator unit lies within the standard temperature limits.
What is pipe filling and riser
These are pipes laid horizontally and carried through the basement of a residential building, which connect the risers to the heating station and water meter. Bottling of cold water supply is done in single copies, bottling of hot water supply - in duplicate.
The diameter of the DHW or cold water filling pipes can be 32-100 mm, and depends on the number of connected consumers. For any water supply scheme, ø 100 mm is too large, but this size is taken taking into account not only the actual condition of the route, but also taking into account the size of salt deposits and rust on the inner walls of metal pipes.
A vertical pipe riser distributes water to the apartments located above it. The standard layout of such wiring includes several risers - for cold and hot water supply, and sometimes separately for heated towel rails. More wiring options:
- Several groups of risers passing through one apartment and providing water to water points located at a great distance from each other;
- A group of risers in one apartment that supplies water to a neighboring apartment or several apartments;
- When organizing hot water supply, pipe jumpers can be used to connect up to seven groups of risers across apartments. The lintels are equipped with Mayevsky taps. This is called a circulation pipeline, or CTP.
The standard diameter of cold and hot water supply pipes for risers is 25-40 mm. Racks for heated towel rails and single risers are mounted from ø 20 mm pipes. Such risers provide both one-pipe and two-pipe home heating systems.
Closed hot water system
The constant circulation of water in a closed hot water supply system is based on the principle of taking cold water from the pipeline and supplying it to the heat exchanger. After heating, the water is supplied to the distribution system throughout the apartment. The working fluid in the heating system and hot water for the technical needs of consumers are separated, since the coolant may have toxic inclusions to improve its heat transfer qualities. In addition, hot water pipes rust faster. Such a scheme is called closed because the consumer uses the heat, and not the coolant itself.
Pipe liner
The main function of the connections is to distribute water to the water collection points in the apartment. The standard diameter of the supply pipes is 15 mm, the grade of pipes is DU15, the material is steel. For PVC or metal-plastic pipes, the diameter should be the same. When repairing or replacing the liner, it is not recommended to use a smaller diameter so as not to change the design pressure parameters that the hot or cold water supply circulation system must comply with.
To organize the correct wiring, tees are most often used; for more complex wiring schemes, manifolds are used. The collector supply requires hidden installation, so the collector should be installed when servicing a large number of rooms in the house. After 10-15 years, metal pipes become overgrown from the inside with salt mineral deposits and rust, so preventive work to restore the system’s functionality consists of cleaning the pipes with steel wire, or replacing old pipes with new ones.
Given the apparent functionality and durability of PVC or metal-plastic pipes, it is recommended to use steel products for liners - they withstand water shocks and temperature changes well. Such deviations in the DHW operating mode can often be observed when the heating system is turned on or turned off in an emergency. Pipe material should be included in the plan for the water supply scheme of a residential building at the stage of drawing up the project and estimate.
What pipe products are recommended for use in cold and hot water supply schemes with constant water circulation:
- Galvanized metal pipes - they have been used for many decades, and they have proven themselves to be the best. The zinc layer on the metal prevents corrosion from developing and does not retain salt deposits. When purchasing galvanized products, you should remember that welding work is not carried out on such a surface, since the weld seam will remain unprotected by zinc - all connections must be made on threads;
- Pipe connections on fittings for soldering copper connections last much longer than steel and even galvanized pipes. Such connections with a solder connection do not need to be maintained, and they can be laid in both open and hidden ways;
- Corrugated pipe line for cold or hot water supply made of stainless steel. Such products are simply and quickly mounted on threaded connections or compression fittings. No special equipment other than two adjustable wrenches is required for this. The guaranteed service life of stainless steel is not limited by the manufacturer. The only thing that will have to be changed over time is the silicone seals.
Dependence of coolant temperature on outside air temperature
The specific table of the relationship between outdoor temperature and coolant depends on factors such as climate, boiler room equipment, and technical and economic indicators. Reasons for using a temperature schedule The basis for the operation of each boiler house serving residential, administrative and other buildings during the heating season is a temperature schedule, which indicates the standards for coolant indicators depending on what the actual outside temperature is.
- Drawing up a schedule makes it possible to prepare the heating for a drop in outside temperature.
- It also saves energy resources.
ATTENTION! In order to control the temperature of the coolant and have the right to recalculate due to non-compliance with the thermal regime, a heat sensor must be installed in the centralized heating system
Malfunctions
Main malfunctions of the water supply system valve:
- when closed, it allows water to pass through,
- liquid flows through the rod,
- presence of leakage through threaded connections.
The causes of malfunctions are wear of the rubber valve gasket, seat shell, worn rod threads, worn out stuffing box, weak seal of threaded connections.
If a mixer with a ceramic axle box begins to make noise, then the cause is a sagging silicone washer. It is best to replace the ceramic valve axle with the same new one or an analogue.
Lever mixers make virtually no noise, but if this does happen, the only solution is to normalize the pressure in the system. To do this, reducers are installed in front of the mixer, which limit the pressure, then the noise stops. A similar approach can be used to eliminate noise in a hygienic shower mixer.
The video shows how to correctly calculate the cost of hot water.
Optimal water temperature in a gas boiler
Usually a lattice fence is installed that does not impede air circulation. Cast iron, aluminum and bimetallic devices are common. Consumer choice: cast iron or aluminum The aesthetics of cast iron radiators is the talk of the town.
They require periodic painting, since the rules require that the working surface of the heating device have a smooth surface and allow dust and dirt to be easily removed. A dirty coating forms on the rough inner surface of the sections, which reduces the heat transfer of the device. But the technical parameters of cast iron products are excellent:
- are slightly susceptible to water corrosion and can be used for more than 45 years;
- have high thermal power per section, therefore they are compact;
- are inert in heat transfer, so they smooth out temperature changes in the room well.
Another type of radiator is made of aluminum. A single-pipe heating system can be vertical or horizontal. In both cases, air pockets appear in the system. The system inlet temperature is maintained at a high temperature to warm all rooms, so the piping system must withstand high water pressure. Two-pipe heating system The principle of operation is to connect each heating device to the supply and return pipelines. The cooled coolant is sent through the return pipeline to the boiler. Additional investments will be required during installation, but there will be no air pockets in the system. Temperature standards for premises In a residential building, the temperature in corner rooms should not be lower than 20 degrees, for interior spaces the standard is 18 degrees, for showers - 25 degrees.
How is it calculated
A control method is selected, then a calculation is made
The calculated winter and reverse order of water supply, the amount of outside air, and the order at the break point of the diagram are taken into account. There are two diagrams: one of them considers only heating, the second considers heating with hot water consumption
For an example of calculation, we will use the methodological development of Roskommunenergo.
The input data for the heat generating station will be:
- Tnv – the value of outside air.
- TV - indoor air.
- T1 – coolant from the source.
- T2 – reverse flow of water.
- T3 – entrance to the building.
We will look at several heat supply options with values of 150, 130 and 115 degrees.
At the same time, at the exit they will have 70°C.
The results obtained are compiled into a single table for subsequent construction of the curve:
So, we have three different schemes that can be used as a basis. It would be more correct to calculate the diagram individually for each system. Here we examined the recommended values, without taking into account the climatic features of the region and the characteristics of the building.
To reduce energy consumption, it is enough to select a low temperature setting of 70 degrees and uniform heat distribution throughout the heating circuit will be ensured. The boiler should be taken with a power reserve so that the system load does not affect the quality operation of the unit.
Protection against low coolant temperature in the return of a solid fuel boiler.
What will happen to a solid fuel boiler if its return temperature is below 50 °C? The answer is simple - a tarry coating will appear on the entire surface of the heat exchanger. This phenomenon will reduce the performance of your boiler, make it much more difficult to clean, and most importantly, can lead to chemical damage to the walls of the boiler heat exchanger. To prevent such a problem, it is necessary to provide appropriate equipment when installing a heating system with a solid fuel boiler.
The task is to ensure the temperature of the coolant that returns to the boiler from the heating system at a level not lower than 50 °C. It is at this temperature that the water vapor contained in the flue gases of a solid fuel boiler begins to condense on the walls of the heat exchanger (transition from a gaseous state to a liquid one). The transition temperature is called the “dew point”. The condensation temperature directly depends on the moisture content of the fuel and the amount of hydrogen and sulfur formations in the combustion products. As a result of a chemical reaction, iron sulfate is obtained - a substance useful in many industries, but not in a solid fuel boiler. Therefore, it is quite natural that manufacturers of many solid fuel boilers remove the boiler from warranty if there is no return water heating system. After all, here we are not dealing with the burning of metal at high temperatures, but with chemical reactions that no boiler steel can withstand.
The simplest solution to the problem of low return temperature is to use a thermal three-way valve (anti-condensation thermostatic mixing valve). The thermal anti-condensation valve is a thermomechanical three-way valve that ensures the admixture of coolant between the primary (boiler) circuit and the coolant from the heating system in order to achieve a fixed boiler water temperature. In essence, the valve releases the coolant that has not yet been heated in a small circle and the boiler heats itself. After reaching the set temperature, the valve automatically opens the coolant to the heating system and operates until the return temperature again drops below the set values.
Solid fuel boiler piping - Anti-condensation valve
Elements
Is a water metering unit a piping unit for a water supply network? consisting of shut-off valves, measuring instruments and fittings. The elevator unit is an element of the heating system that allows you to reduce the temperature of the coolant supplied from the thermal power plant to the set level.
The heating elevator mixes high-temperature coolant from the thermal power plant and cooled coolant from the return heating line of an apartment building.
Briefly about return and flow in the heating system
The water heating system, using a supply from the boiler, supplies heated coolant to the radiators, which are located inside the building. This makes it possible to distribute heat throughout the house. Then the coolant, that is, water or antifreeze, having passed through all available radiators, loses its temperature and is supplied back for heating.
The most simple heating structure consists of a heater, two lines, an expansion tank and a set of radiators. The conduit through which heated water from the heater moves to the batteries is called the supply. And the water conduit, which is located at the bottom of the radiators, where the water loses its original temperature and returns back, will be called return. Since water expands when heated, the system provides a special tank. It solves two problems: a supply of water to saturate the system; accepts excess water, which is obtained during expansion. Water, as a heat carrier, is directed from the boiler to the radiators and back. Its flow is ensured by a pump, or natural circulation.
Supply and return are present in one and two pipe heating systems. But in the first there is no clear distribution into the supply and return pipes, and the entire pipe line is conditionally divided in half. The column that leaves the boiler is called the supply, and the column that comes out from the last radiator is called the return.
In a single-pipe line, heated water from the boiler flows sequentially from one battery to another, losing its temperature. Therefore, at the very end the batteries will be the coldest. This is the main and probably the only disadvantage of such a system.
But the single-pipe version will have more advantages: lower costs for purchasing materials are required compared to a 2-pipe; the diagram looks more attractive. It is easier to hide the pipe, and you can also lay pipes under doorways. The two-pipe system is more efficient - two fittings are installed in parallel into the system (supply and return).
This system is considered more optimal by experts. After all, its work revolves around supplying hot water through one pipe, and cooled water is discharged in the opposite direction through another pipe. In this case, the radiators are connected in parallel, which ensures uniform heating. Which of them establishes the approach must be individual, taking into account many different parameters.
There are only a few general tips to follow:
- The entire line must be completely filled with water; air is a hindrance; if the pipes are airy, the heating quality is poor.
- It is necessary to maintain a sufficiently high fluid circulation rate.
- The difference in supply and return temperatures should be about 30 degrees.
Use an expansion tank
In winter, when the boiler's heating circuit is activated, any activation of hot water results in the heating circuit being turned off so that the hot water supply circuit can turn on. In the summer, when the boiler's heating circuit is not activated, each turn on of the hot water leads to the gas boiler turning on.
Often the user opens the hot water tap to simply rinse his hands. The boiler turns on or switches, hot water flows through the pipes. But the user may simply not wait for it, washing his hands with cold water.
Meanwhile, frequent and useless turning on and switching of the boiler “eats up” its operating life. A possible solution is to install a small expansion tank. It is installed in front of the water heater. If there is such a tank, for the first time after turning on the tap, hot water enters the pipe exclusively from the water heater due to the increase in pressure in the tank. Thus, in case of short-term use of hot water, there is no need to turn on and switch the boiler.
It is recommended to use a tank designed for hot water supply. Using a tank intended for heating will cause an odor because its membrane is made of rubber.
Optimal values in an individual heating system
Autonomous heating helps to avoid many problems that arise with a centralized network, and the optimal temperature of the coolant can be adjusted according to the season.
In the case of individual heating, the concept of standards includes the heat transfer of a heating device per unit area of the room where this device is located. The thermal regime in this situation is ensured by the design features of the heating devices. It is important to ensure that the coolant in the network does not cool below 70 °C. 80 °C is considered optimal
With a gas boiler, it is easier to control heating, because manufacturers limit the ability to heat the coolant to 90 °C. Using sensors to regulate the gas supply, the heating of the coolant can be adjusted.
It is a little more difficult with solid fuel devices; they do not regulate the heating of the liquid, and can easily turn it into steam. And it is impossible to reduce the heat from coal or wood by turning the knob in such a situation. Control of heating of the coolant is quite conditional with high errors and is carried out by rotary thermostats and mechanical dampers.
Electric boilers allow you to smoothly regulate the heating of the coolant from 30 to 90 °C. They are equipped with an excellent overheat protection system.
The influence of temperature on the properties of the coolant
In addition to the factors described above, the temperature of the water in the heating pipes affects its properties. This is the basis of the operating principle of gravity heating systems. As the heating level of water increases, it expands and circulation occurs.
However, if antifreeze is used, exceeding the normal temperature in the radiators can lead to different results. Therefore, for heating with a coolant other than water, you should first find out the permissible heating rates. This does not apply to the temperature of central heating radiators in the apartment, since such systems do not use antifreeze-based liquids.
Antifreeze is used if there is a possibility that low temperatures will affect radiators. Unlike water, it does not begin to change from a liquid to a crystalline state when it reaches 0°C. However, if the heat supply operation exceeds the norms of the temperature table for heating to a greater extent, the following phenomena may occur:
- Foaming
. This entails an increase in the volume of coolant and, as a result, an increase in pressure. The reverse process will not be observed when the antifreeze cools; - Formation of limescale
. Antifreeze contains a certain amount of mineral components. If the heating temperature in the apartment is violated, they begin to precipitate. Over time, this will lead to clogged pipes and radiators; - Increasing the density index.
Malfunctions of the circulation pump may occur if its rated power was not designed for such situations.
Therefore, it is much easier to monitor the water temperature in the heating system of a private home than to control the degree of heating of antifreeze. In addition, when evaporating, ethylene glycol-based compounds emit gas that is harmful to humans. Currently, they are practically not used as a coolant in autonomous heat supply systems.
What to consider when organizing hot water supply for a private home
As a rule, the installation of any water heating device in a private home is carried out by a professional, since this requires preparing a suitable diagram, obtaining permission, and installing ventilation or a chimney if such a need arises.
If you use plastic pipes, the installation process is greatly simplified due to their durability and strength, and these products do not require the use of a welding machine. You should purchase fittings, silicone, tow, spare fasteners for pipes and batteries. You also need a set of tools, consisting of a special soldering iron, scissors, a hammer drill, a screwdriver, a level and a hammer, several types of keys, pliers, metal snips, etc.
The hanging boiler should be located at a distance of at least 50 cm from the ceiling. Reliable fasteners are used for it and radiators. When you set up a boiler room, it is recommended to cover the walls and floor with fire-resistant tiles and do not forget to provide free access to the water heater for periodic maintenance.
It is also necessary to install a chimney and ventilation system. You will also need a circulation pump; it is quite compact and capable of providing constant pressure, as a result of which the water quickly heats up.
If you are working with plastic pipes, you will need an assistant, since the connection is instantaneous and distortions must be avoided. Radiators are installed at the very last moment.
Make sure they are at the same level. The distance to the floor should be from 10 to 15 cm, from the wall - from 2 to 5 cm. By installing shut-off valves and temperature sensors, you can control the water temperature and shut it off if necessary.
If you do not have the necessary installation skills, it is better to turn to professionals. It is important to perform the correct calculations. The first thing you will need to do to properly install the hot water supply of a private house with your own hands is a diagram.
Read material on the topic: How to choose water supply pipes so that they last a long time