Slab foundations are successfully laid under private houses of any type, with maximum effect when constructing on weak and heaving soils.
The technology of constructing and pouring a monolithic slab foundation is considered labor-intensive and costly, but with proper calculation and implementation of all or individual stages on your own, the estimate is reduced by 20-30%.
In this article we will tell you in detail how to correctly pour a monolithic slab under a house yourself, what the process consists of and how to avoid possible mistakes.
Scope and calculation features
The main purpose is to use it as a foundation on soft soils with a maximum load-bearing capacity of up to 2.5 kg/cm2. This includes sands - silty and medium density, clays and plastic loams, peat and moist soils. Moreover, it is the level of soil moisture that largely determines its load-bearing capacity - when wet, it literally “floats”, losing its strength properties. Therefore, drainage, waterproofing and blind areas play an important role in the arrangement of this type of foundation.
Reliable waterproofing is an important component of any foundation Source olestnicah.ru
One of the advantages is often given the argument that you can make a monolithic slab with your own hands. But even if we do not consider the issues of choosing the type of concrete and the parameters of the reinforcement frame, such an important stage remains as calculating the dimensions of the slab. And if there is a certain clarity with the area (the size of the house plus a small margin on each side), then the thickness of the slab is not easy to calculate.
The recommended range of foundation slab thickness for low-rise construction is 10-40 cm.
But this range also includes “light construction” in the form of a garage or summer kitchen, and a two-story house with an attic. If you make the slab not “thick” enough or choose the wrong thickness of the reinforcing rod (or cell size), then it will not be able to withstand the total load. An excessive margin of safety leads to an increase in the cost of an already expensive foundation, and an excessive amount of concreting will make the entire structure heavier, and the soil may not be able to withstand the total load.
There is another option with a diametrically opposite scope of application - the slab is installed on rocky and coarse soils with very high load-bearing properties. In this case, it rather levels the construction site rather than redistributing the load from the structure.
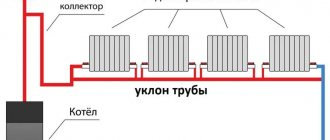
Another feature of this foundation is that the laying of pipelines must be done at the stage of the zero cycle Source xpcenter.ru
Useful tips
When groundwater lies high, a layer of clay up to 10 cm is laid at the bottom of the pit.
To strengthen the soil, up to 50% of sand is replaced with coarse and medium fraction crushed stone. It is better to choose cubic and rounded stones, without using layered bulk materials.
It is important to collect soil correctly; wells are made in different places on the site. The water level is determined by neighboring wells or by filling wells made for collecting soil.
Heaving soil rises and falls up to several centimeters throughout the year; if the monolithic foundation is weak, cracks will appear throughout the house. It is better to provide a 20% safety margin.
What is taken into account when calculating the foundation
When calculating a monolithic slab foundation, the total load is taken into account, which includes:
- weight of the building, including finishing materials;
- the weight of the plate itself;
- engineering systems equipment;
- communications;
- furniture and household appliances;
- wind and snow pressure.
Atmospheric loads are temporary, but they are taken into account as permanent. They are defined as statistical characteristics given for each region in the tables of regulatory documents. They cannot be neglected - in some areas, wind loads and snow pressure are large, and in terms of per square meter of the foundation they are comparable to the specific gravity of equipment, household appliances and furniture.
Such a layer of snow is a serious test for any home Source bgderab.ru
“Amateur” developers use a simpler method of calculating slab thickness. He proceeds from the position that a low-rise building requires a reinforcing frame made of double mesh. The distances from the bottom and top surfaces of the slab to the reinforcement are taken to be 50 mm, the distance between the chords is more than 70 mm, the rod diameter is in the range of 12-16 mm. And the calculation formula comes down to the following amount: 2x50+70+4x(12-16)=218-234 mm. And since the thickness is rounded up in multiples of 50 mm, it turns out that it is equal to 250 mm. The bearing capacity of the foundation is finally “regulated” by choosing the diameter of the reinforcement and the grade of concrete.
But it must be emphasized once again that this is a very approximate method, and in some cases it may not “work”, so all calculations must be carried out by specialists.
Dependence on different types of structures
The design of the foundation of a future building is carried out not only taking into account the type of soil and the location of the land plot, but is also based on the area of the building and the building material from which it will be built. The size of the future house and its walls affect the loads, which should also be reflected in the capital of the structure. For example, for a frame-panel one-story house made of SIP panels, it will be sufficient to arrange a pile-strip shallow foundation type.
A structure made of fragile aerated concrete blocks requires a different type of foundation. The slightest shift of the foundation will lead to cracking of the walls, so a monolithic recessed strip foundation made of reinforced concrete slabs or concrete, with the obligatory viscosity of a reinforcing belt, is required.
Types of slab foundation
There are two types of slab foundations based on execution technology: prefabricated and monolithic.
In the first case, reinforced concrete slabs are laid on the prepared site. And as a leveling and “binding” layer, a cement-sand screed is poured. The load-bearing capacity of such a foundation is low, so it is either built on rocky (or coarse-clastic) soils or for light buildings.
A monolithic slab does not have any disadvantages or limitations in use, except for the high cost of manufacturing. There are even recommendations for using deep slab foundations:
- for heavy structures on bulk soils with deepening to continental soil;
- construction on mixed soils with different load-bearing properties;
- for arranging a basement in conditions of high groundwater levels.
According to the profile, there are three foundation options:
- Solid slab. A house without a base, when the surface of the slab serves as the subfloor of the first floor (for example, a Swedish stove). It can be either monolithic or prefabricated.
- Ribbed plate. There are stiffening ribs in the lower part. If this is a monolithic technology, then additional trenches are dug for them, and the formwork and reinforcement are combined with the common part. If this is a prefabricated technology, then ribbed ready-made slabs are used for the foundation.
Additional stiffening ribs will make the structure more reliable even with a small thickness of the main part of the foundation Source vamnapolzu.ru
- Box foundation. A house with a base on a slab and a concrete floor on the first floor. The slab and plinth can have monolithic, prefabricated or combined technology.
How to make a project yourself
Previously, the foundation drawing was developed and drawn manually, now all this can be done using special online programs. Their use allows even a person with no experience or skills in construction to cope with the task. In general, working with them is guaranteed to provide the following opportunities:
- Saving money on paying for specialist services.
- The opportunity to personally analyze the type of foundation, the required amount of material and calculate its approximate cost.
- The free program will help you independently develop a foundation plan and drawing. Based on the information received, make design changes (if necessary) in subsequent construction.
Structure by layers
This is what the most complete structure of a monolithic slab as the foundation of a house looks like Source pinterest.ru
The standard “pie” of a full profile looks like this:
- leveled and compacted “mainland” soil;
- separating geomembrane (desirable, but not required);
- a cushion made of sand (or two layers - sand and crushed stone)
- footing;
- waterproofing;
- sheet insulation;
- base plate.
In Europe and here, a modification of the foundation called the “Swedish slab” has recently become increasingly popular. The peculiarity is that the warm water floor is not laid in the screed, but in the slab itself.
Swedish foundation slab for a private house with heated floors Source pinterest.com
Formwork
Various types of formwork can be used to cast a monolithic slab, including:
• Removable, assembled from plywood, plastic panels or tightly fitted boards, buried in the ground or placed above the zero level with appropriate supports.
• Fixed, assembled from compacted polystyrene foam and successfully performing the functions of a heat-insulating layer.
When constructing on stable and dense soils, the formwork can only be installed at the top, but if there is the slightest risk of crumbling edges, it should be loaded into the ground.
Regardless of the chosen method, the internal walls of the pit or formwork are covered with waterproofing films and, if possible, insulated.
After assembly, the evenness and stability of the structure must be checked; deviations from the planned geometric dimensions of the slab are not allowed.
Advice! To save money when constructing formwork, you can use low-grade unedged boards or be sure to dig in the outer walls of the formwork before pouring.
Drainage and waterproofing
The main reason for the soil getting wet and losing its load-bearing properties is not groundwater, which lies much deeper than the base of a shallow foundation, but in the perched water. This includes precipitation, seasonal snow melting, as well as water infiltration from nearby bodies of water if their “mirror” is at the same level as the slab. To a lesser extent, but the capillary rise of water in some types of soil also has an effect.
The nature of drainage measures depends on the characteristics of the region and site. If the house is located on a slope, then it is possible to install a cut-off drainage. On flat areas, it is possible to install a comprehensive storm drainage system, including drainage of water from platforms and paths outside the site. But in any case, below the level of the concrete foundation slab, along the perimeter of the blind area, drainage pipes are laid, which are led with a slight slope into a drainage well.
Laying a drainage pipe Source katlavan.ru
Waterproofing is complex. To briefly formulate the essence of the technology, it lies in the fact that the slab is literally wrapped in two layers of rolled insulation. The full list of works looks like this:
- After carrying out the zero cycle and backfilling the sand and gravel cushion, two layers of rolled bitumen insulation sheets are laid on the leveled area.
- All sheets are laid overlapping, and the top layer relative to the bottom is shifted by a width of half a sheet.
- Along the entire perimeter, roll waterproofing should be laid with a margin sufficient to bend the edges towards the end of the slab.
- After pouring and curing the concrete, the protruding edges of the waterproofing are glued with bitumen to the end of the base.
- Carry out waterproofing work to protect the top and side surfaces of the foundation
Types of foundation slabs
- Stiffening ribs down: when the strip base is placed under the base of the slab;
- ribs up: the tape is poured around the perimeter of the slab;
- combined production option: ribs are placed in two ways on one plate.
The ribbed slab reduces the amount of concrete used, without reducing the strength index.
Tapes on a monolithic slab are laid around the perimeter of the slab, under the supporting structures. If the building area is large, then transverse slabs (FBS) are laid for strength. The height of the tape is determined in accordance with the calculated data. The upper ribs - protrusions - act as a base. Insulation is installed in the opening. If necessary, communication cables and heated floors are laid.