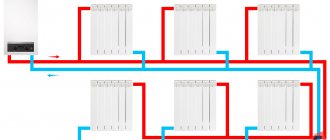
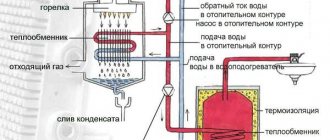
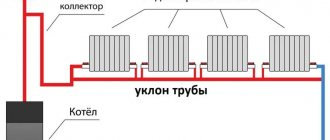
Even before designing water heating, a decision must be made on the material for the pipes. Currently, in Russia, preference is given to polymer pipes, less often - metal-plastic, and even less often - stainless steel. Abroad, copper pipes are most often used for heating. They are often used for wiring water systems in private homes. Many years of experience have shown that copper analogues have the best ratio in terms of reliability/practicality.
The main advantages of using copper pipes:
Durability of course . Copper pipes are not subject to corrosion in natural environments, technical characteristics have remained unchanged for decades. The surface of the inner walls remains smooth , which prevents the formation of deposits, and the outer walls, as a rule, do not require additional protection. The copper pipeline has been in use without repair or replacement for almost as long as the house itself. Durability and heat resistance. Copper is absolutely impermeable to other substances, including oxygen, which is very important to avoid corrosion of heating system elements. High thermal conductivity . The heat transfer coefficient of copper ensures rapid heating of the room and efficient use of the coolant at the highest possible level. Thanks to this, heat transfer is maximized, the efficiency of the heating system increases, and, accordingly, energy consumption decreases. An insignificant coefficient of thermal linear elongation (expansion) is 0.1% of the length when heated from 20°C to 90°C, that is, only 5 mm for a pipe 5 meters long. The “defrosting” of the system is not scary. Due to the strength and ductility of copper, a pipe made from it can withstand several coolant freezes (up to 3 for pipes made of hard grades of copper and up to 6 for soft ones) without destructive consequences for the pipeline. Chlorine, almost always contained in the water of heating and water supply systems, contributes to the formation of a layer of patina on the inner surface of the pipe - a thin, durable protective layer that provides a significant extension of the service life of the copper pipeline.
The main disadvantages of using copper pipes:
Incompatibility with other materials. If there are aluminum elements in the system, active electrochemical reactions begin. When directly connected to products made from other metals, destruction occurs quite quickly. To improve the situation, you can use brass adapters and fittings. But it is better not to combine aluminum and copper in one system - a reaction is possible in which a large amount of gases is released and, in the absence of gas release valves, the system can simply rupture. In an acidic environment, copper begins to deteriorate. Therefore, in the heating system you need to use a coolant with a neutral PH or slightly alkaline. If there are solid particles in the coolant, abrasion occurs quickly , since it is a soft and plastic material. Therefore, a mechanical filter is needed to remove abrasive particles from the environment. Isolation from stray currents is required. Copper is an excellent conductor of electric current, therefore a grounding loop and the presence of dielectric spacers in the system are required. Difficulty of installation work. Requires special equipment and qualified personnel. Copper pipes are afraid of contact with concrete (oxidize). The rate of destruction depends on the composition of the wall, but in any case it is better to lay the pipe in a PVC sheath.
Connections of copper heating pipes are made in various ways: One-piece. By soldering, after connecting the joined parts using the socket method or using fittings, as well as through press fittings using a special tool.; Detachable. With compression fittings and with threads (thread on one end of the fitting only). Instead of copper, bronze or brass fittings can be used. To install compression fittings, no special equipment is required: the pipe is inserted into the corresponding groove until it stops, and then tightened using a nut, pressing the pipe material against the fitting body. For a tight fit, you may need two keys - tighten until completely sealed. This is all the required equipment. But the specificity of crimp connections is such that constant monitoring of tightness is required: periodically they begin to “drip”. Therefore, such connections cannot be walled into walls. Installation of press fittings using special press machines. They themselves are not cheap, and neither is their rental. But the connection turns out to be tight and reliable, but inseparable.
Differences between copper pipelines for heating
Copper has a whole range of positive qualities that make it stand out from other materials. If the construction project allows the use of such expensive elements, then for the internal wiring of the heating system you should purchase a set of copper pipes and fittings in the quantity included in the estimate.
Pros of copper pipelines:
- the ability of metal to expand makes it easy to withstand high temperatures of the coolant, sudden temperature changes and even freezing of water;
- for the same reason, copper perfectly withstands pressure drops in the network, as well as possible water hammer;
- the reddish metal is resistant to hard water containing foreign impurities - lime, chlorine, etc.;
- the material does not have ideal smoothness of the inner walls, however, the low degree of roughness protects against the formation of limescale and creates little resistance to the movement of the coolant;
- copper is known for resisting the development of pathogenic bacteria and mold formation;
- the combination of strength and softness allows you to create pipelines of various designs;
- in some cases, heating wiring serves a decorative function, although safer copper cold water or gas pipeline circuits are recommended for room decoration.
To prevent foreign inclusions from depositing on the pipes and reducing functionality, special requirements are imposed on the coolant: the water must be clean and filtered.
But copper pipes also have their disadvantages, the main one of which is high cost. If we take for comparison two meter-long pipes with a diameter of 26 mm made of metal-plastic and copper, then the first will cost 147 rubles, and the second – 486 rubles. It turns out that copper wiring will be more than 3 times more expensive.
When using metal pipes to install heating circuits, one should not forget that they can heat up to 70-80 ° C, thereby posing a threat to the health of residents
Copper is selective in relation to other metals, so fittings should be selected carefully. Aluminum, duralumin or steel parts cause an electrochemical reaction and rapid corrosion.
Therefore, they usually use either “native” copper connecting elements, or brass, bronze, chrome-plated or nickel-plated. Tin or PIC solder is used only during the soldering process.
Labeling and cost
Copper pipes are available in two types: soft and hard. Solid ones are often used for heating. Release form - linear sections of 2-5 m long or coils in which sections of 5-10 m are twisted.
Dimensions . The outer diameter is indicated in millimeters (usually domestically produced or from the CIS countries) or inches (imported), and the wall thickness is indicated through a fraction or “x”: 22x1 mm (22/1mm) - outer diameter 22mm, wall thickness 1mm, which means inner diameter , according to which heating systems are designed, will be 21mm (22-1=21). For wiring a household heating system, a wall thickness of 0.8-1 mm is sufficient.
In order not to make a mistake with the choice of diameter when installing individual heating, it is easier to “dance” from the boiler outlet. This is the diameter your pipes will be before the first branch. If the system is small, the entire wiring can be done with one pipe, but if it is large enough, you need to follow the rule: after each branch, use a pipe with a diameter that is one step smaller on the dimensional grid. The branch to the heating device (radiator or heated towel rail) also has a diameter that is one step smaller. For example, 24mm comes out of the boiler, at the first branch two branches are separated, which go with 22mm pipes, and 20mm goes from it to the radiators. The “return” is assembled in the same way, but from smaller to larger sizes. If a large area of several floors will be heated, a professional thermal engineering calculation is desirable.
The fittings coming out of the boiler are usually either copper or brass, but in each case, check and remember that other materials cannot be directly connected to copper. In order to avoid a chemical reaction, you will have to use brass or bronze fittings or adapters.
annealed and unannealed pipes . Unannealed pipes have a large margin of safety: they can withstand pressure up to 450 MPa, but do not bend very well: they can only stretch by 6%. To change their characteristics, they are heated to high temperatures and then cooled. The process is called annealing, and the products that come out after it are annealed. The safety factor has become smaller - up to 22 MPa, but the elasticity has increased: the material can stretch by 50-60%. The material has also become more resistant to temperature changes, tolerates ultraviolet radiation without problems and is almost insensitive to high humidity. That’s why annealed copper is used not only in heating, but also in car engines and drives.
Diameter
Previously, it was indicated in inches, but in the latest version of GOST 617 of 2006, the dimensions are given in millimeters. The new document specifies more than 70 standard sizes for outer diameters from 3 to 350 mm only for cold-deformed copper pipes. However, foreign and some Russian manufacturers still mark their products in inches.
To characterize a pipe, the nominal, external, or internal diameter can be indicated. In practice, when selecting connecting elements, they use the concept of conditional passage, meaning the size of the internal clearance. Domestic manufacturers indicate it in millimeters, while foreign manufacturers indicate it in inches.
The throughput of pipelines is calculated based on the internal diameter, and classification is made based on the external size. The nominal diameter is a value approximately equal to the nominal diameter, but with an indication of the exact value.
When converting units of measurement, it should be taken into account that the internal cross-section of an inch pipe (1″) is 33.5 mm, although in the metric system this value is 25.4 mm. The discrepancy is due to the fact that in the document it is indicated by the nominal diameter, and the outer size of imported products is in inches. Therefore, a 1″ pipe inside can be from 25.5 to 27.1 mm. To convert the cross-sectional value from one system to another, use the table:
| Inches | External diameter, mm | Conditional bore, mm |
| 1/4 | 13,5 | 8 |
| 3/8 | 17 | 10 |
| 1/2 | 21,3 | 15 |
| 3/4 | 26,8 | 20 |
| 1 | 33,5 | 25 |
| 1 1/4 | 42,3 | 32 |
| 1 1/2 | 48 | 40 |
| 2 | 60 | 50 |
| 2 1/2 | 75 | 70 |
| 3 | 85,5 | 80 |
| 3 1/2 | 101,3 | 90 |
| 4 | 114 | 100 |
| 5 | 140 | 125 |
When converting inches to millimeters and vice versa, an error is obtained that should be taken into account when choosing pipes of the required diameter. The result is rounded up. Frequently encountered data is shown in the table:
| Inches | Millimeters |
| 1/2 | 20 |
| 1 | 25 |
| 1 1/4 | 32 |
| 1 1/2 | 40 |
| 2 | 50 |
| 2 1/2 | 65 |
| 3 | 89 |
| 4 | 100 |
Criterias of choice
Copper models, due to their high cost, must be carefully selected.
In order not to make a mistake, you need to get acquainted with the main selection criteria:
- Compliance with terms of use. The main advantage of the products is their versatility. Suitable for both plumbing and heating systems, because they are immune to constant temperature changes and high pressure. They can withstand loads up to 40 atmospheres and temperatures up to 500 degrees Celsius. They are resistant to ultraviolet radiation and have a low expansion coefficient (7 times less than polymer ones). Also, thanks to the active bactericidal properties of copper, it is absolutely safe for humans. But it is worth paying attention to the fact that copper reacts poorly to chlorine, so interaction with it will quickly render the pipes unusable.
- Cost of material and installation. The cost of copper is several times higher than its analogues (about 4 times higher than the price of plastic). But if we take into account all the work associated with the installation and additional elements, then the final cost of the work is no higher than that of metal-plastic. A press fitting for plastic is much more expensive than a solder fitting for copper. Consequently, the final installation cost directly depends on the footage and the number of fasteners.
- Life time. The trouble-free service life of a copper pipeline is 50 years or more, which is a very good indicator.
- Ease of installation. Pipeline installation takes place in several stages: preparation of the material, its processing and installation. The process itself takes a long time, because it is necessary to cut the pipes, bend them using a pipe bender, and also carry out complete installation of all elements. In the end, everything must be connected using fittings (soldering and crimping).
You should not combine copper with galvanized steel, because due to electrolytic processes the copper will simply be destroyed.
Advantages
Advantages:
- They can easily withstand heating of several hundred degrees (only at a temperature of 6000 degrees does “annealing” occur, and the pipe begins to lose its strength, acquiring plasticity).
- Capable of withstanding pressure up to 30 atmospheres or more.
- Due to their plasticity, they do not collapse if the water freezes inside.
- Copper has anti-corrosion properties and also does not react to ultraviolet radiation and active chemicals, which increases the service life of the pipe to 50 years or more.
- Do not allow diffusion of air into the coolant through the walls.
- Copper can easily be used at the outlet of a heat generator, because, compared to polymers, it has a low coefficient of thermal expansion (maximum 1.5 mm per linear meter at 900 degrees).
- The internal surface has less roughness compared to steel (but not polymer), which significantly reduces the hydraulic resistance in the system, so less powerful pumps can be used. Due to the absence of roughness, unnecessary deposits do not accumulate inside the pipe.
- Due to the thin walls and fittings, the flow area at the joints remains unchanged, so the hydraulic characteristics of the pipeline do not deteriorate. The entire system is light and compact. Only the outer diameter of the internal section is much larger than that of steel or polymer.
- Copper is safe for humans. It has mild antibacterial properties.
- This is a beautiful material that will not spoil the appearance of the room.
Pipe joining methods
According to docking technology, they are considered universal. Any of several connection methods will do, which is a definite plus.
Depending on your goals, you can choose:
- welding;
- mechanical assembly (pressing, compression connection, clamping with self-locking fittings);
- soldering (hard or soft solder).
For welding, a diameter of 100 mm with a wall thickness of more than 1.5 mm is suitable. Mechanical assembly is only suitable for open areas. If the site is hidden in monoliths or in building structures, then such fittings will be expensive. Domestic heating systems typically use soft soldering. It requires special capillary fittings to operate.
Flaws
Minuses:
- The highest cost among analogues.
- The assembly technique is much more complex than, for example, soldering polypropylene.
- Due to their high thermal conductivity, it is recommended that such pipes be laid in insulating sleeves (foamed), as this will allow heat to be delivered to heating devices with minimal losses.
Do-it-yourself copper pipe soldering technology
Before you start soldering, you need to briefly familiarize yourself with the theory so that the process is easier and clearer. In everyday life, when installing plumbing and heating systems in apartments, soft soldering is used, in which the contact points are heated to 250-300 degrees, which allows the soft solder (tin) to melt. But, despite the apparent ease, such a temperature is dangerous for copper, so everything must be done very carefully and correctly.
Preparation for capillary soldering:
- Cut the pipe to the required size.
- We chamfer the end of the workpiece (this manipulation will reduce the hydraulic resistance at the joint).
- We clean the outer surface of the pipe and the inner surface of the fitting with an abrasive sponge. This will get rid of the oxide film.
- We distribute flux paste over the entire contact area, which will provide soft solder. To make the solder hard, you do not need to use paste.
- With a slight twist, we put the fitting on the pipe until it stops.
- Remove the flux paste from the work surface with a rag.
You can start soldering.
Low temperature soldering of copper pipe:
- We heat the joint until the flux paste begins to melt. To do this, move the burner nozzle smoothly and evenly around the neck.
- After the flux has heated up, apply solder to the entire surface of the connecting seam. We do not touch the solder wire with the burner fire, since the tin needs to melt not from direct contact with the fire, but from the high temperature of the copper product.
- The melting and soldering process is complete. We are waiting for the product to cool completely. The cooling process cannot be accelerated - everything must cool naturally without improvised means.
- At the end of the work, we remove all the flux paste from the part, because it destroys the protective layer of copper products.
Conclusion
Using the information presented above, you can quite easily determine the diameter in mm of a 1 2 inch copper pipe, calculate the specific gravity of such a product, and understand whether it is suitable for the task facing us. However, over time, the skill will appear, and you simply won’t have to do the calculations.
And in order for this skill to develop faster, we recommend that you apply the acquired knowledge in practice more often, and carefully study all the available additional information, first of all, the video in this article.
Did you like the article? Subscribe to our Yandex.Zen channel
How to paint copper pipes
After installation work, the pipeline can be painted to protect it from corrosion and give it an aesthetic appearance. Let's consider which paint is suitable to achieve the above goals.
The following paints would be a good choice:
- polyurethane;
- alkyd;
- PF-115, 156, 167, 187, 223, 519;
- GF-0119.
Prices for PF-115
PF-115
Varnishes that work well include:
- a mixture of ethylene coating with aluminum powder (ratio 9:1);
- VL-51.
It is contraindicated to use oil paints, because they darken when exposed to high temperatures!
Before painting, the surface should be cleaned and coated with lead lead primer No. 81. When painting, you should take into account that the paint is not absorbed into copper, and, therefore, it is necessary to carefully shade the applied composition. It is best to spray paint with a spray can, because with its help you can get a high-quality surface.
Explanation of designations for pipe products
Basic characteristics are grouped in pipe markings.
Conditional indicators are prescribed according to a clearly defined scheme:
- Manufacturing technology : D – cold-deformed, G – pressing.
- Cross-section geometry : KR – round shape.
- Production accuracy indicator : N – within normal limits, P – increased accuracy regarding diameter/wall thickness, I – high accuracy regarding diameter, K – maximum accuracy regarding wall.
- Type of material by plasticity . In addition to the indicated abbreviations M/P/T (soft/semi-hard/hard pipe), the following product markings are used: L – soft with high elasticity, F – semi-hard with increased strength, H – hard with high strength.
- Dimensions – the value of the outer diameter/wall thickness.
- Length : ND and MD - unmeasured and measured pipelines, respectively, KD - rolled multiples of the measured one, BT - supplied in coils.
- Metal grade that determines the composition of the alloy.
- Special conditions : B - high accuracy in length, O - accuracy in curvature, P - regulated tensile standard, N - confirmed Vickers hardness, BU and BS - ordered and spiral winding of the coil, respectively.
Missing data is replaced by an "X".
Marking example: Pipe DKRPM 28/3 3000 M1 GOST 617-2006. The meaning of the designation is a round cold-deformed pipe with increased accuracy of wall dimensions (3 mm) and diameter (28 mm), soft, 3 m long, made of M1 alloy. The product complies with GOST standards
Features of copper solder fittings
One of the simplest and most durable connections of pipelines made of copper components is soldering.
Unlike polymer products, copper fittings, like pipes, are considered to have an eternal service life, they last for at least a century, do not deteriorate under the sun, do not melt from high temperatures and do not crack in the cold, therefore they are used where the tightness and strength of pipelines highways are subject to increased requirements.
The popularity of copper fittings is due to the special characteristics of the metal:
- copper is a known antiseptic that protects pipes from the development of bacteria and fungi;
- installation of communications consisting of copper components is simpler than connecting pipeline systems made of cast iron and steel;
- It is possible to damage copper pipes or fittings only under pressure of more than 200 atm, but such pressure simply cannot exist in communication systems.
Basic properties of copper
Copper is a versatile material that is used in various fields. When using heating pipes, copper stands out among other metals for the following properties:
1. Strength and long service life. Copper does not corrode. The service life of copper products is often about 100 years. 2. Protection against bacteria. In ancient times, copper was used to make drinking vessels precisely because it has bactericidal properties, prevents the proliferation of microbes, and is resistant to moisture and air. 3. Ability to withstand high and low temperatures and strong pressure.
How to connect pipes using capillary soldering?
Soldering takes more time, but the connections made are durable and tight. The best option for solving everyday problems is to use soft solder. The operating temperature does not exceed 250 °C.
The use of hard solder increases strength, but the work will require expensive equipment and special conditions, since the soldering process takes place at a temperature of more than 700 ° C.
With the help of soldering, permanent connections are created, which are made either using the socket method or using fittings. With socket technology, one end of the pipe must be expanded so that when the elements are joined, a gap of 0.2-0.3 mm wide is formed between their walls.
It is filled with solder, after which a sealed connection is created. But let’s take a closer look at soldering with fittings, the most popular among installers.
Materials and tools for work
It is necessary to prepare copper pipes and fittings, but not the first type that comes across, but those specially designed for soldering.
Connectors and adapters for soldering are characterized by a smooth surface and the absence of additional grooves, nuts, rings, etc. They can have a straight, angular, cross shape - depending on the purpose
Tools for performing the work:
- gas burner – propane is sufficient;
- pipe expander (calibrator);
- pipe cutter, since metal scissors deform the shape of the pipe;
- chamfer;
- equipment for cleaning and polishing (fine sandpaper, brushes, rags).
When choosing solder, it is better to choose the option with a tin base. In addition to tin, the solder may contain bismuth or silver. This type is good because its melting point is much lower than that of copper products.
You can read more about solders for soldering copper pipes in this material.
During the soldering process, the solder will take on a liquid state and will be able to hermetically fill the connection gap, while the copper elements will not react to high temperatures.
In addition to solder, flux is required. This is a kind of lubricant for parts of elements that need to be joined. Flux is carefully applied with a brush to the surface of pipes and fittings.
For ease of installation work, you can use special fittings for low-temperature soldering. They differ in that at the ends they have a narrow groove filled with solder.
Low-temperature (soft) soldering is typical for household work, while high-temperature (hard) soldering is used in production. The rigid type is also used when connecting pipes of air conditioning systems and refrigeration units.
Description of the soldering process
Copper is a malleable material, it is not difficult to work with it, but if you have no experience, it is better to first practice on unnecessary sections of pipes.
Image galleryPhoto from Using a pipe cutter, a special tool, we cut the elements. It is better to carry out operations directly during installation, in order to adjust the length if necessary. Insert the bevel cutter into the pipe and rotate it until we remove the edge that appeared during the cutting process. This is necessary so that the inside of the pipe does not narrow. First, using the same bevel remover, but its other side, and then with fine sandpaper, we process the outside of the pipe so that there are no scratches and the copper shines. To increase the efficiency of soldering, it is necessary to thoroughly clean the second part - the corner, the adapter . A suitable tool is a screwdriver with an attachment made from a regular brush. An ordinary glue stationery brush is suitable for applying flux. We take the solution in small portions and distribute it in a thin layer over the surface of the pipe. Place the prepared, cleaned corner on the end of the pipe covered with flux. To make the connection tighter, screw the pipe into the corner with light movements. Before starting soldering, you need to remove excess flux or paste. An ordinary rag will be useful for this. When the surface is completely clean, for ease of work we fix the part in a vice. We take solder in one hand, a torch in the other and begin to carefully solder. After heating the pipe, we place the solder at one point, thanks to the capillary principle it will spread over the entire area. Step 1 – cutting the copper pipe into pieces of a given size. Step 2 – removing the edge with a bevel remover. Step 3 – preparing the outer wall for soldering. Step 4 – processing the inner surface of the corner. Step 5 – applying flux or paste on the end of the pipeStep 6 - twisting the end of the pipe into the cornerStep 7 - cleaning the joint with a ragStep 8 - soldering process with soft solder
Detachable and press connections
To make a press connection, you need a specialized tool - crimping pliers. They are available both manual and electric. After stripping the pipe and fitting, they are combined, pliers are applied to the joint from the outside and crimping is performed. The connection is considered permanent and quite reliable.
Detachable coupling is done following the example of metal-plastic pipes, since the principle of combining a brass fitting with a pipe is exactly the same. Accordingly, the cost of the connector is several times higher than that of a soldering fitting. But for installation you only need 2 wrenches. Details of the work are presented in the video:
Installation instructions using fittings
There are two types of compression fittings - the so-called compression and compression. They create completely different connections, so before starting work you need to decide what kind of connections you would like to see: permanent or conditionally detachable.
Press fittings are similar to solder fittings, but have shallow recesses at the edges with sealing gaskets. Using special press pliers, which have a set of nozzles for different diameters, crimping is carried out.
As a result, it creates a sealed, permanent connection that cannot be repaired, and in the event of an accident can only be replaced.
In the store you can see parts that are identical at first glance, but they differ in characteristics (composition, wall thickness, etc.). Heating fittings are marked with green markings
Pressing creates a strong, reliable connection of parts, while maintaining the geometry of the pipes and does not deform the connecting elements. There is a nuance of pressing “soft” copper products: before the operation, a support sleeve is inserted into the pipe, which resists deformation of the pliable material
The pressing process is simple and does not take much time. The tools required are a standard set for cutting and processing pipes, as well as press pliers with the required attachment.
Pressing is considered a reliable method. If you plan to thermally insulate copper pipes, you can use insulating tubes, which are easy to put on even on curved structures. After pressing, the finished heating network can be masked in grooves, covered with decorative cladding and filled with screed.
The second type of fittings is compression. They differ in design and installation process.
A compression fitting for copper pipes is a prefabricated device consisting of three parts: a brass or copper body, a ferrule, also called a collet, and a nut.
The crimping procedure is as follows:
- a nut is loosely placed on the prepared end of the pipe;
- then the collet is put on;
- last of all, the fitting body is put on until it stops;
- the nut is screwed manually along the thread, while simultaneously pressing the split ring;
- The connection is tightened with an adjustable or sized wrench.
During the compression crimping process, the cutting ring tightly grips the pipe, creating a strong and airtight connection. The nut may become loose over time, so pipelines with this type of installation must be regularly maintained.
The connections are conditionally detachable, since they can be disassembled, however, if necessary, the fragment with the clamped ring will have to be removed and a new fitting installed.
Results
As you can see, copper pipes for heating are a good, but not ideal option. This material has many advantages, but no less disadvantages. Corrosion may occur - this may be the result of an incorrectly selected coolant composition, high pressure or water hammer. Moreover, it is worth considering that the service life of copper heating systems directly depends on proper design and installation, that is, even if high-quality components are used, but they are soldered or laid with “crooked” hands, there will be no long-term operation. And today there are very few specialists who competently work with copper, and their services (in addition to the materials) are also very expensive. Perhaps this is why they rarely install it today, especially since there is a good replacement - polypropylene (reinforced) or metal-plastic.
Finally, a few video lessons with useful information. This video has a little about the types of solders.
And this video material talks about how copper fittings are made. Interesting…
Reviews and operating experience
Some people consider copper pipes an excellent solution, while others do not accept them. But, in fact, this is typical for any technology and material. The only thing that people pay attention to and what is worth listening to is the fact that in an acidic environment, copper begins to deteriorate. Therefore, fill the system with either coolant with a neutral PH or slightly alkaline. It is also not recommended to use steel, aluminum or cast iron radiators. It is imperative to protect the system from stray currents (grounding and dielectric gaskets are required), otherwise chemical or electrochemical destruction begins. But in central heating systems you will not completely get rid of destruction: the coolant in them is saturated with iron, and if solid particles can be retained by a filter, then there is no escape from those dissolved in it.
Another piece of advice from an experienced installer: copper is very sensitive to contact with concrete (it oxidizes). The rate of destruction depends on the composition of the wall, but in any case it is better to lay the pipe in a PVC sheath or any insulator with similar characteristics.
Another tip from the master, but this already concerns soldering: it is important not to overdo it. Firstly, from an overabundance of diligence, you can weld the entire lumen (if a pipe of small diameter is especially important), secondly, when the soft solder overheats, the paste is overheated, which is why it cokes, which leads to the formation of fistulas, and thirdly , do not overdo it with the amount of solder. If you have no experience, practice welding on small pieces of pipe: you can check both the clearance and tightness of the connection. And after gaining at least some experience, you can begin welding the system.
Installation technologies and rules
First, let's look at the general rules regarding the installation of copper pipelines. As you know, metal is an excellent conductor. To provide protection from stray currents, as well as reduce the risk of corrosion, you can use products in a polymer shell.
Image gallery
Photo from
Possibility of using lead solder
Connecting copper and aluminum parts
Use of brass fittings and adapters
Which radiators are best for copper systems?
In private practice it is quite rare, but in industry the assembly of pipelines made of steel and copper is still used. In this case, it is recommended to use steel for risers, and copper for wiring, that is, steel products should be in the first position in terms of coolant current. Magnesium connectors are required.
There are several ways to connect products, the choice of each of them depends on the specific situation:
- capillary soldering with solder;
- compression fittings;
- pressed fittings;
- threaded installation.
The last method is practically not used because it has lost its relevance. Soldering and crimping differ in the degree of labor intensity, execution technique, and the presence of different tools, but are equally in demand. Let's look at three popular pipeline construction technologies.
Installation of copper wiring
When installing copper wiring, two connection methods are used: welding and using fittings. Fittings are used collapsible and pressed. The former are easy to assemble, requiring only wrenches. To connect with press fittings, a special pressing machine is required.
Pipe benders are used to obtain high-quality bends and profiles. and mechanized models are available for sale They practically do not change the internal profile, the nominal diameter does not change.
You can make your own copper heating using compression fittings. The principle is simple. The pipe is combined with the fitting and the nut is fixed. This method may leak after a while, so this wiring is done externally.
Soldering is considered the most reliable way to fasten copper products. The connection can be made end-to-end, but it is safer to flare one side. Place the second section in it with a gas torch, heat the solder and go around it in a circle. To make the solder stick to the surface more firmly, it is treated with flux.
Lead-tin alloys can be used as solder. Their melting point is below 200 °C. After hot work, I cool the joint . In air, cooling takes a long time. The pipe can be placed in a container of water.
Tools used for installing copper pipes:
- pipe cutter or hacksaw;
- file for deburring;
- calibrator;
- pipe bender;
- wrench or gas wrench;
- gas-burner.
Is it worth buying copper products for laying water pipes?
It is impossible to immediately answer why in our country plastic pipes prevail over copper ones. It is quite obvious that the latter are somewhat more expensive than their plastic or steel counterparts, but their price compared to the overall repair picture is a drop in the bucket. Of course, soldering copper products is naturally not an easy task, but in the case of steel materials, the same problems await you. Not everyone knows that copper is a highly toxic material, but only in some cases.
Today, copper pipes have much more serious competitors than rusting steel materials. Modern products made of metal-plastic or polypropylene have a cost that is much lower than the cost of copper products. Moreover, they are easy to install even by an unknowing person in a short time, and also have a service life that is at least no less than that of a copper water supply system.