The term “well” has been known since ancient times as a structure for storing water, but the phrase “wet well” is not understood by everyone.
After all, moisture is a natural attribute of a structure. This name appeared to emphasize the purpose of the mine - drainage of atmospheric precipitation and groundwater from the land. This design plays an important role in the water supply system and disposal of polluted water.
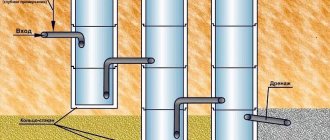
In pressure pipeline networks, a wet well is used as a receiver for water discharged from the system, so a concrete slab is not installed at its bottom, but is lined with gravel or crushed stone so that the liquid can seep into the ground. The emptied pipeline releases a volume of water, which should be easily absorbed in the constructed cushion.
When installing a drainage structure on a sewer network, a filter structure is unacceptable - a concrete slab is installed here and all connections are waterproofed. The function of such a working is twofold - it is both a wet well and an inspection well, but the latter is often a dry well.
In the conditions of private development of a land plot, the drainage device maintains an optimal water balance, providing a sufficient amount of irrigation material during dry periods and preventing the soil from being washed away under buildings located on the territory. Several types of buried plumbing structures can be located simultaneously within one area.
How many rings to buy for a well
You can calculate the approximate depth of the well based on the depth of water carriers in neighboring areas, adjusted for the relief.
This value is divided by the height of one ring and their approximate number is obtained for arranging a well shaft. It’s better to order not back to back, but with a small margin, so that at a crucial moment you don’t have to urgently organize the delivery of 1-2 rings to the site. For example, in the Moscow region, the depth of wells is 10-12 rings. The seams between the installed rings must be filled with a binder solution. The use of traditional methods: tarred tow, etc. is undesirable. The use of rings with closing grooves creates a durable and waterproof joint
This is fraught with additional costs, but the main thing is that the process of lowering the rings should not stop so that the soil does not have time to jam the shaft. It holds the rings so tightly that sometimes it is necessary to compact the column from above using heavy equipment. The remaining rings can be sold to the owners of neighboring plots, used to make a reservoir for collecting rainwater, and used to build a homemade septic tank.
When constructing a well, reinforced concrete rings with perforations are used - for the influx of water through the sides of the shaft and for the introduction of water supplies. To cover the protection of the upper part from debris, special covers are cast corresponding to the diameter of the rings, with a hole and a hatch. Rings of smaller diameter are called repair rings and are used to deepen shallow wells.
Independent hydrogeological surveys
The approximate depth of the mine can be determined in advance. To do this, you need to go around the neighboring areas and find out at what level the water is in the nearby wells. You should ask whether the well was dug for technical or drinking purposes and whether the groundwater level in it is stable.
At the same time, it’s worth asking around whether it was difficult to develop the mine, and whether large boulders were encountered during digging.
The survey method is acceptable if the estate is located on flat terrain with slight hilliness. There, the layers of rocks lie almost horizontally, approximately repeating the shape of the natural relief.
The groundwater table is located approximately at the same level, because in permeable rocks the principle of communicating vessels operates. The difference in the length of the shaft can only be caused by differences in the elevations of the well mouths.
The depth of underground water in a mine planned for construction in a flat area can also be determined in advance using a neighbor’s well as a guide. To do this you will need an aneroid barometer.
The scale of this device is marked with divisions every 0.1 mm. The distance between divisions corresponds to 1 meter difference in elevation.
For example, measurements near an existing well showed a level of 634.7, and at the site of future production, the barometer needle stopped at 633.8. This means that groundwater will appear at a depth of 9 m.
The depth of groundwater can be determined using an aneroid barometer by comparing the readings above the neighbor's well and the planned place to dig your own
The survey method does not work in regions with high occurrence of rocky and semi-rocky rocks. Especially if you have to extract fractured water, which spreads sporadically and sometimes flows into adjacent layers.
Surveys will not be of much help in areas with pronounced hilliness, where it is impossible to accurately represent the geological section without surveys. It is advisable for owners of plots in such areas to contact the local center for designing water supply and sewerage networks or a hydrogeological organization.
More information about searching for the aquifer is provided in this article.
Why are additional rings needed?
When it is impossible to install conventional ones, additional rings are used for the well. They solve problems caused by the width, slope or height of a standard through-hole. The height of the additional ring is less than 40 cm, so it allows you to bring the shaft to the desired height if this is not possible with a regular one. From a specialized company, you can order additional rings based on individual measurements so that they exactly match the structure being built.
When designing a well, much attention is paid to the decorative component. Rarely do owners agree to simply have a head sticking out on the property, covered by a hatch
For such cases, the upper rings with a beautiful relief are cast.
What types of rings are there for a drinking well?
There is no single standard that regulates the sizes of rings for wells. To line a well shaft, rings with an internal diameter of 90-100 cm and a height of 70-100 cm are used. These values are dictated by practicality: if you take less, it will be inconvenient to dig inside, if more, the amount of manual labor will increase significantly. The larger the ring, the heavier it is, which means additional shipping costs.
Concrete rings, indistinguishable from the outside, differ in casting technology and composition:
- Drinkable;
- Sewer;
- Gas pipelines.
The most stringent requirements are imposed on water intake rings. Each ring must have a standard marking. Before going on sale they are subjected to production tests.
You need to order reinforced concrete rings only from certified sellers. Under the guise of well products, you can unknowingly buy simple technical ones, which contain harmful impurities
High-quality reinforced concrete rings have many advantages:
- Lowest price (in comparison with a wooden frame or rubble masonry);
- Solidity;
- Easy to install and repair;
- Resistance to soil pressure;
- Wide range.
For strong and durable well concrete rings, a frame made of reinforcement is used, filled with a mortar of M-500 cement. The wall thickness is from 10 cm.
When producing rings for non-food purposes, casting molds are lubricated with petroleum products. Along with them, an oil film may appear in the new drinking well, which is not easy to get rid of.
In industrial production, vibration is used to compact the solution in the molds, but the surface of the finished ring retains some porosity, so it is impossible to completely clean it of oil.
TRANSPORTATION AND STORAGE
4.1. Transportation and storage of structures - in accordance with GOST 13015.4 and this standard.
4.2. The structures are transported and stored in working position.
4.3. Structures should be stored:
- working chambers - in one row;
- wall rings - in two rows in height in accordance with the diagram shown in Fig. ;
- support rings and plates - no more than six rows in height on spacers (linings) in accordance with the diagram shown in Fig. .
Scheme for storing wall rings of wells
Scheme for storing floor slabs and well bottoms
— gaskets (linings); 2
- mounting loops
Other storage schemes are permitted, provided the safety of structures is ensured and safety requirements are met.
Installing rings in a well shaft
After a promising location for building a well has been identified, a small area is cleared and a circle is marked for excavation. The diameter of the laid shaft should be several centimeters larger than the purchased rings. A small gap will ensure free descent of the column into the prepared pit. After digging, the soil around the mine will settle and compact naturally. This takes several months. You can’t dig a shaft end-to-end so that the rings don’t get pinched.
There are several methods for lowering reinforced concrete rings into a well. They differ in complexity, required equipment and safety. In the first case, a trench is dug and deepened at a marked place, and the first ring is lowered into it. Then the worker digs inside it, gradually deepening the bottom and evenly removing soil from under the walls. If there is a risk of uneven descent, pieces of logs are hammered under the ends of the ring to prevent premature movement. The soil is loaded into a bucket, which is pulled out with a collar or winch. As soon as the first ring has sunk sufficiently, the next one is installed on it.
Work inside the mine is difficult; there may be a shortage of oxygen at depth. For digging and lowering you need at least two workers, and optimally three. One works in the mine, the second lifts the soil upward, the third has time to rest. Standard size rings can be lowered without additional equipment. Using a winch or truck crane significantly speeds up the process. The described method is the safest.
When digging a shaft, you need to constantly monitor the verticality of the recess so that you don’t get a slant or a wave. In such a place, the rings either stop or fall to one side. Correcting the situation is problematic
Even if the mine is lined with rings as it goes deeper, there is a chance that quicksand will open. This is a fluid mass of suspended soil particles. A weak quicksand will cover the bottom with sand or clay, depending on its composition, while a powerful one can turn out and carry away rings.
Second method: First, the shaft is completely excavated until the water begins to rise quickly. Then all the rings are lowered into it one by one. The worker has more space at the bottom, so choosing soil is easier, but there is a great danger that a collapse will occur or quicksand will be revealed. This method is only suitable for dense clay soils that are not prone to crumbling and landslides.
The price for negligence can be very high. When lowering the rings into the finished shaft, they cannot simply be dropped; for high-quality and accurate work, a winch will definitely be required
To prevent the rings from moving during construction and operation, they are produced with a groove for mutual closure. The shaft will be more stable, and the waterproofing seams will be more reliable. Simple rings are reinforced with reinforcement brackets or strips of metal.
Classification of wells for sewerage
Structures related, according to technical terminology, to sewer wells are divided into several types.
The division is made depending on what classifying features we will use. For example, you can divide wells by material of manufacture, by purpose or by the method of their construction.
The following classification characteristics and the corresponding types of modern sewer wells are distinguished. The first is produced by the medium, which is transported by the sewer system.
The drainage networks on which sewer wells are installed are designed to move wastewater of different composition and degree of aggressiveness, these are:
- Household. These include waters that have changed their composition as a result of mixing with waste and garbage. Depending on the contaminants they contain, they are divided into household and fecal.
- Industrial. These include waters that have changed their mechanical and chemical composition as a result of contamination with industrial waste.
- Atmospheric. These include water formed as a result of the active melting of winter precipitation, flood and rain water.
In addition to the listed types of wastewater, the sewerage system receives flows collected by the drainage system, the task of which is to drain the territory or drain groundwater from underground building structures.
Wells of sewer systems are divided according to the material of manufacture into:
- Brick. Brick was once a commonly used material for making wells, but over time there are fewer and fewer brick structures.
- Concrete. Concrete structures are today the traditional material option for a sewer well.
- Plastic. It is obvious that compositions with a polymer base are the material of the future; it will one day replace both brick and concrete.
Plastic or composite ready-made well structures are attractive because they are lightweight and easy to install. They are pleased with their resistance to chemical influences during prolonged contact with aggressive environments. They tolerate sharp and smooth temperature fluctuations well and do not allow or absorb water at all.
Sewage systems are divided into floating and export. The former move wastewater to treatment plants, facilities or discharge fields. The latter only collect wastewater for subsequent pumping and removal. The wells included in both types of systems perform both identical and different functions.
According to their functional responsibilities they are divided into:
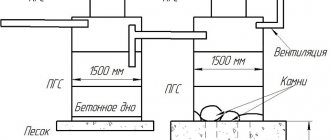
- Cumulative. They are used to accumulate wastewater for subsequent extraction and removal. Naturally, they are constructed in sewerage systems.
- Collector. Designed to collect wastewater from several sewer branches and to direct it to a storage tank, treatment plant or discharge fields. They are installed in both floating and export branched networks.
- Filtering. They are used to dispose of the liquid fraction of wastewater naturally. They play the role of compact treatment facilities that transport pollutant-free media into the ground or into water bodies. They accompany exclusively the floatable type of sewerage.
- Observations. They are constructed on collector sections longer than 50 m, as well as at all turning points and junction points of highways. Necessary for monitoring the operation of the sewer system, for periodic cleaning and repair activities. They are installed in both types of sewers.
- Drops. They are located in areas with sharp changes in altitude. The reasons for the construction include ensuring buried discharge into the reservoir and the need to slow down flows on sections of the pipeline with a large slope. They may be present in both exhaust and floating sewers.
The classification of manholes is much more complex. We'll talk about this a little below, but now we'll look at different types of wells in more detail.
Characteristics
1.3.1. Designs must meet the requirements of GOST 13015:
— in terms of strength, rigidity and crack resistance, while there are no requirements for testing structures by loading;
- according to the actual strength of concrete (at design age and tempering age);
— frost resistance and water resistance of concrete;
- according to the thickness of the protective layer of concrete to the reinforcement;
— to steel grades for reinforcing and embedded products, including for mounting hinges;
- for protection against corrosion.
1.3.2. Structures should be made of heavy concrete in accordance with GOST 26633 classes or grades of compressive strength specified in the working drawings of the structures.
1.3.3. The normalized tempering strength of concrete is taken equal to 70% of the class or grade of concrete in terms of compressive strength.
The specified standardized tempering strength of concrete can be reduced or increased in accordance with the requirements of GOST 13015.
1.3.4. The water absorption of concrete structures must correspond to that established by the design documentation of a particular structure or specified when ordering structures.
1.3.5. For the reinforcement of structures, the following types and classes of reinforcing steel are used:
— thermomechanically strengthened rod of the At-ShS and At-lVC classes according to GOST 10884;
— hot-rolled rod of classes A-1, A-11 and A-111 according to GOST 5781;
— reinforcing wire of class VR-1 according to GOST 6727.
1.3.6. The shape and dimensions of reinforcement and embedded products and their position in structures must correspond to those indicated in the working drawings.
1.3.7. Welded reinforcement and embedded products must meet the requirements of GOST 10922.
1.3.8. In cases provided for by the working drawings of wells, running brackets must be installed inside the wall rings, located along the height of the ring every 300 mm and protruding from the inner surface of the rings by 120 mm.
Running brackets should be made of reinforcing steel class AI or A-P according to GOST 5781.
By agreement between the manufacturer and the consumer, wall rings may be manufactured without running brackets, provided they are installed on the construction site.
1.3.9. The running brackets must be protected from corrosion in accordance with the instructions of the working drawings of the wells.
1.3.10. The values of actual deviations of the geometric parameters of structures should not exceed the limits specified in table. 1.
Table 1
In millimeters
| Name of deviation of geometric parameter | Name of geometric parameter | Prev. off |
| Deviation from linear size | Height (thickness) of the structure: | |
| up to 180 | + 5 | |
| » 300 | + 8 | |
| » 1000 | + 10 | |
| St. 1000 to 1600 | + 12 | |
| » 1600 » 2500 | + 15 | |
| » 2500 | + 20 | |
| Inner diameter of working chambers, wall- | ||
| outer and support rings, outer diameter of floor slabs and bottom, diameter of manholes and holes for pipelines: | ||
| up to 1000 | + 6 | |
| St. 1000 to 1600 | + 8 | |
| » 1600 » 2500 | + 10 | |
| » 2500 | + 12 | |
| Length and width of base and road slabs | + 10 | |
| Position of holes and cutouts | 10 | |
| Deviation from flatness of the lower surface of floor slabs (when measuring | Outer diameter of floor slabs: up to 1000 St. 1000 to 2500 » 2500 | 4 |
| from a conventional plane passing through three points) | 6 8 |
1.3.11. Requirements for the quality of surfaces and appearance of structures are in accordance with GOST 13015. At the same time, the quality of surfaces of structures (with the exception of joint surfaces) must meet the requirements established for category A6. The surfaces forming a joint between structures, which are sealed at the construction site, are subject to the requirements established for category A7.
It is allowed, by agreement between the manufacturer and the consumer, to apply to all surfaces of working chambers, wall and support rings the requirements established for category A7.
Purpose of underground inspection chambers
The sewer circuit is designed for the prompt drainage of domestic wastewater, rain and melt water into specially designated settling tanks, sewer wells or collectors. Inspection wells are installed in the most critical sections of the sewer network.
For the equipment of a straight line 10 m long, the construction of an additional camera is irrational, while on a 100-meter section with intersection nodes, forced turns and level differences, control points are simply necessary.
They make it possible to easily check the functions of a pipeline located at a depth of 2 m and below, and in case of breakdown, to quickly repair it. In a specially equipped chamber, all shut-off and control valves are visible, so replacing worn parts with new ones is not difficult.
The functional purpose of the inspection well is to provide access for inspecting the technical condition and cleaning the drainage transport system
An accident in a section of the underground network that is not equipped with an inspection well is eliminated by excavating the soil (including the use of heavy construction equipment). It is more difficult, longer and more expensive.
Inspection cameras also help pinpoint the location of the leak.
Humanity has been constructing inspection underground chambers for hundreds of years - from the time when the first communication systems for moving water appeared.
During this period, rules for the construction of special facilities arose, which are currently set out in documents such as SNiP and GOST.
The design of the structure depends on the specific characteristics of the soil. There are design differences when constructing wells in water-saturated, low-moisture and loess subsidence rocks. The last category is strengthened by additional compaction of the bottom and the installation of a thickened sand-crushed stone cushion at the base
For example, clause 2.04.03-85 (SNiP) entitled “Sewerage. External networks and structures”, reveals the rules for the construction of inspection wells. The article contains information about where it is necessary to arrange these objects and how to select the correct sizes.
Accepted standards help combine different networks into one seamless structure and simplify installation.
The sectional diagram of the well shows the main parts: the lower tray for connecting pipes, the main working chamber equipped with steps for descending, and a hatch with a lid that goes to the surface
Concrete rings for wells
The main advantages of well rings are their durability, frost resistance and resistance to soil movement. Unlike plastic septic tanks, concrete wells are not at risk of fracture or aggressive action from wastewater components. Nevertheless, there are disadvantages of concrete rings for wells and sewage systems:
- The impossibility of manual transportation, which significantly increases the cost of installing concrete rings for sewerage or a septic tank as a whole. The cost of sewerage can be reduced by making it from other types of material that are inferior in quality and longevity, but nevertheless do not require special financial costs.
- The large size and weight of concrete rings is indispensable without the use of loading assistance. Sometimes the cost includes delivery of products, but you need to clarify this in advance. In addition, if the production is located miles away from the installation site of the well sewage system, then it makes sense to think about an alternative.
- The use of reinforced concrete well rings leads to cracks on the surface and corrosion of the reinforcement - structural fatigue, a significant nuance in the sewerage system. In addition, if a used concrete ring was used, the production was carried out in an artisanal way, or low-quality binder was used, then the well will crumble quickly and the sewerage system will become unusable.
Products in the form of concrete rings for sewerage or a septic tank in a summer cottage are divided into numerous parameters. In connection with this, they differ in various characteristics, sizes and conditions of use. For example:
- Classification of sewerage systems by type of construction. Concrete rings can be straight or with locking connections. The first are a simple cylinder shape, secured with staples and cement mortar. The latter have a protrusion and a notch on the edges, respectively. Thanks to this structural well effect, horizontal or vertical displacement of the sewer well and septic tank is impossible.
- According to the form. Concrete rings also exist in square shapes. They are used mainly for installing highways, but if you want to install a sewer system with them, there is no problem. The only inconvenience is that the size of the reinforced concrete products and their weight do not allow the use of a small area of soil. For the covers, special reinforced concrete floors with double-level hatches are used to provide insulation - the products themselves are cold, and freezing of the sewage system cannot be allowed.
- By fittings. Well rings can be equipped with bottoms and covers. This sewerage design will not allow the smell of sewage to escape into the atmosphere, and will not pose a danger in terms of the flow of feces into groundwater or nearby drinking sources. The manufacturer offers combined septic tanks, then installation will take place in the shortest possible time.
Correct selection of the size of concrete rings and the weight of related products will allow the sewer system to last for a long time
To determine the dimensions, it is important to take into account many factors - from the number of people using the sewer system to the soil conditions and climate of the area
Blitz tips
- It is not recommended to make the trench depth too large , because you will need to add soil, which will subside over time. As a result, the highway may change the correct slope.
- To avoid damage to the pipeline, it is prohibited to place solid objects under the pipes during their installation .
- When choosing a site for the construction of a filtration or storage collector, it is necessary to provide for the possibility of equipment access to clean the structure.
- Despite the fact that a sewer septic tank is a wet type of well, its tightness must be ensured. This is necessary in order to minimize the penetration of wastewater into the environment. To waterproof the ring joint areas, special waterproof compounds are used.
- During the period of providing a waterproofing layer for 3 days, it is necessary to exclude the impact of mechanical loads and low temperatures on the surface. During this time, the treated areas should be regularly moistened using a regular sprayer. You can also cover the surface with a film, which helps reduce moisture evaporation.
Installation of concrete well rings
All work related to the installation of concrete structures must be performed with special equipment. Likewise, the installation of reinforced concrete rings for a well should be carried out using mobile cranes. Work order:
- Additionally, rubber inserts and concrete mortar are also used, which help to more reliably seal the structure and thereby increase its service life.
- The installation process itself depends on what types have been selected. If the walls have a bottom, then they are the first to be laid and only then the subsequent ones are placed on them.
Tongue-and-groove structures shorten the construction process, as they have their own specific fastenings and are quite firmly fastened together. And if their joints are coated with concrete mortar, the structure will last for more than fifty years.
Types of well rings
Well rings can be made of two materials:
- Concrete.
- PVC.
Peculiarities:
- Both have excellent properties and characteristics. They are widely used for the construction of water supply wells.
- With them, the process of constructing a structure is quite simple and all actions are completed very quickly.
Types of concrete rings
The ring for a concrete well is made from:
- Concrete mortar.
- Fittings.
- Various additives that increase its strength and environmental friendliness.
At the moment there are several types that are used for arrangement:
- Supporting.
- Wall.
- Additional ones.
- Castle ones.
- With a bottom.
- Tongue-crested.
More details:
- Support rings for wells are needed if a hatch will be constructed in the future. They are installed in front of the floor slab and can ensure reliable fastening of the hatch.
- Wall rings for wells are ordinary ones, which are installed on top of each other during the construction of the well. All joints must be filled with concrete mortar to ensure their reliable fastening.
In their design, additional rings for wells are the same as wall rings, only they have non-standard sizes. They are used to provide the required depth. They are installed at the very beginning of the wells below and the wall ones are already attached to them.
- Castle wells are very similar to ordinary concrete wells. Their main difference is that they have a special lock. They are also called tongue-and-groove. In addition to the lock on the upper part, there are special ridges on the lower part. The design, which is assembled from this type of rings, is distinguished by its strength.
- There are also certain holes that are filled with concrete during installation. All of them, when securely fastened, are not capable of horizontal shifts. Reinforcement also takes part in their production, which gives them greater strength.
- Rings with a bottom are not particularly complex in their design, since they are made like wall rings, only they are additionally equipped with a bottom. Accordingly, during construction they are laid on the bottom of the structure and serve as a support for it.
- There are also adjustment rings for wells. They are used to increase the depth of the well in the range of 50 cm. This allows you to obtain cleaner water. They are made of reinforced concrete or PVC.
The photo shows all the types that are used in water supply structures.
Typical device
Construction of a brick well.
There is a certain structure of this type of well, which includes:
- sewer hatch, which provides access to underground communications;
- shaft, considered the main part of the device;
- the neck, which is the load-bearing element of the well (it may not be used in pedestrian areas);
- the bottom, where sediments of sand, silt and suspended parts collect.
What can wells be like?
At the moment, there are three types of wells that are used in suburban areas:
- Water pumps.
- Observations.
- Sewer.
Functions of water wells
The main function of this design is to provide water to a residential building. may be different, since the aquifer is located differently in each area. As a rule, wells with water supply are mines and various materials are used to equip them inside:
- Wood that is used to line the entire perimeter of the internal walls of the structure.
- Stone (brick or natural agglomerate) that is used in a similar way.
- Rings. Here the choice of such material for arrangement is quite wide.
Water supply sources
Sources of water supply can be surface and groundwater. The waters of the soil layer and the perched water (the so-called waters of the aeration zone) are fed mainly by atmospheric precipitation and are retained on waterproof layers impenetrable to them. These waters have an unstable flow rate (the number of liters of water per hour) and are susceptible to pollution, therefore they are usually not used in water supply.
Gravity groundwater, usually associated with the surface waters of rivers, seas and lakes, is replenished by precipitation at some distance from the place of its intake and can be used for domestic and drinking needs. These waters have a low flow rate, are also susceptible to pollution and require special attention to the organization of a sanitary protection zone. To obtain free-flow groundwater, shaft wells are used, made of stone, concrete, reinforced concrete, wood, into which water enters through the bottom and walls. Water in wells is installed at the same level as in the aquifer.
Sewer stairs KL-1
We produce ladders for sewer wells of any size at the customer's request.
| Type of stairs | Length (m) | Price |
| KL-1-2.0 | 2,0 | 2430 |
| KL-1-2.5 | 2,5 | 2955 |
| KL-1-3.0 | 3,0 | 3480 |
| KL-1-3.5 | 3,5 | 4000 |
| KL-1-4.0 | 4,0 | 4530 |
| KL-1-4.5 | 4,5 | 5000 |
| KL-1-5.0 | 5,0 | 5570 |
| KL-1-5.5 | 5,5 | 6110 |
| KL-1-6.0 | 6,0 | 6650 |
The price list shows average prices including VAT and delivery.
When building modern drinking wells, special reinforced concrete rings are used. To prevent the work from being delayed, they are immediately brought to the site and unloaded near the place chosen for digging the well. The exact quantity that will be required to construct the mine becomes known only after the aquifer has been found.
About water quality
Water should not only be clean and transparent, but also not harmful to health and not contain pathogenic bacteria. There may be an excess of fluorine or iron, hydrogen sulfide, or silicic acid in the water. Often underground springs contain a lot of salts and have significant hardness. Excess salts are removed with lime, soda, table salt and other reagents. At low alkalinity, water is alkalized. Activated carbons are used to remove organic substances from water (decomposing plants or animals that lead to the appearance of pathogenic bacteria in the water).
nota bene
The Earth's hydrosphere contains about 1.5 billion cubic kilometers of water, but 98% is salt water from the oceans, about 2% is water from glaciers and polar ice, and only 0.06% of the total is fresh land water. The amount of groundwater is about 400 million cubic meters. km, i.e. about 25% of the volume of water in the oceans. Most of these waters are either mineralized and cannot be used without desalination, or are located at great depths.
Approximately 60% of the world's population is constantly lacking fresh water. The great civilizations and cultures of antiquity have always owed their flourishing to the art of man to extract water, sometimes in extremely difficult natural conditions. The first water pipelines known to us were built before our era in Ancient Rome and Greece. At the beginning of the century e. the first water pipelines were built in Crimea and Georgia, in the 12th century - in Novgorod, in the 12th-16th centuries. - in Kyiv and Pskov, in the 15th century - in the Moscow Kremlin. In the 18th century, a canal was built in St. Petersburg to supply water to the Winter Palace and Summer Garden, as well as water pipelines in Petrodvorets and Tsarskoye Selo.
In the Middle Ages, one resident spent 10–15 liters of water per day, but by the end of the 19th century this figure tripled, and today only for household and drinking needs one person spends from 150 to 600 liters of water per day. Taking into account water consumption by industry and agriculture, the total water consumption per inhabitant per day reaches more than 6,000 liters.