A foundation made of reinforced concrete slabs is considered one of the most economical options for forming the foundation of structures.
Its use has certain limitations caused by the shallow depth of burial and insufficient load-bearing capacity.
However, in a number of cases this option is considered as the most optimal design in terms of cost and reliability.
When choosing this type of foundation, you should proceed from the actual loads and soil conditions (see other types of foundation).
Slab foundation - what is it?
A monolithic slab for a house belongs to floating, non-buried foundations; it can also be shallow.
It got its name due to the fact that a reinforced concrete base is poured under the entire area of the house, forming a large slab. A prerequisite is the presence of a sand and gravel cushion, which redistributes the load from the house to the ground and serves as a damper during frost heaving. Often such a foundation is the only possible solution. For example, on unstable, loose soils or on clays with a large freezing depth.
The construction of a monolithic slab foundation is simple and reliable, but its production requires a large amount of reinforcement and large volumes of high-grade concrete (not lower than B30), because the entire area occupied by the building is reinforced and concreted, and with a margin for greater stability. That’s why such a foundation is considered expensive. In principle, this is true, but it must be considered. In some cases, its cost is lower than deep strip laying - due to less excavation work and less concrete.
The depth of the monolithic slab is determined depending on the weight of the house and the type of soil. With shallow depth on heaving soils in winter, the house along with the base can rise and fall. If the reinforcement and slab thickness are correctly calculated, this does not affect the integrity of the building. The plate compensates for all changes due to elastic force. In the spring, after the soil has melted, the house “sits” into place.
There are four types of slab foundations:
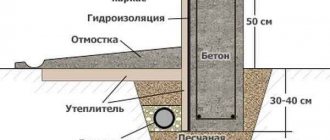
- Classical. A reinforced concrete slab is placed on a sand and gravel bed with or without insulation. The thickness of the concrete layer is 20-50 cm, depending on the soil and the mass of the building. The thickness of the layers of the cushion depends on the depth of the fertile layer - it must be completely removed. The resulting pit can be filled 2/3 with sand and gravel.
- Insulated Swedish stove (USH) with built-in heated floor. Firstly, it differs in that the slab formwork is permanent - made of L-shaped polystyrene foam blocks. This significantly reduces heating costs - heat loss is minimal. Also, heated floor pipes are laid on top of the insulation, reinforcement is laid on them (sometimes under them), and everything is filled with concrete, the thickness of the concrete layer is 10 cm. All communications, including water supply and sewerage, are laid at the stage of preparing the foundation - in a sand cushion. That is, after making the foundation, the heating system is ready and the engineering systems are connected. This approach allows you to speed up construction, but the foundation itself is expensive. This type of foundation requires competent engineering calculations and the same execution: you cannot make mistakes when calculating and laying communications, since alterations are impossible. Questions also arise regarding the repair of systems immured in the foundation. It is impossible, so they use expensive materials with a long warranty.
- Russian - a plate with stiffening ribs. To strengthen the structure for heavy houses and in difficult operating conditions (severe frost heaving), Russian scientists came up with the idea of making more massive stiffeners. They are usually installed under load-bearing walls. In this case, the complexity of the work increases - the stiffeners are installed separately, and the slab separately. But the bearing capacity of such a foundation is much higher, which makes it possible to reduce the thickness of the slab to 10-15 cm.
Advantages of insulating a slab base
Horizontal insulation of the slab
High-quality insulation of the monolithic foundation slab guarantees the durability of the building and long-term operation without the need for unplanned repair work. Particularly relevant is the insulation of the foundation slab under residential buildings, when it is possible to avoid significant heat loss on the first floors of the house.
Insulation of the foundation slab must be performed for the following reasons:
- Providing increased waterproofing of the foundation.
- Significant reduction in heat loss.
- Saving money on heating a residential building, real heat saving mode.
- Preventing the formation of condensation that can destroy the building structures.
- Improving living comfort.
- Stabilization of temperature in the interior of a residential building in use.
How to make a floating foundation with your own hands
The small volume of excavation work and the possibility of self-production without the use of heavy construction equipment make floating foundations popular among individual developers when constructing various light buildings, such as low-rise buildings and outbuildings, auxiliary structures and technical facilities.
All work on the construction of the foundation can be divided into several stages: preparatory and the process of performing the work itself.
At the preparation stage, a drawing of the structure being constructed is drawn up and the need for the materials used is calculated, after which these materials are purchased and the necessary tools and equipment are prepared.
The use of factory-made concrete and a concrete pump will reduce the time required to complete the work and ensure high-quality pouring of the concrete slab
When the preparatory work has been completed, you can begin to carry it out in the following sequence:
| Illustration | Description of action |
| Marking is being carried out at the construction site. | |
| A pit is dug and the foundation is compacted. | |
| The formwork is being installed. | |
| Reinforcement is being laid. | |
| Concrete is being poured. | |
| The concrete is leveled to a given level in accordance with the installed formwork. | |
| The surface of the slab is smoothed. |
After the slab has been poured, it is necessary to give some time for the concrete to harden, after which the installation of enclosing structures can be carried out.
Types of reinforced concrete foundation slabs, arrangement of flat and ribbed
The main criterion for distinguishing reinforced concrete slab foundations is their internal structure. On this basis, power structures are divided into two types:
- Monolithic.
- Prefabricated monolithic.
The first technique is a classic sequence of technological operations for pouring concrete into formwork onto a prepared base of non-metallic materials. In this case, the slab is poured with reinforcement to increase the rigidity and resistance of the foundation to tensile and other moments.
The technology for constructing a prefabricated monolithic base involves the use of ready-made reinforced concrete slabs , which are laid on a sand and crushed stone substrate and then filled with concrete mortar. The strength and load-bearing capacity of the foundation in this case is ensured by factory blocks.
The surface shape of the slabs can be flat or ribbed.
Products with a completely flat base are used in cases where the foundation absorbs a distributed load over its entire area. Slabs of the second type are thinner, but are complicated by stiffening ribs, which account for most of the pressure from the design structure.
The construction of a slab ribbed base with your own hands involves additional digging of trenches. The space that is formed between the relief bends is filled with a mixture of non-metallic materials.
Construction technology
If you plan to use a slab foundation as the floor of the first floor, then the structure must be carefully insulated
A floating foundation is built in several stages. First of all, it is necessary to prepare the construction area: remove unnecessary green spaces, clear the area of debris and carry out markings. After this, they dig a pit of the required depth. At the same time, you should not forget that below the base of the slab there will be a layer of sand and crushed stone. If the volume of work when digging a pit is significant, then it is better to involve construction equipment.
After this, work is carried out in this order:
- The bottom of the pit is leveled and thoroughly compacted. The permissible difference is at least 50 mm. If there are more significant differences in heights at the bottom, then with maximum load on the base, the slab structure may crack and begin to collapse.
- It is also recommended to additionally install a drainage system at the bottom of the pit and cover the surface with geotextiles. This way you can protect the gravel-sand cushion from being washed away by groundwater.
- Now we begin to manufacture a cushion for a monolithic reinforced concrete slab. For this we use coarse sand or crushed stone. A mixture of these materials can also be used. Typically the height of the pillow is 100-400 mm. The thickness of this layer depends on the calculated height of the foundation slab and the characteristics of the soil. After pouring the sand or mixture, the layer is moistened with water and compacted well.
- If you plan to use a slab foundation as the floor of the first floor, then the structure must be carefully insulated. This needs to be done at this stage. To do this, a thick polyethylene film is spread on a compacted cushion. Then a layer of extruded polystyrene foam is laid. The thickness of the material slabs depends on the climatic conditions of the region and is determined in each specific case separately.
- After this, you can proceed to the manufacture of formwork. For this, it is better to use laminated boards, since the edge of the base will be smoother, and the products can be reused. A smoother edge of the slab will make it easier to install the insulation. The laminated boards are fastened together with self-tapping screws. For rigidity, spacers are installed on the reverse side every 0.5-1 m.
Next we move on to reinforcement.
The steel frame is made in the form of a spatial structure from a rod of the required thickness
The steel frame is made in the form of a spatial structure from a rod of the required thickness (usually class 3 reinforcement with a diameter of 12-14 mm is used). To fasten rods together, it is better to use wire rather than welding to provide greater flexibility and not create additional stress at the joints.
Since the reinforcement frame must be protected from corrosion on all sides by a layer of concrete of at least 5 cm, first a 50 mm layer of concrete is poured into the formwork. After it hardens, a reinforcement cage is installed. When installing, the frame should not approach the surface of the formwork more than 50 mm. Now we pour the rest of the concrete mixture.
The poured concrete composition must be compacted using special equipment.
Finally, the surface of the concrete slab must be checked for evenness using a level. If irregularities are noticed, they are corrected. After this, the surface of the base is covered with plastic film for a couple of weeks. In the first few days, the concrete surface is moistened with water. This will ensure more uniform evaporation of moisture from the concrete and its high-quality hardening.
After removing the formwork, you can insulate the side walls of the slab foundation with polystyrene.
Materials for thermal insulation of foundations
Insulation of the foundation of the house
Insulation of the foundation is a mandatory measure to protect the foundation of the building from adverse external influences.
When choosing insulation, it is important to proceed from such indicators as:
- high mechanical strength;
- waterproof;
- low vapor absorption.
How to insulate the foundation of a house? Today, the market offers several suitable materials for insulating the foundation from the outside with your own hands. We will consider each of these materials in more detail.
Extruded polystyrene foam
Extruded polystyrene foam has recently been used as the optimal insulation for foundations.
It has the following properties:
- resistance to biological influences;
- complete safety for human health;
- high moisture resistance;
- frost resistance.
Water absorption during prolonged wetness is practically zero. Foundation insulation – polystyrene foam – has standard dimensions and high mechanical strength. This determines its use as an insulating material for floors, walls, roofs and concrete foundations of buildings.
Thermal insulation of the base with extruded polystyrene foamInstallation instructions for extruded polystyrene foam:
- Insulation of foundations with extruded polystyrene foam should be carried out to a height of at least 50 cm above ground level.
- It is advisable to carry out installation after applying the waterproofing layer. To do this, you can use a water-based bitumen solution.
- If waterproof cement-based solutions are used as waterproofing, the material can be glued to the base with a special adhesive for thermal insulation.
- After the slab foundation has been insulated, the thermal insulation is covered with a protective geotextile fabric.
- Then drainage pipes are laid, and the base from the outside is covered with crushed stone or other material.
Polyurethane foam
Spraying polyurethane foam
Another effective material used as foundation insulation is polyurethane foam. It has the following properties:
- retains its qualities in soil saturated with moisture;
- thanks to spraying, it fits tightly to the foundation, has no seams or “cold bridges”;
- some types of this material have waterproofing properties;
- Resistant to chemicals.
Polyurethane foam is not only a thermal insulation material. It also protects against moisture and absorbs noise. Installation of this material occurs by spraying onto the foundation layer by layer, using special equipment.
Thus, it is possible to insulate the foundation slab, as well as other types of foundations.
Another advantage of polyurethane foam coating is its solidity. With uniform spraying, no seams or gaps are formed, that is, cold bridges are not formed.
Regular foam
Thermal insulation of the base with foam plastic
Is it necessary to insulate the base? Of course, yes, because due to the possible formation of numerous cold bridges when connecting the foundation to the walls, optimal thermal insulation is necessary.
Some home owners, when deciding how to insulate the foundation for the winter, traditionally opt for ordinary polystyrene foam. This material can only be used if there is no danger of flooding.
People are attracted by the price of this option. But when it comes to thermal insulation of the foundation, it is better not to skimp. It makes more sense to choose a more practical, moisture-resistant, homogeneous, strong material that will last for many years.
Ordinary polystyrene foam is more suitable for internal insulation, for example, as insulation of a loggia or glazed balcony.
How to build a bathhouse on a “floating” slab?
In the standard version, the arrangement of a floating foundation is very simple - a reinforced concrete monolithic foundation located under the entire area of the building at once. It is made deep on normal soil, and shallow where there is sand underfoot.
How you can build a floating foundation for your bathhouse with your own hands:
Stage I. The entire layer of vegetation is removed from the entire place where the bathhouse will be, plus 1 m for the blind area. The removed layer is transferred to the garden. A pit is dug to the design level. It is better to hire an excavator for this
It is important not to dig, otherwise the foundation may simply burst at the point of digging. This is a very serious mistake
To prevent the edges of the pit from crumbling, it is better to dig them with a slight slope.
Stage II. A layer of crushed stone 10 cm thick is poured, it is laid in several stages, and compacted well (for example, with a log with a handle). Then - a layer of sand that fixes the crushed stone and does not allow it to “walk around”. And its resistance to frost helps the new foundation to resist cold weather.
Stage III. A waterproofing layer is laid - usually a dense, expensive polyethylene film. It is necessary so that moisture does not then seep into the foundation, and also the valuable concrete “milk” does not leak during the pouring of the solution. Then a small layer of footing is poured - M-100.
Stage IV. The formwork is being built. When the foundation is immersed in the ground, the walls of the pit can perform this role, but they also need to be waterproofed. Boards with a width of 25 mm, which are 50-100 mm thicker than the height of the foundation, are well suited for formwork. A control cord is laid along the upper edge of the formwork; only one side of it is fixed in it, while the other with an attached load is lowered on the other side. When pouring the solution, you can remove the cord.
V stage. The reinforcement is laid - this is the most critical stage. Metal rods should protrude from the foundation where the walls are built; this is necessary to achieve a strong connection with the foundation. However, such reinforcement cannot be welded; it can only be tied with soft wire. The rods in the corners are closed in a semicircle, their ends are inserted into the side walls of the foundation, and a solid flexible structure emerges.
Stage VI. At this stage, the base is concreted: the solution is laid in layers up to 15 cm, then carefully leveled and compacted by bayonet.
Concrete must be poured in one step, for which it is better to use a concrete mixer. It is better to use the following recipe: for 1 part cement – 1 part sand and water. Concrete must be compacted until a wet layer appears on the surface. Then take a wooden strip and level everything out.
On the first day, the foundation is wetted every 4-5 hours, then covered with film to prevent cracks from occurring. The next day they are wetted only 3 times, then only in the morning and evening. And when it dries, the formwork is removed, and after a month you can continue building the bathhouse, or even better, after a year.
Concrete panel house and its layout
The choice in favor of a house made of reinforced concrete is influenced by the presence of a reinforced concrete products plant (RCP) or a house-building plant (DSK) near the construction site, which produces parts for individual construction. You can, of course, use standard designs, but this will impose certain restrictions on the layout of the house.
Panels are different
When choosing panels for building a house, you need to know and understand the differences between them.
Precast concrete factories, for example, often produced parts for industrial facilities and social facilities of standard construction - kindergartens, schools, cultural centers, shops... The use of these structures for the construction of a residential building involves the use of parts such as columns, crossbars, beams. And this, in turn, causes not entirely justified, extra volumes of interior finishing work, and for the interior, concrete panels of such series are not the best choice.
The fact is that panels from a concrete factory are usually not self-supporting. They are intended for “sheathing” the frame of a building made of columns, crossbars or beams. Thus, from the outside the building turns out to have smooth walls, but the columns and crossbars “stick out” inside the rooms and have to be “hidden” somehow.
Panels for “cladding” the building frame
DSK produce products directly intended for the construction of residential buildings. As a result, the house receives smooth walls, ceilings and right angles without protrusions or differences. This greatly simplifies the finishing work and, subsequently, the placement of furniture.
Products for building construction
Concreting
During the process of concreting the base, the mortar must be laid in several layers, the optimal thickness of each is about 15 cm. All layers must be carefully leveled and compacted by bayonet.
You can level the top layer using an ordinary smooth wooden strip. In this case, the concrete must be compacted until a wet, shiny layer appears on the surface.
The formwork can be removed already on the fourth or fifth day, but further construction work can only be continued after 1 month, although, according to technologists, the optimal holding time should be 1 year.
Slab foundation reinforcement
The key to a successful slab foundation is high-quality reinforcement. Reinforcing the slab foundation gives confidence that the foundation will not suffer over time. Thanks to the reinforcement, the slab foundation easily withstands all temperature changes.
When reinforcing a slab foundation, it is important to correctly calculate the load and select reinforcement of the required cross-section. Typically, reinforcement of at least 12 mm is used for slab foundations. The reinforcement bars are fastened together with tying wire - this is the most accessible and correct way of fastening reinforcement during reinforcement.
Conditions influencing the choice of foundation
Construction of a brick strip foundation: a – foundation; b – base; c – blind area; 1 – sand cushion; 2 – brickwork; 3 – backfill; 4 – bitumen coating; 5 – plaster; 6 – waterproofing (roofing material); 7 – facing brick; 8 – adobe masonry.
The device of a floating base is advisable in the following cases:
- loose soil, heaving, lack of dense areas;
- the need to absorb water and retain it for a significant time;
- high pressure of underground groundwater;
- the depth of soil freezing is quite high and poses a threat when constructing a monolithic strip foundation.
The presence of water and soil quality are determined using geodetic instruments or examinations; their range includes technology for their determination, although you can do without expensive research - just look at the neighboring buildings and assess their condition.
The size of the floating foundation is determined by the size of the residential building itself and is added up to 60-80 cm on all sides. The choice in its favor occurs when the soil is not very dense and there is no possibility of using any other. This type of base differs from others in the way it is laid.
Device
Simply choosing the right type of slabs is not enough. It is necessary to carefully evaluate their required dimensions, and first of all the thickness. The calculation of these parameters is based on the loads included in the project.
The main attention is paid to:
- punching loads;
- bending forces;
- effects of frost heaving of soil.
An analysis of many years of practice shows that for a frame house of two floors, the floors of which are made of reinforced concrete, 200 mm thick slabs must be placed in the base. If the structure of the house is lighter, you can get by with a 150 mm slab
Important: these figures refer only to the simplest cases with minimal load. As the weight of the house increases and its dimensions increase, the required thickness of the slab also increases
When it is known in advance that the house will be used all year round, it is recommended to carry out thermal insulation.
A thermal protection layer is formed both below the slab and above it. These materials are also worth considering to make the right choice. Hydraulic protection in areas where groundwater is separated from the surface by 1 m of soil or more is carried out in a simplified format. But when the level of soil liquid is high, this practice is contraindicated. The reliability and strength of a slab foundation largely depends on how well the sand cushion underneath is made.
There is gravel at the top. This material prevents moisture from concentrating under the base. The water diverted deeper into the sand layer, through which it passes even further. Additionally, the sand mass ensures uniform pressure distribution and dampens the effects of heaving forces. Under garages where the car is to be repaired (and not just stored), the depth of the foundation is greater than usual, and the complexity of the work increases.
Most often, a monolithic slab is installed under garages using a floating design. It is suitable for absolutely any soil and effectively suppresses the destruction of the garage when the earth moves. As in home construction, there is no need to pour additional floor screed. There are no special problems in installing heated floors without using classical radiator heating or in addition to it
Attention: the secondary importance of the structure compared to the house does not allow it to be considered a less significant or secondary object
Concreting the formwork for the base
The final stage is concreting the foundation formwork. The concrete mixture is poured in several layers, and the thickness of each layer should not exceed 15 cm.
Each layer is carefully leveled and compacted using the bayonet method. The finished concrete mixture is poured in one go, so it is better to use concrete mixers or concrete pumps to complete the work.
The concrete is compacted until a wet sheen forms on the finished surface. To level the top layer, you can use special wooden slats.
On the first day of pouring, it is recommended to wet the base with water every 5 hours, then cover with polyethylene. This will prevent cracks from appearing when the concrete dries quickly. In subsequent days, the foundation base is wetted only 2-3 times a day. Dismantling of the formwork is carried out after the concrete has completely dried.
Now every individual developer knows what floating foundations are and on what types of soil they can be built. Due to their practicality and durability, such foundations are becoming increasingly popular and in demand in private residential construction.
Construction of formwork and metal frame
Before a monolithic reinforced concrete slab is poured, the developer must build formwork for it:
- To install such a structure, elements of natural solid wood (40mm) or plywood (up to 21mm) are usually used. A box is assembled from such material, the individual elements of which are fixed to each other using fasteners.
- The height of the formwork should slightly exceed the thickness of the future slab.
- From the outside, the developer must support the formwork (if it is removable) with jibs and stops. This is done to give rigidity to the box so that it can withstand the weight of the concrete mixture.
- Reinforcement is laid on a compacted sand-crushed stone bed (it is customary to use rods with a diameter of up to 14 mm), across and along. Care should be taken to ensure that the step does not exceed 30cm. Since the reinforcement should be located at a distance of 5 cm from the edge of the slab, special supports are placed under it, through which the necessary gap is ensured. If you plan to create a powerful foundation structure, then experts recommend laying the reinforcement in two or three layers. It should be tied together to make the metal frame as strong as possible. Welding is not used in this case, since the resulting seam will be exposed to moisture during the operation of the building, which can cause corrosion.
- Once the process of creating the formwork and metal cage has been completed, you can begin pouring the concrete. Initially, a layer 100 mm thick is created, on the surface of which waterproofing material and insulation will be laid.
The principle of operation of a slab foundation
Situation
The building density is growing, people increasingly have to build on “bad” soils (weak, constantly wet, heaving, frozen...).
Modern projects of country houses have become much more complex in terms of architectural and planning solutions: different parts of the building are built at different heights (options of one and a half floors, attached garages, special solutions for staircases and landings...), uneven distribution of load-bearing walls over the building area. Houses are now bigger, higher, heavier.
Problem
On top of the foundation and on the natural foundation there are uneven impacts from the house. From below, complex soils either tend to form local failures under the building, or forces of frost heaving push the building out, and then, when thawed, sag. There is a danger of deformation and destruction of supporting structures.
Solution
- Increase the supporting area of the foundation, reducing the load from the house on the natural foundation.
- Maximize the spatial rigidity of the foundation and evenly redistribute the pressure from top to bottom.
- Use a heat insulator to separate the heated rooms from the ground under the house - thus eliminating uneven freezing under the building (in winter, the ground under the slab does not thaw).
All these methods of dealing with “unevenness” are inherent in the principle of operation of an insulated monolithic slab. This is a kind of single platform under the house, which is not subject to local bending (if properly designed), and without deformation is able to actually move with the ground - “float”.
Prefabricated foundation made of blocks.
Modern construction provides various options that will help install reliable and durable load-bearing foundations of structures
The foundation made of FBS blocks enjoys well-deserved attention - many people use it in the construction of houses. Such a structure is constructed when there is a need to build a foundation quickly and without inviting qualified workers
Laying this foundation will only take a couple of days. First, blocks are installed at all corners of the external walls. Then they move on to installing ordinary blocks of all other walls. All rows should be connected with a solution about two centimeters wide. The joints between the blocks should not be the same in height.
In order for the foundation not to be destroyed by moisture and low temperatures and to last for a long time, it is necessary to carry out work on waterproofing and insulating the foundation. For this you can use various materials. For example, rolled hydroglass insulation, which is attached to the blocks using a special mastic and resin using a thermal method.
Types of foundations in construction
There are several types of foundations in construction. Each of them is intended for a specific case. Let's talk about each of them in more detail: Strip foundation. Most common in low-rise and private housing construction. They are a concrete strip with reinforcement. It is located along the perimeter of the entire building. This foundation is perfect for houses with basements and garages. On such a foundation you can build both heavy brick houses and light ones made of wood. In the first case, it will be deepened, but for the construction of light structures a strong deepening is not required.
Columnar foundation. The name speaks for itself. It is erected by placing pillars in the corners of the building and at the intersections of walls. Between the pillars, lintels are made of concrete, brick or rubble. With such a foundation, it is impossible to install a basement in the house. In addition, it is suitable for the construction of light houses. It is best to build a columnar foundation on stable soils.
Monolithic. It is a single slab poured from concrete with reinforcement. This option gives freedom of planning and protects the structure from deformation due to soil subsidence. Its installation does not require special equipment, which allows you to carry out the work yourself.Knowing the strengths of each type of foundation, you can easily choose the one suitable for building your home.
Why do experts recommend using penoplex for insulation?
In recent years, many developers prefer to insulate the foundation with penoplex. The choice of this material is due to the fact that it is highly resistant to moisture and also has the lowest thermal conductivity. Due to the fact that the slab supporting structure will have to come into contact with a damp environment for many decades, insulating the foundation with penoplex will protect the building from its harmful effects.
Extruded polystyrene foam is ideal for thermal insulation of monolithic foundation structures, as it can withstand compressive loads. Polyurethane foam boards and penoplex are cellular materials with a closed structure, due to which moisture is not able to penetrate into their cavities. That is why they are used when carrying out insulation measures.
Types of monolithic slab foundation
Depending on the characteristics of the soil, the building being constructed and the climate of the region, one of the following types of monolithic foundation is chosen:
- solid or classic. The construction technology involves excavating the fertile soil layer, filling the pit with sand and gravel, and then constructing a reinforced concrete base. The thickness of the latter in private construction, as a rule, is 20-50 cm, but depends on the type of soil and the characteristics of the building being constructed. If necessary, thermal insulation is carried out. This foundation option is excellent for highly heaving soils, where movement is possible in both vertical and horizontal planes;
- Russian, or monolithic slab with stiffeners. In addition to the monolithic slab, stiffening ribs are installed below or above. They are made in the locations of load-bearing walls to strengthen the structure, but at the same time the complexity of constructing the foundation increases, because you have to fill not only the slab, but also the stiffeners, but the slab can be made thinner, saving on concrete and without losing strength. Stiffening ribs are, in fact, an analogue of a strip foundation. They can be poured from concrete or made from blocks. The first option is preferable, since in this case the structure will be completely monolithic. The use of ready-made blocks will also require the use of special equipment;
- insulated Swedish stove (USP). The technology is recommended for areas with harsh climates and is excellent for the northern regions of our country. The peculiarity is the use of a heated floor system, which is hidden in a concrete slab. In addition, permanent formwork made of expanded polystyrene is used, which serves as thermal insulation, and polyethylene film for waterproofing. It turns out that the base warms up, but heat leaks are minimized due to the presence of thermal insulation. Naturally, the cost of construction will be higher than that of the classic version.
Please note that the slab foundation can be either monolithic or prefabricated. All the advantages and nuances of a monolithic foundation are discussed above.
A prefabricated foundation is created on the basis of road slabs or FBS blocks, which, after installation, are filled with a layer of leveling screed. Prefabricated slab foundations require the use of special equipment for the installation of heavy slabs, therefore this is a longer and more expensive solution, but at the same time the performance qualities are inferior to a monolithic slab foundation.
Types of waterproofing
If you nevertheless come to the conclusion that there is a need to provide waterproofing, you should take into account the following points at the initial stage of constructing the base and using moisture-proofing materials:
- Before constructing the slab itself, the fertile layer is first destroyed on the site.
- For a more stable position of the structure, a cushion is made under the base from a layer of sand and crushed stone.
- Large crushed stone can easily damage moisture-proofing film or rolled materials, so it is better to use its small fractions. If the crushed stone is not placed evenly, it will simply be impossible to ensure the tightness of the overlaps or joints of the material.
Due to these reasons, builders often first fill the surface of the site with concrete to get an even layer, and then make a cushion. To ensure waterproofing of the foundation, the following materials are used:
- Roll materials are the most common option. This group also often includes various moisture-proofing films. The most popular representative is roofing felt.
- Penetrating compounds. After being applied to concrete, the substances create a potential difference, thereby changing its structure.
- Additives to concrete. Today, there are many substances that are introduced into the concrete solution, and then the base is poured.
- Coating materials. They are mainly used for waterproofing strip foundations; they are not particularly suitable for slabs, since it is not possible to coat the base of the base.
For waterproofing monolithic slabs, the most suitable option is rolled materials, additives and compositions. The last two options significantly reduce costs and time losses. Rolled materials may be more expensive, depending on regional prices. In addition, laying roofing felt or other materials of this group can take quite a lot of time. However, at the same time, roll materials are considered one of the most reliable.
Why choose a slab foundation
In low-rise construction, which is what we are actually interested in, this type of foundation for many reasons will be preferable to its competitors (both strip and pile structures). This is explained by advantages of both a purely technical and construction-related nature.
Strengths of solid foundations
Universality in foundation geology.
A floating structure can be correctly used on all types of soils, including weak-bearing, heaving, horizontally mobile, high groundwater levels, permafrost...
There are some restrictions on the terrain - it is difficult to build such a foundation on a slope; most likely, piles will be preferable. However, there are American-tested technologies for constructing slabs on hillocks, which in their design (in the lower part of the site) have elements of high monolithic strips. Another “centaur” suitable for such places is a pile foundation with a low grillage in the form of a monolithic slab.
Good load-bearing capacity.
This quality is due to the specific mechanics of the “house/slab/soil” interaction. In the next chapter we will look at this point in detail. Briefly, the slab has a large support area, so the pressure on the foundation soil is very low (from 0.1 kgf/cm2). Consequently, a two-story stone house on a slab can be built with confidence. They say that the elevator shaft of the Ostankino Tower stands on a monolithic slab.
High spatial rigidity.
It is due to the absence of seams and joints, the use of rigid reinforcement, the massiveness of the structure and high material consumption. A slab foundation is excellent for houses with “inelastic” walls, which are very afraid of even the smallest (1-3 mm) movements of the supporting structure - brick, aerated concrete, cinder block, shell rock and other mineral materials.
In the presence of excessively heaving soils and significant sensitivity of buildings to uneven deformations, it is recommended to build them on shallow and non-buried monolithic reinforced concrete slabs, under which cushions made of non-heaving materials are placed.
SP 50–101–2004 “Design and installation of foundations and foundations of buildings and structures.”
Good insulating properties.
When properly executed, it does not allow water to pass through and prevents heat loss through the floor.
Simple construction technology, built quickly.
Easy to mark, minimum excavation work, simplified formwork design, easy to reinforce and concrete. Can be manufactured by low-skilled builders.
Conditional disadvantages of a slab foundation
Technically, it is very difficult to combine a solid slab and a basement in a structure.
The slab can be poured only in favorable weather (it is slightly inferior to prefabricated and pile driven foundations).
High price. Increased material consumption (concrete, reinforcement), of course, leaves its mark. But if you look at the problem as a whole, the picture changes dramatically - we save a lot on other materials, construction stages, and production operations:
- the slab becomes the subfloor of the first floor - no need to make an overlap;
- You can lay a water heated floor in the mass of the slab, rather than pouring a separate screed for it;
- for the manufacture and fastening of formwork panels, less boards or sheet materials are needed (at least twice as much as strip structures);
- no need to pay for removal/planning of a large volume of selected soil;
- the height of the external walls is reduced, since it is possible to obtain a lower base (and these are expensive facade finishing materials, labor costs...);
- lifting equipment, concrete pumps, excavators, driving pile drivers, drilling machines are not needed, everything is limited to mixer vehicles;
- you can build it yourself and not hire highly paid professional builders, there is less risk of suffering financially from the “human factor” (simpler technology).
It turns out that the main disadvantage of slab foundations is the low awareness of domestic developers about their advantages. But in the northern part of the USA and Scandinavian countries, monolithic slabs have become the No. 1 foundation.
How to pour correctly
To independently erect a slab, it is necessary to evaluate the soil composition and groundwater level (GWL); compaction of the sand backfill with water and a vibrating plate plays a special role. Next, you should definitely initially plan communications with duplication, for problem-free drainage (gutter). For a floating slab, plantar and ring drainage is provided. The insulation is ordinary dense polystyrene foam.
Monolithic floating foundation option
What is this type of foundation? Simply put, it is a slab of reinforced concrete, freely located on a cushion (base) of bulk building materials.
- This type of floating foundation is chosen when constructing fairly heavy structures made of stone, concrete blocks or brick.
- Another name that may be familiar to you is. It is made using a clean solution, without the use of large stones, and gravel or small and medium-sized crushed stone is suitable as fillers.
To construct such a foundation you will need formwork. A vibrator is considered the most suitable equipment in the compaction process; it significantly improves the quality of concrete. I would like to note that such a foundation does not require a large base thickness, even 40 cm is enough.
Diagram of a concrete mixer.
This is what is important - the size and shape must correspond exactly to the parameters of the structure. So, where to start building a floating foundation with your own hands? The technology for constructing floating foundations involves the initial steps of laying a cushion (base) under the foundation
So, where to start building a floating foundation with your own hands? The technology for constructing floating foundations involves the initial steps of laying a cushion (base) under the foundation.
To do this, you will need crushed stone, soil, coarse sand, or a mixture of them. The thickness of the base should be approximately 40 cm.
Next, proceed to the manufacture of panel formwork 30 cm high. Any flat boards that need to be secured with pegs from the outside are suitable for its construction. The distance between them should not exceed one and a half meters.
Another important point involves filling the stiffeners. To construct them, grooves are dug and roofing felt or roofing felt is laid on their bottom. This is necessary to retain moisture in the solution.
Slab floating foundations are subject to mandatory reinforcement. It is carried out after completion of preliminary work. To do this, reinforcement is laid out across the entire base. Uniformity is the main requirement when performing these works. And don’t forget that reinforcement is also laid along the ditches.
After these procedures, you can proceed to pouring the foundation with concrete. What materials are used as reinforcing elements?
Scheme of pouring a concrete foundation.
This can be thick wire, rods (metal), small sections of pipes (iron), profiles, and so on. The mixture for pouring a floating foundation is prepared from Portland cement M400. It is mixed with crushed stone in a ratio of 1 to 2. When using coarse sand, the ratio will look different - 1:1:1. The strength of your foundation will also depend on such factors as the quality of mixing
Therefore, pay special attention to this process.
After pouring is completed, the surface of the slab is compacted and leveled using a level. If there is a need to level some areas, you need to add a solution.
It is best if someone helps you at this stage of the work, since performing this procedure together is much more convenient. Use a long rule in your work. You can make it yourself or purchase a ready-made factory version (aluminum).
- A very important point is that the foundation must be poured simultaneously. If you have any doubts about this, it is better to fill the entire area, but not completely, but half. You can continue the next day. It is strictly not recommended to fill the slab in parts.
- After the pouring is completed, the surface of the finished slab is covered with any sheet material or film. 14 days in this condition will be enough. Do not forget to carry out the procedure of moistening the foundation from time to time, then its hardening will be better and more correct.
- After hardening, the formwork is dismantled, and a brick plinth is laid in its place. As with other types of foundations, the base is equipped with special openings for ventilation of the underground space.
If there is no ventilation, you are at risk of mold growth. The size of the ventilation vents should be at least 15x15 cm, and it is advisable to locate them at a distance of 15 cm above the ground.
It is possible to install a floating foundation yourself, but it is possible to use the services of professional companies. The approximate price for such work is 4,000 rubles per sq. m. m.
The sequence of insulation with polystyrene foam
If the insulation of the foundation is not done during laying, but of an already constructed building, then it is necessary to dig a trench to a laying depth of a convenient width (about 40-50 cm), and then prepare the base for laying the heat insulator by cleaning, washing and drying it.
A layer of waterproofing is applied to the foundation wall - either roofing material or bitumen mastic. If the first type of waterproofing is used, then polymer glue will be required to attach polystyrene foam boards, and mastic can act as an adhesive. No additional fasteners are required.
For external insulation of a monolith, slabs 5 cm thick are sufficient, which is equivalent to the thermal insulation properties of 9.5 cm of mineral wool and a meter of brickwork.
It is recommended to use polyurethane foam on the crests of locks and at corner joints to thicken the thermal insulation layer.
Then follows another layer of waterproofing - mastic or roofing felt, to protect the mounting foam, which is vulnerable to moisture. Ideally, the insulation should cover not only the foundation, but also part of the base. By the way, you can use plastic dowels for fastening on the base.
When the main work is completed, the polystyrene foam can be covered with earth. If the soils are clayey, then it is recommended to pour expanded clay or sand into the trench near the foundation, under the future blind area, to a depth of 30-40 cm.
Tools and materials for working with polystyrene foam:
- Bitumen mastic or polymer glue.
- Polyurethane foam.
- Ruberoid.
- Construction knife.
- Blowtorch or hair dryer.
- Hammer.
- Swing brush.
- Level.
- Rope.
Foundation slab cost
The cost of building a slab foundation (labor + materials) includes:
– work on marking the slab foundation
– excavation work, bed of crushed stone and sand, installation of waterproofing
– knitting the frame of the slab foundation reinforcement
– erection of slab foundation formwork
– concreting the slab foundation
By choosing a slab foundation, you will never face the problem of foundation repair. A slab for difficult soils is in many cases the most preferable. This is not the cheapest, but the surest choice.
Floating foundation - slab on bulk soil
Filled soil is a problem for many people, but it is created by circumstances, and most often the cause is ravine terrain. But it happens that a person becomes the owner of such a plot not entirely of his own free will. When selling it, they simply do not warn that the previous owner carried out some work.
Initially, you need to find out what type of soil will be under the house: sandstone, clay or soil. The best option would be to wait the required time (2-3 years) and only then begin construction, but if necessary, you can try to influence the soil with a vibrating plate (the optimal solution is to hire a road roller for several days).
It’s worth immediately taking into account that even with good compaction, the price for a floating foundation slab will still be higher than for conventional analogues on soil compacted over centuries.
Pouring the solution and summing up
The very last difficult moment remains - this is the actual pouring of the foundation. Due to the fact that maximum strength is required, it is better to increase the grade of concrete from M300 to M400.
If it is possible to hire automixers to immediately deliver the finished solution, then this will be ideal, but if this is not possible, then it is quite possible to do it yourself. The only condition is the maximum pouring time, 2 days, but ideally all the work is carried out in 1 day, so that when the concrete hardens, it does not feel the difference, which is important.
After the work is completed, you need to leave the slab for 28 days, the first 12 of which the slab is watered with water once a day, because the foundation has one bad property: when hardening, the first time it absorbs water in such an amount that it is easy to knead it at first It’s impossible, and if you don’t water it afterwards, microcracks will appear.
Based on materials from the site: https://moifundament.ru
Question asked by: sergey.grachikov
A monolithic frame building 20x20 2 floors was built.
Built on a monolithic non-buried slab 40cm thick. On bulk soil, which was compacted by a roller (without vibration) for about 4 days. Then we went over it with a vibrating plate, poured water on it, and again with a stove.
The area was filled with dune grass. Reinforcement 14 arm step 20. The slab contains 19 monolithic columns 40x40.
There are no pillars. The slab was reinforced at the pressure point of the columns with 10th reinforcement. Both upper and lower reinforcement.
I am attaching a photo report. I would like to add: before this there was an old house on the site. Demolished.
Then they started to sleep. The project was made by a designer from a design institute according to SNIP. The only thing is that he didn’t want to make a non-buried slab.
Apparently it's not worth the risk. We didn’t listen – now we’re worried. That is, the only deviation from the project is the depth of the slab.
Please help me with advice and criticism. Please voice your opinion. What are the risks?
What can happen? The walls were filled with a 40 cm expanded clay concrete block. The cross-section of the slab resembles the letter P (under the walls the thickness of the slab is 60 cm), that is, like a ribbon around the perimeter that is 20 cm deeper than the slab.
and 40cm wide. Now the building is in this stage: So far everything is holding up. city of Astrakhan.
GWL - about 2-2.5 m. The blind area is insulated on one side for now (it stood in this condition for one winter). 50mm extrusion insulation under the wall (along the perimeter) under the slab itself there is nothing except geotextile, sand cushion, waterproofing.
QUESTION:
1. Was it worth building this way or was a different foundation needed (piles for columns), or was it better to bury the slab?
2. We are planning to complete the 3rd floor - a metal structure made of channels with a total weight of 8-9 tons plus sandwich panels as a roof. Fill the walls with aerated concrete (there seems to be nothing easier - we are not considering wall sandwiches)
3. In some places, in the area of the lintels, which were made from angles that were not welded together, small, barely noticeable cracks appeared in the masonry. Shrinkage or does the foundation sit on one side?
Bulk soils have a disturbed structure, varying degrees of homogeneity and uneven density. They form spontaneously or plannedly, as a result of alluvium or explosion, in industrial or household waste dumps, during the organization of dumps or fills.
A foundation on bulk soil causes certain difficulties during its construction, but in most cases the task is feasible. Today, entire microdistricts are built on artificially raised lowlands and filled-in ravines, increasing the bearing capacity of complex soils in various ways. But it should be noted that not all types of foundations can be built on embankments.
- erected according to plan, according to design documentation; filled as a result of the development of pits or underground workings, when comparing hills or planning large areas, as well as those resulting from production processes (slag, molding earth, etc.); arising from mixed waste - household or industrial.
Planned embankments are distinguished by their uniform composition and uniform compressibility.
They are erected either by alluvial or dry method. In the first case, hydromechanization is used, and in the second, bulldozers, scrapers, road transport, etc. The layers are compacted using road rollers and tamping mechanisms.
The second group of bulk soils most often has a uniform composition, as is the case with planned embankments, but their density and compressibility in different areas can differ significantly from each other. Similar dumps:
- they are washed industrially; they are poured in layers in an organized manner; they are poured along the slope to the full height; they are erected randomly.
The reclamation of waste from technological processes is carried out according to the same scheme as during the construction of planned embankments. When dumping in layers, dumps are compacted under their own weight and with the help of vehicles delivering earth, slag, etc. In the case of embankment construction at a natural angle, characteristic heterogeneity in the composition and location of the dumped layers appears.
As a rule, such soil acquires density only due to its own weight. A randomly constructed embankment appears as a result of the chaotic dumping of earth or industrial waste, which leads to varying degrees of soil compaction in nearby areas. A landfill of heterogeneous household and industrial waste with the presence of organic waste is uneven in its structure. The compressibility of bulk soils of similar composition has unstable indicators over the entire area of the embankment. Depending on the age of filling, embankments are divided into: compacted - the natural compaction process is completed; non-compacted - the compaction stage continues. The period of self-compaction of bulk soils depends on the type and structure of the constituent layers.
It is quite difficult to predict how an embankment will behave after a structure is erected on it. Natural soil has been compressed for centuries and millennia, so its load-bearing capacity is much higher. But when there are hills, ravines and marshy soils at the construction site, it is often necessary to pre-install embankments, since the rough terrain does not provide any other chance of using the area. Therefore, owners of territories with complex terrain need to know which foundation on bulk soil is considered more reliable.