This allows you to completely isolate the interior from the penetration of cold. Thermal insulation is a guarantee that the heat will remain inside the house, and heating costs will be significantly lower.
Choosing insulation for the foundation
The answer to the question of how to insulate the foundation of a house from the outside is ambiguous. Modern stores offer a wide range of materials. When choosing, they are guided by the type of soil on which the building is erected, the climatic conditions of the region, as well as the degree of load on the structure. There are five insulation products that have an optimal price-quality ratio.
Expanded polystyrene
Expanded polystyrene or polystyrene foam is an inexpensive, practical material. It is widely used for thermal insulation of various structures, including foundations.
Among its advantages are:
- ease of installation;
- light weight;
- excellent thermal insulation qualities;
- foam does not absorb moisture;
- does not shrink during operation;
- does not lose its properties under the aggressive influence of salt or chlorinated water, acids, alkalis;
- it can be used together with mastics, lime, plaster and other materials.
Expanded polystyrene comes in the form of large rectangular sheets. It cuts easily with a regular knife. Therefore, even a novice master can handle its installation.
A significant disadvantage of expanded polystyrene is its low strength. It is damaged even by minor mechanical impacts. Therefore, such material needs additional protection, for example, brick lining.
For heat and moisture insulation of the foundations of houses, it is better to purchase polystyrene foam with a thickness of at least 50 mm. Its average price across the country varies from 2,500 to 3,000 rubles per cubic meter. Service life – up to 40 years.
Extruded polystyrene foam
Extruded polystyrene foam (EPS) is a type of foam. During its production, another technological process is added - extrusion. Thanks to this, the characteristics of the material are improved.
EPPS has the following properties:
- high density;
- complete impermeability to moisture and steam;
- sufficient strength;
- chemical and biological inertness.
- light weight.
To insulate the foundation, a 40 mm thick EPS slab is sufficient. It is mounted using adhesive or disc dowels.
The most popular brands of EPPS are Penoplex and TechnoNIKOL. The cost of a cubic meter of such material varies from 4,500 to 5,000 rubles. The service life, subject to installation technology, is 50 years.
Polyurethane foam
Polyurethane foam (PPU) is a liquid insulation material that is applied to the base using a special sprayer. It hardens quickly, forming a durable coating.
Compared to polystyrene foam and EPS, it has the following advantages:
- when using polyurethane foam, a continuous surface without joints is obtained, which increases the thermal insulation characteristics of the material;
- the product fills cavities and cracks that exist in the concrete foundation, which prevents its destruction;
- easy to apply on complex shaped surfaces;
- has high adhesive properties.
PPU is resistant to aggressive environmental conditions. It can withstand sudden temperature changes, does not deform, and does not release toxic substances into the air.
The price for two canisters of PU foam components weighing 50 kg each on average ranges around 25,000 - 30,000 rubles. With a layer thickness of 5 cm, this is enough to process about 40 square meters of surface. The service life of polyurethane foam is up to 40 years.
Expanded clay
Expanded clay is a material obtained from melted clay. Recently it has been rarely used, since in terms of characteristics it is significantly inferior to polyurethane foam, polyurethane foam and polyethylene foam. Its main advantage is its low price. 1 cubic meter costs about 1,500 rubles.
Expanded clay is distinguished by its environmental friendliness. Since only natural ingredients are used in its production, it does not emit any harmful substances into the air. The service life of such material is more than 50 years.
Its significant disadvantage is fragility. If the technology for manufacturing the insulating layer is violated, the expanded clay granules crumble. This worsens its thermal insulation properties. The downside of expanded clay is also the need for a blind area when laying it.
Mastics
Mastic is a liquid multicomponent composition based on bitumen. More often it is used as a base layer before laying other materials, since its thermal insulation properties are very low.
To achieve a positive result, you need to apply it in three to four layers.
The mastic well fills cracks and voids in the base, which increases the strength of the structure. It reliably protects against moisture.
Scope of application
EPPS is used in civil and industrial construction, greenhouse farming, in household appliances, in the construction of highways, runways, and pipeline laying. In the construction industry, EPS is used to insulate all house structures: from the foundation to the roof.
EPPS is one of the best materials for insulation
Insulation of foundations for almost all buildings in Russia is a necessary measure. According to the climatic zoning map, only in the southern regions of the Russian Federation can one do without this work. In the rest of the area, thermal insulation of the foundations must be carried out, and the further north you go, the larger the layer of insulation must be laid.
Since expanded polystyrene is produced in sheets, it is convenient for thermal insulation of all types of foundations - strip, pile, slab.
Moreover, the strip foundation can be insulated both from the inside and outside. For ease of installation, polystyrene foam sheets have a groove along the edge. For strip foundations, in addition to insulating the foundation itself, insulating the blind area is also important, especially on heaving and moist soils. Therefore, first of all you need to take care of drainage.
What is the best way to insulate?
When planning work on installing thermal insulation for the foundation, the issue of choosing and purchasing suitable insulation is initially resolved. The material for foundation insulation should have the following characteristics:
- Be resistant to deformation against the background of constant pressure from the soil;
- Do not absorb moisture from the soil.
On the modern market, insulation materials are presented in a wide range, and a newcomer to the construction industry may get confused in the abundance of offers. It is worth saying that the common insulation “mineral wool” is not suitable for thermal insulation of the foundation. Not only is it not durable, but it also absorbs moisture well, as a result of which all its positive performance characteristics are negated.
Despite fire resistance and low thermal conductivity, mineral wool has a significant drawback - high hygroscopicity
In modern construction of private houses, two materials are best suited for foundation insulation:
- Penoplex;
- Polyurethane foam.
Polyurethane foam is a modern insulating material that guarantees thermal, sound and water protection of a concrete structure. The material is sprayed onto the surface using special equipment in several layers. This application technology eliminates the appearance of gaps and seams. The advantages of the material include:
- Possibility to apply thermal insulation coating without seams or gaps;
- Excellent adhesion characteristics;
- Low thermal permeability;
- Steam protection;
- Increased reliability;
- Long service life;
- There is no need to purchase additional material for steam and water protection of the foundation.
The main and rather significant drawback is that special equipment is required to lay the material, as a result of which the process becomes impossible to implement at home. In addition, polyurethane foam has a high cost.
Penoplex, in turn, does not require special skills or special equipment for installation. Among other things, it has the following advantages:
- The cellular structure does not allow moisture to pass inside, as a result of which the slabs do not collapse over time after freezing;
- Increased strength characteristics;
- Ensuring a long service life of the foundation;
- Low cost;
- Long service life of the material;
- Preservation of thermal insulation characteristics throughout the entire service life;
- Rodents do not use the material as food, unlike regular foam.
Penoplex insulation reduces heat loss by 20% and helps the foundation last longer
Penoplex is an improved version of polystyrene foam. The material allows moisture to pass through very easily, and after several cycles of defrosting and freezing it will simply crumble into segments. Let us add that several years ago, expanded clay was also in demand on the construction market as insulation for the foundation. The material is inferior to penoplex due to its high cost, as well as reduced efficiency in providing thermal insulation.
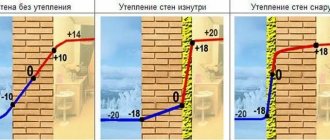
Does it make sense to insulate from the inside?
Internal foundation insulation is justified in cases where external insulation is ineffective or impossible. It is carried out during finishing or major repairs of the basement and ground floor, to increase the temperature in recessed rooms and insulate the floor of the first floor. However, the foundation will not be protected from damage due to freezing, which will lead to a reduction in service life.
The insulation is glued directly onto the concrete and additionally secured with mushroom dowels. After completing the installation of all the plates, the insulation surface is covered with a layer of glue 2 - 3 mm thick. Without waiting for complete drying, a fiberglass mesh is pressed into it with a spatula. Then holes are drilled for the dowels and the slabs are secured. After drying, the surface is treated with coarse sandpaper and a layer of cement putty is applied.
In basements, not only the walls, but also the ceiling are insulated.
To insulate the foundation with extruded polystyrene foam, builder qualifications and special tools are not required. Therefore, all work can be done independently. The result in the form of warm floors and reduced fuel costs will please you in the first winter.
The need for thermal insulation of the foundation
Insulation of the basement foundation
Insulating the foundation of a private house with polystyrene foam from the outside is mandatory. This also applies to other buildings, especially those containing a basement. To achieve high-quality results in installing thermal insulation, many use foam plastic.
A poorly insulated building loses up to 50 percent of heat through holes in the insulating coating, causing additional economic costs for heating. A fatal mistake when installing house insulation is neglecting the thermal protection of the foundation, believing that it will be enough to just finish the walls of the structure.
Good thermal insulation of the base is characterized by two functions:
- minimizing heat consumption;
- Preservation of the foundation from freezing and deformation.
The fact is that the predominant type of soil in our country is heaving. Due to the effects of cold, the depth of soil freezing can be several meters. During a thaw, the volume of soil changes, which in turn negatively affects the structure of the foundation of the house.
Before starting installation work, it is necessary to take into account that the installation of the thermal insulation coating must be complete. The presence of any cracks, defects and parts in the insulation layer has a detrimental effect on the building’s ability to maintain a temperature suitable for comfortable living. Only a dense air layer containing an insulation ball can completely contain the loss of warm air.
What is extruded polystyrene foam
Not everyone clearly understands what polystyrene foam actually is. In general, this is nothing more than ordinary and well-known foam plastic, used in everyday practice, mainly for packaging fragile items. This is a durable, lightweight, heat-saving, biodegradable and almost insoluble material obtained by filling styrene granules with gas and then heating them.
When exposed to temperature, the granules “swell” until they occupy the entire volume available to them and sinter together.
Extruded or extruded polystyrene foam is distinguished by a special manufacturing technology. For ordinary polystyrene foam, polystyrene granules are simply heated with water vapor, while to obtain EPS, several processes are used at once: the granules are mixed and heated, a foaming agent is introduced, and then extruded under high pressure, i.e. pushed through the molding hole.
This technology provides greater uniformity and, therefore, greater strength of EPS compared to foam plastic.
A little about the product
Extruded polystyrene foam is an analogue of foam plastic, consisting of small edges. Production involves foaming the material using agents, which can be freon or carbon dioxide. Numerous tests have confirmed the negative impact of the former on the Earth's ozone layer. In this regard, manufacturers are increasingly trying to produce polystyrene foam using CO₂. The granules themselves are obtained by passing the mixture through a special matrix with small cells. As a result, finished sheets and panels are formed. This form was not chosen by chance, since laying extruded polystyrene foam in the form of small slabs is much easier and more convenient.
Types of material
Expanded polystyrene appeared at the beginning of the 20th century and was patented in 1928. This is quite an interesting material, widely used in construction. The main quality is the ability to retain heat.
Many people consider expanded polystyrene and polystyrene foam to be the same material, which is incorrect. It differs from polystyrene foam: it is more durable, resistant to external influences, and homogeneous. Its cost is higher than that of conventional foam.
Expanded polystyrene is produced by adding gas to the polymer mass. When heated, it increases. Depending on the type of material, different gases are used. Simple forms of the material are created from naturally occurring gas. More complex ones are filled with carbon dioxide.
- Pressless is the most common type. Drying removes all moisture. Next, at a temperature of 80 degrees, foaming occurs, followed by drying and heating. The finished mixture is poured into a mold where the polystyrene foam hardens. Obtained by this method is considered brittle. Its preparation requires less isopetane, which makes the final cost of the product affordable for most.
- Extruded – similar with a pressless appearance. The difference is in the use of equipment. In this case, an extruder is used, after which the type of material is named.
- Extrusion is created as a result of processing the final mass. Used for preparing disposable tableware and packaging.
- Pressing is the most expensive method of creating expanded polystyrene. After foaming the mass, processing with a press is provided. This makes it more durable and strong.
- Autoclave is less common. Manufacturing takes place in an autoclave.
Varieties of expanded polystyrene
Each type has its own advantages that distinguish it from the rest. The safety aspect for humans is important.
Preparatory stage
Expanded polystyrene PSB-S
First you need to calculate how many insulation boards will be needed for the foundation. The dimensions of a standard polystyrene foam board are 600x1200 mm, thickness from 20 to 100 mm. For the foundation of a residential building, slabs 50 mm thick are usually used, laid in two layers. To find out how many slabs will be needed, the total length of the foundation is multiplied by its height and divided by 0.72 - the area of one sheet of polystyrene foam.
For example, if a 2 m high foundation is insulated in a 10x8 m house, the thermal insulation area is equal to 72 square meters. Dividing it by 0.72, we get the number of sheets - 100 pieces. Since the insulation will be carried out in two layers, it is necessary to buy 200 slabs 50 mm thick.
This, however, is a very average calculation, based on the fact that the insulation thickness will be exactly 100 mm. But this value can be greater - it all depends on the climatic conditions of the region, the foundation material, and the type of insulation.
There is a special system for calculating thickness, which requires knowing the R index - this is a constant value of the required heat transfer resistance established by SNiP for each region. You can check it with your local architecture department, or take it from the table below:
| City (region) | R - required heat transfer resistance m2×°K/W |
| Moscow | 3.28 |
| Krasnodar | 2.44 |
| Sochi | 1.79 |
| Rostov-on-Don | 2.75 |
| Saint Petersburg | 3.23 |
| Krasnoyarsk | 4.84 |
| Voronezh | 3.12 |
| Yakutsk | 5.28 |
| Irkutsk | 4.05 |
| Volgograd | 2.91 |
| Astrakhan | 2.76 |
| Ekaterinburg | 3.65 |
| Nizhny Novgorod | 3.36 |
| Vladivostok | 3.25 |
| Magadan | 4.33 |
| Chelyabinsk | 3.64 |
| Tver | 3.31 |
| Novosibirsk | 3.93 |
| Samara | 3.33 |
| Permian | 3.64 |
| Ufa | 3.48 |
| Kazan | 3.45 |
| Omsk | 3.82 |
Calculator for calculating the thickness of foundation insulation
In order not to bother the reader with calculation formulas, below is a special calculator that will allow you to quickly and accurately find the required thermal insulation thickness. The result obtained is rounded up, leading to the standard thickness of the panels of the selected insulation:
In addition to polystyrene foam you will need:
- mastic or roofing felt;
- gravel;
- glue;
- mushroom dowels;
- putty or polyurethane foam;
- level;
- notched spatula;
- cement mortar;
- sand;
- reinforcing mesh;
- roller
When all the materials have been prepared, a trench is dug along the perimeter of the foundation. You need to dig to the freezing level, that is, to a depth of 1.5-2 m. To make it convenient to work in the trench, its width should be 0.8-1 m. Of course, soil excavation is carried out exclusively by hand, since equipment can damage the foundation. The walls of the base must be thoroughly cleaned of soil, unevenness and cracks must be repaired with mortar.
Small laying
The actively developing suburban housing construction market requires reducing material costs and saving labor resources. The use of new construction technologies and materials that are used in the construction of various parts of structures helps to achieve significant savings in resources, reduce labor intensity and reduce construction time. One of these areas was the use of PENOPLEX FOUNDATION ® slabs for thermal insulation of shallow foundations. After all, it is known that a significant share of the total cost of buildings is the cost of constructing foundations. Frost-protected shallow foundations are similar to conventional foundations, with the exception of the location of the PENOPLEX FOUNDATION ® thermal insulation boards and the depth of foundation.
The base of the foundation is located at a depth of about 30-40 cm below ground level. The foundations have vertical insulation located on the outer side from the base to a level above ground level. When constructing foundations in colder climatic conditions, the “wings” of thermal insulation (PENOPLEX FOUNDATION ® slabs) are located horizontally at the level of the base of the foundation. The colder the climate, the wider the thermal insulation extends and the thicker its layer will be.
To protect the foundation soils from flooding with surface and groundwater, an asphalt or concrete blind area is installed along the perimeter of the building along the sand preparation to the width of the thermal insulation skirt. Insulating the blind area with extruded polystyrene foam can reduce heat loss and the cost of heating the building.
Thus, depending on the climatic conditions of the construction area, using heat flows from the building in use by changing the thickness and width of the thermal insulation, it is possible to move the soil freezing limit beyond the base of the foundation.
The considered effective shallow foundations, in comparison with traditional deep foundations, make it possible to reduce the cost of constructing foundations according to the following indicators:
- concrete consumption by 50-80%;
- labor costs by 40-70%;
- cost by 50% or more.
For the effective use of PENOPLEX FOUNDATION ® slabs in the structure under consideration, the Organization Standard “Use of thermal insulation from PENOPLEX ® extrusion polystyrene foam slabs in the design and construction of shallow foundations on heaving soils” was developed, STO 36554501-012-2008.
The standard was developed by specialists from NIIOSP named after. N.M. Gersevanova is a branch of the Federal State Unitary Enterprise “Research Center “Construction”, taking into account the experience of using thermally insulated shallow foundations (TFMZ) in America and Europe, as well as the characteristics of engineering-geological, hydrogeological, climatic conditions and experience in the construction of low-rise buildings in the Russian Federation.
Advantages of home insulation Penoplex® Foundation
- Low thermal conductivity coefficient – 0.034, which means consistently high thermal insulation properties;
- Moisture resistance;
- Resistance to temperature changes and the ability to install in any weather;
- Low vapor permeability;
- Light weight slabs with the best thermal conductivity coefficient;
- Convenient plate geometry and ease of installation;
- The presence of an L-shaped edge on all sides, which allows the slabs to be tightly joined like a construction set;
- Biostability;
- Durability;
- Environmentally friendly.
Instructions for thermal insulation of the foundation
- Step 1. The site is marked, and then the soil is excavated;
- Step 2. The dug pit is filled with non-heaving material (coarse sand, sand-gravel mixture), or as it is also called a “sand cushion”;
- Step 3. A drainage system, sewerage and drainage system are installed in the soil cushion;
- Step 4. The base is compacted with a vibrating plate;
- Step 5. PENOPLEX FOUNDATION ® slabs are laid on the prepared and compacted base in accordance with the selected scheme;
- Step 6. Install the waterproofing layer;
- Step 7. The formwork and reinforcement frame of the foundation slab are installed;
- Step 8. The foundation slab (foundation strip) is poured;
- Step 9. The foundation sinuses are filled with non-heaving soil, for example, a sand-gravel mixture or coarse sand;
- Step 10. Insulation of the blind area with extruded polystyrene foam PENOPLEX ®.
House insulation PENOPLEX FOUNDATION ®
You can buy Penoplex external insulation in Moscow, St. Petersburg and other cities of Russia. Find your nearest point of sale in the “Where to Buy” section.
Why is Penoplex the best solution for insulating the foundation of a house from the outside?
Before you begin insulation, you should take care of purchasing a high-quality and durable heat insulator. Insulating the foundation of a house from the outside with polystyrene foam, the price of which is lower than Penoplex, is not economically profitable. Such material will not serve the structure for more than 5-7 years, which means you will have to spend money on dismantling and re-insulating it. Choose modern insulation, the quality of which has been tested by time - improved Penoplex polystyrene foam, made by extrusion.
- The popular extruded polystyrene foam is a 100% moisture-resistant material, so it does not require additional waterproofing from groundwater.
- The thermal conductivity coefficient of PenoplexFundament or PenoplexGEO slabs is 0.03 W/m°C, which is 33% more efficient than traditional polystyrene foam, so you will need 1.5-2 times less insulation.
- The increased strength characteristics of expanded polystyrene are 3 times higher than polystyrene foam, and therefore guarantee reliable protection of waterproofing from damage.
- The insulation retains its performance properties even in extreme conditions of the Far North or constant exposure to moisture.
- The service life of Penoplex is almost 10 times higher than its foam counterpart, so the material will more than pay off every penny spent in just a couple of heating seasons.
Technical characteristics of PENOPLEX
| Physical and mechanical properties | Technical standards | Unit change | "PENOPLEX" | |
| Compressive strength at 10% linear deformation, not less | GOST EN 826-2011 | MPa (t/m2) | 0,20 (20) | |
| Static bending strength | GOST 17177-94 | MPa | 0,25 | |
| Water absorption in 24 hours, no more | GOST 15588-86 | % by volume | 0,4 | |
| Fire resistance category | FZ-123 | group | G3 (with fire retardants) | |
| Thermal conductivity coefficient λlab. | GOST 30256-94 | W/m∙ºK | 0,033 | |
| Standard sizes | thickness | TU 5767-006-54349294-2014 | mm | 20, 30, 40, 50, 60, 80, 100, 120, 150 |
| width | 600 | |||
| length | 1200 | |||
| Operating temperature range | TU 5767-006-54349294-2014 | ºС | -100….+75 |
Depending on the type of foundation, the optimal technology for insulating the foundation from the outside is selected. Let's take a closer look.
How to choose
When buying EPS, you must definitely ask for a quality certificate.
The sheets themselves also need to be inspected. They can be of different colors, but the color must be uniform. It is advisable to break a piece of the sheet; a characteristic crack should be heard. Then look at the structure; regular polyhedra will be visible on the fault lines. When you press on the sheet with your finger, it should spring back, but a small dent may remain. All insulation sheets must be the same thickness
When choosing EPS for foundation insulation, you need to pay attention to the density. For these works, the density of polystyrene foam must be at least 35 kg/cube
m.
A very important point: how thick should the EPS sheet be? The answer to this question can be found in SP 50.13330.2012, which provides indicators and requirements for thermal protection of buildings.
A key indicator of the thermal protection of a structure is heat transfer resistance. For ease of use, the Rules provide the values of the reduced resistance to heat transfer of enclosing structures, broken down by degree-day of the heating period. For each construction area, the normalized heat transfer resistance is calculated, adjusted by a coefficient that takes into account the conditions of the region.
The heat transfer resistance of the enclosing structure consists of the sum of the thermal resistances of each material (layer) of the structure, taking into account the heat transfer coefficients of the internal and external surfaces of the structure. Thermal resistance is the ratio of the thickness of the structure to the thermal conductivity coefficient of the material of the structure (sq. m*ºС/W), i.e. the structure is homogeneous.
Returning to the question of choosing the thickness of the EPS for the base, you need to use the formula:
The thickness of the sheet must be selected depending on the conditions
δth – thickness of the insulation layer (m);
R0 – reduced heat transfer resistance of the building envelope of the construction area, according to the table taking into account GSOP (sq. m*ºС/W);
δ – foundation thickness (m);
λ – thermal conductivity coefficient of the foundation material (W/m*ºС);
λth is the thermal conductivity coefficient of the insulation (W/m*ºС).
Insulating the foundation using polystyrene foam
Polystyrene foam is not capable of collapsing when in contact with asphalt or paving slabs.
Among the many insulation materials for foundations, including mineral wool, glass wool and expanded clay, the most suitable material should be noted - polystyrene foam. Due to its ability to maintain its functions in any climatic conditions, the product has gained incredible popularity among builders.
The characteristics of polystyrene foam are reliability, low cost and ease of use. In addition, its main component is air, which itself has excellent thermal insulation properties.
Foam plastic for foundation insulation has the following properties:
- stability when interacting with asphalt and concrete;
- resistance to water and fire;
- ability to retain heat;
- resistance to temperature fluctuations;
- maintaining shape and volume when exposed to external factors.
A significant disadvantage of polystyrene foam is fragility. To prevent the formation of various defects on it, the surface should be treated with glue.
Polystyrene foam is recommended for insulation of foundations built on clay soil. In addition, it is an excellent insulation option designed for underground use. This is due to its good moisture resistance and resistance to sudden temperature changes.
Types of foam plastic for insulating the foundations of houses:
- press - plate, foam thickness - from two centimeters;
- tiled polystyrene foam, parameters – 1*1*0.05 m;
- polyurethane foam (liquid);
Most often, foam is used for insulation. The reason for this choice is its size, which has a beneficial effect on installation and finishing procedures.
Horizontal installation method
Slab foundation insulation scheme
Horizontal insulation is used for slab and strip foundations, for which polystyrene foam up to 10 cm thick is used.
Step 1. First, the site is cleared of soil, leveling the bottom, the last few centimeters are removed manually.
Step 2. The base is covered with sand, which needs to be compacted.
Step 3. Temporary formwork is performed, which is filled with a layer of concrete without reinforcement.
Step 4. Then, when it hardens, laying the slabs begins.
Step 5. A thick film is placed on top as waterproofing, which is glued with tape.
Step 6. Formwork is made, then reinforcement is made and the foundation is poured.
Step 7. When the formwork hardens, it is removed and additional thermal insulation of the side walls is performed.
Installed insulation
Video - Monolithic slab foundation. Insulation and waterproofing
Video - Monolithic slab - technology
Foundation thermal insulation
The use of modern methods of thermal insulation is of great importance, especially in areas with harsh climatic conditions. This prevents a significant portion of heat loss and freezing of soils, which increase in volume, which leads to a rise in their level.
Foundation insulation with polystyrene foam
Insulating the foundation of a house from the outside with polystyrene foam is an excellent option for improving the thermal insulation qualities of the base of the house and preventing freezing.
Expanded polystyrene is an improved type of foam. Its use is more profitable, and installation is easier.
The video describes in detail how to insulate the base of a residential building with your own hands.
The process works as follows:
Preparing the base. This stage can be carried out both during the construction of the building and after its completion. To do this, you need to dig out the foundation, clean it of soil, debris, rust and grease. Sheet selection
In this case, you need to pay attention to two factors: density and thickness. They mainly use sheets with fire retardant additives and a density of 35 kg/m3. Waterproofing
This will prevent the influence of groundwater and its penetration through the insulator layer. Fastening polystyrene foam sheets with contact adhesive. You can attach two layers, but so that the panels of the second layer cover the joints of the first. Protection of insulation with a reinforcing mesh to avoid strong mechanical stress and the penetration of rodents. A layer of cement mortar can be applied to the protective mesh. Providing drainage. This step is considered mandatory when constructing a building on wet soils. Basement insulation. The base also needs to be insulated in the same way, followed by finishing. After the glue has dried, the panels are additionally secured with nails. Soil insulation. The event involves isolating the surrounding land with a blind area insulated with polystyrene foam slabs.
Knot
Insulating the foundation and blind area can significantly increase the temperature in the structure and protect the foundation from destruction.
Insulation of the foundation with liquid polyurethane foam
It is considered a fairly effective method that reduces heat loss by 20–25%.
To do this, two liquid components are mixed with each other, forming a thick foam. When applied, it increases in volume and hardens, forming a protective seamless layer with excellent thermal insulation and waterproofing properties. The optimal application thickness is considered to be 60 mm.
Wooden building
The polyurethane foam layer can be applied at a temperature not lower than +5 C. Surface preparation involves cleaning from contaminants, and surface quality is an unimportant factor.
As the foam hardens, it changes color. When performing work, various problems may arise related to equipment and neglect of weather conditions.
For example, when applied in sub-zero temperatures, cracks may appear that must be repaired in the future, otherwise water may accumulate in them and freeze. After polymerization, the polyurethane foam layer has low plasticity.
Incision
Foundation insulation using EPS
As a rule, not all insulation materials are suitable for thermal insulation of the base. To choose the right material for this purpose, you need to consider its service life: it must be as durable as the building itself.
Insulation with extruded polystyrene foam (EPS) is considered a more reliable method than, say, polystyrene foam, since this material is more durable and has excellent performance characteristics.
Blind area with trays
For this purpose, you need to purchase heat insulation boards and suitable glue for attaching it. After this, a number of preparatory activities should be carried out:
- Dig a trench around the foundation, digging into the ground.
- Apply EPS to the freezing depth of the ground.
- Clean the foundation from debris and dirt.
- Apply a special primer in two layers, wait for it to dry and absorb into the concrete.
- Provide waterproofing with bitumen mastic.
- Apply glue to the boards.
Attaching the slabs to the outer part of the foundation is allowed 1 minute after applying the glue. If the panels have a large area, you need to apply the glue in several strips using a comb spatula. If the slabs have locks, then a few days later the seams are sealed with polyurethane foam, and the slabs themselves are additionally secured with dowel nails.
Two-story mansion
Preparation and waterproofing
The preparatory process has its own nuances for each type of foundation. A “tape” of standard depth should be manually dug into a trench up to one meter wide and to the freezing depth. No technique is used in this case, so as not to accidentally “injure” the foundation. The surface is cleaned and leveled - the protrusions are chipped off and cracks are sealed with cement.
Waterproofing
Then a waterproofing layer is applied: bitumen mastic using a roller or liquid rubber from a spray bottle
It is important that the waterproofing material is applied in a continuous layer and does not contain organic solvents that have a destructive effect on XPS
Even more effective protection for strip foundations will be provided by a combination of bitumen and rolled material. Ruberoid, fiberglass, etc. are applied to the mastic in a heated state with an overlap of up to 150 mm, the joints are coated with bitumen. In the same way, a slab foundation can be insulated from moisture.
If the foundation is on stilts
With a pile foundation, a combination of a waterproofing compound and a drainage system is required to protect against groundwater. The drainage is installed in the following sequence:
- a shallow trench is dug;
- the bottom of the trench is covered with crushed stone;
- geotextiles are laid on top of the crushed stone;
- pipes for drainage of water are laid at an angle from the house;
- on top of the pipes there is another layer of geotextile;
- a top layer of crushed stone is laid.
Basement insulation with penoplex
Technology for insulating the base in the same plane as the walls of the house:
- Marking. Since the insulation boards should be several centimeters higher than the waterproofing layer, horizontal markings should be made with a pencil along the entire surface of the wall.
- Cleaning the outside of the wall. The wall surface is pre-prepared for gluing with polystyrene foam. To do this, it is thoroughly cleaned from the outside of dust and dirt. After this, the surface is primed. After the primer has dried, you can proceed to the next step.
- Connecting slabs. Pasting the walls of a house with polystyrene foam is done using special glue, starting from the corner. The slabs are marked and cut with a sharp wallpaper knife.
- Applying glue to the wall and slabs. Using a special notched trowel, the adhesive is applied to the surface of the base. Pre-prepared fragments of slabs are smeared with glue and attached to the wall, the joints between the slabs and the ends outside the house are carefully sealed.
- Next, using a hammer drill, dowels are drilled and inserted, followed by driving in nails. After covering the entire surface of the outside of the house with slabs, a special primer layer is applied to provide the basis for all subsequent layers.
- Strengthening the slope angle. A metal corner is attached around the entire perimeter of the wall. For installation, the same adhesive is used as for the slabs.
- Installation of reinforcing mesh. The reinforcing mesh is pre-cut to the size of the slabs, lubricated with adhesive and glued on top of the polystyrene foam. The technology for strengthening the reinforcing mesh is the same as for installing the corner.
- Finishing work and installation of drip linings. Materials for external work are used to putty the base area. It is left to dry and primed again followed by painting. To prevent moisture penetration, flashings are installed.
If coating defects occur, they can be easily eliminated by re-priming and painting.
The technology of thermal insulation with foam plastic is the same as that of penoplex. Date: September 25, 2021
Expert advice
Polystyrene foam is a fairly flammable material. To eliminate the possibility of fire, manufacturers use fire retardants. Polystyrene foam with fire retardants is marked FS.
When choosing expanded polystyrene and penoplex for insulating the foundation base, you need to look at the density of the material indicated in the marking. For foundation insulation work, polystyrene foam with a rating of 35 and higher is suitable.
Some homeowners choose to use penetrating insulation and insulation. Before using them, you need to consult with a specialist about the compatibility of this insulation with a certain type of foundation.
When insulating the entire base, it is worth leaving ventilation holes so that there is always fresh air in the interior. In winter, the holes in the base are plugged with special plugs. This will provide thermal insulation.
Insulating the base with foam plastic requires waterproofing and high-quality protection of the blind area using a layer of thermal insulation.