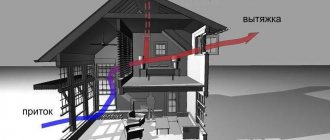
The exhaust ventilation system is one of the most common engineering networks in modern buildings. This applies to private houses, apartments, public and industrial buildings. Exhaust ventilation in a private home in almost all cases consists of exhaust ducts in the wall, even if the developer does not think about the supply system.
Exhaust ventilation systems come in different types. It is classified according to several factors. In addition to choosing the right type of exhaust ventilation, it is important to correctly select all its elements and equipment location options. We will try to consider in more detail the principle of operation of exhaust ventilation, the design and installation, as well as the calculation of the exhaust ventilation of a room.
Physical basis of ventilation
The movement of air flows is based on the simplest physical processes. The gas-air mass is processed and transported thanks to existing convection processes. To use this natural process, heat and heating sources are placed in the lowest areas, and supply elements, on the contrary, are as close as possible to the ceiling.
In its general meaning, the term “convection” represents the redistribution of thermal energy between heated and cold gas flows. Convection processes can occur naturally or forcefully.
In a closed space, the overall temperature is determined by the degree of heating of the air. The value is not constant throughout the entire space, it varies with height. The phenomenon is caused by a non-uniform concentration of molecules at constant pressure inside the room. At a higher temperature, the concentration of gas particles is lower, which means its mass is lower. Therefore, there is a concept that heated air is “lighter” and cold air is “heavier”. This fact explains the design of ventilation systems: exhaust units are located at the top, and supply units are located at the bottom.
Air movement usually occurs from bottom to top
A well-designed exhaust ventilation system in combination with natural convection processes allows you to maintain the set level of temperature and humidity indoors.
Conclusion
Thus, drawing a line above all of the above, it can be argued that the process of installing ventilation is a rather complex and labor-intensive process.
It is very important to take into account absolutely everything, even the smallest and seemingly insignificant details. Because even they are capable of completely ruining the entire structure and calling into question the correct operation of the technology.
If you are seriously thinking about installing ventilation in your home with your own hands, then first evaluate your strength. Think about whether you have done something similar before.
If you are not confident in yourself, then it is better to hire a specialist in your field to eliminate all possible difficulties that may arise.
If you are confident in yourself, then first read all the above information again. Also, once again analyze all the types of technology and decide which one suits you best.
You can also look at various drawings on the Internet; fortunately, there are enough of them on the Internet. We wish you good luck and success in the construction and installation of this structure!
What is a ventilation system
In a general sense, a ventilation system is the movement of air between the external environment and an enclosed space. From a heated and stuffy room, the air mass removes excess heat and moisture, which brings the indoor microclimate into compliance with sanitary and hygienic requirements. The ventilation system can be part of the interior design of the room and is part of the general communications network of the building.
The air masses are driven by a special ventilation system, which includes a complex of technological equipment and cleaning filters. Its main tasks are: collecting, removing, moving and purifying air.
The main difference between ventilation and air conditioning is the controlled complete cycle of renewal of air masses through inflow and outlet. While air conditioners only heat or cool the air, increase humidity and ionization.
A regular air conditioner simply circulates the air in a room.
Supply ventilation helps to completely clean the air, prevent the spread of viruses and fungi, and increase humidity to the recommended level. In emergency situations, ventilation allows you to quickly replace the air inside a room using a system of pipelines, fans, heaters, and filters.
Pros and cons of pre-chamber engines
Mentioning internal combustion engines running on gasoline, we can confidently declare their inefficiency, since the device was imperfect and showed its worst sides in motion. Therefore, none of the manufacturers wanted to rely on such a choice, and as a result, such designs are not currently used. Of course, initially people preferred such analogues because of their efficiency in fuel consumption and, at the same time, a reduction in the toxicity of emitted waste. But users changed their minds after testing the units for durability while driving.
The situation is completely different when it comes to diesel engines, which are our main object of study. The advantages of an engine with a pre-chamber engine are the insignificant smoke of the power plant, regardless of the driving method and, which is also significant, such installations do not require selected fuel.
Let's return to the negative sides, where would we be without them. An unheated engine does not start well. Why is this happening? The bottom line is that for a stable start-up, the pre-chamber must initially be well heated, but due to the fact that electric glow plugs are installed in this system, the air is not fully heated.
In conclusion, it can be noted that the operating principle of such engines has few disadvantages, so you can safely give it preference. Enjoy your travels and don't forget to leave your comments below.
Types of ventilation systems
All ventilation systems can be divided into several types according to different criteria.
Depending on the method of generating pressure, the following ventilation systems are distinguished:
- Artificial. Air movement occurs with the participation of injection units: blowers, fans. When the pressure inside the pipes increases, air masses can be moved over significant distances. Most often used in central ventilation systems.
- Natural. Occurs where the movement of air flows occurs naturally due to the difference in temperature and air pressure at different ends of the pipes. The advantages of installing such a system for residential premises include low installation costs and no need for special equipment. But in such systems it is impossible to predict or control their operation, so they are more often used as auxiliary systems.
Scheme of natural and artificial ventilation
- Combined. The most commonly used type of ventilation, combining the advantages of artificial and natural systems.
According to the area of influence, the following varieties are distinguished:
- General exchange. It has a wide area of influence, for example, all rooms of a residential building. Exhaust air is removed through ventilation shafts from the interior, where the concentration of negative substances is low and they are evenly distributed.
- Local. An air duct is connected to certain places, which draws out harmful emissions and removes them outside. It is mounted indoors, where the release of harmful substances into the air occurs pointwise. In residential buildings, this is most often the kitchen, in particular the stove. Setting up a local network is cheaper than a general exchange network, but it is designed for less air flow.
Depending on the functioning scheme, supply, exhaust and supply and exhaust systems are distinguished. Exhaust structures are intended only to remove contaminated air. The supply ventilation system ensures the supply of fresh air masses. Systems where air is exhausted and forced in are the most popular.
For supply ventilation, air ducts are made in the walls
Supply and exhaust ventilation provide optimal service in premises of various purposes and sizes.
Depending on the technical design of the system, there are:
- Collapsible modular systems include various modules: heater, noise muffler, fan, filter elements, automatic control unit, auxiliary units. The advantage of modular designs is the ability to select units with the required characteristics. The disadvantages are considered to be complex installation involving specialists.
- Monoblock ones represent ready-made kits in a single block. The design is easy to install and does not require complex maintenance and care. The cost of monoblock systems is higher than modular ones.
The presence of several types of ventilation allows you to select and install the most suitable one for specific conditions.
Special supply ventilation capable of working in a specific location
This system is called the “air shower”. In other words, it is an air flow that has a certain direction and high speed. These systems must direct fresh air directly to the work site. Reducing the heating of the environment depends on their work. Such ventilation is capable of blowing workers who are forced to work under powerful thermal radiation.
Local ventilation is installed in areas of the building that are fenced off with sliding screens, where air at a low temperature is pumped.
Natural ventilation schemes.
Most often, this type of air conditioning is used in industry. Ventilation becomes an air curtain, a kind of air partition separating gates or hot stoves.
With its help you can direct the air flow in the desired direction. Installation of such ventilation is less expensive when compared with general ventilation. In factory workshops, when there is an abundance of harmful impurities, a mixed system is most often installed.
General ventilation handles toxic substances; local ventilation only serves individual work areas.
Features of natural supply and exhaust ventilation
Unlike structures with artificial generation, natural ventilation systems use existing air flows from living rooms to the kitchen and bathroom. Movement occurs along corridors that act as flowing spaces. Such ventilation can be installed even inside houses with a non-standard layout.
The overall air movement does not change
The main ventilation unit is placed on the upper central part of the house. When laying pipes, it is taken into account that clean air should enter the living rooms and be exhausted through utility rooms and the kitchen. Supply air ducts are located on the border of living rooms, and exhaust elements are located inside the utility room, bathroom, and kitchen.
Diffusers (the outer part of the air duct) are made of plastic or thin sheet metal. They act as a distributor of clean air and an exhaust outlet. The external outlet of the pipeline is placed higher than the roof. This prevents secondary intake of waste material.
This is the most financially accessible, oldest and easiest to install type of ventilation. Its effectiveness depends on the difference between external and internal air temperatures, atmospheric pressure parameters, wind direction and the stable flow of supply air into the room. To comply with the last condition, you will have to make an effort: keeping the window open all the time is not the best option. For this purpose, now consider using window or wall supply valves. Repair and maintenance of natural ventilation systems is not very difficult and comes down to timely cleaning of ventilation ducts and supply valves.
| Advantages | Flaws |
| Easy installation | Dependency on weather conditions |
| No operating costs | Heat loss in the cold season |
| Silent operation | Low efficiency at high humidity indoors (not suitable for baths, swimming pools) |
Prechamber-torch ignition in F1. Like the Volga GAZ-3102.
Photo: LAT Photographic
The need to extract the maximum amount of power from the minimum amount of energy expended prompted Formula 1 engineers to turn to the technology used on large trucks. AUTOSPORT technical expert Craig Scarborough described the operating principle of pre-chamber-torch ignition, which was used in Mercedes and Ferrari, and which was previously used on... government Volgas in the USSR.
There was a time when an F1 driver could easily be fired for simply comparing Grand Prix cars to trucks. But the irony is that at least half of the peloton now uses combustion efficiency technology, which is used on heavy trucks...
Since the introduction of the new turbocharged regulations in Grand Prix racing in 2014, there has been a restriction on the maximum available amount of fuel per race - now it is 100 kg, and from next year it will be 105 kg.
This, in turn, limited the maximum permissible instantaneous fuel consumption and the maximum pressure under which the fuel is supplied to the combustion chamber. For engineers, such strict limits became a real challenge - they had to come up with a way, under these restrictions, to achieve the same power output of power plants.
Features of forced supply and exhaust ventilation
The operation of this system is based on the interaction with two different air flows, which are carried through installed air ducts. Depending on the power and throughput of the mechanisms involved, a given volume of air masses is processed.
All working units and equipment are located inside a single housing, which can be assembled in any convenient place: on an external wall, attic or attic.
Forced ventilation
| Advantages | Flaws |
| Based on the interaction of supply and exhaust ventilation. But in this case, both inflow and exhaust are carried out forcibly through the operation of technical equipment. | The calculation of the ventilation system and the power of the equipment must be carried out by specialists. Since technical devices are involved in the work process, timely repair and maintenance of ventilation systems is necessary. |
| High efficiency in large houses | Calculation, installation and commissioning work must be carried out by specialists |
| Automatic operation | Equipment costs |
| Maintaining specified air humidity parameters | |
| Possibility to install a recuperator and ensure energy-efficient operation of the system |
Supply and exhaust ventilation unit installed in the attic
Depending on additional equipment, supply and exhaust ventilation can perform the following functions:
- increased air humidity;
- ion saturation;
- cooling or heating of the air mass;
- purification, filtration, elimination of harmful microorganisms.
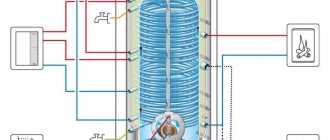
A modern supply and exhaust ventilation system as part of the module has a recuperator - a heat exchange chamber where encountering air flows exchange energy. Heat is taken from the heated outgoing air and given to the incoming air (or vice versa, if the air conditioner is running in the room in the summer).
The principle of operation of the recuperator
The ventilation operating cycle with two circuits and a recuperator consists of the following stages:
- warm air from the room is conducted through the recuperator, heating the heat exchanger installed in it;
- “exhaust” air is removed outside;
- clean cool air is taken from the outside and passed through the heated heat exchanger of the recuperator, taking away heat from it
- fresh heated air is supplied to the room.
To expand the functionality, the design is supplemented with filter systems, automatic timers, control units, condensate collection trays, control units, sensors, and noise suppressors.
Scheme of supply and exhaust ventilation with automation system
The main principles of this type of ventilation are efficiency and effectiveness. The main advantages include:
- simple installation and maintenance of supply and exhaust ventilation;
- high-quality cleaning of incoming air masses;
- integrity of blocks;
- modular design.
Air conditioning characteristics
Indoor ventilation and air conditioning must be created together to provide the most comfortable and pleasant conditions for living and working. However, these two systems have certain significant differences that every person involved in the process of creating them should be aware of. Initially, it is important to note that conditioning can be accomplished by two different methods.
Initially, a ventilation system can be created that, along with air renewal, can additionally cool it. To do this, it is necessary to purchase specialized equipment that will be equipped with expensive internal components, which, when air enters from outside, will not only ionize and purify it, but also cool it. In this case, you will have to concentrate only on creating a high-quality ventilation system, which will have an unusually high cost. However, in this case, it will be much easier to do all the work yourself, since only one system will be installed as a result.
Air conditioning can also be implemented using specialized equipment designed for these purposes. If it is installed in one small room, then a standard split system is suitable for this, namely an air conditioner, which is a combination of indoor and outdoor units connected to each other. If you have to deal with an integral large building, for which it is important to carry out air conditioning, then in this case expensive multi-channel installations are suitable.
They are usually a separate device, very large in size and unusually high power. It is mounted in a separate room created for it, and pipes are led from it to different rooms through special channels, and they are hidden in the walls. In this case, one unit can easily handle the air conditioning of an entire building. The installation of such equipment is considered to be quite complex and specific work, and it must be done at the stage of construction or major repairs of the structure, since a lot of pollution arises in the process, and you also have to make holes in the walls.
Also, air conditioning of a certain building can be implemented using a multi-split system, which differs in that there is one outdoor unit to which it is possible to connect several internal elements at once, and they can be located in different rooms of the same building. This solution is considered optimal if there is a not too large building with no more than five rooms.
What parameters should you use to choose a recuperator?
The first thing you should pay attention to when choosing a model of a supply and exhaust recuperator is whether its technical characteristics correspond to the main parameters of the ventilated room: volume, height, required air exchange rate, etc. Independent calculation of the performance of a ventilation system is not an easy task for the uninitiated. To solve it, the developer will have to familiarize himself with the requirements of sanitary and constantly changing building standards, study the laws of air flow dynamics, take into account the number of people living in the house, combine the knowledge gained and calculate the performance of the supply and exhaust equipment.
The main calculation parameter is the volume of air that should enter the room within one hour. In accordance with sanitary standards, this volume should be equal to 30 m³ per adult (minimum indicated). In practice, the performance of supply and exhaust ventilation, and, consequently, of the recuperator, should be higher. This is due to resistance losses in air ducts, large volumes of rooms and other factors.
It is better to entrust the calculation work to specialists. Indeed, in case of an error, replacing the recuperator will require significant financial costs.
Main parameters of the ventilation system
The main working element is a fan, but not the usual propeller, but an impeller, which is a wheel with blades - this design allows you to reduce the size of the equipment.
The efficiency of the installed structure directly depends on the accuracy and correctness of the preliminary calculations. For example, it is equally bad if insufficient or excessive engine power is selected. In the first case, the engine will wear out and soon enough it will have to be replaced. If the power is excessive, this means regularly inflated maintenance and electricity costs.
Calculations of performance and dynamic parameters of air flows are made using algebraic formulas. It is recommended to entrust the calculations to a specialist who will not only do it correctly, but also obtain the necessary approvals from the fire inspectorate.
Firefighters check the operation of the supply and exhaust ventilation
The calculations take into account the following data:
- Premises parameters: purpose - residential or non-residential, internal area, number of floors, humidity level.
- The number and type of activity of people simultaneously present inside the building.
- Required level of air exchange according to SNiP 2.04.05-91. For example, in living rooms it is 3 cubic meters per hour per 1 meter of living space.
- Pipeline cross-section and installation diagrams.
Prechamber engine and prechamber
The prechamber (prechamber) is a special cavity that is located in the cylinder head of the internal combustion engine. This cavity is structurally connected to the main combustion chamber in the space above the piston through one or more channels. The prechamber (prechamber) engine can be either gasoline or diesel.
An internal combustion engine of this type is a design in which mixture formation and filling of cylinders occurs as follows:
- the fuel-air mixture is supplied to the prechamber;
- then partial ignition of the mixture occurs;
- as a result of combustion, the pressure in the prechamber increases;
- under the influence of such pressure, heated fuel vapors and gases from partial combustion in the pre-chamber penetrate into the main combustion chamber in the space above the piston;
What standards exist for ventilation systems?
Recommended air exchange parameters depend on various conditions and are prescribed in the relevant regulations, which must be taken into account during design. In general, for domestic premises, when rooms for different purposes are concentrated on one floor, the following amount of air should change in an hour:
- office – 60 cubic meters;
- common living rooms or halls – 40 cubic meters;
- corridors – 10 cubes;
- bathrooms and showers – 70 cubic meters;
- smoking rooms - over 100 cubic meters.
In living rooms, air mass exchange is calculated per person. It should be more than 30 cubic meters per hour. If the calculation is made based on living space, then the standard is 3 cubic meters per 1 meter.
For non-residential premises, the average standard is 20 cubic meters per meter of area. If the area is large, then ventilation systems include a multi-component system of paired fans.
What formulas are used in calculations
The main parameter that needs to be calculated in any system is how much air should be changed within an hour.
For residential apartments, the value is determined according to the living area: V=2xSxH, where S is the area of the living room, 2 is the coefficient of air mass exchange rate per 1 hour, H is the height of the room.
For work premises, the calculation is made based on the number of personnel: V=Nx35, where N is the number of people simultaneously present in the room.
When calculating the power of a ventilation station, the formula is used: P=ΔT * V * Сv/1000, where V is the volume of air mass consumed per hour, Сv is the heat capacity of the air mass, ΔT is the temperature difference of the air mass at the ends of the pipeline. The accepted value of heat capacity is 0.336 W * h/m³ * °C.
Another important indicator is the cross-sectional area of the duct, measured in square centimeters. There are 2 types of sections: square and round. By calculating the cross-sectional area, it is possible to determine the width and height of a rectangular pipe or the diameter of a round one.
Video description of ventilation calculations
More about the calculation of ventilation in the video:
Ssection = V * 2.8/w, where Ssection is the cross-sectional area, V is the volume of air mass (m³/hour), w is the air flow speed inside the highway (m/sec) (average from 2 to 3), 2.8 – dimensional matching coefficient.
For installation, it is necessary to calculate how many diffusers (intake and outlet openings) and their parameters are required. The dimensions of the nozzles are calculated based on the cross-sectional area of the main pipeline, multiplied by 1.5 or 2. To calculate the number of diffusers, use the formula: N=V/(2820 * W * d2), where V is the volume of air mass consumed per hour, W is speed of movement of the air mass, D – diameter of the round diffuser.
For rectangular diffusers, the formula is transformed as follows: N=π * V/(2820 * W * 4 * A * B), π is the number pi, A and B are the section parameters.
In any case, calculations of ventilation systems should be carried out by professionals - if something is forgotten or not taken into account, then the cost of the mistake is the need to redo the calculations and work.
A full calculation of supply ventilation is done using specific software
Window inlet valve
You can install a special supply ventilation valve into the window. This is a special plastic product with a damper to regulate air flow. Available in 2 variations:
- for blind windows. Involves making a hole in the profile and installing an external protective canopy. The valve is mounted in the hole. A decorative cover with a handle for adjusting the flow is installed on the inside;
- for opening doors. Mounted inside the frame. In this case, it is necessary to replace the seal section with a special material. There is no need to make a hole in the profile.