In order not to get confused in all types of foundations and soils, let's try to figure everything out in order. First, we will analyze the types of monolithic strips, and then specifically for each type of strip foundation we will determine the depth of installation.
Factors influencing the depth of strip foundations
It’s probably worth starting with the fact that the strip foundations themselves are divided into three main types:
- Non-buried
- Shallow
- Recessed
Each of these types is laid to a certain depth, which depends on several main factors:
- Soil freezing depth
- Soil type
- Ground water level
It is worth noting that the depth of a strip foundation is the distance from the surface of the soil to the base of the foundation, and not the depth to which the trench is dug. In addition to the foundation, there may be a cushion in the trench.
Now let's figure out how these factors affect each type of strip foundation separately.
Formula for determining value
To correctly determine the depth of the tape, you must first calculate the GPP in the area. Calculations are made according to the formula: Df=kx Dfn, where:
- Dfn – standard indicator of GPP;
- Df – calculated indicator of GPP;
- K – coefficient taking into account the influence of heating.
After the calculations have been made, the properties of the soil are determined at the site where the foundation will be located, for which soil samples are taken. This procedure is best left to professionals.
Then they calculate at what depth the groundwater is located. This is done by drilling a hole up to 3 m deep, into which a tube is lowered, which is used to measure the liquid level at different times of the year. A similar procedure is necessary to determine whether groundwater is capable of rising above 2 m to the GLP.
Based on the data obtained, the depth can be calculated using Table 2 of SNiP 2.02.01-83.
Non-buried strip foundation
A non-buried strip foundation is used extremely rarely in the construction of private houses, because it is a very weak support for the future structure. As a rule, it is all located on top of the ground, and inside there is only a sand or sand-gravel cushion.
I won’t write much about the non-buried strip foundation, especially since a whole article was already devoted to it earlier. And in general, such a foundation does not have the very concept of depth.
Features of foam block material
Foam concrete blocks are made from cellular concrete by pouring it into special forms. The resulting layers are cut into elements suitable for building houses.
Types of foam blocks
The material is divided into three types depending on density. For private construction the following are relevant:
- structural elements of grades D1000-1200;
- structural and thermal insulation blocks of grades D900-500;
- thermal insulation segments of grades D500-300.
The high density of foam concrete allows the construction of a two-story building with a reinforcing belt.
Properties of building materials
Foam block buildings are becoming relevant for owners of suburban areas. This is facilitated by the properties of the material:
- a unique “breathable” structure, thanks to which sweating of the walls is eliminated;
- the ability to retain heat in winter and provide coolness in summer;
- profitability - due to heat conservation, home heating costs are eliminated;
- good sound insulation;
- environmental cleanliness;
- ease of processing and strength of walls.
Low cost elements based on sand, water, cement and special foam. Small costs for construction consumables allow you to invest more money in arranging a high-quality foundation for your home.
What is the load of foam block buildings?
Compared to buildings made of bricks, foam block buildings are lighter. If a square meter of a brick wall weighs 1.8 tons, then foam blocks have a mass of 0.9. Therefore, it would be inappropriate to construct massive foundations. For a dwelling made of foam block, a monolithic strip, slab or pile base is sufficient. Regardless of the type of foundation, it is worth considering the criteria for its construction and design.
Calculation of the depth of laying shallow strip foundations
This is the most capricious foundation in terms of depth. Firstly, it is not as reliable as a buried one, and secondly, in order for such a strip foundation to withstand the load of the structure, and also to restrain all heaving forces transmitted from the ground, its calculation must be approached with special responsibility.
I have already described in detail how to pour a shallow strip foundation in one of the previous articles. Therefore, we will not go into details.
Such a strip foundation is laid at a depth that is significantly higher than the depth of soil freezing, which is why it is called shallow. Unlike a buried one, it can be significantly affected by soil heaving forces.
Also, an important difference between shallow foundations is that it must be made monolithic not only below the ground level, but also immediately, after placing the formwork, pour the above-ground part of the foundation - the base. This will greatly strengthen the entire strip foundation.
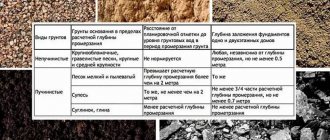
The depth of a shallow foundation directly depends on all three factors described above. In order not to get confused, let's look at the table.
Table No. 1: Depth of laying a shallow strip foundation (minimum), depending on the type and depth of soil freezing
| Soil freezing depth, m | depth , m | |
| The soil is slightly heaving | Non-heaving soil, hard rocks | |
| more than 2.5 | — | 1,5 |
| 1,5 — 2,5 | 3.0 or more | 1,0 |
| 1,0 — 1,5 | 2,0 — 3,0 | 0,8 |
| less than 1.0 | less than 2.0 | 0,5 |
| Note: In order to find out what the depth of soil freezing in your region, look below at table No. 2, which gives values for some cities, taking into account the type of soil. Click on the table to enlarge. | ||
Table No. 2: Soil freezing depth in some regions
Note: In addition to the fact that the depth of laying a strip foundation is influenced by the depth of freezing and the type of soil, you should not ignore another very important factor - the groundwater level, which we will discuss further.
Dependence of the depth of the strip foundation on the groundwater level (GWL)
There are two options for the location of groundwater - when it is located below the depth of soil freezing, and when it is located above.
The groundwater level is below the soil freezing depth
This can be considered a good indicator, and in this case, groundwater in most types of soil does not have a particular effect on the depth of installation of a monolithic reinforced concrete strip.
The only limitation, in this case, is that in soils such as loams, clays and the like, the tape must be laid at least half the freezing depth of such soil. In other, “good” soils, this factor does not affect the laying of the foundation.
In other words, if the freezing depth in your region is, say, 1.5 meters, then a shallow strip foundation must be built at least 0.75 meters deep.
The groundwater level is above the soil freezing depth
If the groundwater is located high, then the depth of digging a trench for a strip foundation does not depend on its level only on rocky soils, coarse-grained sand, gravel and the like.
On any other types of soil, with high groundwater level, the monolithic tape will have to be buried below the freezing depth by 10-20 cm (). In this case, it will become a buried foundation.
Average values for different types of buildings
Another indicator that should be taken into account when calculating is soil resistance. For the main types of soil it is as follows
- dry dense clay – 1.6-3.0;
- coarse sand – 3.6-4.6;
- medium-grained – 2.5-3.6;
- fine-grained – 2.2-3.4;
- sandy loam – 2.6-3.6;
- loam – 1.6-3.0;
- gravel, crushed stone, pebbles – 5.1-6.5.
After this, you need to determine the weight pressure of the building. For main building structures these indicators are as follows (in kg/cm2):
- plank walls with insulation – 30-50;
- log – 80-120;
- expanded clay concrete – 460-580;
- brick – 570-970;
- overlap on wooden beams – 120-160;
- basement – 170-300;
- reinforced concrete – 320-550.
By calculating the weight of the building and comparing the result with the calculated soil resistance, you can determine whether a strip foundation is suitable for your building. It also happens that you have to think about how to make the building lighter or choose a different type of foundation. We provided a complete example of calculating a strip foundation here.
Recessed strip foundation
A recessed strip foundation is considered the most reliable of all strips. It is laid 10-20 cm below the freezing depth of the soil. Another condition for its construction is that the soil under its base must be more or less hard.
In the case of swampy soils, peat bogs and the like, the strip foundation is laid at a depth that is below these layers. In some cases, it is enough to dig a trench to hard soil, and then build a sand or sand-gravel bed to a level that is just below the freezing depth of the soil in your region.
When the soil on a construction site is very bad for laying a strip foundation, or its installation requires enormous costs, you can try to calculate another type of foundation, for example, a slab foundation. Perhaps it will be both cheaper and more reliable.
Selection of formwork
Do-it-yourself formwork for a strip foundation without monolithic concrete preparation
The speed of the pouring work as a whole depends on the formwork arrangement. It is economical to choose a non-removable option. But for 2 floors, the best option would be block formwork made of metal or a modular option made of plastic.
The design of such equipment allows you to work in a pit without any problems, and it can be assembled in just a few days.
Many developers are in a hurry to dismantle the formwork; this should not be done. You will break off the edges of the unset concrete. You can speed up the process by adding an additive or plasticizer to the concrete, but in winter you will have to do this anyway.
For small volumes of concreting up to 20 cubic meters, it is better to make the formwork yourself from boards and timber, but in other cases it is cost-effective to rent it.
How to reduce the depth of a strip foundation
After all the calculations have been made regarding the depth of the strip foundation, it often happens that, taking into account the soil and the region, it needs to be laid very deep. This raises the question of how to reduce costs and reduce depth.
There are several ways to reduce the depth of strip foundations, all of them are based on reducing the importance of the main factors affecting the foundation.
Reducing the depth of soil freezing
We, of course, will not be able to change the climate in the region, but we will be able to change the depth of freezing, specifically under the base of the foundation, by insulating the foundation itself and the soil adjacent to it from the outside.
This way we can reduce the depth of the foundation, as well as reduce costs.
Drainage of groundwater from strip foundation
Another effective way to reduce the depth of a strip foundation is to drain water from it.
This is done by installing a good drainage system, which will remove a significant part of the water from the foundation and prevent it from having a detrimental effect on it.
Sand or sand-gravel cushion under the foundation
In the case where the heaving layers of soil lie deep enough in the area, the strip foundation will also have to be laid to a greater depth. It can be reduced by replacing the heaving soil with a sand or sand-gravel cushion.
In other words, it is necessary to dig a deep trench down to hard ground rocks, and then place a massive sand and gravel cushion there, which will distribute the load from the foundation and the house onto the ground evenly and will not allow heaving forces to have a detrimental effect on the foundation.
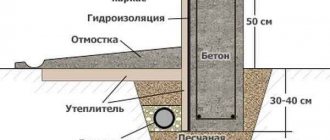
It is advisable to make a pillow not only under the base of the foundation, but also next to it, as shown in the diagram.
It is worth noting that the most reliable method of reducing the depth of a strip foundation is a combined method, i.e. and the installation of a pillow, and insulation, as well as a drainage device, if necessary.
Columnar base
This type of base is good for use on a small budget.
Pillars as a foundation for a house are the most budget-friendly solution, so they are often used for garage construction or for a one-story country house.
They are made from blocks, bricks or by pouring into formwork. Thanks to the use of technological materials, this type of base is time-consuming.
Waterproofing and a sand cushion are laid at the base of each pillar. Supporting elements are placed in places of the greatest vertical load: the corners of the house and the intersection of load-bearing walls of the structure. It is very important that the pillars are strictly vertical. With this type of foundation, the depth of the foundation for a one-story brick house is no more than 0.8 m, of which 30 cm is the cushion and waterproofing, and 0.5 m is the height of the pillar.
Mistakes and mistakes
The main mistake is neglecting accurate calculations, using average numbers and foundation parameters “like your neighbor’s.”
If you cannot calculate the depth and width of the tape yourself, contact a professional, but you cannot build a building without an accurate calculation.
The second mistake is saving on the quality of materials . It leads to deterioration of the characteristics of the foundation, and this will affect the reliability of the entire house.
Third, neglect of geological research. There is a big difference in bearing capacity between soil types, and the type and parameters of the foundation directly depend on it. There is no room for error here.
Construction stages
The first stage of construction is marking the site, strictly according to the drawing of the future foundation. Marking is carried out using pegs with string stretched over them.
Next - earthworks . The depth and width of the trench should be 15-20 cm greater than the base parameters - this is necessary for arranging a cushion, installing formwork, and bedding.
The third stage is the production of formwork. To simplify the process and make the base warmer and protect it from freezing, you can use permanent formwork made of polystyrene foam.
After installing the formwork, reinforcement is installed in the trench and a cushion of sand or crushed stone is poured. Further:
- pouring concrete,
- its solidification,
- dismantling removable formwork.
The last stage is waterproofing, thermal insulation of the base, if permanent formwork was not used.
Common mistakes and ways to avoid them
Laying a sand cushion without compaction. This leads to uneven subsidence of the pillars and deformation of the strip part. It is necessary to compact the soil under the pillow and the pillow itself.- Unevenness of the trench bottom is allowed. As a result, the thickness of the concrete pour is uneven and it dries unevenly. To avoid this, you should use construction laser levels when laying a trench.
- Dig trenches and leave them for several days . As a result, the earth crumbles from the walls and creates differences at the bottom. You need to dig and fill the holes in one day.
Advantages and disadvantages of LF, operating conditions
It is not difficult to understand why the strip foundation is so named - everything is clear from its geometry. The base is a reinforced concrete strip, which is built around the perimeter of the future house.
The tape exactly repeats the layout of the house, including the bay window, internal load-bearing walls, veranda, and so on. Due to this design, the foundation evenly distributes the load from the walls.
A traditional strip foundation is built from concrete, which is poured into prepared formwork. The tape must be reinforced with metal rods, creating a lattice from them.
Due to the device, such a base has many advantages:
A simple design that does not require heavy equipment for construction - ordinary tools are enough to do all the excavation work, make formwork and concrete mortar, right on the site.- Relatively low cost - due to the small footprint compared to a slab foundation, for example.
- The ability to withstand high loads - on such a foundation you can build a two-story brick house.
- Frost resistance.
- Possibility of construction without the involvement of work crews.
- Fast construction.
But the strip foundation also has certain disadvantages. First of all, it is only suitable for dense, non-heaving soils.
If the soil is heaving, it is possible to build a strip foundation, but its depth and width of the base will be much greater, which complicates the construction. If the soil has weak bearing capacity, a strip base is not suitable .
The second, relative disadvantage is its own large mass, to which is added the weight of the house. If calculated incorrectly, this leads to subsidence of the building.