When connecting private homes to an external power supply system, homeowners are faced with various problems and errors:
- discrepancy between the technical characteristics of the input equipment and the actual loads on the electrical network;
- insufficient level of electrical safety of the home electrical installation, the reason for which is the lack of necessary protection devices against electric shock;
- errors during connection of protective devices and violation of the sequence of their connection.
All this is caused by the lack of objective information about how to properly supply electricity to the house and what equipment should be equipped with the incoming electrical panel.
More precisely, many answers can be found to existing questions, but it is not so easy to find reliable information in them.
Rules for the installation of electrical installations, building codes, requirements of local power grid companies - if you delve into all this at the same time, you can quickly reach a dead end. Therefore, we would like to introduce you to the real experience of FORUMHOUSE users and the recommendations of specialists from the Legrand Group, our partners in the “HOUSE IN A YEAR” project with FORUMHOUSE.
Connecting power-receiving equipment in a private home is an issue that should be addressed by professionals. However, after reading the article, you can take note of a few recommendations for yourself.
Today you will learn:
- what are the requirements for the design of electrical panels;
- what devices electrical panels should be equipped with, and what functions the installed equipment performs;
- how to ensure selectivity of the home electrical installation;
- how to choose a protective device based on its performance characteristics;
- in what sequence to connect protective devices (RCDs, automatic circuit breakers, circuit breakers (CB)).
Organization of the entry point
During the connection process, a cable line (underground or overhead) is drawn from the street electricity metering panel (MU), located on the power transmission line tap-off support, to the distribution panel (DP), mounted indoors.
The metering panel (MCB) often contains only an input machine and an electricity meter. Circuit breakers, residual current devices and other elements, which will be discussed below, are installed in the distribution panel (DP), which is installed directly in the house.
In some cases, equipment for the control room and control panel can be installed in the same building.
The operating parameters of the equipment installed in the metering panel, its list and quantity - all this must be specified in the power supply project (or at least must be calculated by specialized specialists). But there are requirements that apply directly to the design of the electrical panel.
Sergey Savelyev Head of Technical Department of Legrand Group in Russia
The design of the electrical panel must ensure convenient supply of the power cable; it must contain neutral buses and grounding buses. At the same time, the electrical panel must have internal space sufficient to accommodate numerous outgoing cables, and its reserve necessary for possible expansion and modernization of the electrical installation.
We add that the body of the shield must be resistant to fire or made of self-extinguishing material. At the same time, he is obliged to reliably protect the built-in equipment from possible damage. A lock built into the door or dashboard handle will help prevent intentional damage, and protection from dust and moisture is guaranteed by the IP protection degree specified in the specification. If the shield is intended to be installed outdoors or indoors, where increased protection from moisture, dust and mechanical damage is required, then it is better to give preference to shields of class IP65 – IK09.
In order to avoid disagreements during the connection process with specialists from energy supply companies (whose requirements often contradict each other), a power supply project should be developed and agreed upon simultaneously with the architectural design.
If the connection point is organized in accordance with the requirements of the agreed electrical project, the owner of the site, as a rule, does not have problems during the connection process and further checks by regulatory organizations. Consequently, the work associated with installing and completing the electrical panel will not be in vain.
Let's talk about what the configuration of a home switchboard should be.
ASSEMBLY OF ELECTRICAL SHIELD. DIAGRAMS
Assembling an electrical panel always begins with studying the electrical supply diagram of your private home or apartment. There are two ways to get the schema:
- You can draw a diagram for assembling an electrical panel yourself in conventional programs, such as Photoshop, AutoCAD, Compass or Excel. But using this diagram for assembly is only possible in standard, typical cases. Because often such diagrams are understandable only to the authors, are confusing, unfinished, and most importantly, do not contain all the necessary information for assembling the shield. Below are examples of how you can draw up a diagram for assembling an electrical panel yourself. When you order a shield assembly from me, I design and draw the electrical circuit for free.
- An ideal option if you already have a ready-made power supply project for your house or apartment. It must have an electrical panel diagram.
Input switch and meter
The starting point of a home electrical installation is considered to be the input switch to which the electric meter is connected, and other devices located after the meter.
Sergey Savelyev
The rating of the input AV is determined by the energy supply organization based on the allocated power. For example, with a three-phase input and 15 kW of allocated power, the rating is 25A. With a 1-phase input and 7.5 kW, the rating is 40 A. Moreover, if the power is more than 11 kW, the power supply must be three-phase. If there are three-phase consumers in the project, three-phase connection is allowed with an allocated power of less than 11 kW.
Where to start?
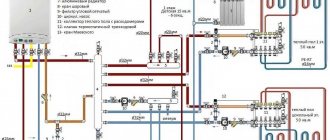
Every experienced electrician will confirm that it is much easier to begin work on installing an electrical panel and wiring, having before your eyes a floor plan indicating the intended placement of household appliances, lighting fixtures, as well as sockets and junction boxes. Having decided on the number and power of consumers, it is necessary to draw up a diagram of the electrical panel itself. A single line diagram might look like this:
In this diagram, all consumers are divided into 20 groups, for each of which the following is indicated:
- wire grade and core cross-section, mm²;
- power;
- current consumption;
- type of circuit breaker indicating the rated current.
For the uninitiated, such a diagram looks quite complicated, so you can use a simplified schematic representation of the location of the electrical panel components.
For greater clarity, the electrical panel diagram can be depicted as follows:
Or even like this:
Where
- 1 - introductory AB;
- 2 - counter;
- 3 - zero bus;
- 4 - grounding bus;
- 5–10 — AV consumers.
Having such a diagram in hand, it is much easier to figure out how to properly assemble an electrical panel.
Transfer input device
If the electrical installation includes a source of autonomous power supply (for example, a diesel generator), then the system must have a reserve input device, which is installed after the electricity meter. We are talking about a switch that allows you to manually connect consumers to a generator or to an external power supply system. This device does not allow simultaneous use of two different power sources (transformer substation and diesel generator). This is its key advantage.
SPD
To protect the electrical installation from high-voltage pulses, from the consequences of a direct lightning strike and, as a result, from possible fires, it is necessary to integrate a surge protection device (SPD) into the system.
In the general diagram, SPDs are located immediately after the QF1 input device. In addition, the SPD should be connected to the circuit through a separate protection device QF2 (circuit breaker or fuse). The number of poles of the input device and SPD should be selected based on the number of phases and the operating mode of the neutral. (see diagram). When entering air into a building, installation of an SPD is mandatory!
Fire protection RCD
Fire safety residual current devices are designed to protect against fire. Devices that operate at a rated differential current of 100 to 300 mA are used as fire protection RCDs. This is a fairly high setting and does not protect a person from electric shock. For this reason, certain consumer groups are equipped with additional (more sensitive) RCDs.
Recently, selective fire protection RCDs have become widespread.
Sergey Savelyev
Type “S” (selective RCD with response delay) - designed to ensure that in case of ground faults in lines (for example, in socket lines), only downstream RCDs of a specific line are triggered, and the fire RCD at the input continues to operate, powering healthy sections of the electrical wiring.
Cross module
In modern power supply systems, several groups of electrical consumers are often used (socket group, lighting, etc.). And in order to distribute the electricity supplied to the panel from the input cable between different groups, it is recommended to install a modular distribution block (cross-module) on the DIN rail. The cross-module allows you to insert one conductor into the panel, designed for a large load, and receive at the output several lines of a smaller cross-section (which depends on the load on a particular group of consumers).
In addition, installing a cross-module ensures reliable electrical connections and simplifies the process of connecting additional devices to an existing electrical panel.
Application of aluminum cables for installation of automation
It is not recommended to install automation in a distribution panel, connecting it with aluminum wire, due to:
- low strength (breaks when bent);
- Twisted aluminum wires are almost impossible to solder and very difficult to weld. This leads to a high probability of contact failure over time.
- With equal cross sections, it is capable of passing smaller currents;
- in accordance with the requirements of the PUE (clause 7.1.34 - Cables and wires with copper conductors should be used in buildings).
However, if you can find 8030, 8176 aluminum-iron alloy wires, you can use them. These grades have improved mechanical properties. The manufacturer claims flexibility 6, the highest class. This was achieved by changing the structure of the existing crystallization lattice of the material.
Such a wire can be bent at an angle of up to 90° for 15 times without damage.
The material has a number of significant advantages over copper:
- the alloy weighs significantly less (by about 60%);
- this wire is almost 70% cheaper than copper wire, designed for the same current and power.
Therefore, starting from October 16, 2017, the Ministry of Energy allowed the use of aluminum (in this version) in the installation of electrical wiring in apartments and residential buildings. The basis is order No. 968.
RCDs and circuit breakers (AB) for individual groups
Each consumer line leaving the cross-module is protected by separate circuit breakers and RCDs. When it comes to installing them in a distribution panel, two questions immediately arise:
- How to choose the right protective devices based on rating and differential cutoff current?
- How and in what sequence are RCDs and machines connected to each other?
We will try to give detailed answers to them. First, let's find out what functions the presented devices perform:
- An RCD protects a person from electric shock, but it cannot protect itself and the electrical installation from overcurrents and short circuit currents. Therefore, the power supply system must be equipped with both RCD and AV at the same time.
- Automatic switches do not react in any way to leakage currents, but protect the circuit from overloads and short circuits.
The protective action of an RCD is based on the principle of limiting (due to quick shutdown) the duration of current flow through the human body when it unintentionally touches live elements. Under normal conditions, the current flowing through the neutral wire is exactly equal to the current in the phase wire. If a difference occurs between them due to leakage to the ground through damaged insulation or through the human body, the device reacts to this by immediately turning off the network.
To understand what rating protection devices should have, let’s turn to the opinion of a specialist.
Sergey Savelyev
Socket lines (cable cross-section 2.5 mm²) are protected by 16A AB, lighting lines (cable cross-section 1.5 mm²) by 6 or 10 A AB. Consumers with a power of more than 3.5 kW are connected to the panel with a separate cable through a separate AB. In this case, the cable cross-section and AB rating must be calculated.
The AB housing is always marked with a letter designation of the device’s operating current category (for example, B16, C16). The number after the letter indicates the device rating in amperes. In household systems, AVs of the following categories are used: “B” and “C”. Devices of category “B” operate almost instantly when the current in the circuit increases to 3–5 nominal values. Category “C” devices are designed for instantaneous shutdown at 5–10 ratings. Consequently, category “B” circuit breakers are the most sensitive to short-circuit currents and are especially recommended for wooden house construction.
Now, as for the RCD: these devices are selected according to three parameters at once:
- According to rated current. The designation of the rated current is written in amperes and applied to the device body. In this case, the letters indicating the disconnection category (which are used to mark circuit breakers or differential circuit breakers) are not written on the RCD body.
- By rated differential current - the main parameter of the RCD, indicated in milliamps (10 mA, 30 mA, etc.).
- According to the category of leakage currents: devices of the group - “AC” - are triggered only by alternating leakage current. More sensitive devices (group “A”) respond to both alternating and pulsating leakage currents. In simple home systems, it is allowed to use devices from the “AC” group.
Sergey Savelyev
A 30 mA RCD is placed “at the head” of a group of circuit breakers (for example, 3-4 circuit breakers are connected to one RCD). The rated current of the RCD must be no less than that of the higher-level circuit breaker (as a rule, the higher-level circuit breaker is the input circuit breaker).
So, several AVs can be connected to each RCD, protecting separate groups of consumers.
If the rating of the RCD is greater than or equal to the rating of the higher-level circuit breaker, then several circuit breakers can be connected to such a RCD (even if the total rating of the circuit breakers is greater than the rating of the RCD). If the rating of the RCD is less than the higher-level CB, then several machines can be connected to the RCD, only under one condition: if their total rating does not exceed the rated current of the RCD.
Simply put, the RCD itself is under reliable protection if an AV whose rating is less than or equal to the rating of the RCD is connected to the circuit before or after the device.
And also about the nominal value of the RCD.
R0c0t FORUMHOUSE user
It is recommended to protect rooms with high levels of humidity (bathrooms, showers) with an RCD with a differential breaking current of 10 mA, if they have a separate line. In other cases, for example, if one line is allocated to several rooms (kitchen, bathroom, etc.), you should use an RCD with a differential operating current of no more than 30 mA (SP 31-110-2003).
Which is better: rigid or flexible wire when installing a distribution panel?
The main difference between a rigid wire used for an electrical panel and a flexible one is the ability of a flexible wire to bend in the desired direction up to 12 times (decreases over time), as well as the ease with which it bends.
As a rule, to connect automation in the distribution board, professional electricians use flexible wire PuGV. Because it is more convenient to work with it. For work carried out independently by residents or unskilled workers, rigid wire is often used.
In both the first and second cases, the required build quality can be achieved. However, a wiring diagram assembled using a flexible wire looks more aesthetically pleasing.
Sequence of connecting RCDs and circuit breakers
The first connection rule: if a phase is taken from one RCD, then zero from all consumers connected to this phase must return to the original RCD. That is, the neutral and phase wires should not be mixed with other neutrals and phases after the RCD.
In the diagram we see two circuit breakers going to the lighting groups (protection of lighting lines using an RCD is not mandatory). The fire protection RCD is not indicated in this diagram. The socket groups are protected by a protective shutdown with a rating of 40 A and 30 mA.
Connection is simple:
- the lighting groups are not connected to the RCD, so the neutral and phase wires are branched off to them after the input circuit breaker;
- the phase for the socket groups is taken from one RCD;
- The zero of the socket group is connected to a separate zero busbar, which is also connected to the RCD.
When completing electrical panels, you should avoid situations in which an unlimited number of lines are connected to one RCD. To ensure this condition, the standard panel is equipped with several residual current devices. In this case, RCDs are grouped by type of connected premises and by type of load. For example, the socket group of the bathroom is connected to an RCD with a nominal value of 10 mA, and the socket groups of the kitchen and living quarters are connected to an RCD with a nominal value of 30 mA.
How to connect the phase and neutral wires
Simultaneous disconnection of phase and neutral is justified especially in situations where three-phase voltage is introduced into a house or non-residential building. In such situations, there is a greater risk that one of the phases may short circuit to zero. This is a short circuit mode to which the machine protecting this phase must respond. But in those fractions of a second while it is triggered, an overvoltage will occur in the other two phases. That is, instead of the required 220 V, there may be all 380 V - the voltage difference between the two phases with a conventional three-phase connection.
Not a single household appliance is designed for such voltage, and the more powerful it is, the more current it passes, and the greater the likelihood of it burning out due to overvoltage. Where the fuse of a low-power device immediately blows, powerful equipment will still “tolerate” a heavy load for some time, and during this time the switching power supply or transformer may fail. Therefore, it is preferable to protect equipment such as boilers, dishwashers and washing machines with two-pole circuit breakers that cut two circuits at once.
Keep in mind that phase imbalance is also harmful to the source that powers the building. A generator, a transformer booth, a substation - all this will deteriorate very soon. For such purposes, there are special three-phase circuit breakers, which, in the event of a large imbalance or failure in one of the phases, can immediately turn off all three phases simultaneously. For more critical circuits, it is recommended to connect a four-phase circuit breaker, which also de-energizes the neutral wire.
Differential machines
In practice, instead of residual current devices, differential circuit breakers are often used.
These are devices that combine RCD and AV in one housing. It makes sense to use automatic devices if this device will protect a separate line or an individual consumer. If you protect several lines with a difautomatic device, then each will need to additionally install its own AB (unless, of course, the selectivity of the system is important to you, and you do not want to violate it).
How to determine what has knocked out the traffic jams
Often the machine goes off immediately when the lights are turned on. In this case, the user must be able to determine that the protection has worked. If, when turning off a household appliance, the machine is knocked out, the lever will be in the off position or will occupy an intermediate position. When there is a significant load, several breakers may trip.
For devices equipped with a button, the corresponding button will be in a depressed state. It is slightly larger in size than the power button and is painted white. Such devices are turned on by pressing this white button.
If plugs with a fusible insert are knocked out, it will be quite difficult to visually determine the operation if the body is opaque. To determine the malfunction, you will need a special device.