Sometimes, when planning to build your own house, circumstances develop in such a way that the usual, reliable and relatively inexpensive strip foundation scheme becomes simply impossible. Typically, such conclusions are reached in cases where an assessment of the condition of soils on a site indicates their insufficient bearing capacity or a pronounced tendency to frost heaving. You can, of course, lay a deep tape, lowering its base below the freezing level of the soil, but this extremely complicates the project and leads to a large increase in the cost of its implementation. In addition, this may be hampered by the location of underground aquifers being too close. As an alternative, the option of constructing a shallow slab foundation is being considered.
Slab foundation thickness calculation
This type of foundation has another common name - “floating”, which quite accurately characterizes its features. Indeed, the uniform distribution of the load from the building and the mass of the slab itself over a large area leads to the fact that the specific pressure is minimal, and the reinforced concrete foundation of the building seems to “float” on the surface, without settling deeper and repeating seasonal vertical vibrations of the soil. But this significant advantage is only fully revealed when the dimensions of the slab foundation, and in particular its thickness, correspond to both the actual operating conditions of the building and the parameters of the building erected on such a foundation.
Let's take a closer look at this issue: slab foundation thickness calculation, depending on the conditions of the construction site, and on the specifics of the building planned for construction.
Cement prices
cement
Types of monolithic slab foundation
Before calculating the required thickness of a monolithic slab foundation, we will consider the types of these same slabs and construction methods.
Comparison of slabs for foundation construction.
The first method is the construction of a foundation using industrially manufactured reinforced concrete slabs or blocks . They are produced in special workshops and factories in accordance with GOST and with a given thickness of reinforced concrete slabs. Their connection into a monolithic base occurs using a specific technology, by pouring cement mortar into the free space between the blocks.
The second method includes building a monolithic foundation yourself, right on the spot . The technology, among other things, includes calculating the amount of required materials: reinforcement class A400 (Bpl), concrete B15-B25, slab thickness.
The complexity of the production technology for such a foundation lies in the fact that it is necessary to calculate not only the amount of material required, but also the optimal parameters for the thickness and height of the foundation layer.
When choosing between these two options, it is advisable to take into account the advice of experts: the first type is suitable only for soils that are not heaving and do not freeze to great depths. Otherwise, the foundation will begin to burst at the junction of the slabs. The second type is more reliable, since the structure itself will be monolithic and homogeneous.
Calculator operation algorithm
If this menu item is selected, the calculator will calculate the minimum content of working longitudinal reinforcement for the foundation structure in accordance with SP 52-101-2003. The minimum percentage of reinforcement for reinforced concrete products lies in the range of 0.1-0.25% of the cross-sectional area of the concrete, equal to the product of the width of the tape and the working height of the tape.
SP 52-101-2003 Clause 8.3.4 (analogous to the Manual for SP 52-101-2003 Clause 5.11, Guidelines for the design of concrete and reinforced concrete structures made of heavy concrete, clause 3.8)
Manual to SP 52-101-2003 Clause 5.11
In our case, the minimum percentage of reinforcement will be 0.1% for the tension zone. Due to the fact that in a strip foundation the stretched zone can be both the top and bottom of the strip, the percentage of reinforcement will be 0.1% for the top chord and 0.1% for the bottom chord of the strip.
Manual to SP 52-101-2003 Clause 5.17
Guidelines for the design of concrete and reinforced concrete products made of heavy concrete, paragraph 3.11
Guidelines for the design of concrete and reinforced concrete structures made of heavy concrete, paragraph 3.94
To build a strip foundation yourself, you must first carry out precise planning. The need for careful calculations is explained by the fact that the foundation is one of the most important structural elements of any building or home. Mistakes made at the beginning of construction can provoke negative consequences during the operation of the house.
We suggest you familiarize yourself with Cervical osteochondrosis: is it possible to go to the bathhouse?
Once the concrete is poured, it should be covered with film to prevent drying out and left to gain strength for at least 2 weeks.
Main elements of a tiled monolithic foundation
Let's consider the main elements of a monolithic foundation in the form of a slab:
- cushion, the calculation of which will be based on factors such as soil heaving (freezing depth, presence of groundwater, soil type);
- the base, which will include the calculation of the distance between the reinforcing mesh, since according to the technology there should be two of them, as well as its total thickness.
Before starting the construction of the structure, it is necessary to stock up on reference books and information about the climatic conditions of the area where the construction of the house will take place.
Load safety factors.
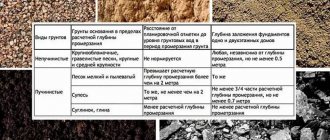
Study of soil characteristics
Before starting to calculate any type of foundation, the characteristics of the foundation under it are determined. The main and most important points include:
- water saturation;
- bearing capacity.
When constructing large facilities, before starting the development of project documentation, full-fledged geological surveys are carried out, which include:
- drilling of the wells;
- laboratory research;
- development of a report on the characteristics of the foundation.
The report provides all the values obtained during the first two steps. A full range of geological surveys is expensive. When designing a private house, it is most often not necessary. Soil studies are carried out using two methods:
- pits;
- wells.
The cutting of pits is done manually. To do this, dig a hole with a shovel, 50 cm deep below the expected level of the base of the foundation. The soil is studied by section, approximately the type of bearing layer and the presence of water in it are determined. If the soil is too saturated with water, it is recommended to use pile supports for the building.
The second option for studying the characteristics of the foundation for a house is carried out using a hand drill. The analysis is carried out on pieces of soil on the blades.
Important! When conducting events, it is necessary to select several points to study. They should be located under the building site. This will allow you to study the soil type most thoroughly.
Having decided on the base, the optimal specific pressure on the ground is determined for it. The value will be required in further calculations, an example of which is presented below. The value is taken according to the table.
| Type of soil being tested | Optimal specific ground pressure, kg/cm2 |
| The sand is dusty and fine | 0,35 |
| Medium sand | 0,25 |
| Sandy loam* | 0,50 |
| Loam | 0,35 |
| Plastic clay | 0,25 |
| Hard clay* | 0,50 |
*With this type of foundation soil, the strip option may be more economical, so you need to calculate the estimate for two types of foundation and choose the one that will cost less.
Foundation calculation procedure
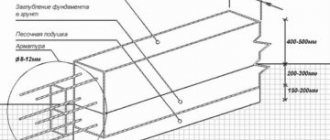
In order to correctly calculate the thickness of all foundation elements for building a house, it is necessary to proceed in stages. The first thing you need to decide on is a sand cushion .
The function of the sand cushion is to protect the base from exposure to excess moisture and groundwater. In addition, sand, when pressed, creates a strong soil layer. According to general building codes, a sand cushion is always placed under a monolithic foundation slab. To calculate its height, you need to consider:
- The height can vary in size from 15 to 60 centimeters and will depend on the depth of soil freezing on the land plot where the house is being built, the types and depth of soils that predominate in the region, the presence of groundwater;
- The sand must be compacted well, for which, after backfilling, it must be watered for several days. This can compensate for a couple of centimeters of shrinkage;
- Some experts recommend pouring a layer of fine crushed stone on top of the sand, the thickness of which should not exceed 5-10 centimeters from the total height of the sand cushion.
Based on this, we can come to the following conclusion. In places where the depth of soil freezing is high (more than 1 meter), there is underground water, and the soil is unstable and subject to constant heaving, the thickness of the sand cushion should be up to 60 centimeters. In places with a shallower soil freezing depth, in the absence of groundwater and the presence of dense layers of soil, you can make a cushion of 20 to 30 centimeters. Having received these dimensions, you can calculate the amount of material required.
Advantages of a foundation slab
The advantages of the design include:
- construction on soils with poor characteristics;
- the possibility of constructing large objects;
- possibility of self-filling;
- high load-bearing capacity;
- prevention of local deformations;
- resistance to frost heaving forces.
The weaknesses of this type of foundation include:
- inappropriate for use on sloped areas;
- high consumption of concrete and reinforcement;
- Compared to ready-made foundation elements, the installation of a monolithic slab requires additional time for concrete to gain strength;
- complex calculation.
Calculation
Let's look at how materials are calculated for an 8 by 8 meter slab. We will make reinforcement in increments of 20 centimeters, rods with a diameter of 14 in two layers, for vertical rods 8 millimeters, the spacing is the same. We take the concrete used for the slab of class B20 (in strength it corresponds to grade M250) for preparation of class B7.5. Let's take the thickness of the slab to be 25 cm.
- Concrete for slab B20: 8.2 x 8.2 = 67.24 m²;
- Let's calculate the cubic capacity, that is, the volume of concrete required: 67.24 m² x 0.25 m = 16.81 m³;
- Consumption of the amount of material for reinforcement, taking into account the provision of a protective layer for the slab: 8200 – 60 = 8140 millimeters rod length. Based on a step of 20 cm, we calculate their number for 1 direction, divide 8200 by 200 = 41 pieces x 2 sides = 82 pieces x 2 layers of the entire slab = 164 rods;
- Let's calculate the total length: 164 x 8.14 = 1334.96 meters. The weight of 1 meter of 14-diameter reinforcement is 1.2 kilograms. Thus, the mass of the entire working reinforcement is: 1334.96 meters x 1.2 = 1601.252 kilograms;
- Let's move on to the vertical reinforcement bars, its length will be equal to the difference of 25 cm and 6 cm = 19 cm. Let's take a step of 40 centimeters, we get 21 pieces x 21 pieces = 441 units, we get the mass from the expression 441 x 0.19 x 0.395 = 33, 1 kg;
- We calculate the consumption of class B7.5 concrete for preparation as: 8.2 x 8.2 x 0.05 (specified thickness) = 3.3 meters³;
- We calculate geotextiles and waterproofing of the slab as the area of the slab adding a little margin: 67.24 meters²;
- We consider the sand cushion by multiplying the sides of the slab and the height of the cushion, taking into account that it extends beyond its boundaries by 0.1 meter on each side, that is, 8.4 x 8.4 x 0.5 = 32.5 cubic meters of sand.
Note that for two-story houses made of aerated concrete (gas silicate), frame houses and garages (made of brick), the thickness of the slab will be 20-25 centimeters. For heavier buildings, as well as two-story houses made of brick, concrete, timber, the thickness should be 25-30 cm. For light structures, for example, garages and gazebos, it is enough to take a foundation slab thickness of 10-15 centimeters.
Reinforcement of a foundation 10-15 cm thick is done in one layer, 20-30 cm thick - in two layers (volumetric).
Instructions for using the calculator
There are many online calculators on the Internet that help calculate the parameters of strip foundations for all important positions. Calculating reinforcement with their help takes literally a couple of minutes.
For example, on the website you only need to enter your own data into the appropriate windows of the program and click the “calculate” button.
A reinforcement diagram is given, in which the main parameters must be indicated - the number of working rods in one row, the total number of rows, the distance between vertical bars, etc. The cost of fittings per unit is indicated in a separate window.
As a result, the program displays the quantity of reinforcement and the total price. The calculation is simple and quick; in addition to the reinforcement, the resource provides the parameters of all elements of the tape - formwork, amount of concrete, etc.
The disadvantage of this calculator is the need to know in advance the reinforcement scheme, the diameter of the rods and the market value of the material.
If you need to determine the number and cross-section of rods, the resource is useless. It provides only quantitative information, without touching on qualitative aspects, which is sometimes not quite what is needed.
IMPORTANT!
Not all online calculators work using this algorithm. There are others that determine exactly the dimensions and general parameters of the reinforcement cage, which will be useful for obtaining primary information. The cost of the material should be found out directly from the sellers, since there are many specific factors in this matter.
Cheaper alternatives to USP
Slab pile foundation (PSF) on TISE piles. Cheaper and more reliable.
Alexander is engaged in such foundations. He has published a book and has a YouTube channel.
Don't expect a radical cost reduction. But it will be cheaper due to less insulation and concrete.
TISE piles with plank lining and wooden ceiling.
This is a real alternative that crosses out:
- cubic meters of concrete
- fittings
- foundation preparation (excavation, crushed stone, sand, compaction)
- drainage
- blind area
Drainage and blind area will still have to be done. You can postpone them for a year or two. This will alleviate the financial burden on construction. Plus, both the first and second in this foundation are simpler, and therefore a little cheaper.
True, with such a foundation there is only a wooden house: frame or SIP.
Use of reinforcement for construction purposes
Reinforcing bars primarily serve to protect the concrete base from significant loads and, as a result, the formation of destruction and cracks. Concrete by itself cannot provide strength characteristics, especially with a large area of use or pouring.
First of all, reinforcement, steel or composite, allows the foundation to cope with sudden temperature changes and soil mobility. Here it immediately becomes
In turn, the concrete coating saves the reinforcement from melting under the influence of fire and protects it from corrosion, however, the latter applies to steel material, but if modern fiberglass reinforcement is used in the work, then it is not at all afraid of corrosion.
The uneven surface of the reinforcement allows materials to firmly adhere when pouring concrete mortar. Reinforcement bars are laid longitudinally and transversely for the strength of the entire structure. In this case, installation should be carried out according to all rules.
In addition, it is necessary to select the method of connecting the reinforcement. If these are steel rods, then you can use knitting wire and welding, if it is composite, then wire.
What it is?
The reinforced concrete slab type base is a cast reinforced structure made of concrete mortar poured in one plane.
As a rule, a reinforced concrete slab occupies the entire area under the design structure. The significant consumption of concrete in this case is compensated by the increased strength, practicality and long service life of the foundation.
Scope of application
Reinforced concrete slab foundations have sufficient performance characteristics to be used in construction:
brick,- wooden,
- frame-panel one-story houses,
- buildings made of foam concrete,
- garages,
- summer kitchens and other lightweight structures.
Due to the large supporting area, the foundation remains stable against subsidence on almost all types of soil and at any level of underground sources.
Rules for drawing up a slab foundation plan for a private house
The simplicity of the slab foundation design is quite deceptive. To ensure reliability, it is necessary to correctly calculate the main parameters and select the optimal design option.
When drawing up a foundation project, you must:
- calculate operational loads from the entire structure and climatic influences;
- take into account the structure and composition of the soil, the level of freezing and the depth of groundwater;
- take into account the terrain and develop measures to form a perfectly flat area;
- choose the optimal design (type) of the slab base;
- choose the right grades of materials (primarily concrete and reinforcing elements) taking into account SNiP and GOST standards;
- calculate the required depth of the slab;
- develop a drainage system plan.
When making calculations, it is necessary to determine the total loads, which consist of the weight of the entire structure of the house and the foundation slab itself, the weight of all utilities, operational loads (furniture, interior decoration, stoves and fireplaces, household appliances, residents and guests), climatic influences (wind, snow). accumulation).
All factors are taken into account at maximum values with a certain margin of safety.
Construction technology
Most often, this type of foundation is used in difficult geological conditions. Therefore, the design and construction of “floating” structures are subject to serious requirements, described in detail in regulatory documents, the main of which are:
SNiP 3.03.01-87 “Load-bearing and enclosing structures”;
SP 50-101-2004 Design and installation of foundations and foundations of buildings and structures."
The construction scheme assumes:
Conducting various types of surveys - geological, hydrological and others.
Studying research results.
Collection of necessary documentation.
Calculation of the thickness of a monolithic concrete slab for the foundation.
Removing turf, sampling soil and other manipulations - drainage, creating a cushion.
Laying underground networks and communications.
Knitting, laying reinforcement for the frame.
The construction technology of this type of foundation does not involve the use of heavy equipment. You can do the bookmarking yourself, but to avoid mistakes it is better to contact a specialist. They will carry out work in accordance with the requirements of current legislation, in compliance with all safety standards and regulations.
Initial data
Slab foundation: load calculation is carried out if the following necessary initial data :
- Soil type and characteristics . Determined experimentally using available materials. To do this, dig a hole one and a half meters deep. The soil is carefully examined for the presence of moisture, the basic composition and approximate density are determined.
- The material from which the house is planned to be built.
- Having chosen a slab foundation: the thickness calculation is also carried out for the snow cover in a given area (maximum snow thickness).
- Brand of cement for pouring supports for a frame house.
After all the calculations have been carried out, the necessary data for the manufacture of the structure will be obtained: specific load of the house and foundation on the ground, permissible thickness of the support slab, burial depth .
Important! To obtain reliable results, several such holes should be dug in different parts of the construction site.