The ability to use water as a coolant allowed humanity to invent effective heating of their homes. An open heating system is a classic option that is still popular due to its simple operating principle and the minimum number of necessary devices.
What an open system looks like in practice
How a heating system works without a pump - options and methods of installation
In order to be able to live in a built country house at any time of the year, it needs high-quality heating. Among the wide variety of heating devices, it is sometimes difficult to decide what exactly is needed in a given situation. One of the simplest options that you can arrange yourself is a heating system without a pump, that is, with a natural type of coolant circulation. It is this type of heating that we will talk about later in the material.
Multi-level floor
To zone the space, craftsmen install floors at different levels. They advise installing a podium to separate the kitchen and dining room. This option is considered one of the most practical because, among other things, the owners have additional free space where they can hide something.
It is convenient to use boxes or crates for this. Wicker baskets will look good. But such space can remain free.
However, such a design should not be made if there are small children in the family, since the podium can become an obstacle for him. In addition, various floor coverings can be used.
They will zone the space between the living room and the kitchen and protect the podium from damage. For example, tiles are laid in the kitchen area, and laminate flooring in the dining room. The main thing is to choose colors and textures and combine the finishes correctly.
Date: September 25, 2021
In what cases can you do without a pump?
The movement of coolant inside the heating circuit occurs under the influence of the laws of physics. This means that when heated, the liquid rises, and as it cools, it falls again, thereby heating the room.
Most of all, a heating system without a circulation pump is in demand precisely in country houses and dachas, since in suburban conditions the power supply is not always stable or absent altogether. In this regard, heating equipment with a forced circulation type is impractical.
It is noteworthy that it is quite possible to install heating with natural coolant circulation yourself. In addition, such a system is very convenient to use.
What it is?
Thanks to artificial heating of premises for various purposes, it is possible to compensate for heat losses and maintain the specified temperature values. Thermal comfort conditions for living require the operation of an open or closed heating system. Any type of heat supply network has undeniable advantages and certain disadvantages that must be taken into account when choosing a scheme.
Advantages and disadvantages
An open system is based on thermodynamic laws. Its main advantages include:
- energy independence;
- natural circulation of coolant;
- ease of maintenance;
- silent operation;
- minimum equipment;
- high level of reliability;
- ease of self-installation.
Significant disadvantages include bulkiness, the risk of cavitation, which destroys system elements, and low efficiency. Among other things, the operation of an open heating network requires strict control of the coolant level, as well as the impossibility of using antifreeze.
Differences from a closed system
Autonomous heating systems have a number of significant differences from a closed heating network. Features and main differences must be taken into account when choosing the optimal heating option for a room.
| Options | Open | Closed |
| Connection with the atmosphere | Permanent | Absent |
| Storage tank | Spacious round or rectangular tank with drain pipe | Double-chamber with membrane, designed for maximum pressure |
| Installation location | At the highest point of the mounted system | Not of fundamental importance |
In conditions of centralized heating (apartments), an open system is based on supplying hot water directly to the taps. The heat carrier first undergoes additional deaeration and mandatory cleaning, and after use it is discharged into the sewer.
Structure and types of systems with a natural type of circulation
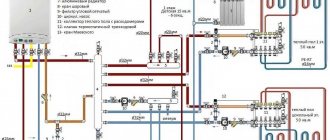
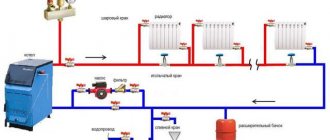
Typically, a heating circuit without a pump includes a list of required components:
- heating device - a boiler or stove that can be heated with the type of fuel available in a particular region;
- expansion tank, which allows you to relieve excess pressure or add water to the heating circuit;
- pipes that form the circuit along which water will move in the system;
- batteries that allow you to heat the room more efficiently by increasing the area of the heat-transferring surface.
The diameter of heating pipes with natural circulation will be slightly larger than if a circulation pump is used.
Based on what kind of coolant will be used, heating systems with natural circulation can be water or steam.
Here are the distinctive features of each type of heating.
Pipe selection
When choosing heating pipes, not only the diameter is of great importance, but also the material from which they are made, and, more precisely, the smoothness of their walls, since this fundamentally affects the system.
Also, the choice of material is greatly influenced by the boiler, since in the case of solid fuel, preference should be given to steel, galvanized pipes or stainless steel products, due to the high temperature of the working fluid.
However, metal-plastic and reinforced pipes require the use of fittings, which significantly narrows the clearance; reinforced polypropylene pipes will be an ideal option at an operating temperature of 70C and a peak temperature of 95C.
Products made from special PPS plastic have an operating temperature of 95C, and a peak temperature of up to 110C, which allows use in an open system.
Heating with water as coolant
The functional features of water heating systems with a natural type of coolant circulation are determined by a number of characteristics.
Based on which expansion tank is used to equip a heating system with natural coolant circulation, there are:
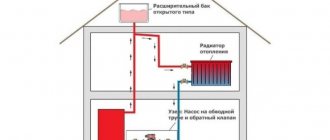
- Open systems . In this case, the expansion tank is installed as high as possible in order to create excess pressure in the expansion tank. In addition, thanks to this you can get rid of air pockets in the heating circuit. From time to time, water that has partially evaporated during heating operation is added to the pipes through an open expansion tank.
- Closed systems . In such heating with natural circulation, the expansion tank is replaced by a special membrane hydraulic storage cylinder. It provides additional pressure in the circuit within 1.5 atmospheres. For safety reasons, systems of this design are usually equipped with a block with a pressure gauge, the task of which is to adjust the pressure inside the pipeline.
Another fundamental point that distinguishes the design of heating systems with a natural type of water circulation is the connection diagram of the heating elements.
According to the method of connecting heating devices to a gas boiler without a pump, the following options can be distinguished:
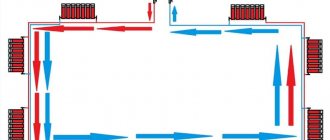
- Single-pipe heating distribution . With this type of heating, all radiators are connected in series to the same pipe. That is, water passes through each subsequent heating device and only after that it moves on. Among the advantages of single-pipe distribution equipment are the simplicity of its installation, as well as low material consumption.
- Two-pipe wiring in a heating system with a natural circulation type. In this case, all radiators that are part of the heating system are connected to the pipeline in parallel. In this case, the temperature of the coolant that enters each radiator is the same. After the water has passed through the entire radiator and cooled, it returns through the return pipe to the boiler heat exchanger.
It is believed that a two-pipe wiring diagram is the most appropriate from the point of view of the efficiency of heating a home. True, to equip such a system, you will need quite a lot of pipes and additional elements for installing the heating circuit.
It is worth noting that when deciding how to make heating without a pump, take into account your practical skills, as well as your financial capabilities for purchasing consumables.
Emergency options
Every piping scheme must include a circuit in case of emergency situations. His task includes:
— protection against pressure drops;
— protection against temperature increases above the permitted limit;
— prevention of moisture formation.
Safety valve in the harness
Its task is precisely to relieve excess pressure from the system. It is mounted at the boiler outlet separately or as part of a safety group.
Emergency heat exchanger in the solid fuel boiler connection system
Its task is most responsible - to prevent overheating of both the boiler and the system in general. Overheating can happen for 2 reasons:
— too much fuel was loaded into the boiler. The heat received exceeded the demand.
— the electricity was turned off and the pump stopped working.
For normal operation of this circuit, it is also necessary to install a temperature sensor with a valve and a cooling unit in the water supply pipe to the boiler. As soon as the coolant temperature exceeds the maximum allowed, the sensor signals this and provokes the opening of the valve.
After the valve is activated, water begins to fill the cooling unit, reducing the temperature of the main coolant.
Auxiliary heating circuit for a solid fuel boiler
One of the options for cooling the system. Its peculiarity is that you will need to connect a storage tank for the DHW circuit.
This scheme will work as follows: in normal operating mode, the pump will operate, creating a certain pressure. It will prevent the auxiliary circuit from coming into operation. But as soon as the electricity is turned off, the pump will stop working, the pressure will disappear, and the backup circuit will come into operation.
Result: the water temperature in the system will drop to the desired value.
Let’s say right away that this scheme is suitable for absolutely any type of heating system!
This mixer maintains the lowest temperature of the coolant at the inlet to the boiler so that condensation does not form on the walls of the device. what we talked about at the very beginning of the article. Thus, in a solid fuel boiler this is one of the most necessary components!
The mixer is installed on the return pipe using a bypass.
If the temperature in the return pipe is low (below the set value), the thermomixer will provide an influx of hot water.
Steam heating type
Some consumers confuse steam heating with water heating. In essence, these systems are very similar, except that the coolant is steam rather than water.
Inside the heating boiler of a natural circulation system, water is heated to boiling point and converted into steam, which is then moved into the pipeline and then supplied to each radiator in the circuit.
The design of a steam heating system with natural coolant circulation includes the following components:
- a special heating boiler, inside which water is heated to boiling point and steam is accumulated;
- valve for releasing steam into the heating system;
- pipeline;
- heating radiators.
Please note that the steam type heating system is operated at very high temperatures, so it is strictly forbidden to use plastic pipes to construct the pipeline.
The classification of steam-type heating according to wiring diagrams and other criteria is exactly the same as for water heating systems. Recently, a boiler has also been used to heat a private home, which also has its advantages.
Which scheme is better, forced or natural?
A natural system is better if you need to organize heating for a small one-story private house. In this case, there is no point in spending money on pumping equipment when the natural coolant current will be sufficient to heat the entire building.
Forced circulation circuits are best used in large one-story or multi-story buildings. Thanks to the rapid movement of the coolant in the network, buildings of significant size will be heated well and evenly. Natural circulation circuits will not cope with this task.
How to install heating correctly
In order for a finished heating system with a natural circulation type to function correctly and efficiently, it is important to adhere to certain rules when installing it.
In general, the installation diagram looks like this:
- Heating radiators must be installed under the windows, preferably at the same level and maintaining the required indentations.
- Next, install the heat generator, that is, the selected boiler.
- Install the expansion tank.
- The pipes are laid out and the previously fixed elements are joined into a single system.
- The heating circuit is filled with water and a preliminary check for the tightness of the connections is performed.
- The final stage is to start the heating boiler. If everything works correctly, then the house will be warm.
Please pay attention to some nuances:
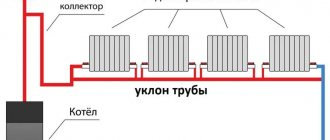
- The boiler should be located at the lowest point of the system.
- The pipes must be installed with a slope towards the return flow.
- There should be as few turns in the pipeline as possible.
- To increase heating efficiency, pipes with a larger diameter are required.
We hope this article will be useful to you, and you will be able to independently install a heating system without a circulation pump in your country house.
Article source: https://teplospec.com/montazh-remont/kak-ustroena-sistema-otopleniya-bez-nasosa-varianty-i-sposoby-ustroystva.html
Gravity heating system with natural circulation - calculations, slopes, types
For private country houses and cottages, a heating system with natural coolant circulation is often installed. This decision has its positive and negative sides. The scheme is performed in four different ways.
A system with gravity circulation is sensitive to errors made during heating installation.
The principle of operation of a natural circulation system
The heating scheme for a private house with natural circulation is popular due to the following advantages:
- Easy installation and maintenance.
No need to install additional equipment.
- Energy independence – no additional energy costs are required during operation. When the power goes out, the heating system continues to operate.
The operating principle of water heating, using gravity circulation, is based on physical laws. When heated, the density and weight of the liquid decreases, and when the liquid medium cools, the parameters return to their original state.
At the same time, there is practically no pressure in the heating system. In thermotechnical formulas, a ratio of 1 atm is accepted for every 10 m of water column pressure. Calculation of the heating system of a 2-story building will show that hydrostatic pressure does not exceed 1 atm, in one-story buildings 0.5-0.7 atm.
Since the liquid increases in volume when heated, an expansion tank is required for natural circulation. The water passing through the boiler water circuit heats up, which leads to an increase in volume. The expansion tank should be located on the coolant supply, at the very top of the heating system. The purpose of the buffer tank is to compensate for the increase in liquid volume.
A self-circulating heating system can be used in private homes, making the following connections possible:
Connection to heated floors - requires installing a circulation pump, only on a water circuit laid in the floor. The rest of the system will continue to operate with natural circulation. After a power outage, the room will continue to be heated using the installed radiators.
Types of heating systems with gravity circulation
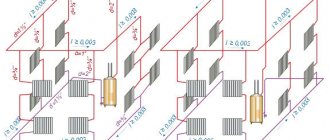
Despite the simple design of a water heating system with self-circulation of coolant, there are at least four popular installation schemes. The choice of wiring type depends on the characteristics of the building itself and the expected performance.
To determine which scheme will work, in each individual case it is necessary to perform a hydraulic calculation of the system, take into account the characteristics of the heating unit, calculate the diameter of the pipe, etc. You may need professional help when performing the calculations.
Closed system with gravity circulation
In EU countries, closed systems are the most popular among other solutions. In the Russian Federation, the scheme has not yet received widespread use. The operating principles of a closed-type water heating system with pumpless circulation are as follows:
- When heated, the coolant expands and water is displaced from the heating circuit.
Under pressure, the liquid enters a closed membrane expansion tank. The design of the container consists of a cavity divided by a membrane into two parts. One half of the tank is filled with gas (most models use nitrogen). The second part remains empty for filling with coolant.
How to properly make water heating with natural circulation
All gravity systems have a common drawback - the lack of pressure in the system. Any violations during installation work, a large number of turns, non-compliance with slopes, immediately affect the performance of the water circuit.
To make proper heating without a pump, take into account the following:
Type and diameter of pipes used for the water circuit.
What pipe slope is needed for gravity circulation
The design standards for an in-house heating system with gravity circulation are specified in detail in building codes. The requirements take into account that the movement of liquid inside the water circuit will be hampered by hydraulic resistance, obstacles in the form of corners and turns, etc.
The slope of heating pipes is regulated by SNiP. According to the standards specified in the document, a slope of 10 mm is required for each linear meter. Compliance with this condition guarantees unhindered movement of fluid in the water circuit.
Violation of the slope when laying pipes leads to airing of the system, insufficient heating of radiators remote from the boiler, and, as a result, a decrease in thermal efficiency.
What pipes are used for installation
The choice of pipes for the manufacture of the heating circuit is important. Each material has its own thermal characteristics, hydraulic resistance, etc. When performing installation work yourself, additionally take into account the complexity of installation.
The most commonly used building materials are:
- Steel pipes - the advantages of the material include: affordable cost, resistance to high pressure, thermal conductivity and strength. The disadvantage of steel is its complex installation, which is impossible without the use of welding equipment.
Metal-plastic pipes - have a smooth inner surface that prevents the circuit from clogging, light weight and linear expansion, no corrosion. The popularity of metal-plastic pipes is somewhat limited by their short service life (15 years) and the high cost of the material.
Polypropylene pipes are widely used due to their ease of installation, high tightness and strength, long service life and resistance to freezing. Polypropylene pipes are installed using a soldering iron. Service life of at least 25 years.