Design
Multi-sectional houses designed according to the block-sectional principle. The series includes both ready-made houses and block sections - row, corner, rotary block inserts. The block-sectional principle allows you to “assemble” houses of various shapes from sections - straight, angular, curved. Block sections are designated by indexes 85-0хх, ready-made house projects are designated by indexes 114-85-хх.
The number of storeys of the houses is 5 or 9 (10) floors.
The material of the walls is brick, most often white silicate; there are houses made of red brick. Plaster is used occasionally. A combination of red and white bricks can be used for decoration. Load-bearing walls - external and transverse internal. The floors are hollow-core reinforced concrete slabs with a thickness of 220 mm.
The roof is flat with bitumen coating, internal gutters. The ceiling height is 2.48 m. The first floor is usually residential. All floors have balconies or loggias.
Heating is central water. Cold water supply, hot water supply and sewerage are centralized. The apartments are equipped with a gas stove.
The 9-storey modifications have 1 passenger elevator and a garbage chute.
Stone 5-storey buildings series 114
MAIN TYPES OF RESIDENTIAL BUILDINGS
Residential facilities can be divided into the following groups:
– wooden buildings;
– stone buildings of pre-revolutionary construction (including architectural monuments);
– stone buildings built before the 60s;
– stone 4-5 storey buildings of the 1-306s series built in the 60-80s;
– stone 5-storey buildings of the 114 series, erected since the 80s;
– large-panel buildings of series 1-335-С;
– large-panel buildings of the 1-335AC and 1-335KS series;
– large-panel buildings of the 1-464AC series;
– large-panel buildings of series 135;
– frame buildings with prestressed floors, series 120;
– modern multi-storey buildings carried out according to individual projects or reuse projects: brick 4-5 storeys, frame (up to 12 storeys high), with load-bearing reinforced concrete walls (up to 20 storeys high).
Wooden buildings
Wooden buildings: foundations of wooden or stone chairs, strip rubble or reinforced concrete, walls made of logs, paving stones or backfill, plank floors on wooden beams, attic roofs with a wooden rafter system or mansard.
Main defects
: low resistance to heat transfer of enclosing structures.
Main damage:
roof leaks, rot of rafter system elements and attic floors, rot of lower crowns, bathroom walls and over canopies.
Pre-revolutionary stone buildings
Including architectural monuments) 1-3 floors high
The foundations are rubble strip foundations with lime-sand mortar.
The walls are made of solid clay bricks on lime-sand mortar grade M10. The lintels are brick (wedge, beam or arched), steel or wooden. In some cases, belts of steel strips with eyelets were installed at the floor level.
Staircases – stone on vaults, stone on steel stringers, wooden, steel.
Floors - planks on wooden beams, above basements - can be vaulted on steel beams or vaulted.
Attic roofs with wooden rafter system and steel roofing.
Partitions - brick or plank.
Main defects
: low resistance to heat transfer of walls and attic floors, masonry in terms of mortar strength and normal adhesion strength does not meet the requirements of seismic resistance standards, there is no masonry reinforcement, anti-seismic belts and seams, the requirements for the presence and location of internal walls, the width of partitions and openings may not be met, there is no vertical and horizontal waterproofing of foundations.
Major damage
(determined by operating conditions): deepening of walls in the “cultural layer” of soil, roof leaks, rot of elements of the rafter system and attic floors, destruction of masonry walls in soaking areas, fungal damage to the base of walls and basement walls, there may be cracks in walls and brick lintels .
Stone buildings built before the 60s, up to 4 floors high
Rubble strip foundations.
The walls are made of solid clay bricks on lime-sand or cement-sand mortar. Lintels - brick, steel, wood and ordinary.
Stairs made of stone or reinforced concrete on steel stringers, wooden or steel.
The ceilings are planks on wooden beams, vaulted on steel beams. There may be reinforced concrete floors under bathrooms, above basements and shops.
Attic roofs with wooden rafter system and steel roofing.
Main defects and damage
correspond to the above list, except for the strength of the solution and adhesion (may correspond).
Stone 4-5 storey buildings series 1-306c
There are several options for stone 4-5 storey residential buildings of the 1-306s series: 1-306s-44, 1-306s-47, 1-306s-48, differing in number of floors, layout, composition of structural anti-seismic measures (distance between transverse walls, reinforced concrete cores) .
The standard project of the 1-306s-48 series has been put into operation since 1967, designed for 5-storey residential buildings for areas with seismicity of 7-8 points, has the following characteristics:
Load-bearing frame
- a combination of longitudinal and transverse main stone walls, united by disks of reinforced concrete floors that are rigid in their plane.
In addition to the external ones, the building has one longitudinal and transverse walls with a pitch of 8.8 m.
Vertical loads from interfloor and attic floors and roofs are carried primarily by external and internal longitudinal walls.
Foundations
– strip, monolithic reinforced concrete or from prefabricated reinforced concrete pads and blocks. The basement walls are monolithic reinforced concrete or made of foundation blocks of the FBS24.6.6 and FBS24.4.6 grades on top of which a monolithic reinforced concrete belt is arranged.
Walls of the above-ground part of the building
– load-bearing, made of solid or hollow clay brick M75 and cement-sand mortar M75. The nominal thickness of external walls is 640 or 510 mm (according to the climatic region), internal - 380 mm.
The walls are reinforced with complex structures in the form of longitudinal and transverse frames, composed of monolithic reinforced concrete belts at the floor level and racks framing the openings of the external walls, at the intersections of the walls and in the piers of the internal walls. Normal adhesion strength is category 3 0.6 kgf/cm2 (in modern standards there are only two categories starting from 1.2 kgf/cm2).
The wall joints are reinforced with mesh reinforcement.
The cornice is made of prefabricated reinforced concrete slabs.
The lintels of window and door openings in external walls are reinforced concrete blocks, and the lintels of door openings in internal walls are reinforced concrete.
The walls are plastered or exposed masonry, made with jointing.
Partitions
– brick, gypsum concrete 80 mm thick, inter-apartment partitions – double with an air gap or brick.
Interfloor and attic floors
– prefabricated reinforced concrete, composed of panels with round voids 5860 mm long, grades predominantly S-PK59-12 for a calculated uniformly distributed load of 450 kgf/m2 (without taking into account the panels’ own weight). The seams between the panels are filled with M100 grade mortar and embroidered.
Stairs
– two-flight, composed of prefabricated reinforced concrete ribbed flights and platforms.
Roof.
The project provides two roof options: combined with a roll roof or an attic with a slate roof.
The balconies are made from prefabricated reinforced concrete slabs with embedded parts, for anchoring with welded reinforcement outlets in the reinforced concrete belt.
Early standard projects of the 1-306s-44(47) series are distinguished by the absence of complex structures, the presence of wooden partitions, and the number of storeys (4 floors).
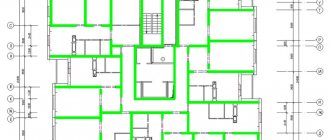
Stone 5-storey buildings series 114
Stone buildings of series 114 are five-story with a basement, built since the 80s, and have the following design characteristics.
Supporting frame of the building
- a combination of longitudinal and transverse main stone walls combined with reinforced concrete floors.
In addition to the external ones, the building has one longitudinal and transverse load-bearing walls.
Vertical loads from interfloor and attic floors and roofs are carried primarily by external and internal longitudinal walls.
Foundations
under brick walls - strip reinforced concrete, made of foundation blocks and pillows. The basement walls are made of foundation blocks of the FBS24.6.6 and FBS24.4.6 grades. A monolithic reinforced concrete belt is installed along the top of the walls.
Walls.
The outer walls of the building with a nominal thickness of 640 mm and the internal walls with a thickness of 380 mm are load-bearing, made of hollow clay bricks with cement-sand mortar.
The walls are reinforced with complex structures in the form of longitudinal and transverse frames, composed of monolithic reinforced concrete belts at the floor level and racks framing the openings of the external walls, at the intersections of the walls and in the piers of the internal walls.
The wall joints are reinforced with mesh reinforcement.
The lintels of window and door openings are prefabricated reinforced concrete.
Facades, as a rule, are not plastered.
Partitions
– brick 120 mm thick, reinforced.
Floors
– prefabricated reinforced concrete panels with round voids with nominal dimensions mainly 6300×1200×220 mm. Anti-seismic belts are provided at the floor level. In the ceiling, panels were used for a design load of 450 kgf/m2 (without taking into account the self-weight of the panels), and in areas with brick partitions - for a load of 600 kgf/m2.
Roof -
gable attic. The roof is made of corrugated asbestos-cement sheets, the drainage is not organized externally.
Stairs
– two-flight, composed of prefabricated reinforced concrete flights and platforms. Closed staircase with openings in the external walls.
Loggias
fenced with brick walls, covered with reinforced concrete hollow panels.
Main defects and damage:
freezing and condensation formation in the upper part of the end walls of the 5th floor (along seismic belts).
Advantages
- High heat and sound insulation thanks to brick walls, hollow-core slab floors, thick load-bearing walls between apartments
- Isolated rooms
- Kitchen 8-9 (sometimes even 10) m2 in most apartments
- In most apartments, the living room is located next to the kitchen and is not separated from it by a load-bearing wall, which allows you to create an opening between the rooms
- Separate bathroom with space for a washing machine
- Balconies or loggias in all apartments, wide six-meter loggias in many modifications
- A large number of multi-room apartments. Some houses have non-standard five-room apartments
- Three- and four-room apartments face two sides of the world
- The design life of series 85 houses is much longer than the life of panel houses and is 150 years
Typical redevelopment and repairs
Typical redevelopment of Brezhnevka
involves the performance of certain construction work that requires approval from the relevant authorities. Often a combination of a bath and toilet, a balcony and a room adjacent to it is carried out. In some cases, a large room is divided into several small ones.
Important! For the listed works, it is necessary to obtain the appropriate permission and first legalize the redevelopment.
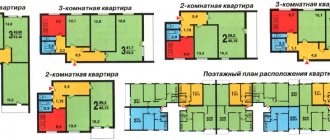
Redevelopment options with dimensions
When carrying out redevelopment, you must remember that the minimum size of the room should be 8 square meters. m. Layout of Brezhnevka 2-room apartment
implies an expansion of space. To do this, the bathroom is combined to increase its area. You can remove a separate corridor, expanding the living room and making it a walk-through. The second room can be divided into 2 small bedrooms for parents and a child.
Brezhnevka 3-room
can expand by getting rid of built-in wardrobes and mezzanines. It can also combine a bathroom.
Ways to increase kitchen space
If Brezhnevka has a layout
assumes there is a balcony in the kitchen, then they can be combined. Thanks to this, the area of the kitchen space will increase. As a rule, the kitchen is adjacent to a load-bearing wall. Therefore, it cannot be completely demolished. You can only make an arched opening between it and the living room. If there is a pantry nearby, you can combine it with the kitchen.
Combining a small kitchen and living room
Layout of Brezhnevka with 2 rooms
assumes the presence of a small kitchen, which they often try to combine with the living room. This is a rather labor-intensive option. To implement such a project, it is necessary to take into account several nuances:
- The wall that will be demolished should not be load-bearing;
- The project must be agreed with the relevant authorities and legalized.
Combining a bathroom
Combination is possible if the bathroom is separated by a non-load-bearing wall. It is necessary to take into account several points, including the number of people living in the apartment and the convenience of such redevelopment. Removing the wall will increase the area of the room and make it more convenient to place everything you need.
Dismantling of cabinets
Some Brezhnevkas have built-in cabinets necessary for storing things. Modern furniture allows you to conveniently and hiddenly place everything you need. Therefore, such cabinets are losing their relevance. Their walls are not load-bearing. Therefore, you can get rid of them to increase space.
Other options
Various options are used for redevelopment. And you don't always have to tear down walls. Zoning can be carried out:
- Special partitions. It could be simply drywall or a closet that divides the room into several rooms and allows you to store things at the same time;
- Room design. You can divide and visually enlarge the space using cladding and color schemes;
- Zoning with light;
- Creating a ceiling niche, raising the floor.