Thermal insulation of the foundation is no less important than the thermal insulation of the walls, especially in areas with a harsh climate. Frozen soil cannot protect the foundation of a house from moisture and cold, and the foundation itself, after repeated freezing, begins to collapse faster. To get rid of these problems and reduce the cost of heating your home, you need to know how to insulate the foundation of a house from the outside, and how you can do it yourself.
How to insulate the foundation of a house from the outside
Foundation insulation is a one-time investment that will increase the lifespan of your home
Why insulate the foundation
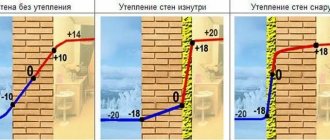
Thermal losses of the building through the foundation are small - from 5% to 15%. Its position and the peculiarities of the “physics” of heat transfer affect it.
About 15% of losses remain on the foundation and floor, but how much this is in absolute value depends only on the owner of the house Source ps-b.ru
There are only three ways to transfer thermal energy: radiation, convection (for gas and liquid media) and thermal conductivity.
Radiation is clearly not “about the foundation”, but about the heating system devices. They have a higher temperature compared to air and surrounding objects and serve as sources rather than “receivers”. But the walls of a heated room during the cold season emit energy in the infrared spectrum to the street. To see this background, just look at them through a thermal imager. It is especially bright in uninsulated areas and “cold bridges”.
It’s so easy to see how heat escapes through uninsulated walls Source rte-france.com
Natural convection is characterized by an upward flow of warm air and a downward flow of cold air. Of course, the temperature of the foundation cannot affect this process. It is important here to insulate the roof and ceiling so that they do not quickly “cool” the warm air.
Of the above three methods of transferring thermal energy, it is “thanks to” the thermal conductivity of structural materials that a cold foundation affects heat loss and heating costs of the house. And the thermal conductivity of reinforced concrete, from which the foundation is usually made, is quite high, so its low temperature is transferred to the walls and load-bearing partitions.
The air in the room cools due to the enclosing structures, which release heat to the environment. For the underground part of the foundation it is soil, for the base and walls it is air. Insulating the foundation reduces these losses.
Follow manufacturer's instructions
Before insulating the foundation with your own hands, you need to study the instructions or consult with a specialist. If it is recommended to use a protective layer of foil with dimples between the insulation and the ground, it is better to lay it down. If the manufacturer says that there is no such need, you don’t need to do it!
The money will be wasted. Also, you should not make a reinforced layer of putty and mesh on the foundation walls, under the insulation.
Video description
The heat loss of a building and the purposes of insulating the foundation are described in detail in the video:
But there is also another function of thermal insulation of the foundation of a house - increasing the service life of the foundation. Building materials have such a criterion as frost resistance. Its numerical expression means how many freezing cycles (assuming water saturation) must pass before signs of destruction appear. Therefore, for regions with cold and long winters, insulation and waterproofing of the foundation is a prerequisite to ensure the strength and durability of the structure.
Use suitable glue
Good thermal insulation must be well attached to the wall. A common mistake is using the wrong glue.
It is known that both polystyrene and styrodur are not resistant to solvents.
- Not knowing the chemical composition of cementitious materials, many people buy cement adhesive for fear of damage to the insulation.
- Thus, they damage the waterproofing layers!
- Therefore, you need to use the glue recommended by the manufacturer for application.
It is worth paying attention that insulating boards cannot be fastened mechanically, as the studs can damage the waterproofing.
Technologies and materials
There are only two types of foundations that need to be insulated: slab and strip. For columnar and pile foundations, we can only talk about thermal insulation of the floor of the first floor and the insulation (basement) - a kind of screen that protects the subfloor. But piles and pillars do not directly insulate.
Plate
The technology for insulating a slab foundation is no different from the thermal insulation of concrete floors on the ground:
- a solid base of compacted soil;
- geomembrane as protection against capillary rise of groundwater;
- crushed stone-sand cushion to improve the bearing capacity of the soil and proper load distribution;
- roll waterproofing;
- sheet insulation (expanded polystyrene or EPS);
- plate.
Eps is the best material for insulating slab foundations Source rmnt.ru
See also: Catalog of companies that specialize in foundation repair and design.
The Swedes have slightly improved the technology and already at the stage of pouring the base they install a “warm floor” into the slab. In our country it is often done the old fashioned way - in a screed or under the finishing floor covering. Scandinavians are “boring” people and already know in advance where not only the partitions will be located, but also how the furniture will stand (one of the conditions for the correct operation of the “warm floor”). Our people have a different character - they are not only furniture, but also interior walls are often moved from place to place.
Strip foundation
Insulation of this type of base has a wider selection of materials and technologies:
- permanent formwork;
- fastening sheets of foam plastic or extruded polystyrene foam;
- spraying liquid polyurethane foam;
- filling of expanded clay.
Among foundation insulation materials, only one popular thermal insulation material is missing - mineral wool. When saturated with water, any type of water loses its thermal insulation properties. And although it not only easily absorbs, but also easily releases moisture, it is impossible to create conditions for its weathering for the foundation.
Places for foundation insulation Source anticafe-sandbox.ru
The cheapest way
Characteristics of expanded clay
Filling an expanded clay insulation cushion is, of course, the most affordable of all the methods mentioned. It creates a space that drains water and maintains the temperature of the floors. Usually it is used to fill the internal formwork located along the walls and the space under the proposed basement floor.
Preparing the base for installation:
- cleaning the surface with a wire brush;
- identification of cracks and damage to the slab, their elimination;
- treatment of joints between floors and walls with polyurethane foam.
Laying communications:
- protection and fixation of pipes using special sleeves in which
- communications are placed, or the use of polyethylene for winding;
- fixing communications to the floor.
Waterproofing device:
laying overlapping dense layers of polyethylene with fastening the joints or applying bitumen mastic to the entire surface.
Displaying beacons:
when setting, their parallelism and compliance with the same level is monitored;
Laying expanded clay:
- Dry – backfilling with dry expanded clay without additional sealing materials;
- Wet - consists of two layers: first expanded clay + concrete, and after it sets - a second layer of pure concrete with additional leveling.
Technologies for insulating strip foundations
Each type of insulation has its own characteristics, which dictate the methods of its application.
Permanent formwork
This is the only method of insulation that is possible only at the stage of construction of a monolithic strip foundation. In fact, this technology can be called “two in one”, when the formwork made of thermal insulating materials remains as part of the structure upon completion of construction. Moreover, permanent formwork solves two problems - how to insulate the foundation of a house from the outside and from the inside.
Structurally, there are two types: block and panel. When pouring a strip foundation, shields are used. The blocks have walls and wide transverse bridges, which reduces the strength of the reinforced concrete base.
Ready-made kits have a set of polymer jumpers that can be used to adjust the width of the foundation Source visualizepicture.com
Influence of negative factors
Up to 80% of the territory of the Russian Federation is located in the recreation of heaving soils. Such soil, when freezing (seasonal or perennial), is capable of increasing in volume, which entails a rise in the surface of up to 0.35 m. Since the soil freezes with the concrete elements of the foundation, as it rises, it pulls the structure itself with it. Several such cycles - and at least deformation of the structure is ensured.
No matter how reliable the waterproofing is, some amount of moisture will still get into the porous concrete. These drops will be invisible to the human eye, however, under the influence of negative temperatures, wet concrete is known to collapse.
It is known for certain that the basement accounts for up to 20% of all heat loss in a building. Unheated basements do not require insulation; they are insulated in the basement area to prevent freezing of the ceiling boundary between the heated room and the unheated basement.
Video description
You can get acquainted with the features of polystyrene foam insulation technology in the video:
Insulation with sprayed polyurethane foam
Among all polymer insulation, sprayed polyurethane foam is the most expensive type. Its advantage is that the thermal insulation layer has no seams, and foamed polyurethane has very good adhesion to all types of building materials.
Application of polyurethane foam to a surface cleared of dirt is very quick. There are two types of materials: two-component and one-component.
In the first case, professional equipment is needed, the work of which is to supply both components under pressure to the working head, where they are mixed and foamed.
Single-component polyurethane foam is produced in liter aerosol cans, and even an untrained beginner can handle them correctly. But this technology is good for a small area of work, or when it is necessary to apply a small layer up to 2 cm thick.
Spraying polyurethane foam is similar to painting with a spray gun, so it is better to cover the cladding of the house. Source ppuspb.ru
If the soils are dry, the water level is low and proper drainage work has been carried out, then waterproofing of the foundation and base need not be carried out - there are no seams, and the water absorption of hardened polyurethane foam is small (no more than 2%). When finishing the base with plaster, reinforcement is not necessary - there are no joints, like with foam plastic slabs, and, therefore, there are no prerequisites for cracks to occur.
In addition to the price, polyurethane foam has one more small drawback, which is a consequence of its advantage - good adhesion. When carrying out work on insulating the basement, it is necessary to protect walls that already have finishing (or do not require it) - this is easier than cleaning off hardened foam.
Insulation with expanded clay
Recently, this bulk material is rarely used for foundation insulation. Its use is limited by two factors: quite high, compared to polymer insulation, water absorption and thermal conductivity.
The thickness of bulk thermal insulation can reach 60 cm Source obustroeno.com
The first indicator lies in the range of 8-20% of the volume. Moreover, such water absorption is typical for “fresh” expanded clay - over time it becomes even higher. For comparison, for ordinary polystyrene it is no more than 4%. Therefore, waterproofing of both the foundation and the entire insulation layer is necessary.
It is impossible to ensure complete “tightness” of expanded clay, and it will take a long time to dry underground, wrapped in film - its use is not recommended in conditions of high seasonal rise of groundwater.
Thermal conductivity also does not meet modern requirements for thermal protection of buildings - 0.07–0.18 (W/m*°C) versus 0.02–0.04 for polyurethane foam, 0.03–0.04 for EPS/EPS. Therefore, the recommended thickness of bulk thermal insulation for our middle latitudes lies in the range of 40–60 cm.
The insulation scheme looks like this:
- dig a trench of the estimated width (or clear the cavity of the pit) to the heel of the foundation;
- lay a waterproofing film over the entire area of the trench - foundation-bottom-wall;
- fill and level expanded clay;
- cover with film on top;
- pour a layer of sand;
- make a blind area.
Typical scheme for insulating a foundation with expanded clay Source sevparitet.ru
The advantage of expanded clay is its environmental friendliness and low price. Although, taking into account waterproofing and a large volume of materials, the cost of work in the end will not be so low. In addition, the base will have to be insulated using one of the above methods.
Installation of a foam insulation layer
Let's start insulating the foundation with penoplex by choosing the material. Penoplex slabs are available in two standard sizes: 0.6 m x 1.2 m and 0.6 m x 2.4 m. We do not give any specific decision on thickness - everything is purely individual and depends on the thickness of the wall and the material, from which it is folded.
Penoplex is glued to the base with a special glue; it is sold in bags in the form of a dry mixture. We will not dwell on glue brands - every self-respecting company producing dry mixes necessarily produces glue for penoplex foam.
- While the mastic was drying, its surface was covered with dust, so we treated the waterproofing with a primer. The primer increases adhesion and improves the quality of gluing.
- Apply an even layer of adhesive mixture to the foam board. We also apply glue to the wall. Press tightly. And so on until the entire surface is sealed.
- At 4-5 points of each sheet we drill and hammer in additional fasteners - a dowel-fungus.
Note! With a planned insulation thickness of 10 cm, it is better to take twice as much material, but 5 cm thick, and glue it in two layers so that the slab of the second layer overlaps the joint of the first.
Decorative finishing of the outside of the foundation
Advantages when constructing thermal insulation
So, the above factors pose sufficient danger to think about preventing negative temperatures from reaching the foundation. The benefits of thermal insulation are as follows:
- Eliminates or significantly reduces the impact of heaving forces on the structure
- Reduces heat loss and saves energy costs
- Maintains the temperature parameters of the building set by the owner
- Removes condensation from basement surfaces
- Protects waterproofing from damage and extends its service life