- The correct roofing pie diagram
- Base Layers
- Vapor barrier layer
- Thermal insulation
- Ventilation
- Waterproofing layer
Much has been said about the importance of such a structural element of a building as the roof. Here are the features of the architectural appearance, and protection from atmospheric influences, and the durability of the house. Modern approaches to the design of the attic space make it possible to make maximum use of its volume. This makes it possible to save money, but requires, one might say, a scrupulous approach, since the design of a residential attic involves the inclusion of thermal insulation, protective films, etc.
The roof in section has a layered structure. This is the so-called roofing pie, each layer in which performs a specific function, but it is very important that they are placed in the correct order. Any mistake made during their installation can negatively affect the performance characteristics of the roof and its durability.
What is a roofing cake for an attic roof?
Structurally, all roofs are divided into two main types:
- “cold” - do not involve installation in the attic of residential premises, the roofing cake does not include thermal insulation;
- “warm” - immediately or subsequently focused on exploiting the space under the attic as residential or utility.
Regardless of the design and architecture, for every house the roof is one of the most important functional protective and decorative elements. It protects the building from external atmospheric factors and various mechanical influences, and also prevents the outflow of heat from the building during the cold season. Heat always tends upward, and if it is not contained, heat loss through the roof alone can reach 35%, and this is a significant overexpenditure of energy resources and operating funds. To minimize heat loss, and, consequently, costs, specialized thermal insulation materials must be used during construction or reconstruction. The difference is that in the case of a cold attic, the floor is insulated, and when arranging a residential attic, both the floor and the roof slopes are insulated. When insulating the floor of a cold attic, the maximum possible layer is laid in it to prevent heat loss. In the ceiling of a warm attic, a smaller layer of thermal insulation is laid, mainly to increase acoustic comfort, while the main “line of defense” is precisely in the slopes. The attic roofing pie consists of several functional layers.
- Vapor barrier - prevents steam released as a result of vital activity from entering subsequent layers of the roof. Even impermeable films with taped joints do not guarantee absolute tightness and retain the bulk of fumes, but some amount still gets inside.
- Thermal insulation is the main functional layer formed from a specialized thermal insulation material. It prevents the outflow of warm air in cold times, overheating of the under-roof space in the hot season, and also provides acoustic comfort, which is no less important for residential premises. The thickness of the insulation is selected based on the standards for thermal resistance of enclosing structures for a specific region of residence and type of thermal insulation. For the bulk of the regions and most materials, a layer of 200 mm is considered the minimum, for the southern regions - from 150 mm.
- Waterproofing – protective membranes laid on top of insulation under the final roofing covering are also called windproof membranes. Vapor-permeable membranes prevent moisture from entering from outside, prevent convective heat transfer (weathering) and release steam from the insulation. It is removed by ventilation of the under-roof space. The use of impermeable films as waterproofing and wind protection is gradually disappearing, since their use requires the construction of two ventilation gaps: between the insulation and the film, and between the film and the roofing. Whereas the membranes are laid directly on the insulation without a gap, which simplifies installation.
The key to the energy efficiency of the design and long years of operation is dry insulation, since when moistened it does not lose its thermal insulation properties. The insulation is maintained in its original condition thanks to a vapor barrier that traps the bulk of vapors from the inside and waterproofing that prevents it from getting wet from the outside.
Specifics of joint formation
The roofing components (the so-called pictures) are connected to each other by means of seams. Seam fastenings are seams that occur when connecting metal roofing panels. The seams can be single, double, standing (they are the most reliable, they are used to fix side and vertical roofing panels), lying - they are designed for standard horizontal mating of sheets.
Seam roofing made of zinc-titanium
Seam roofing on a house
Snap-on types of folds help to significantly reduce the time allocated for installation work; moreover, they can be attached to both the insulation and the sheathing. Such roof arrangement options are applicable for commercial and public buildings, dachas and country cottages.
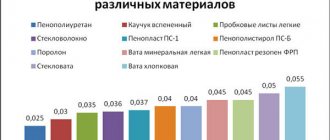
Stone wool for attic insulation
One of the most common insulation materials in pitched roofs is stone wool, as the optimal material in terms of performance and cost. It has such properties as:
- low thermal conductivity;
- biostability;
- fire resistance;
- non-flammability;
- sound absorption;
- minimal hygroscopicity;
- durability;
- practicality (and ease of installation, and preservation of the original parameters for the entire service life).
When vapor passes through the fibers, the stone wool is not moistened, its thermal conductivity and volume remain unchanged, that is, during operation the insulation remains dry and effective and does not lose its properties.
ra093FORUMHOUSE Member
Please give advice on how best to insulate the attic of a 10x10 m timber house, Middle Urals. The pie is now standard: flexible tiles, ventilation gap 50 mm, membrane, rafters 200x50 mm. The attic is quite low, I don’t want to lower the ceiling too much.
I see options:
- 200 mm stone wool. Then straight finishing. The rafters look like cold bridges. But how much heat do they take away, considering that 200 mm, and my house itself is made of 190 mm timber, essentially like a cold bridge.
- 50 mm gap between the wool and the membrane, 150 mm of wool, there is already a 30 mm pier plate on the rafters. It turns out more expensive, but it seems to me it should be warmer than 200 mm of wool. The downside is that the ceiling will be lowered a little more.
What other options are there that are not too expensive? Of course, I would like to blow out everything with 150-200 polyurethane foam or lay it all out with slabs, but the price turns out to be very high. Can he handle the entire feast with 100 mm slabs? Judging by the advertised thermal conductivity, it will be like 200 mm of wool.
Anatoly Zemlyanko Technical specialist of ROCKWOOL company
Definitely the first option. 200 mm stone wool, which is the most effective vapor-permeable and breathable material. All other materials will act as a vapor barrier, so it is not advisable to mix these insulation materials. Logs are not cold bridges, since the thermal conductivity coefficient of wood is quite low, which indicates its effectiveness.
Special integrated solutions
For special tasks today, a complete roofing system is used. For example, this is offered by Astron. It is made of steel panels with aluminum-zinc coating and special fixing clips. Such panels have a thickness of 0.66 to 0.75 mm and a width of 600 mm.
The ribs have a height of 50 mm, i.e. quite high and provide additional rigidity, making it possible to install purlins in increments of 1.5 m.
At the same time, the fastening system is movable, which allows the panels to move slightly during thermal expansion. This technical point allows you to avoid deformation of the paintings. Will the same metal tiles or soft roofing be movable? That's another question.
Only metal and ceramic tiles from some manufacturers can boast of such comprehensive solutions.
Insulation technology for pitched roofs
For the most part, when the attic floor is initially planned as a residential floor, insulation is carried out as follows.
Anatoly Zemyanko Technical Specialist
When the insulation is installed before installing the waterproofing layer and roofing - the most risky, but also the most popular installation procedure in Russia.
Risky, because it is not always possible to install insulation and cover it with waterproofing in one day, and if the weather turns bad and it rains, both the rafters and the thermal insulation will get wet, which is unacceptable when insulating the roof; the thermal insulation must be dry. But even when insulating an already closed circuit, mistakes are often made. On the forum there is approximately an equal number of “What should I do?” questions asked after installing the roofing.
AGontarForumHouse Member
Help is needed. We have a country house with a 2-pitched roof (attic). On the roof (from outside to inside): corrugated metal sheet, roofing felt, sheathing, rafters. The fact that it is necessary to disassemble and make a counter-lattice is understandable, but the house is not for permanent residence, but rather a weekend cottage (spring, summer, autumn) and a couple of times in the winter, so I want to minimize costs. I need advice on what can be done to prevent the roof from rotting.
Today I see 2 options:
- fill the corners of the rafters with sheathing with 50 mm slats and stretch the membrane, then insulation;
- stretch the membrane from the inside along the rafters (leaving the thickness of the rafters as a ventilation gap), and somehow attach the insulation on top.
Anatoly Zemyanko Technical Specialist
Mount bars between the rafters to create a ventilated gap, then install a windproof membrane with a snake, and lay insulation in the free space. On top of the entire structure, make a lathing with a vapor barrier and a final coating.
kolkapFORUMHOUSE Member
Colleagues have a question, I want to make an attic, the ceiling and rafters are 50x200 mm timber, sheathing and temporary roofing material have been made, I want to cover it with metal tiles and insulate it. How to properly insulate and do it wisely?
Anatoly Zemyanko Technical Specialist
Standard roof:
- – metal tiles;
- – sheathing;
- – counter-lattice;
- – sealing tape;
- – hydro-windproof membrane;
- – self-adhesive tape;
- – logs;
- – stone wool insulation;
- – vapor barrier;
- – self-adhesive tape;
- – sheathing;
- – finishing coating.
“Classical” technology for insulating a pitched roof - in a training video.
Interior layout of a house with a seam roof in the village of Zeleny Bor
Conventionally, we divided the house into several blocks. The first of them can be called economic and technical. It is located right at the entrance and consists of a vestibule, a hall, a large common dressing room, a laundry room equipped with the latest technology and a boiler room with an entrance from the street - we have already mentioned it earlier.
The second block is intended for family leisure and receiving guests. It has a spacious and bright living room with those same almost four-meter ceilings, as well as a functional kitchen-dining room, from which you can access the terrace through glass sliding doors.
The third block is a place for relaxation and solitude. In this area we placed the master bedroom and two children's rooms. Each room has its own dressing room, bathroom, as well as a corridor - one for everyone.
That's probably all we wanted to share with you today. A photo of a house with a seam roof, into the design of which we invested all our knowledge, experience, skills and imagination, will tell you more. Watch, rate, enjoy!
Views from different sides (photos below):
If you liked the project, mark it on social networks.
Efficiency of single-layer insulation
As for the method of laying insulation, for a long time there was an opinion that cross-insulation is more effective.
id1932564FORUMHOUSE Member
Tell me what to do: the roof is attic, the insulation is 200 mm in size for the rafters, I bought rolled mineral wool insulation for the roof. There is an idea to add 50 mm cross-insulation from the inside. The builders did not approve. Does this make sense? Tatarstan region.
Anatoly Zemyanko Technical Specialist
It is better to insulate in one layer than in several. Increasing the speed of work by reducing the number of technological operations, reducing waste due to cutting layers when performing run-ups.
Six fragments of walls with stone wool slabs were tested in the climatic chamber of NIIMosstroy:
- In three layers and in one layer - the plates are joined without a gap (good installation).
- Three layers and one layer - slabs with a gap of 2 mm (normal installation).
- In three layers and in one layer - a gap of 5 m (everything is bad - it needs to be redone).
A seam width of up to 2 mm is acceptable in most building structures and appears in the standards. This is due to the fact that under climatic conditions, convection at a seam of such width is not intense. Therefore, it is not detected by a thermal imager as a cold bridge. Previously, there were studies on the uniformity of two-layer and single-layer insulation while maintaining the width of the seam.
The research revealed the following:
- Single-layer and multi-layer insulation used in external enclosing structures are equivalent in their effectiveness.
- A gap of 2 mm between adjacent insulation boards has virtually no effect on heat transfer resistance.
Anatoly Zemyanko Technical Specialist
Advantages of minimizing thermal insulation layers (2x100 mm and 1x150 mm are better than 4x50 mm and 3x50 mm):
- reduction of labor costs during the preparation and installation of insulation;
- reduction of material scraps during work;
- insulation with a thickness of 100 mm or more is less prone to deflection than a thickness of 50 mm, due to which it is more securely held in the frame, which is important when installing on vertical and inclined surfaces;
- A single-layer solution is ultimately cheaper than insulation with two or more layers.
General recommendations for selection and installation
If a decision is made to use folding technology, the roof slope should not exceed 14°. If this indicator varies between 7-14°, it is advisable to arrange a solid base. The recommended type of seam here is a double seam, supplemented with silicone sealant.
The most convenient sheet length for installation is no more than 10 m. If the dimensions of the workpieces are larger, the installation procedure should be supplemented with floating clamps.
Seam roofing on a pitched roof
Seam roofing made of steel
When the key material is zinc-titanium, you need to carefully ensure that workers handle the coating as carefully as possible - do not scratch or throw sheets, only soft pencils and markers are suitable for marking. If deep scratches occur, there is a high risk of corrosion. For all manipulations with such products, you should stock up on special roofing tools: hammers, shaped and straight scissors, marking devices, a set of bending pliers.
Laying seam roofing
Seam roofing on a country house
The roof in question is installed either on a solid base or on a sheathing of 50x50 mm beams, in this case the pitch between them is 250 mm. If the last indicator is not strictly observed, this is fraught with deflection of the sheets, which, in turn, can cause weakening and deformation of the seams of the structure. Neglect of the rules causes corrosion and leaks.
Green seam roofing
Finally, homeowners purchasing roofing in rolls should ensure that the thickness of the layers is uniform. Regardless of the type of coating, before purchasing it, you must read the product certificate, which specifies all the technical characteristics of the sheets.
Signs of a “correct” pitched roof
High-quality materials, coupled with compliance with insulation technology, guarantee a long service life of the roof without “crying” walls in the attic, mold and mildew. A properly insulated pitched roof provides a comfortable microclimate in the attic without the need to increase the power of the boiler in winter or the air conditioner in summer. You can technically verify the effectiveness of roof insulation by examining it with a thermal imager. The device will show the absence or presence of zones through which owners “drown” the street. But even without equipment in winter, the main sign of mistakes made can be seen with the naked eye - “garlands” of icicles. On a roof where the insulation is done correctly, the snow lies in a uniform mass, without melting, and there is nowhere for icicles to come from.
Device
Ideally, the design of the roofing pie should consist of the following elements:
- interior decoration (direct ceiling lining);
- vapor barrier;
- thermal insulation (insulation);
- waterproofing;
- clearances for ventilation;
- anti-icing system;
- roof.
The roofing pie also includes decorative elements (vanes), gutters, drainage systems and other roof equipment. If everything is clear with the interior decoration (depending on the chosen interior), then we will deal with the insulating elements and other “layers”.
Conclusion
In order for a pitched roof to fulfill its purpose and reliably protect the house not only from external influences, but also from increased operating costs due to heat loss, it must be well insulated. In this case, living in the attic will be as comfortable as possible without overpayments, and the need for major repairs will not arise soon.
About single-layer insulation - in the previous material. Owners of wooden houses will find the article about insulating a timber house with stone wool useful. The video shows how to choose and lay stone wool correctly.
Subscribe to our Telegram channelExclusive posts every week
Waterproofing
The waterproofing layer of the roof protects the insulation from moisture that can get into it during a leak or due to condensation on the inside of the roof covering.
The simplest waterproofing is the same polyethylene or propylene film. But now waterproofing diffusion membranes are much more often used - materials that retain moisture that enters them from the outside, while freely allowing water vapor to pass through.
Membranes are the optimal waterproofing material when constructing a roofing pie. They help to avoid the effect of “locking” moisture inside the insulation, which can occur when using conventional film.
The fact is that it is impossible to completely avoid moisture inside the insulation. The vapor barrier, although minimal, allows water vapor to pass through. If the waterproofing layer of the roof is made from ordinary film, this moisture will leave the insulation with great difficulty, so more and more of it will accumulate every day. And the membrane will simply let water vapor pass through.
Flat roof frame on a wooden base
The frame of the described roofs is made of wooden beams laid like an interfloor ceiling. Full-size timber lumber or composite lumber (laminated veneer lumber) can be used. Often beams are made from boards with a section of 100x150 mm.
The beams are laid with support on the walls, similar to interfloor ceilings. If the building is wooden or frame, then the beams rest on the upper crown of logs or the upper frame. If it is brick or block, then on a pre-fixed Mauerlat. A timber with a cross section of 150x150 mm or 150x100 mm is usually used as a Mauerlat. It is mounted on the upper chord of the walls using anchors or studs. To protect the wooden Mauerlat from the wall material, 1-2 layers of waterproofing (roofing felt) are laid between them.
Cuts are made on the beams for the Mauerlat, they are laid and secured with metal corners or nails. The pitch between the beams is maintained at 50-120 mm (depending on the calculated load).
When installing beams, it is important to ensure a roof slope of 1-6°. Despite the fact that the roof is called flat, it is not absolutely horizontal. A slight slope is necessary to ensure that water moves towards the drain and thus prevents it from stagnating.
What tools will be needed for installation?
A professional roofer has a wide variety of tools in his suitcase. When installing a roof, you cannot do without a seam hammer, mallet, metal shears, mandrels, pliers, and various pliers. This entire impressive list will not allow you to begin the construction of a seam roof without special devices for forming seam seams:
- Manual machine for creating folded knots. In everyday life it is also called “frame” or “hapa”. With this device you can create a folded seam in two steps. It may seem like a manual process would be labor-intensive, but that's not entirely true. Moreover, such a device is indispensable when the roof has a large slope or a non-standard configuration.
- Semi-automatic device . Such a unit is fixed at the site of the planned seam and a metal cable is pulled along it. The machine leaves behind a double standing seam. If we compare it with the “hapa”, then undoubtedly this option has higher productivity. In addition, the “semi-automatic” is less harmful to the polymer coating of the metal.
- Electric machine . A modern device that saves the roofer time and effort, practically eliminating the human factor. The device is installed in the location of the planned unit, after which it is launched and monitored as it independently fastens the elements into a sealed double standing seam.
Types of flat roofs on beams
The following types of flat roofs can be built on wooden floors:
That is, all possible types - without restrictions.
An unused roof is a regular one, completed with a waterproofing topcoat. It is intended solely to protect the premises from environmental conditions and has no other purpose. It is forbidden to use it as a place of rest, move in large groups, or install terrace furniture and flowerpots. The covering of such a roof is designed for the fact that 1-2 people will periodically climb onto it, solely for maintenance of the structure.
A used roof is already more interesting and complex. In addition to its direct protective functions, such a roof plays the role of additional usable space for the homeowner. The design pie ends not with waterproofing (prone to damage), but with a protective covering - paving stones, decking, wooden flooring, paving slabs, turf layer, crushed stone or gravel.
Inversion roof is an inverted roof, a qualitatively different option. It can be either exploited or unexploited. Its peculiarity is the inverted order of placing layers in the pie. If in a conventional roof the waterproofing is laid on top of the insulation, then in an inversion roof the opposite is true. The waterproofing lies under the insulation, and the vapor barrier is completely excluded from the structure of the cake. Due to this, the waterproofing is protected from the street environment and its service life is increased.
However, under the influence of unfavorable street conditions, the insulation becomes insulated, so the choice of this type of insulation in inversion roofs is limited. Only EPS (extruded polystyrene foam) and nothing more! This material has virtually zero water absorption, high density and strength. On top of the EPS in inversion roofs is loaded with washed gravel, paving stones, paving slabs or a turf layer.
An interesting option for used roofs (including inversion ones) is green roofing . It can also be supported on wooden beams. The pie of such a roof ends with a soil layer on which plants are planted. There are other elements that are not used for other types of roofs: a drainage layer (gravel, expanded clay, crushed pumice or geomats), a filtration layer (geotextile).
Seam covering materials
The following types of metals are used for seam panels (also called paintings):
- Galvanized steel with polymer coating. Consists of cold-rolled steel sheet with a thickness of no more than 0.55 mm. It is galvanized on both sides, so roofing steel is impervious to rust and has good adhesion to other materials. This is a durable material that is not subject to peeling.
- Roofing aluminum. Aluminum is a durable and lightweight material with a plastic structure. Aluminum seam panels are available in a very wide range of colours.
- Copper grade M1. This durable and anti-corrosion coating has the unique property of changing its original appearance over time. At first it has a brown tint, after 2–3 years of use it turns dark chocolate, and after 10–15 years it becomes covered with a malachite-green patina.
- Titanium-zinc coating. Plastic material that looks great and lasts a very long time. The only drawback is the complexity of installation, which only professionals can do.
The choice of materials for seam panels is very wide. The price depends on the thickness and specific properties of a particular material. The service life is largely determined by the density of the rolled product, the implementation of a competent approach during installation, and also depends on the quality of the polymer coating on the surface.
For which buildings is a flat roof on beams suitable?
The main share of such roofs falls on private houses and cottages, whose owners value futuristic style, convenience and practicality. Also - for covering verandas, terraces, balconies, garages. As a rule, all these buildings are wooden or frame, requiring a lightweight roof structure. But this is not a mandatory rule. The wall material can be anything - brick, aerated concrete, foam concrete, etc. In this case, wooden beams often crash into the mauerlat - a wooden beam that runs along the perimeter of the walls and is connected to them using anchor bolts or studs.
Flat roofing is especially attractive to developers because its horizontal surface can be used as a usable area. Moreover, this is possible even for a roof with wooden beams at its base.
Of course, you shouldn’t use the freed up meters for a parking lot, swimming pool or tennis court. Still, such projects require a more monumental foundation. But wooden beams can easily support an open terrace, an observation deck, or a home greenhouse. The main thing is to make the calculation correctly and not skimp on the thickness of the lumber.