Often the concept of “heating” is associated with cast iron radiators, which used to be in every apartment.
Such radiators took a long time to warm up, but kept the house warm for a long time, and, in general, they functioned quite well, the only negative by and large is their unsightly appearance. With the advent of new materials and technologies, everything has changed. Nowadays, a worthy replacement for old heating radiators has become a heated floor system, for which the heating line is installed in the floor. Today, all new buildings are equipped with such floor structures.
Having decided to lay heating pipes in the floor under a screed, you need to decide what type of pipes will work reliably for a long period. This decision at first glance seems quite simple, but practice shows that it depends on many factors.
We also suggest that you read the article - how to choose a heated floor for tiles, where we will look in detail at what types of heated floors there are, their pros and cons, and how to install.
General information about the two-pipe heating system
Any heating system with a liquid coolant consists of one or more closed circuits connecting radiators and a boiler.
In a two-pipe distribution, hot coolant is supplied through one branch of the circuit and returned through the other, hence the name.
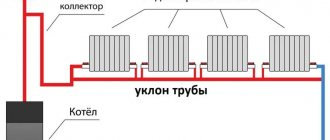
Diagram of a typical two-pipe heating system in a private house.
Classification signs:
- The organization of coolant movement is gravity and forced.
- Design – open or closed, horizontal or vertical.
- Pipe routing – radial, dead-end, ring.
By combining properties, you can achieve the best suitability for operating conditions.
Combination of engineering solutions
These approaches to organizing heating can be combined and complementary if necessary. As a result, a high-performance and inexpensive heating system for a two-story house will be assembled.
In order to accurately assess the strengths and weaknesses of each of the listed varieties, you should study them in detail.
Advantages and disadvantages
The pros and cons of a two-pipe system should be considered taking into account the operational properties and technical characteristics.
| Advantages | Flaws |
| Same coolant temperature in all radiators | Increased pipe consumption - 2 branches need to be led to the radiator, inlet and outlet |
| Adjusting the heat output of each battery | Large diameter riser pipes and supply pipes to the first radiators in the circuit |
| Low hydraulic resistance | |
| Operation of the entire system in case of failure of one or more radiators | |
| Use in high-rise buildings | |
| Flexibility of hose options – in the floor, in the walls, along the walls, under the ceiling and behind a false ceiling |
The table shows common to all two-pipe networks. However, each wiring option may have negative qualities that limit its use, which we will consider later.
How a single-pipe heating system works: we explain it in diagrams
Gas boilers
Individual gas heating in an apartment building requires not only the preparation of all paperwork, but also a careful approach when choosing a boiler that will be entrusted with the heating task.
As a rule, consumers choose a double-circuit unit, which will provide apartment residents not only with heat, but also with hot water.
Today they produce small-sized wall-mounted devices with closed combustion chambers. This type of boiler simplifies installation tasks, since they do not require a gas duct, since this function is performed by a fan. It “pushes” air from the street, and then also removes combustion waste through special pipes.
The benefits of a two-chamber wall-mounted gas boiler are obvious:
- It combines both a heating system and a boiler for heating water.
- Saving fuel significantly reduces heating costs.
- Equipped with an electronic sensor and thermometers, such boilers can be adjusted and configured at your discretion.
If 10-15 years ago people wondered whether it was possible to install individual heating in an apartment, today many consumers are simply switching to alternative heating sources. If the apartment is not located in a harsh climate, it is recommended to connect electric heating in the apartment instead of gas.
Schemes of open and closed two-pipe heating systems
Coolant circulation is carried out in three ways:
- gravity (gravity);
- forced using a pump;
- combined.
In addition, systems are divided into open and closed. This indicator characterizes the interaction of the coolant and the atmosphere.
When heated, the volume of any coolant liquid increases. It is known that liquid is practically uncompressible, so to accommodate the “excess” a separate device is required - an expansion tank.
Open type
Scheme of a two-pipe open-type heating system.
In open systems, the tank is installed at the highest point, it is connected to the atmosphere by a pipe.
The advantages of an open system are simplicity and a minimum of additional devices. Any type of expansion tank can be used as an expansion tank.
.
Ready-made expansion tank for open-type CO.
Add water to the tank as needed. For this:
- install taps and connect the system to the water supply;
- add coolant through the opening hatch.
Attention! An open system must not be filled with antifreeze - evaporated gases can be toxic.
Closed type
In closed systems, a sealed expansion tank with an elastic diaphragm or balloon membrane inside is used. The membrane divides the device into 2 parts. Air is pumped into one chamber with a pump at a pressure of 1.2–1.5 atm, and the second is connected to the heating system pipe.
When the coolant heats up and expands, its excess fills the tank. When the temperature of the liquid drops, the membrane squeezes the coolant into the system. Preliminary injection of air into the tank allows you to maintain the pressure necessary for the operation of the boiler, the automation of which turns off the power at a pressure of less than 1.2 atm.
Antifreeze or glycols can be used in sealed structures.
Scheme of a two-pipe closed-type heating system.
In closed networks, the tank is located close to the boiler, which simplifies monitoring the performance of the entire structure.
Gravity flow schemes
Gravity (gravity) systems work due to the laws of physics. At normal atmospheric pressure, being heated to 50°C, water has a density of 988 kg/m3, and at 85°C - 968 kg/m3.
Scheme of a two-pipe open-type gravity system.
In the heating circuit, hot water (lighter) rises through the pipes, and the coolant cooled in the radiators moves down, returning to the boiler through the “return”. The circulation pump is not used.
Advantages of gravity systems:
- rare cases of airing - low coolant speed slowly squeezes air into the expansion tank;
- long service life due to the absence of a circulation pump and a membrane expansion tank, which have a limited resource;
- use of cheap coolant (water) - in case of leaks, you don’t have to buy antifreeze;
- self-regulation - when the air temperature in the building decreases, the water in the system cools faster, which increases the circulation rate, increasing the temperature in the rooms.
Independence from electricity allows you to operate the system in country houses where the power supply is often cut off, as well as install solid fuel boilers - when the circulation pump is turned off, the boiler will not boil or explode.
Gravity-flow systems also have a number of disadvantages:
- low pressure drop forces the use of large diameter pipes (up to 75-100 mm) in risers and up to 50 mm in supply branches;
- maximum contour length – 30 m;
- long warm-up after switching on, caused by the slow movement of the coolant;
- pipelines are laid at an angle to the horizon, and the expansion tank cannot be moved outside the heated room, which affects the attractiveness of the interior;
- not suitable for buildings above 3 floors.
As a result, gravity systems are preferable:
- in areas with interruptions in power supply;
- for rooms where the appearance of the structure is not important;
- for country houses no higher than 7-9 meters;
- for solid fuel boilers (coal, firewood, briquettes), which cannot be stopped instantly during a power outage.
Bypass with circulation pump.
Some of the shortcomings are eliminated by installing a bypass with a pump into the gap in the supply pipe. In normal mode, the coolant is pumped into the system by a circulation pump; when the electricity is turned off, the flow is directed through an open pipe by gravity.
Forced circulation circuits
(Repeat).
In a system with forced circulation, the same scheme of a two-pipe closed-type heating system can be used. In systems with forced circulation, a pump must be installed: as part of the boiler or remotely. Installation is carried out in front of the boiler in the return pipe, where the coolant temperature is minimal.
The pump gives the circuit advantages:
- Radiators warm up quickly, as the coolant speed increases;
- powerful pumps allow you to create large circuits;
- all radiators have approximately the same temperature;
- in closed systems it is permissible to use antifreeze, which will not freeze and will not rupture the system during prolonged shutdowns;
- pipelines do not require slopes;
- pipes of smaller diameter are used, which reduces costs.
Flaws:
- frequent cases of airing due to the rapid speed of coolant movement;
- Volatility - you will need to install powerful autonomous power supplies;
- high price of powerful and in-boiler pumps.
Attention! For systems with solid fuel boilers, an uninterruptible power supply must be provided. The boiler cannot be stopped quickly and in the absence of circulation the coolant overheats, boils and the heat exchanger explodes.
Preferred Use:
- large buildings with extended heating circuits;
- an area with high-quality electricity supply or houses with electricity backup.
Most modern types of dual-circuit systems use forced circulation.
How to prepare a legal framework
Paperwork
So, the owner of the apartment has decided on the technical parameters of the equipment.
There remains one, but very significant question - obtaining permission to install this equipment in your apartment.
Only the interdepartmental commission responsible for the use of the housing stock can answer the question: is it possible to provide individual heating in an apartment in an apartment building?
This is where you will have to apply for the appropriate permission.
First of all, you need to prepare the following package of documents:
- application for installation of individual heating
- consent of all apartment owners
- protocol of a meeting of all residents of the house with consent to install individual heating in a specific apartment
- title documents for the apartment
- technical passport of the apartment and its copy
- if the house is an architectural monument, then the conclusion of the relevant authority on the legality and possibility of redevelopment
In addition, you will need a lot of various technical documentation, starting with the apartment redevelopment project and ending with copies of documents for the purchased equipment.
To collect all the necessary documents and permits, you will have to go around more than one service and organization. If you intend to install an electric boiler, then you must apply for permission to the city electrical networks. Permission to install a gas boiler is issued by the city gas service. Its specialists will inspect your home to ensure there is a working chimney.
Permission to disconnect from the communal heating system is given by the city heating network. The apartment renovation project will be approved by the design organization. In addition, this project must be coordinated with the SES authorities and the fire department.
When the entire package has been assembled, all necessary permits have been received and approved, you can safely purchase equipment and enter into an agreement with professional contractors who will quickly, correctly and safely install individual heating in your apartment. However, that's not all. The last step will be to receive the acceptance certificate.
Types of pipe routing and heating systems construction
The types of heating system are determined by the spatial placement of radiators and pipes.
There are different layout schemes:
- horizontal or vertical;
- upper or lower wiring;
- with direct and reverse flow of coolant;
- pipe distribution to radiators - dead-end, radial, ring.
Each type and their combinations have quality characteristics that determine the choice depending on operating conditions.
Top or bottom wiring
Scheme of a two-pipe heating system with overhead wiring.
The upper distribution can be arranged in systems with gravitational and forced circulation, as well as in their combined version. The hot coolant is supplied through the central riser into the upper horizontal pipe from which it is distributed among the risers. The pipes are located under the ceiling of the upper floor.
| Advantages | Flaws |
| The difference in pressure allows the use of a large number of radiators | The pipes give off some of the heat in the upper part of the room, which reduces efficiency |
| Suitable for various construction schemes | Requires large diameter wiring, which is more expensive |
| Low hydraulic resistance | The appearance is not suitable for some interiors |
| Possibility of installing thermostats on each radiator or riser | Sometimes the expansion tank will have to be taken out into an unheated attic and high-quality insulation carried out |
| Low network pressure (up to 3-4 atm) is suitable for all types of radiators, including aluminum | Additional equipment will be required to install heated floors. |
The diameter of the pipes and the length of the circuits increases the volume of coolant, for pumping which powerful pumps are purchased.
Scheme of a two-pipe heating system with bottom wiring.
Systems with bottom wiring are distinguished by the location of the supply pipe and return pipe below the level of the radiators.
Mostly such schemes are used in systems with forced circulation.
Advantages of lower wiring:
- pipelines can be hidden in the floor or walls;
- there is no need to make a common riser, which allows you to organize heating for the first floor built, and equip the second and subsequent floors as needed;
- By installing collectors, you can organize a “warm floor” system.
An example of a collector unit that distributes coolant along the contours of a “warm floor”.
Among the disadvantages, users note frequent airing, and installers note difficulties with initial setup and balancing.
Vertical and horizontal wiring
Scheme of horizontal and vertical distribution of two-pipe CO.
The horizontal and vertical schemes differ in the presence of a main riser.
Vertical types are mainly used in multi-story buildings. The horizontal view is suitable for buildings of any number of storeys; when arranging, the design is taken into account and a pump of the required power is selected.
Designers and installers distinguish between several basic diagrams for pipe routing in heating systems.
Three basic diagrams of pipe routing.
The dead-end circuit is installed in most country houses and has another name - with reverse (counter) movement of the coolant. Supply and discharge pipes are connected to each radiator. Circulation is carried out by a pump. The main advantage of the system is that the coolant reaches all radiators at the same temperature, and with the help of regulators it is possible to maintain the required microclimate in each room.
Flaws:
- a large number of welded and coupling connections;
- a professional hydraulic calculation is required if there are more than 3 radiators in one circuit;
- There is often noise from moving coolant.
A Tichelman loop or a scheme with a parallel movement of the coolant is used in the lower horizontal distribution and allows you to hide the pipes under the floor covering or in the screed. According to reviews from installers, the associated scheme requires minimal configuration. The Tichelman loop works great with a large number of radiators, but will require an increased pipe diameter.
When installing radial distribution, collectors are used that are installed on each floor of the building.
Diagram of radial wiring of two-pipe CO to radiators with bottom connection.
The circuit feeds each radiator separately and allows the installation of a “warm floor” system. An important disadvantage is the high cost of purchasing pipes.
Horizontal connection
Let's talk about the horizontal connection in a little more detail, since this method is optimal for two-pipe wiring. There are three schemes: passing, dead-end and radial. In the first case, both hot and cooled coolant flow in the same direction. This method is good because heating is carried out evenly and in a timely manner.
With a dead-end scheme, the picture is somewhat different. Hot and cold coolants move towards each other. With this wiring, the temperature of the radiator is influenced by its proximity to the heating boiler. The closer the battery is to the source, the hotter it is. This leads to uneven heating of the rooms in the house - those furthest from the boiler will be much colder.
The optimal wiring diagram is radial. Each heating device has its own line from the main collector. Of course, in terms of costs - both money and effort - such a system is the most demanding. But in the end we get the maximum level of comfort.
This happens due to two things. Firstly, heating occurs evenly and simultaneously, so the required air temperature is maintained in all rooms. Secondly, if there is a need to repair one of the heating devices, turning off the required section does not in any way affect the others.
There is a third advantage: when radiating pipes, as a rule, they are located under the floor, which allows you to maintain the overall aesthetic appearance of the room at the desired level.
What type of wiring to choose
The choice of construction scheme depends on the expected operating conditions:
- In buildings above 2 floors, heating is installed with main risers in a vertical pattern.
- In areas with frequent or prolonged power outages, preference is given to gravity systems with non-volatile boilers.
- For large objects, systems with forced circulation are installed, built using a horizontal type of wiring. The most suitable scheme in is the Tichelman loop.
- For independent execution, inexperienced users choose a dead-end wiring with several arms.
- When pouring pipes into the floor, it is advisable to choose a radial scheme with collectors on each floor - in the event of an emergency pipe rupture, you can turn off 1 radiator, postponing costly repairs with opening the floors.
- Small country houses, bathhouses and utility rooms are equipped according to a dead-end scheme.
Each specific case must be considered individually, taking into account the advantages and disadvantages of the types and types of heating systems.
Problems of high-rise buildings
Owners of apartments located on the top floors of multi-storey buildings often have a question: is it possible to install individual heating in an apartment on the top floor?
In fact, residents of upper floors have fewer problems with disconnecting from central heating, since to disconnect they only need to make jumpers to the lower risers and that’s it. Whereas in apartments located on the lower floors, when the central heating is disconnected, a disruption of the heating in adjacent rooms may occur.
Installing individual heating in an apartment in an apartment building will require a lot of both material and moral costs. You will have to spend a lot of time going through all the authorities and carrying out technical work. But all your efforts will pay off thanks to further savings and improved comfort in your apartment.
You can switch to autonomous heating only for the whole house:
Hydraulic calculation of a two-pipe heating system
The purpose of the hydraulic calculation is to determine the minimum required pipe diameter already at the design stage and select (if necessary) a circulation pump of sufficient power.
The general sequence boils down to the following steps:
- Calculation of the required power of radiators and construction of a general heat balance diagram.
- Determination of coolant flow in each arm of the circuit.
- Calculation of pipeline diameters.
- Selecting the required pump performance.
Only specialists with thermal engineering education can make accurate calculations, and we recommend contacting a specialized organization.
For most craftsmen who want to independently equip the heating system of a small house , you can limit yourself to an approximate calculation and include a 10-15% reserve for the power of the batteries, boiler, pipe diameter and pump performance.
Determination of the minimum required power
To accurately calculate the thermal power of radiators (and, accordingly, the boiler), you can use a calculator.
Houses made from standard building materials and with high-quality insulation will require 1.5-2 kW of radiator thermal power per 10 m2 of area in the northern regions, 1-1.5 in the middle zone and 0.6-1 kW in the southern regions.
The calculation is done for each room, and then all the indicators are added up. The data is plotted on a single diagram for further calculations.
Coolant flow
The amount of coolant required per unit time is calculated for each arm of the circuit.
To do this, use the formula: G=860* q/ ΔT , where
- G—coolant flow rate kg/h;
- q is the thermal power of radiators in the calculated area (kW);
- ΔT is the difference in coolant temperature at the inlet and outlet of the radiator, usually taken to be 20 °C.
For example, for a branch with a total radiator power of 3 kW and a coolant in the form of water, a flow rate of 860 * 3/20 = 129 kg/hour will be required.
For further calculations, the result is converted into data for water at a temperature of 60°C (the most common parameter in individual houses).
Use the formula: GV = G /3600ρ , where
- GV - water flow, measured in l/sec;
- ρ is the density of water at 60°C.
Result: 129/3600*0.983=0.035 l/sec.
Next, you need to find the resulting value in the hydraulic calculation tables for pipes; they can be found on the websites of pipe manufacturers.
An example of such a table.
For our example, a pipe with an internal diameter of at least 16 mm will be sufficient.
Important! Steel pipes are marked with the outer diameter, polypropylene pipes with the inner diameter.
Calculations are carried out separately for each circuit and displayed on the diagram. By adding up the flow rate by section, a general indicator is obtained, which is taken into account when choosing riser pipes and a circulation pump.
How many approvals do you need to collect?
For individual heating, the apartment needs to be redesigned. Both the destruction of walls and partitions and their construction consist of a labor-intensive process. It will take a long time to receive each completed paper. It is necessary to take into account installation work and the purchase of materials, so reconstruction begins with the preparatory stages:
- determined with the collection of a documentary package;
- develop a project;
- purchase equipment;
- install an autonomous system.
The regulation for any redevelopment is the Housing Code of the Russian Federation, Article 26. The reconstruction of residential premises is carried out according to technical requirements; each stage of work must be agreed with the local government. To contact the regional authority, you need to collect documents that will serve as an appendix to the main application.
General documentary support for the submitted application, filled out according to the standard form:
- title documentation - this can be a certificate of ownership, transfer of an apartment by inheritance, a purchase and sale agreement;
- photocopy of technical passport;
- redevelopment of an apartment in the project;
- information about all registered persons in the residential area;
- written notarial consent of each registered person;
- confirmation that the building is not an architectural monument.
Redevelopment may be refused if it worsens the condition of the house or threatens the safety of residents. Project documentation for autonomous heating is coordinated with authorized organizations from the field of gas and heat supply.
To disconnect the heating circuit in an apartment from the general system, you need to obtain permission from the city or regional heating networks. Specialists of this level will agree to an agreement provided that the installations do not disrupt the functionality of the building's utilities and equipment. Only a security threat can lead to the refusal of a request for heating autonomy. Applications for an individual heating system are accepted by the housing management organization.
Actions consist of the following steps:
- receive a consent letter;
- contact the gas service;
- receive technical specifications;
- take apartment property documents;
- order a project;
- purchase equipment that meets the specifications.
SNiP41-01-2003 contains the basic requirements for heating and ventilation devices. You can be exempt from registration by concluding an agreement with an organization that provides such services.
Recommendations for choosing pipes
The efficiency and durability of a heated floor is primarily determined by the choice of pipe material and the quality of installation. Each type of pipe is characterized by a set of advantages and disadvantages that should be carefully studied before making a final decision.
Products from popular brands will cost more, but they are guaranteed to last the stated period. Cheap pipes from dubious companies will not provide such confidence; such products will easily fail at the most unexpected moment. In this case, the cost of repairs and compensation for damage to flooded neighbors will far exceed the savings on purchase.
As for cost, polypropylene products are considered the most affordable. Pipes made of cross-linked polyethylene and metal-plastic will cost more. Copper pipes, as well as fittings for them, are the most expensive option for pipe products.
Ban on individual heating in an apartment building
To carry out the reconstruction of a residential premises, the owner of this premises or a person authorized by him directly submits to the approval body at the location of the residential premises being converted: 1) an application for reconstruction in the form approved by the federal executive body authorized by the Government of the Russian Federation; 2) title documents for the residential premises being rebuilt (originals or notarized copies); 3) a project for the reconstruction of the residential premises being rebuilt, prepared and executed in accordance with the established procedure; 4) technical passport of the residential premises being rebuilt; Thus, you need to contact the local government body (district administration) with an application for reconstruction of the apartment, attaching the above documents.
However, it should be borne in mind that in accordance with Art.
What must be observed during the transition?
The legislation imposes the following requirements for the premises where autonomous heating will be installed:
- Room area: from 4 m² with a ceiling height of 2.5 m.
- Door width: at least 80 cm.
- The room must have at least one window.
- Do not place a gas stove or heating appliances close to the boiler. A distance of at least 30 cm must be maintained between them.
- The boiler is installed on a load-bearing wall at least 1.5 m from the floor.
If individual heating is installed in an apartment with your own hands, then you need to strictly follow the instructions included with the boiler. But only gas service workers should connect the boiler.
Circuit mounting options
The main pipeline transporting the coolant can not only have different configurations, called wiring, but also be installed differently.
When choosing an installation option, you should take into account aesthetic, energy and economic feasibility.
The installation of the highway can be done in two ways: open or hidden:
- The open installation method is simpler and cheaper - the circuit is laid in accordance with the selected wiring diagram, and the only additional work required is to secure the pipes to prevent their deformation. In addition, in this case, the main line, in addition to transporting the coolant, also performs a heat transfer function, that is, it additionally heats the premises. At the same time, a pipeline left in sight spoils the interior, it is not protected from external damage and is itself a source of danger: you can get burned on it, flammable materials left nearby can ignite, and if the pipeline ruptures, not only damage to the external and internal decoration of the room, but also there is a risk of injury.
- Installing a pipeline in a hidden way involves laying pipes in channels made in the wall, floor, under the baseboard or behind the suspended ceiling. A simplified option is to make a false wall or use boxes and various pipe covers. Concealed installation ensures safety and looks more aesthetically pleasing.
We recommend that you read: How to select and install ventilation clamps for securing air ducts
Important! Pipes hidden from view increase energy costs. In addition, the labor costs for equipping such a highway and the consumption of materials increase, and when using false walls and overlays, the usable space of the premises decreases.
Installation process
Installation work to install the heating system is carried out in accordance with technological requirements and is carried out in several stages. Failure to comply with clear rules and requirements can cause incorrect operation of the equipment and lead to an emergency.
Marking
First of all, markings are applied in places where pipes will pass and radiators will be installed.
In order for the elements of the highway to be at the same level, as required by the technology, marks are placed using a level.
Radiator installation
At the next stage, the batteries are attached to their seats. To do this, holes for fasteners are drilled at the marked points with a hammer drill, which need to be secured with dowels.
Radiators are hung on the installed fasteners, and fittings are screwed to them.
Pipe laying
Then they begin to pull the pipes. Their assembly begins from the beginning of the wiring and, accordingly, the return. Using a soldering iron, fittings are welded to the edges of the pipes that will connect the line to the heating boiler. The soldering process consists of stripping the edges of the pipes from foil and inserting them into the nozzle of a heated soldering iron; in parallel, the fitting is heated in the same way to the desired temperature (usually 260 °C).
Next, the parts are joined with hot edges in a straight line and pressed tightly - this forms a homogeneous permanent connection. Similarly, the edges of the contour parts are connected along the entire perimeter of the apartment. To avoid deformation of the pipes, they are fixed to the wall with fasteners every 65–70 cm.
At the junction of radiators with plastic elements of the heating system, corner valves are welded. The system is ready for connection to a gas boiler, the installation and connection of which is best left to qualified specialists due to the complexity of the work and increased safety measures for its implementation.