Heating systems – requirements and choice
In modern construction, various types of heating systems and many model diagrams of related equipment are used. It is impossible to call one or another solution optimal, since when installing and choosing them, it is necessary to take into account specific conditions and a variety of initial data. However, there are several rules that any heating communications are subject to.
- The heating system in the house must ensure proper temperature regulation. In addition, heat must be efficiently transferred and distributed throughout all heated rooms. The heating system for a private home must meet several criteria, the main ones being:
- High efficiency at minimal cost. According to this indicator, the heating system must produce the required amount of heat for high-quality heating of the premises. At the same time, the costs of its installation and operation must be minimized.
- High degree of automation. In this regard, communications to ensure home heating should be used with minimal human intervention. This maximizes their safety.
Modern heating system with multiple heat sources Source homemarket.ua
- High reliability and wear resistance of all system components. Equipment purchased for installation of communications must be as reliable as possible with a long service life and a warranty from the manufacturer.
Quite often, when installing heating mains, the principle is applied - the simpler, the more reliable.
Types of radiator connections
The main methods of connecting heating system devices are several types:
- Lateral (standard) connection;
- Diagonal connection;
- Bottom (saddle) connection.
Side connection
Lateral radiator connection.
Connection from the end of the device - supply and return are located on one side of the radiator. This is the most common and effective connection method; it allows you to remove the maximum amount of heat and use the entire heat transfer of the radiator. As a rule, the supply is at the top and the return is at the bottom. When using a special headset, it is possible to connect from bottom to bottom, this allows you to hide the pipelines as much as possible, but reduces the heat transfer of the radiator by 20 - 30%.
Diagonal connection
Diagonal radiator connection.
Connection diagonally to the radiator - the supply is on one side of the device from the top, the return is on the other side from the bottom. This type of connection is used in cases where the length of a sectional radiator exceeds 12 sections, and a panel radiator is 1200 mm. When installing long radiators with side connections, there is uneven heating of the radiator surface in the part furthest from the pipelines. To ensure that the radiator heats up evenly, a diagonal connection is used.
Bottom connection
Bottom connection from the ends of the radiator
Connection from the bottom of the device - supply and return are located at the bottom of the radiator. This connection is used for the most hidden installation of pipelines. When installing a sectional heating device and connecting it using the bottom method, the supply pipe approaches on one side of the radiator, and the return pipe on the other side of the bottom pipe. However, the heat transfer efficiency of radiators with this scheme is reduced by 15-20%.
Bottom radiator connection.
In the case when the bottom connection is used for a steel panel radiator, then all the pipes on the radiator are located at the bottom end. The design of the radiator itself is made in such a way that the supply flows through the manifold first to the upper part, and then the return flow is collected in the lower radiator manifold, thereby not reducing the heat transfer of the radiator.
Bottom connection in a single-pipe heating circuit.
Types of autonomous heating systems
It is worth immediately noting that it is better to entrust the installation of heating systems to professionals. All heating systems are, first of all, classified according to the type of fuel that is used to heat the coolant. If for some reason the optimal type of fuel changes frequently in your area, then you may want to consider combination boilers, which allow you to use multiple types of fuel or energy sources.
A striking example is solid fuel boilers with the ability to connect gas or electricity. There are models on the market that combine several methods of increasing the temperature of the coolant - gas, electricity, solid or liquid fuel.
Such boilers are endowed with all the advantages of standard devices operating on one type of fuel. However, they increase many times over, since several types are combined in one device. Now let's look at the types of heating systems in more detail.
Water heating system with a modern radiator Source www.remontnik.ru
Water heating
This type is the most common. The relative ease of installation and availability of the coolant - water, will retain the relevance of water heating for many years to come. To ensure optimal heating, various installation schemes are used. This can be a two-pipe heating system or a single-pipe heating system.
Radiators made of cast iron, steel or aluminum act as heat exchangers in such systems. Also, bimetallic equipment or converter-type batteries are popular. The pipeline is made of metal or special plastic. Such a system can be built on the basis of almost any heating boiler.
Advantages:
- the ability to control the temperature of system components;
- the possibility of installing a pipeline of a smaller cross-section relative to a steam and air heating system;
- high degree of safety during operation;
- fairly low financial costs and minimal requirements for the quantity of consumables;
- no noise during operation;
- uniform heating of all components included in the system.
"Leningrad heating" wiring Source aquasistem.ru
Disadvantages:
- the likelihood of clogging the system with air locks;
- the need for constant monitoring for the performance of the thermal energy source;
- when using metal communications, there is a high probability of corrosion;
- when using old-style radiators, the system warms up slowly;
- difficulties during installation work;
- sensitivity to low ambient temperatures with the risk of system defrosting.
Air heating
In such systems, the room is heated by air flow. Ambient air is taken in by intakes and supplied to the heating element of the system. It can be gas or electric equipment. A water heat exchanger can also be used.
The heated air is forced into the room by means of a fan. When a new portion is taken in, already heated air from the rooms is mixed with fresh air from the street. To do this, it is advisable to install a filter element in the system that will trap dust and other unwanted fractions.
The process is performed cyclically until the room temperature is raised to the required level. The thermostat installed in the system switches off at the desired level and turns on the equipment when it deviates minus one degree.
House air heating diagram Source build-experts.ru
Air heating systems offer high flexibility for the installation of various modules and add-ons. If you install a water cooler or an evaporator from an air conditioner in a channel with a heater, then in the summer you can use communications to create coolness in the room.
If there is a heat pump function in the air conditioner evaporator, in winter this circuit is also used as a heating element. The air supply channel itself can be equipped with a humidifier, sterilizer, ionizer and many other additional devices.
Advantages:
- the ability to install all types of air treatment at “one point”, from filtration to humidification.
- additional operating mode options – air conditioning or heat pump;
- due to controlled ventilation, up to 30% of energy resources are saved in relation to other types of heating;
- excellent comfortable characteristics combining heating, ventilation and air filtration as standard equipment;
- temperature control using a thermostat can be done via the Internet;
- the system is not afraid of low temperatures, has high reliability and a long service life;
- ease of use, since all elements of the system are easily accessible and can be quickly replaced.
Air heating using a fireplace Source stroikairemont.com
Disadvantages:
- most of the work on installing the system should be planned at the building design stage;
- air communications require a certain space in the internal volume of the room.
Water heating devices
The following can serve as heating elements for rooms:
- traditional radiators installed under window openings and near cold walls, for example, on the north side of the building;
- pipe underfloor heating circuits, otherwise heated floors;
- baseboard heaters;
- in-floor convectors.
Water radiator heating is the most reliable and cheapest option among those listed. It is quite possible to install and connect batteries yourself; the main thing is to correctly select the number of sections according to power. Disadvantages are poor heating of the lower zone of the room and the placement of appliances in plain sight, which is not always consistent with the interior design.
All commercially available radiators are divided into 4 groups according to the material of manufacture:
- Aluminum - sectional and monolithic. In fact, they are cast from silumin, an alloy of aluminum and silicon, and are the most efficient in terms of heating speed.
- Bimetallic. A complete analogue of aluminum batteries, only the frame is made of steel pipes inside. Scope of application: multi-apartment high-rise buildings with central heating, where the coolant is supplied at a pressure of over 10 bar.
- Steel panel. Relatively cheap monolithic radiators made from sheets of stamped metal plus additional fins.
- Cast iron sectional. Heavy, heat-intensive and expensive devices with an original design. Due to their considerable weight, some models are equipped with legs - it is unrealistic to hang such an “accordion” on the wall.
Note. We are talking about cast iron radiators in a modern design. Soviet-style MS-140 batteries are outdated in all respects.
In terms of demand, steel appliances occupy a leading position - they are inexpensive, and from the point of view of heat transfer, thin metal is not much inferior to silumin. Next come aluminum, bimetallic and cast iron heaters. Choose which ones you like best.
Construction of heated floors
The underfloor heating system consists of the following elements:
- heating circuits made of metal-plastic or polyethylene pipes, filled with cement screed or laid between joists (in a wooden house);
- distribution manifold with flow meters and thermostatic valves to regulate water flow in each loop;
- mixing unit - a circulation pump plus a valve (two- or three-way) that maintains the coolant temperature in the range of 35...55 °C.
The mixing unit and the manifold are connected to the boiler by two lines - supply and return. Water heated to 60...80 degrees is mixed in portions by valve into the circuits as the circulating coolant cools.
Warm floors are the most comfortable and economical heating method, although installation costs are 2-3 times higher than installing a radiator network. The optimal heating option is shown in the photo - floor water circuits + batteries, controlled by thermal heads.
Warm floors at the installation stage - laying out pipes on top of the insulation, attaching a damper strip for subsequent filling with cement-sand mortar
Skirting and in-floor convectors
Both types of heaters are similar in the design of the water heat exchanger - a copper coil with thin plates mounted on it - ribs. In the floor-standing version, the heating part is covered with a decorative casing that looks like a plinth; gaps are left at the top and bottom for the passage of air.
The heat exchanger of the in-floor convector is installed in a housing located below the level of the finished floor. Some models are equipped with low-noise fans that increase the heater's performance. The coolant is supplied through pipes laid hidden under the screed.
The described devices fit well into the design of the room, and underfloor convectors are indispensable near transparent external walls made entirely of glass. But ordinary homeowners are in no hurry to purchase these devices because:
- copper-aluminum convector radiators are not a cheap pleasure;
- to fully heat a cottage located in the middle zone, you will have to install heaters around the perimeter of all rooms;
- in-floor heat exchangers without fans are ineffective;
- the same products with fans emit a quiet monotonous hum.
Baseboard heating device (pictured left) and in-floor convector (right)
Hence the conclusion: a convector is a useful thing for certain places where it is difficult to place conventional batteries. But heating an entire building with such devices is unreasonably expensive.
Video description
Watch the video to see what air heating is in a house:
Steam heating
This closed heating system remains a fairly popular solution in our time. Various types of fuel are well suited for its operation - solid, gas and electricity. Combined temperature sources are also used, which are given priority during installation work. Proper selection of a steam boiler helps to significantly save on living space heating costs.
The principle of operation of such a system is to bring water to the boiling point. The resulting steam is sent to the heating system. Passing through the communications, it cools and flows back into the steam boiler in the form of condensate. How reliable the system will be during operation directly depends on the model of the steam boiler. It is selected based on the structural features of the heated building and its area.
Advantages:
- quickly achieving the required temperature in the building, regardless of its area;
- low probability of failure at low ambient temperatures;
- cyclical heating process;
- environmental safety of the system.
Boiler for steam heating Source build-experts.ru
See also: Catalog of projects of two-story houses with a boiler room and fireplace
Flaws:
- explosion hazard of the steam boiler and the need for constant monitoring during operation;
- high complexity of installation work;
- high price of components;
- for commissioning it is necessary to obtain permission from the regulatory authorities;
- a fairly high noise level when filling the system with steam;
- negative impact on the operational capabilities of the high coolant temperature system;
- there is no possibility to fully control the temperature conditions indoors.
Gas heating
In areas with main gas communications, natural gas heating is installed. Essentially, this is a type of water heating. It’s just that in this case gas acts as the main source of energy. However, both air and steam systems can be implemented on this basis.
In the absence of main gas lines, you can organize a small gas storage facility, which needs to be filled with liquefied gas for the heating season. Such storage facilities are called gas tanks and gas is delivered and stored in liquefied form.
Floor-standing gas boiler Source www.ural.org
Advantages:
- long service life of the system equipment;
- high level of fuel economy;
- ecological purity of the energy source.
Flaws:
- high complexity of installation work;
- high cost of system components;
- the need to obtain permission from regulatory authorities;
- the need for constant monitoring by service departments;
- in the absence of a main connection, additional costs for the necessary equipment;
- In the absence of main gas lines, using liquefied gas in a gas tank will cost more than natural gas, plus you will have to regularly spend time refueling the system.
Electric heating
The three main advantages of electric heating systems are the possibility of full automation, safety and environmental friendliness. There is only one minus – the cost of electricity is still quite high. But if the financial issue is not in the foreground, then convenience outweighs the cost of the issue.
Most electric heating systems do not require the use of coolants. In convectors, infrared heaters, electric fireplaces and similar devices, electricity is directly converted into heat. The only exception is electric boilers that heat water for the heating system and/or domestic use.
Wall-mounted electric boiler Source avatars.mds.yandex.net
Advantages:
- fairly affordable prices for system components;
- the use of electric boilers in hot water supply systems simultaneously with heating of premises;
- mobility of many system components;
- no need for maintenance with serious financial costs;
- ample opportunities for automating the process and maintaining optimal temperature conditions in the building;
- environmental safety of the heat source.
Flaws:
- High cost of electricity.
- The heating system requires fairly high power to operate. However, even the standard 10-15 kW is usually more than enough to heat a house of 100-150 m².
- If there are frequent interruptions in the power supply “on the line”, then it is necessary to provide for the presence of an uninterruptible power supply and/or a generator. However, the same applies to other heating systems, because for the operation of automation and pumps they require an uninterrupted power supply.
Warm floors - an alternative to radiator heating
Any of the described circuit units can be connected to a water floor. It is easy to install to the heating system, and the benefits from it are relatively greater than from clear and bulky radiators. Let us consider in detail the advantages of this type of heating:
- Undoubted fuel savings for heating the entire volume of the room. You can spend energy only on heating water, which will do everything else - from the floors, according to the principle of convection, heat will go up, thereby creating an overall pleasant atmosphere.
- Increased usable space due to the absence of heating radiators. The entire structure is hidden under the floor covering and does not reveal itself in any way.
- If desired, installation can be done independently, which allows you to save on contacting professionals.
The private water floor heating system has already earned universal approval from users, as it lives up to all the qualities declared by the manufacturer.
Video description
Watch the video to see all the pitfalls when installing heating in a private home:
See also: Catalog of companies that specialize in electrical and heating.
Geothermal heating
When choosing energy resources provided by the earth as a heat source, this means obtaining an environmentally friendly and economical home heating system. Along with gas heating, one of the energy sources is geothermal heat from the earth. The soil absorbs about 98% of all energy coming from the sun. There is always heat in the deep layers and this does not depend on the time of year and temperature on the surface.
The geothermal heating system consists of two circuits - external and internal. External communications are responsible for switching between the heat exchanger and the internal circuit of the system. They are deep underground.
Geothermal heating scheme Source respect-stroy.com
The internal circuit is a classic one-pipe system or a two-pipe heating system for a private house with radiators. The coolant in them is either water or another suitable liquid, for example, special oil.
Advantages
- minimal dependence of the system on climatic conditions;
- low costs for operating the system;
- stable flow of thermal energy in the required quantity;
- environmental safety of the heat source.
Flaws:
- high complexity of installation work;
- high cost of system components;
- low payback of the system - about 8 years;
- it is necessary to construct a collector.
Options for a two-pipe system
The main difference between a two-pipe heating scheme for a private house is the connection of each battery to both direct and reverse current mains, which doubles the pipe consumption. But the home owner has the opportunity to regulate the level of heat transfer of each individual heating device. As a result, it is possible to provide different temperature microclimates in the rooms.
When installing a vertical two-pipe heating system, the lower as well as the upper heating distribution diagram from the boiler is applicable. Now in more detail about each of them.
Vertical system with bottom wiring
Set it up as follows:
- From the heating boiler, a supply main pipeline is run along the floor of the lower floor of the house or through the basement.
- Next, risers are launched upward from the main pipe, which ensure that the coolant enters the batteries.
- A return flow pipe departs from each battery, which carries the cooled coolant back to the boiler.
When designing the lower wiring of an autonomous heating system, the need to constantly remove air from the pipeline is taken into account. This requirement is met by installing an air pipe, as well as installing an expansion tank, and using Mayevsky taps on all radiators located on the top floor of the house.
Vertical system with top wiring
In this scheme, the coolant from the boiler is supplied to the attic through the main pipeline or to the very ceiling of the upper floor. Then the water (coolant) goes down several risers, passes through all the batteries, and returns back to the heating boiler through the main pipeline.
To periodically remove air bubbles, an expansion tank is installed in this system. This version of the heating device is much more effective than the previous method with lower pipe routing, since higher pressure is created in the risers and radiators.
Horizontal heating system - three main types
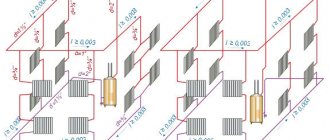
The installation of a horizontal two-pipe autonomous heating system with forced circulation is the most common option for heating a private home. In this case, one of three schemes is used:
- Dead end circuit (A). The advantage is the low pipe consumption. The disadvantage lies in the large length of the circulation circuit of the radiator farthest from the boiler. This makes it very difficult to adjust the system.
- Scheme with associated movement of water (B). Due to the equal length of all circulation circuits, it is easier to adjust the system. During implementation, a large number of pipes will be required, which increase the cost of work and also spoil the interior of the house with their appearance.
- Scheme with collector (beam) distribution (B). Since each radiator is connected separately to the central collector, it is very easy to ensure uniform distribution of all rooms. In practice, heating installation according to this scheme is the most expensive due to the high consumption of materials. The pipes are hidden in a concrete screed, which greatly increases the attractiveness of the interior. The radial (collector) floor heating distribution scheme is becoming increasingly popular among individual developers.
This is what it looks like:
When choosing a standard wiring diagram, it is necessary to take into account many factors, ranging from the area of the house to the materials used in its construction. It is better to resolve such issues with specialists to eliminate the possibility of error. After all, we are talking about heating the house, the main condition for comfortable living in private housing.
Installation methods
Let's touch on methods for installing heat-carrying communications. There is no clear opinion on this issue, so it is better to contact a company that installs heating systems for advice. The most common installation options are a single-pipe or two-pipe heating communications system. We will not dwell on them, but will tell you about two lesser-known methods.
Collector system
The main unit with this installation method in this system is the collector, which is responsible for the distribution of the coolant.
Manifold for a single-pipe heating system Source termoresurs.ru
Central heating of apartment buildings
Through main pipelines, coolant from the central boiler room is supplied to the heating unit of an apartment building and is further distributed among the apartments. In this case, additional adjustment of the degree of hot water supply is carried out directly at the heating point, for which circular pumps are used. This method of supplying coolant to the end consumer is called independent (more details: “Central heating is both pros and cons”).
In addition, dependent heating systems are used in apartment buildings. In this case, the coolant is transported to apartment radiators without additional distribution directly from the thermal power plant. In this case, the water temperature is determined regardless of whether it is supplied through a distribution point or directly to consumers.
Video description
This video will show you how to make a collector for a heated floor with your own hands:
A collector heating system, also known as a radiant heating system, consists of the following elements:
- collector;
- pump;
- heating devices;
- safety devices;
- expansion tank;
- pipeline;
In turn, the collector assembly is mounted in two parts:
- Input - it is connected to the heating unit, receiving the coolant at the required temperature, and distributes it along the circuits of the system.
- Output - return circuits are connected to it, which release the cooled coolant, which is redirected to the boiler for the next heating.
The main difference and advantage of this installation method is the ability to independently connect heating devices to the system. This allows you to simplify repair work and more accurately regulate the temperature in the room. The disadvantage is the high costs of communication and installation.
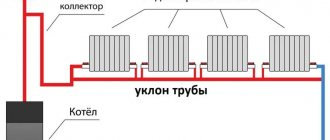
Leningradka system
Another interesting solution is the Leningrad heating system. The Leningradka heating system in a private house allows you to level out heat loss by the coolant when moving away from the boiler.
This is the main problem of classical type heating systems - achieving the same temperature along the entire length of the line. To solve this problem, it is necessary to increase the number of heating devices as they move away from the heat source.
Radiator installed according to the “Leningradka” scheme Source plusteplo.ru
Types of water systems
Any system can be classified into the following categories:
- Single-circuit with diagonal, parallel or reverse diagonal connection.
- Double circuit. With a system for generating hot water for domestic needs.
- Collector.
Each of them has advantages, disadvantages and features. Let's look at everything in detail:
- The first option is easy to understand and self-assemble, since it has the simplest scheme - the water makes a full circle around the system and returns, cooled, to the heat exchanger of the heating unit. There it heats up again and the cycle repeats. The advantage of such a system is less use of materials during construction, the disadvantage is lower efficiency, since already over a short length of the system pipes, the water significantly loses temperature.
- The double-circuit heating system differs favorably from the first option by the constant supply of heated coolant to any length of the pipeline. This allows all radiators, and therefore the rooms, to be heated evenly. The principle of operation is also simple - one pipe supplies hot media, the second pipe removes cold masses.
- A collector or storage system is a large-diameter pipe from which water exits through smaller pipes. This design is installed in each radiator, representing a separate circuit branched from the entire system. This type of heating has greater efficiency than the above.
The statement that a complete shutdown of the boiler will be required to replace the defective section is incorrect. The design can be replaced point by point if there are shut-off valves at the inlet and outlet of the system. In addition, this feature allows the user to regulate the temperature of the media.
Shut-off valves are installed in larger quantities than on a single-circuit system, which does not look the best, as does the large length of pipes throughout the house. You have to choose between the quality of heating and the beauty of the interior. The great advantage of a double-circuit heating system is the production of hot water for domestic needs.
However, the problems also increase significantly: firstly, each radiator must have its own circulation pump - it will not be possible to operate alone over the entire area, and secondly, the number of pipelines is even greater than that of a double-circuit system. There are advantages: in case of problems, the radiator can be easily replaced without shutting down the entire system, heating occurs much faster, each heating section is subject to adjustment. If necessary, the design switches to other schemes of water heating systems - for example, heated floors.
Choosing your own wiring is simple - it all depends on the needs of the owners, the size of the room where temperature support and actual heat loss are required. Types of water heating systems can solve different problems when selected correctly.
Differences in Sealing
All heating systems are divided into two types - open and closed heating systems, the difference is that open communications communicate with the atmosphere, while closed ones do not.
Open systems
An open heating system has a leaky expansion tank. A drain pipe is installed in it, which drains excess water into the sewer or outside the building. The shape of the vessel does not matter in this case. The tank is located at the highest point of thermal communications.
Scheme of an open type heating system Source avatars.mds.yandex.net
Since the tank has an easy-to-open lid, the system can be filled with water manually using buckets or a hose. The pressure in the circuits is always equal to atmospheric pressure and for this reason such systems do not require the installation of monitoring devices and are safer during operation.
Closed systems
A closed-type heating system with a pump and expansion tank is more complex to install. The elements included in the composition are completely sealed and the shape of the tank is important; it is selected in such a way as to withstand pressure with a minimum wall thickness.
Such systems require more careful attention because they contain high pressure. To ensure safety during operation, it is necessary to install control devices and an emergency valve on the expansion tank.
Closed heating system with forced circulation Source dpa.cv.ua
Criteria for choosing a boiler for autonomous heating of a private house
When choosing the type of boiler for heating, there are no alternatives only if gas is supplied to the house; it is the cheapest type of fuel and, in comparison with other sources (electricity is not considered), has a number of operational advantages - it does not require space for storing reserves, highlight There are fewer combustion products released into the environment and does not pollute the chimney system as intensively.
The main parameters that people pay attention to when choosing a boiler are:
- Unit power: directly related to the area of heated premises and temperature conditions, which are usually chosen based on building codes and GOSTs.
- Number of circuits: if the house does not have hot water supply, it is more practical to choose a dual-circuit model that can heat water.
- Location: usually the unit is installed downstairs in the basement on the floor; there are also hanging options for small houses.
- Material of manufacture of the unit and heat exchanger: cast iron, stainless steel, copper.
- Type of combustion chamber according to the method of supplying air to the firebox: open or closed.
- Availability of automatic control and monitoring systems, possibility of programming operating modes.
- The ability of the boiler to work with alternative fuels: relevant for liquid fuel modifications.
Rice. 14 Design of the Rinnai gas boiler
When choosing a boiler, the following tips may be useful:
- If there is no hot water supply in the house, it is rational and cheaper to choose a double-circuit boiler model than to install a separate single-circuit unit and a gas water heater, an electric boiler.
- When using electricity, the night tariff is much cheaper than the day tariff, in this case you can save on the cost of electricity. To do this, at night they warm up the entire house, with the exception of the bedrooms, and during the day they turn off the boiler for a long time or operate it in the minimum heating mode.
- For reliable operation of all boilers controlled by automation powered from the mains, you should purchase an electric generator with automatic switching on in case of power failure - this will allow the boiler equipment to continue operating in case of emergency situations on the power line.
Rice. 15 Construction of a Kolton solid fuel boiler
How to choose a heating unit
Factors influencing the choice of a boiler (or several water heating devices):
- energy carrier used;
- heat generator power;
- dependence on external energy sources;
- price;
- functionality, ease of use.
Note. The heater selection criteria are arranged in order of priority. It is important for the user that the unit consumes cheap fuel and produces enough heat. Price plays a secondary role; comfort and functionality come in third place.
All household boilers are usually divided into groups according to the type of fuel (energy carrier) burned:
- gas;
- electrical;
- solid fuel;
- liquid fuel, consuming diesel fuel and waste oil;
- universal, operating on 2-3 types of energy carriers.
Each of the listed groups is divided into varieties according to the operating principle, installation method and other criteria. We will review existing boilers and give a number of useful recommendations.
Types of gas boilers
To organize heating in private homes, 3 types of units using natural gas are sold:
- Atmospheric. The combustion chamber is open, combustion air is taken from the boiler room. The operating efficiency is in the range of 86...88%.
- Supercharged (aka turbocharged). Air is forced into the closed firebox by a fan controlled by an electronic circuit. Boiler efficiency is 90...93%.
- Condensation. Structurally similar to turbocharged heaters, but the heat exchanger and burner are designed in such a way that in a certain mode the boiler uses the latent heat of combustion of the fuel. Efficiency – 95%.
Reference. All heat generators are capable of burning 2 types of fuel - natural gas and liquefied propane-butane mixture (LPG). To switch to LPG, the fuel jets are replaced and the automation is adjusted.
Boilers are manufactured in wall, floor and parapet versions. The first group is ready-made mini-boiler rooms, equipped with their own expansion tank and pump. The second type is high-power units, or those that do not depend on electricity. Parapet models are placed near the outer wall, the chimney goes directly to the street.
Among the large assortment of gas water heaters, it is not easy to make the right choice. Our recommendations are:
- If you are on a limited budget, purchase an atmospheric wall-mounted boiler. But remember - open-chamber heaters require a traditional chimney.
- To work together with the gravity system, you will need a non-volatile floor-mounted atmospheric unit.
Floor-mounted non-volatile heater equipped with a single-stage burner, mechanical automatic safety system EuroSIT and a cast iron heat exchanger
- It is better to install a forced-air heat generator in an apartment or cottage without a ready-made chimney. Organize the removal of combustion products through a coaxial pipe laid through the outer wall.
- To supply hot water to 1-2 consumers, buy a dual-circuit model. If the consumption in the DHW network is high, you will need an indirect heating boiler connected to a conventional single-circuit heater.
- Read the detailed description of all gas heaters presented in a separate article.
A condensing boiler is the most economical among gas-using devices. The disadvantage of the unit is the complexity, high price of the equipment and its repair.
Electric hot water installations
A feature of electric boilers of any type is their high efficiency, reaching 99%. The second positive point is the low installation costs and purchase of the heaters themselves. The units should be used as auxiliary heat sources, operating at night at half the light tariff.
There are 3 types of electric boilers (all are available in wall-mounted versions):
- With traditional tubular heaters - heating elements. Modern devices are equipped with an expansion tank and a circulation pump.
- Electrode. Heating of the coolant occurs due to a chemical reaction resulting from the passage of current through the water layer between the 2 electrodes.
- Induction. Here the coolant is heated by the steel core of a sealed coil, which creates eddy currents in it.
Heat generator with tubular heaters (TEN) in section
To install electric heating, it is better to take a classic heating element boiler, which does not require serious wiring. The device is reliable and easy to repair - you can always replace a burnt heating element yourself. An induction heat generator is expensive and cannot be repaired in the event of a breakdown, and an electrode heat generator is highly dependent on the salt content in the coolant.
Advice. Don't listen to salespeople who call induction boilers energy-saving. All electrical installations heat water equally efficiently - losses do not exceed 2%, the rest of the energy is converted into heat.
Classification of solid fuel boilers
For heating country cottages, 3 types of solid fuel units are used:
- direct combustion - atmospheric and turbocharged;
- pyrolysis;
- automatic pellet and coal.
There are many myths about the efficiency of TT boilers. Manufacturers of pyrolysis heat generators claim an efficiency of 85-86%, pellet heat generators - up to 90%. In reality, the figures are much more modest: traditional wood-burning units - 75%, pyrolysis units - 75%, boilers using pellets and coal chips - up to 86%.
Construction of a direct combustion boiler with a fire tube heat exchanger
Reference. In addition to the listed types of heaters, there are long-burning TT boilers with an increased size of the firebox. How to distinguish such installations from classic wood-burning heat generators, read the corresponding publication.
Recommendations for choosing a solid fuel boiler:
- A steel direct combustion apparatus equipped with a chain draft regulator is perfect for burning wood, coal and briquettes. Turbocharged examples are automated and burn wood better, but rely on electricity.
- Pay attention to the volume of the firebox of a traditional boiler - the duration of combustion depends on this indicator.
- Automated pellet units are a good solution for lovers of comfortable heating. You don’t have to chop and carry wood, remove coal dust, just clean the firebox and burner weekly.
- Do not mess with pyrolysis TT boilers, they are a priori more expensive than conventional ones, demanding on the quality of fuel, and in addition they consume electricity.
- Avoid models with water-filled grates if you plan to burn with coal. The temperature difference forms a hard crust on the surface of the grate, which is not easy to knock off.
Grate of a TT boiler made of pipes filled with coolant
When choosing a heat generator, remember the old saying “the miser pays twice.” It is better to take a high-quality classic device with a cast-iron heat exchanger than a cheap “pellet generator” with electronics of unknown origin.
Diesel and combined models
This heating equipment is used much less frequently than gas, wood and electric boilers. Diesel fuel is more expensive than other energy sources, and waste oil is a specific fuel that is clearly unsuitable for the average homeowner. Accordingly, such heating devices are operated only in certain conditions when access to other resources is limited.
Multi-fuel boilers from different manufacturers combine 2-3 energy sources, for example, wood + electricity, gas + coal. Advantage: you buy one heat generator and get two. Disadvantage: the unit cannot boast of high efficiency and functionality. The most popular option is shown in the photo - a TT boiler, equipped with a heating element unit for electrically heating water after the flame in the firebox has died out.
Electric wood heater from the Russian company Teplodar
Heat generator power calculation
To select a boiler based on performance, you should find out the load on the heating system of the house. That is, calculate the heat losses of the building. We propose to calculate this indicator in a simplified way:
- If a living room is separated from the street by one wall with 1 window opening, then 0.1 kW of heat is consumed to heat a square meter of area.
- A room with two external walls (corner) and 1 window – 0.12 kW/m².
- The same, with 2 light openings - 0.13 kW/m².
An important nuance. The calculation is performed for each room separately, then the results are summed up.
The algorithm is suitable for buildings with floor heights up to 3 meters. If the ceilings are higher, heat consumption is calculated based on the volume of the room. Accordingly, in a room with 1 fence and a window, the volume value is 35 W/m³, in a corner room – 40 W/m³, in a corner room with two openings – 45 W/m³.
Having determined the need for thermal energy at home, we select the power of the boiler installation according to the instructions:
- The performance of a unit operating only for heating is taken with a margin of 20%. That is, we multiply the found amount of heat by a factor of 1.2.
- The heat generator providing hot water supply must be taken with a reserve of 50% (coefficient 1.5).
- For TT boilers, the increasing coefficients are 1.5 and 2, respectively.
If you live in an area with a mild southern climate, then the coefficients should not be used. Conversely, residents of the northern regions should increase the initial heat loss figure by 1.5-2 times.
Calculation of heat losses by volume of residential premises
The third option is automatic boilers
Fuel loading into the chamber and combustion control are carried out automatically. The advantage is autonomy (5-9 days on one load), the disadvantage is the high cost.
Such boilers are equipped with a loading hopper for supplying solid fuel and automation. The operating principle is quite simple. Fuel of a certain fraction is loaded into a bunker, from which it is supplied to the loading chamber as it burns.
Let us note the automatic boilers of the Polish manufacturer Metal-Fach
with a steel heat exchanger (P265GH steel with a thickness of up to 6.00 mm is used),
efficiency
over 90
%
, a modern, innovative type controller
FL 310LGRTC
, which allows servicing one mixer and up to four circulation pumps with continuous logic and PID control functions, an upper combustion chamber, retort burner of the following lines:
- SEG (work on coal of various fractions)/SEG BIO (pellets, oats, grape and olive seeds, other agricultural solid waste and coal are used as fuel). These are devices with automatic fuel supply, the ability to connect room (internal) and weather (external) sensors, a lambda probe and the STRAŻAK (FIREMAN) protective system, which prevents the ignition of granules;
- SD DUO
, coal is used as solid fuel, including sunflower seeds, coal dust, and any hardwood (in manual mode). The boilers are equipped with a fuel dispenser, two loading chambers, an automatic device responsible for supplying fuel; if necessary, a lambda probe can be connected; - SD DUO BIO
, configured for burning pellets, agricultural waste, grain crops (wheat, oats), as well as coal, hardwood and coal. The devices are equipped with an automatic tray loading device with a feed screw, an ignition device, a lambda probe (if necessary), and the STRAŻAK (FIREMAN) protection system, which prevents fuel from igniting outside the firebox. - SMART
and
SMART EKO
, running on pea fraction coal, pellets, with a unique Ekoenergia burner. These boilers can operate in both manual and automatic modes, which guarantees stability in the heat supply to the premises. The MASTER 500 controller allows you to control two pumps and a room thermostat.
Separately, we note the automatic boilers of the Russian company Vulkan
, developed on the basis of proven European manufacturers of heating equipment.
They are unpretentious in operation and fully adapted to Russian operating conditions. They work on coal of various fractions ( up to 40.00 mm
), including pellets, pellets (fraction
from 6.00 to 8.00 mm
), heat exchangers are made of boiler steel 6-8 mm thick, have a screw supply of solid fuel from a bunker.
These automatic coal boilers are capable of operating autonomously from five to ten days, and are equipped with electronics from various European manufacturers, which allows you to control two circuits of the heating system and the hot water supply system (DHW) simultaneously.
Anyone can understand the controls thanks to a simple and intuitive menu (interface). Additionally, a GSM module
for remote monitoring and control using mobile communications, an automatic ash removal system and automatic ignition.
, Vulkan automatic boilers
one of the best offers on the Russian market.
Heating with forced circulation
So, we see that systems with natural circulation of liquid have a number of rather significant disadvantages. An alternative to them are systems with forced circulation, which use additional equipment that increases the flow of coolant in the system. Namely the circulation pump.
Yes, this type of water heating at home will be more expensive and complex, but you get many advantages:
- Possibility to heat a large room. We have already said that natural circulation is not suitable for large houses. If you are the owner of just such a thing, then your only option is a forced circulation system.
- Complication of the system. By installing a pump, you do not depend on such an indicator as pressure. Therefore, what was an obstacle in a gravity system is not a problem in a forced one. For example, you can now increase the number of pipe bends if the layout of your home requires it.
- Use of smaller pipes. Agree, the neat appearance of the heating system is not the last indicator that is worth paying attention to.
- Less dependence of heating quality on the presence of air in the system. With self-circulation, the entry of air into the system would significantly complicate the transportation of coolant through the pipes. A forced system solves this problem, but in the case of installing metal pipes, special expansion tanks with air vents and fuses should be used in order to avoid corrosion of the system.
- Possibility of using more wear-resistant and lightweight plastic pipes.
- Concealed installation of pipes is possible. You can hide pipes in screeds and walls without any problems
Boiler power calculation
Regardless of the type of fuel used (solid or liquid, gas or electricity), the principle of connecting all heating systems is the same. The only difference is at the boiler installation stage. In this case, its power is calculated using a single formula:
where W is the specific power required for heating 10 square meters. m of room; S – total area of the house.
For Russian regions, the following power values are taken into account: • for houses located in central Russia up to 1.5 kW; • for Siberia and the North: for every 10 sq. m up to 2 kW; • for southern regions: up to 0.9 kW.
Since 10 sq.m. is sufficient for heating. m of a residential building located in central Russia requires up to 1.5 kW of power, then, for example, for heating 100 sq. m you will need a 15 kW boiler:
(100 x 1.5)/10 = 15 kW
This figure is increased by 15-20% (power reserve for possible heat loss, which is inevitably lost even with ideal insulation of the building). Thus, to heat a house of 100 sq. m will need (15 + 2.3) = 17.3 kW.
Recommended boiler power
Option one - classic boilers
The first option is traditional, classic, which has been used for thousands of years in conventional stoves, put in firewood or coal, and adjusted the air supply with a damper. The main disadvantages are the need for constant supervision and low efficiency, the inability to accurately regulate the combustion process. Advantages - the simplest boiler in technical terms and maintenance, operating on almost any type of solid fuel.
Examples of classic boilers:
- ZOTA Carbon
with a steel heat exchanger, operating on coal with a fraction of
10.00 - 50.00 mm
, power
from 15.00 to 60.00 kW
, with top fuel loading, a movable grate and a design that ensures maximum afterburning of fuel and precise oxygen supply to firebox; - Buderus Logano
with a steel heat exchanger, can work either separately or in combination with a gas or liquid fuel boiler with a capacity of
12, 16, 20, 24, 27, 32, 45 kW
, in systems with natural and forced circulation of coolant, is small in size and heat exchanger protection, large volume of ash pan and loading chamber, works on wood (logs up to 33.00 and 53.00 cm long), coal, coke.
The burning time of such boilers is 3-7 hours.
What are combi boilers
Since electric heating is expensive, you can use an alternative solution and choose a boiler that can operate on two types of fuel. For example, you can purchase electrical equipment that can also perform the functions of a gas water heater. Or you can choose a solid fuel boiler that can also work with electricity for some time.
As long as there are no interruptions in the gas supply, such a boiler will work properly according to the generally accepted scheme, but as soon as any problems arise, it will be possible to switch to another type of fuel and thereby provide stable heating to the house.
A combination boiler is more expensive than a regular boiler, but such expenses will be completely justified: your home is guaranteed not to be left without heat, and even if one system fails, the second will immediately be able to support it. The temperature level will remain at the same values, and it will be comfortable to be in the room.
It is quite difficult to independently design and implement an individual heating system, but it is still possible. Your home will receive reliable heating, which will not depend on the presence or absence of gas pipes.
You need to enable JavaScript or update your player!
Traditional heating systems
Most often, water or various antifreeze liquids that circulate through pipes are used for heating. The liquid is heated using gas boilers, which can operate on liquid, solid and gas fuels. Recently, electrode and induction boilers have been used as heating elements.
Water heating is popular due to the availability and efficiency of the coolant among owners of cottages and other suburban housing. The water system is easy to install yourself. The positive thing is that the volume of water in the system remains constant.
The disadvantages of water heating are the long time it takes to warm up the room, possible leaks and pipe ruptures. Do not turn off the water system in winter, as the water will freeze and burst the pipes.