As part of the “HOUSE IN A YEAR” project with FORUMHOUSE, we decided to answer questions from portal users regarding the selection and installation of recuperators.
One of these installations will be put into operation at our construction site, which determined the topic of this article. Questions regarding the types of ventilation systems and the criteria by which recuperators should be selected will be analyzed with the help of manufacturers - engineers from the TURKOV company.
In this article:
- types of ventilation systems;
- what are the advantages of a recuperator;
- what parameters should be used to select a recuperator;
- basic and additional functions of the recuperator;
- sanitary standards for installation and connection of the recuperator.
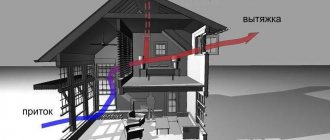
So, why was a supply and exhaust system chosen? To fully understand the issue, let’s consider the types of modern supply and exhaust systems.
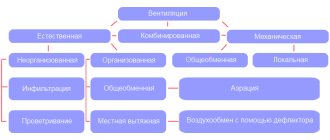
Natural ventilation
Natural impulse ventilation is a system that includes wall and window supply valves (providing fresh air into the room), as well as a system of exhaust air ducts (removing waste air from toilets, bathrooms and kitchens). The possibility of air exchange in the presence of natural ventilation is ensured by the difference in temperatures inside and outside the room.
The advantages of such a system are its simplicity and low cost; the disadvantages include low efficiency and insufficient quality of air exchange. Also, the disadvantages include a large load on the heating system and seasonal instability. For example, in the summer, when the temperature of indoor and outdoor air equalizes, air exchange in the room practically stops. In winter, on the contrary, the system works more efficiently, but this requires additional costs for heating the air coming from the street.
CONSULTATION WITH A SPECIALIST
CALL US 8 (495) 185-02-02
All supply systems are required to be equipped with filter elements, ensuring not only air supply, but also air purification. In cities with a high degree of pollution, this factor is of no small importance.
Inexpensive models purify the air from large dirt and dust, and more complex devices, in addition to large particles, also filter out pollen, viruses and other allergens - for example, car exhaust fumes. Thus, by installing a fresh air ventilation valve in a wall or window, you will not only provide your home with fresh air, but also protect yourself and your loved ones from irritable reactions resulting from the presence of contaminants in the air.
Combined system
Combined ventilation is a system with forced exhaust and natural air flow. Its disadvantages:
- The energy efficiency of the combined system is even lower than that of natural ventilation. The fact is that fans create a stable flow of exhaust air, and this significantly increases the load on the heating system.
- Low quality of air exchange in the house (the hood does not work all the time, but only when using bathrooms and kitchens). Even with constant operation of exhaust fans, the air exchange in the room will not reach the level necessary for comfortable living.
The advantages of the combined system are its relatively low cost and the absence of seasonal problems with draft in the exhaust duct. However, in terms of air exchange and functionality, the combined system falls far short of full-fledged supply and exhaust ventilation.
INSTALLATION
To make ventilation, at the second stage, in the wall using a diamond tool it is necessary to drill a through channel with a slope of 2 degrees towards the street:
- with a diameter of 180 mm for the Marley MEnV 180 in the walls of brick and concrete houses;
- with a diameter of 152-160 mm for the Marley MEnV 180 in the walls of energy-efficient houses built using Canadian technology or SIP houses;
- diameter 120 mm. for the supply ventilation channel.
When carrying out diamond drilling work, special equipment with a hydraulic lifting ring and a professional construction vacuum cleaner is used. However, in some cases there are minor risks to finishing:
— the compact body of the recuperator does not cover a hole with a diameter of 1.5-2 cm, on plastered or painted walls, necessary for attaching a diamond drilling installation. Subsequently, it can be decorated, covered with a weather station, or used to store the recuperator’s remote control;
— local damage to the walls in the places where the diamond drilling unit is attached is possible if installation work is carried out in rooms with finishing made of plasterboard sheets, including metal profiles;
— contamination of the walls and floor is possible if the finishing does not ensure a tight connection of the hydraulic ring to the wall (brick joints, tiles, etc.);
— possible destruction of façade overhead elements, ceramic tiles, façade finishing tiles in drilling areas.
Important! Be aware of possible hidden communications. The Customer is responsible for the destruction of hidden communications (electrical wiring, water supply and heating pipes, air conditioning routes, etc.).
When installing the recuperator there will be no dust, dirt or debris. The work is noisy and is carried out taking into account the requirements of the “Law on Silence”.
Classic coercive system
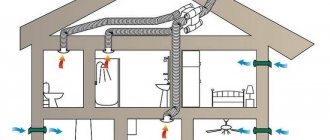
Classic forced ventilation ensures the circulation of air flows in specified modes and volumes. This system is equipped with supply and exhaust air ducts, as well as specialized ventilation equipment capable of maintaining stable air exchange in the room all year round. Such systems have one big disadvantage: they are very energy-consuming when used in winter. This is explained by the fact that the cold air flow from the street must be constantly heated to a comfortable room temperature.
Forced system with recuperator
Forced ventilation with a recuperator is the most advanced system capable of circulating air flows in specified modes and volumes. Its operation involves minimal energy consumption. After all, the flow from the street is first heated by the recuperator (due to the heat contained in the exhaust air), and then the air is additionally heated to a temperature comfortable for humans. In many developed countries, such a technical solution has already become a construction standard enshrined in legislation.
Taking into account the growing requirements for the comfort of residential premises, it is advisable to equip any new house not just with standard ventilation ducts, but with a multifunctional and economical forced ventilation system. A recuperator-based system provides a supply of clean air at a comfortable temperature and simultaneously removes waste air masses outside the room. At the same time, heat (and sometimes moisture) is selected and transferred from the exhaust flow to the supply flow.
TROUBLE-SHOOTING
1. The LED on the operating recuperator is constantly on.
A constant signal on a working recuperator reminds you of the need to clean or replace the filters. After performing routine maintenance, a short press (1-2 seconds) on the binding button in standby mode is required.
2. The recuperator does not respond to the control panel.
The lack of a signal is most often due to the loss of electrical power in the remote control battery. The battery needs to be replaced (2016).
3. Spontaneous shutdown.
The MARLEY-RUS service department has observed cases of spontaneous shutdown of the recuperator. Restarting in such cases is done using the damper lever. The reason for this malfunction lies in the damper fasteners, which were not fixed during installation. Which causes the micro limit switch located to the right of the choke lever to turn off. The solution to this problem is to secure 2 screws - it takes 20 seconds!
Why did you choose an enthalpy recuperator?
Firstly, unlike classical ventilation, the recuperator allows you to significantly save on equipment operation. Secondly, the cost of a recuperator is not much higher than the cost of classic ventilation equipment. Thirdly, during operation of the recuperator, 80% of the heat of the exhaust air is returned back to the supply air, which significantly reduces the cost of heating it.
On hot summer days, heat exchange occurs in the opposite direction, which also allows you to save on air conditioning. Simultaneously with the transfer of heat in the heat exchanger, moisture is transferred from the exhaust air to the supply air. In physics there is such a thing as “dew point”. This is the moment when the relative humidity of the air reaches 100% and the moisture changes from a gaseous state to a liquid state (condensation). Condensation appears on the surface of the recuperator, and the lower the temperature outside, the greater the likelihood of condensation forming on the recuperator. Since the enthalpy recuperator allows moisture to be transferred from the exhaust air to the supply air, the “dew point” shifts to a zone of very low temperatures. The recuperator allows you to maintain a higher relative humidity of the supply air (compared to classical ventilation), and also significantly increases frost resistance and eliminates the need for condensate removal.
The presence of the above functions fully explains the choice of such an air handling unit.
We present a functional diagram of the installation.
Where: • M1 and M2 – supply and exhaust fans; • D (1, 2, 3) – temperature sensors; • K (1, 2, 3) – heat exchangers; • F (1, 2) – air filters.
What parameters should you use to choose a recuperator?
The first thing you need to pay attention to when choosing a model of a supply and exhaust heat exchanger is the wording used by the manufacturer or seller of the equipment. We often hear the following: “efficiency up to 99%”, “efficiency up to 100%”, “operation down to -50ºС” - all these phrases are nothing more than a manifestation of a marketing strategy with a simultaneous attempt to mislead the buyer. As experience in operating recuperators in the Russian climate has shown, metal recuperators operate stably when the temperature drops to -10ºС. Then the process of reducing efficiency begins due to freezing of the recuperator. To prevent this from happening, many manufacturers use additional heating sources (electrical preheating).
The second thing you need to pay attention to is the thickness of the equipment casing, the material from which the casing frame is made and the presence of cold bridges in the casing. Let's return to the experience of use again: let's look at the features of the 30mm thick case. This housing cannot withstand a drop in street temperature to -5ºС and must be additionally insulated. If the case is made of an aluminum frame, then additional insulation will also become an integral part of it. After all, aluminum is one large bridge of cold, “spreading” along the entire perimeter of the case.
Third: one of the common mistakes when choosing a recuperator is that the buyer does not take into account the free pressure of the fans. He sees only the magic figure - 500 m³ and the price - 50 thousand rubles, and the buyer learns that the fan has a pressure of 0 Pa at 500 m³ only after finishing the house renovation, that is, during the operation of the already installed equipment.
The fourth selection criterion is the presence of automation and the ability to connect optional components to it. Automation can significantly reduce operating costs and achieve maximum comfort when operating equipment.
As for performance: the main calculation parameter is the volume of air that should enter the room within one hour. In accordance with sanitary standards, this volume should be equal to 60 m³ per adult or one times per hour of the total cubic capacity of the premises served (living room, kitchen, bedrooms). When choosing a recuperator, you need to look not only at the performance of the installation, but also at the pressure of the fans that pump your ventilation network around the house.
It is better to entrust the calculation of the required productivity to specialists. Indeed, in case of an error, replacing the recuperator will require significant financial costs.
Shuvalov Dmitry engineer
When calculating and choosing an installation, to obtain more accurate information, you will have to read specialized literature and forums, call manufacturers and suppliers of equipment (the topic is very broad). It's always better to turn to specialists. And for those people who are not deterred by this advice, it is still recommended to confirm the correct choice with the equipment manufacturer or distributor.
However, there are several recommendations that will help the developer choose a recuperator model, based on his own ideas about comfort and practicality.
Selecting a recuperator by design type
It cannot be said that any recuperator is worse or better; each type of recuperator has its own strengths and areas of application. The efficiency of a rotary and plate recuperator is absolutely the same, since the efficiency depends on two parameters: the area of the heat exchange surface of the recuperator and the direction of the air flow in the recuperator.
The design of the rotary heat exchanger allows partial mixing of the supply and exhaust flows, since the air flow insulator in it is a brush. A brush with fine bristles, in itself, is a poor insulator between air flows, and a slight imbalance in the system leads to an even greater flow of exhaust air into the supply channel. Also, the weak link in a rotary recuperator is the engine and the belt that spins the rotor: additional moving parts reduce the overall reliability of the equipment and also increase energy costs for recuperation. The rotary heat exchanger can only be installed in one position, which also reduces the possibility of its use at home. The main objects for the use of rotary heat exchangers are shopping centers, hypermarkets and other public buildings with a large area, where air flow is only for the benefit of the building owners.
We present a diagram of the operation of a rotary recuperator.
Plate recuperators, unlike rotary devices, are not so massive, but at the same time they are easy to install and reliable in operation. Among plate recuperators, membrane-type equipment deserves special attention. A special polymer membrane built into the recuperator returns moisture from the exhaust air to the supply air. At the same time, it prevents the formation of condensation, as well as the formation of ice inside the device (during its operation at low temperatures).
Based on plate recuperators, it is possible to build multi-stage recuperation, which allows you to avoid direct contact of the coldest air flow (coming from the street) with the warmest (coming from the house). And in conjunction with an enthalpy recuperator, this technology allows you to avoid freezing of the recuperator. A smooth decrease in the temperature of the exhaust air and a gradual increase in the temperature of the supply air inside the recuperator make the device resistant even to temperatures in the far north. As practice shows, such equipment works successfully in the most severe climatic conditions, for example, Yakutsk.
PiterPro user FORUMHOUSE
Plate heat exchangers use different materials. Plastic and metal heat exchangers freeze. Membrane heat exchangers use a thin film that only allows moisture to pass through. There are two or three heat exchangers in such an installation, depending on the model.
Efficiency is one of the main characteristics of a recuperator, and special attention should be paid to its value before purchasing an installation.
How to install a supply valve - instructions
Before installation, you need to decide 2 questions: where to put the ventilation valve and how to drill a neat hole in the wall. We will give the following recommendations regarding placement:
- Ventilators with a pipe diameter of 50–60 mm are best placed between the heating radiator and the window sill. Provided that the gap height is sufficient. Then the cold street air will immediately mix with the rising convective flow from the battery.
- We place a device with an air duct more than Ø100 mm on the side of the window opening, making an indentation of 30 cm (to prevent freezing). The second option is between the window and the ceiling, the minimum distance from the ceiling is 15 cm. In both cases, the ventilator is located in the zone of convection flow from the radiator.
- The height of the passive valve above the floor is 180...200 cm.
- When installing the recuperator valve, maintain a distance of 0.5 m from all structures - ceiling, window, nearest corner, as shown in the drawing.
- Place the transfer device in a convenient place without restrictions.
Comment. If the room is heated with heated floors, then the passive type ventilator can be placed at any distance from the window; the minimum distance remains the same - 30 cm.
It is better to entrust drilling of a reinforced concrete wall to professionals armed with a machine with a diamond bit of the required diameter. You can make a hole in a brick yourself, although you will have to tinker. Using a long thin drill, make many holes around the circumference, then carefully knock out the middle.
Two important points. Before starting work, make sure that in the selected area of the structure there is no electrical wiring or heating pipes laid in a hidden way. Second: the hole is drilled with an inclination of 2–3° towards the street to allow condensate to escape.
How to properly install a supply valve into a wall:
- We cut the air pipe flush with the structure or with a small outlet - as specified in the manufacturer’s installation instructions. The Vents telescopic air duct cannot be trimmed.
- We insert the pipe into the hole and fill the gaps with construction foam. Cement-sand mortar cannot be used.
- We attach a grille with a mosquito net to the outside. We observe the correct position of the element - the visor is at the top, the blinds are directed downwards.
- We insert a heat-insulating element inside the air duct and, if necessary, cut it to length.
- We disassemble the valve head, attach the body to the pipe and the inner surface of the wall with dowels. We install the filter, dampers and lid with the inlet slots facing up.
Assembly diagram of the interior of the room ventilator
The installation technology of the recuperator valve is identical. First, an air duct is embedded in the wall, an external grille is attached, then the elements of the unit are installed from the inside - a ceramic heat exchanger, a fan and other elements. Differences: thermal insulation is mounted outside the pipe, a power cable is supplied to the fan.
Reference. There are ventilator models with a fan powered by its own solar battery. An example is the Vents valve PSS-102, shown in the photo.
Valve model with solar powered fan
Recommendations for additional functionality
It is important to choose a recuperator for your home that has sensitive and reliable automation. After all, there is nothing worse than equipment that is constantly involved in work and requires attention with enviable regularity. Modern automation of recuperators opens up additional opportunities for users:
- separate adjustment of supply and exhaust fans;
- air conditioning control;
- humidifier control;
- automation and dispatching.
And the design features allow you to equip the device with additional options and systems:
- automatic fan power control system – VAV system (maintaining constant air flow);
- automatic air flow control system based on a CO2 sensor (adjusts the air flow pressure depending on the carbon dioxide content in the exhaust duct);
- timer with several events per day;
- water or electric air heaters;
- additional air dampers;
This also includes an improved filtration system.
When choosing equipment, you need to consider the air handling unit as a climate complex that will maintain air flow, as well as temperature and humidity (if necessary) in a given mode. Installing additional heaters, coolers, VAV valves, humidifiers or dehumidifiers is already becoming a vital necessity today.
Shuvalov Dmitry
If the recuperator itself cannot maintain the required supply air temperature, then the device should be retrofitted with a heater of appropriate power. On average, if the calculated temperature in the channel does not fall below +14...+15°C, then the heater does not need to be installed. My opinion is this: it is better not to turn on the heater if it is not needed, than when it is needed, there will be nothing to turn on.
The above systems and devices make it possible to minimize human participation in system management and improve the quality of the microclimate in the house. A modern climate system is capable of constantly monitoring the performance of all components of optional equipment and, if necessary, warning the user about problems in the operation of the system and changes in the microclimate in the room. When using a VAV system, the operating costs of the installation are significantly reduced by temporarily and/or partially disconnecting individual rooms from the ventilation system.
Currently, there are models of recuperators that are capable of connecting to individual Smart Home systems using the ModBus or KNX protocols. Such devices are ideal for connoisseurs of advanced and modern functionality.
Problems
Problem #1 . CO2 levels affect my productivity. I have plastic windows in my apartment, so when the windows are closed, the CO2 level rises to unproductive levels within 2 hours. Opening the windows is drafty, cold and noisy, we needed a better solution.
Problem #2 . Moscow has dirty air: it negatively affects health. I am at home at least 10 hours a day. Therefore, the air in the apartment needs to be purified.
Additional selection criteria
When choosing a recuperator, it is important to pay attention to the noise level it creates during operation. This indicator depends on the material from which the device case is made, on the thickness of the case, on the power of the fans and on other parameters.
According to the type of installation, recuperators can be suspended (mounted on the ceiling) or floor-mounted (installed on a flat horizontal surface or hung on a wall). Exits for ventilation ducts can be either on both sides (“through” layout) or on one side (“vertical” layout). Which recuperator you need depends on the specific parameters of your ventilation system and on where exactly the supply and exhaust equipment will be installed.
Recommendations for installing a recuperator
Installation recommendations mainly concern the premises in which the recuperator should be installed. First of all, boiler rooms are used for installation (if we are talking about private households). Recuperators are also installed in basements, attics and other technical rooms.
If this does not conflict with the requirements of the technical documentation, then the installation can be installed in any unheated room, while the distribution of ventilation ducts, if possible, should be installed in rooms with heating.
Ventilation ducts passing through unheated rooms (as well as outdoors) should be made as insulated as possible. Air ducts running from the equipment to the street (supply and exhaust) are also necessarily insulated. It is also necessary to thermally insulate the passages of air ducts through external walls.
Considering the noise the equipment can make during operation, it is best to place it away from bedrooms and other living rooms.
As for placing the recuperator in an apartment: the best place for it would be a balcony or some technical room.
If this is not possible, you can allocate free space in the dressing room for installing a recuperator.
Be that as it may, the location of the installation largely depends on the layout of the apartment or house, on the layout and location of the ventilation network and on the dimensions of the device.
It is recommended to pay special attention to such an element as the crossbar. Already existing crossbars can become a big problem when laying a ventilation network. You can only get around this element through a technical room or a built-in closet, which is not always possible. Therefore, you should think about the ventilation design even when designing a house, having previously provided for the presence of passage windows in the crossbar. The same recommendation applies to roof passages.