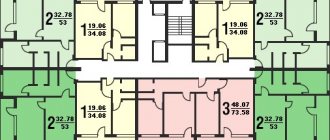
Five-story building 125 series
Type of house - panel Floors - 5/9-10 Height of residential premises - 255 cm Apartments - 1,2,3,4 rooms Manufacturer - local reinforced concrete structures Years of construction - 1970s - 1980s, a 9-storey modification is currently being built Cities of distribution — USSR (all-Union series), including in Moscow Developer: Design Bureau for Reinforced Concrete of the State Construction Committee of the RSFSR
series 111-125 against the background of p-44t
The layout of apartments in five-story buildings of the 125 series (it is different in 9-story buildings):
Good afternoon, Sergey. I am contacting you regarding the possibility of remodeling the 125 series house. There I have a two-room apartment on the 5th floor. I want to trim a little bit, about 15-20 centimeters, of part of the main wall that is in the corridor. I just have a living room, and between the room and the corridor there is a partition with a door. I would like to slightly expand the corridor at the expense of the living room, and part of the load-bearing wall. Anything that sticks out should be trimmed. I just want to install a built-in wardrobe in the corridor, but the corridor is narrow, the wardrobe is 65-70 centimeters deep, even the hanger won’t fit properly with clothes. Will it be possible to coordinate the cutting of part of the load-bearing wall in a two-room panel apartment on the 5th floor out of 10?
Answer to the question
Good afternoon, Ibrahim
Thanks for reaching out
Comments on the text below:
I am contacting you regarding the possibility of remodeling the 125 series house. There I have a two-room apartment on the 5th floor. - So
I want to trim a little, about 15-20 centimeters, part of the main wall that is in the corridor. I just have a living room, and between the room and the corridor there is a partition with a door. I would like to slightly expand the corridor at the expense of the living room, and part of the load-bearing wall. Anything that sticks out should be trimmed. I just want to install a built-in wardrobe in the corridor, and the corridor is narrow, the wardrobe is 65-70 centimeters deep, even a hanger won’t fit properly with clothes. Will it be possible to coordinate the cutting of part of the load-bearing wall in a two-room panel apartment on the 5th floor out of 10?
- It's clear. It is possible to expand the corridor at the expense of the living room. However, in my opinion, they will not allow cutting the load-bearing wall. In this regard, it will be necessary to consult with the author of the house project, but most likely they will not be allowed to cut part of the load-bearing wall by 15-20 cm.
One of the goals of a major renovation is to make the apartment more comfortable and functional. This is achieved by changing the original layout. The article presents options for redevelopment of apartments of different sizes, solving different problems.
Apartment plan 81 series. Typical series of houses
The majority of housing in apartment buildings in Moscow and the Moscow region are apartments in serial (standard) buildings. A series of houses is a group of residential buildings with identical apartment layouts, engineering structures and building materials used. The layouts in such houses are called standard. You can combine different series of houses based on wall material or time.
Based on the building materials used, three main types can be distinguished:
- Brick houses
are standard series, the external walls of which are built of brick. - Panel houses
are standard series built from prefabricated reinforced concrete panels. - Block houses
are standard series, the external walls of which are built from concrete blocks.
Based on time, four main periods of construction can be distinguished:
- Stalin series are standard series of houses designed in the 1950s. The houses are mostly brick or block. Distinctive features are high ceilings, spacious rooms, large corridors and kitchens.
- Khrushchev series - standard series of houses designed between 1956 and 1964. The houses are mostly panel, sometimes brick. Distinctive features are small kitchens, lack of elevators, combined bathrooms, poor heat and sound insulation.
- Brezhnev series are standard series of houses designed in the USSR from 1965 to the end of the 1980s. There are both brick, panel and block projects. The number of floors gradually increased, first to 9, and then to 17 floors. Later projects are distinguished by a wide variety of designs and successful standard layouts. The most successful Brezhnev series were modified and are still being built today.
- Modern series are standard series of houses designed since the early 1990s. They differ from the previous ones in an attempt to add individual features to standard houses, houses of variable number of storeys and combined houses appear, apartment layouts become more spacious, and the quality of the exterior and interior decoration of buildings increases.
The site features most of the model series of homes built since the 1950s. Those. 90% of all possible options for standard apartments and houses presented on the market in Moscow and the Moscow region.
When choosing an apartment, we are usually guided by its most obvious characteristics: area, area, view from the window. In fact, the quality and living conditions primarily depend on the residential building: apartment layout, number of floors, sound insulation - these and many other parameters you purchase along with your new home. And the comfort of your stay will depend on how carefully you treat them.
At first glance, all the houses are approximately the same. In fact, there are many types of them, in other words, series. Series of houses are groups of residential buildings, almost or completely identical within each group in appearance, apartment layouts, and materials used in construction. Such houses are the architectural basis for residential areas.
Housing construction began to develop in Russia during the “Khrushchev Thaw”, when for the first time the task of a planned economy was not the development of heavy industry, but the improvement of people’s living conditions. The new course was aimed at building houses with separate full-fledged apartments for each family, as opposed to communal apartments. Many series from the 80s, 70s and even 60s serve well to this day, and, moreover, most people prefer these houses.
Each region is characterized by certain series of buildings depending on the geographical location, climatic and seismic conditions. In Vladivostok you can most often find houses of series 81, 83, 125. About them in order.
81 series - large-block type of house.
Floors - 5, 9.
Apartments - 1, 2, 3 rooms.
Years of construction: 1970s. - Until now.
Such buildings are located on Lermontov, Lugovaya, Trudovaya streets. Sakhalinskaya, 100-letiya Ave (Vtoraya Rechka district), Kotelnikova 16 (Balyaev district), Krasnoye Znamya 125.
83 series - panel type of house.
Number of floors - 5-10.
The years of construction are the same as those of the 81st series.
Most of these houses are in microdistricts 64-71. Streets: Neybuta, Ladygina, Kariernaya, Kuznetsova, Kalinina, Tukhachevskogo 62 (BAM area), Irtyshskaya 30a, Karbysheva 52, 54 and many, many others.
Two-room apartments in houses of this series are the most popular in Vladivostok, due to their layout: a large kitchen of 8 to 10 square meters and a loggia.
125 series - panel type of house.
Number of floors - 5/9-10.
Ceiling height - 255 cm.
Apartments - 1, 2, 3, 4 rooms.
Years of construction: 1970s - 1980s; The 9-story modification is currently being built.
This series includes houses at the following addresses: Davydova 40, Irtyshskaya 40, 40/2, Shoshina 3, 5, 15, 19, 25a (BAM district), Kirova 101; Gulbinovicha 29, Burachka 17 (Churkin); Karbysheva 6; Heroes of Varyag 2, 4, 6, 8, 10; Kiparisovaya 2, 4, 6, 14, 16
Houses of the 125th series are the favorites of Vladivostok residents. They are less common than those listed above and are located on the outskirts and hills of the city. According to residents, the advantage of the layout of this series is the large area of the kitchen and corridor; the rooms have a square shape, and not an elongated rectangular one as in the houses of the 83 series.
Usually, advertisements for the sale of apartments indicate the series of the house, therefore, by taking care of this issue in advance, you can find housing that meets all your wishes.
114-85 or simply 85 is an all-Union standard series of multi-apartment brick residential buildings in the USSR. The series was developed by TsNIIEP Dwellings in 1969 based on the 1-447S series. Series 85 houses were built from 1974 to the mid-2000s. The houses in this series belong to the Brezhnevkas of the late period (“improved” or “new layout”). Five-story modification. Recognizable by the alternation of wide loggias recessed into the facade and protruding small balconies, from the entrances - two paired loggias recessed into the facade
Series:
114-85
House type:
brick
Manufacturer:
The manufacturers of this series of houses are local construction companies.
Years of construction:
1970-2000s
Number of floors:
5 or 9 (10) floors.
Number of rooms in apartments:
The number of rooms in the apartments of this series ranges from 1 to 4, however, in some modifications there are no one- and four-room apartments
Height of living quarters:
2.48 m
Number of apartments per floor:
3 less often 2
Number of sections (entrances):
Multi-sectional houses designed according to the block-sectional principle. The series includes both ready-made houses and block sections - row, corner, rotary block inserts. The block-sectional principle allows you to “assemble” houses of various shapes from sections - straight, angular, curved. Block sections are designated by indexes 85-0хх, ready-made house projects are designated by indexes 114-85-хх.
Elevators:
9-storey modifications have 1 passenger elevator
Stairs:
double-flight from prefabricated reinforced concrete marches and platforms
Ventilation:
natural exhaust ventilation
Garbage removal:
available on each interfloor platform
Loggias:
There is
Balconies:
There is
Baths:
standard (not seated)
Bathrooms:
separate
Load-bearing walls:
Load-bearing walls - external and transverse internal walls
Wall material:
The wall material is brick, most often white silicate; there are houses made of red brick
Floors:
Floors - hollow-core reinforced concrete slabs 220 mm thick
Series 114-85 includes a large number of modifications: standard projects with a height of 5 and 9 floors, as well as small-family and projects for rural construction. Advantages: the apartments have loggias, a variety of planning solutions, separate bathrooms, good heat and sound insulation. Disadvantages: some modifications of the series do not have one- and four-room apartments
Types of redevelopment and their approval
All types of redevelopment can be divided into several categories. They will differ in the degree of complexity and the number of necessary approval documents. There are three such types:
- Redevelopment without prior approval. Documents (apartment plan “before” and after” and a completed application for redevelopment) are submitted to the MFC (multifunctional center) for review after completion of the work. Such work includes work that does not affect load-bearing walls:
- rearrangement of plumbing fixtures in the bathroom and toilet (without changing the boundaries), replacement with similar ones;
- installation of an air conditioner without gating load-bearing walls (installation of a satellite dish requires approval);
- dismantling built-in cabinets and storage rooms;
- moving the sink and electric stove in the kitchen.
An example of redevelopment without prior approval
An example of redevelopment according to the project
For the last type of redevelopment, documentation will be required: a work production log, drawing up Hidden Work Reports. Also, the work is carried out under the control of the organization that compiled the project. Upon completion of the work, the procedure is the same - obtaining the Certificate and making changes to the BTI.
Redevelopment options for a 1-room apartment
In each case, the apartment owners have different requirements. Everyone has a different lifestyle, habits and ideas about comfort. So the options for reworking the same standard project can differ significantly. The most typical ones, which occur in the vast majority of cases, are the combination of a bathroom, sometimes with an increase in its area, the destruction of storage rooms and built-in cabinets. These are usually supplemented by individual requests that suit the needs of the hosts.
Select a bedroom (from a one-room to a two-room)
The most common request for remodeling a one-room apartment is to allocate a bedroom. In some cases this is possible, in others it is difficult. The apartment redevelopment option shown in the photo essentially converts a 1-room apartment into a two-room apartment. This happens due to the transfer of a large number of partitions.
Allocation of a bedroom in a one-room apartment
We begin to consider changes from the input. The bathroom doors were moved to another wall and the former pantry/closet was converted into a walk-in closet. The area of the hallway has been increased due to the area of the room; there is a partitioned off space for a spacious dressing room. Previously, the small hallway had 4 doors, which made its use extremely inconvenient. In the proposed redevelopment option, the functionality of the hallway is much higher.
The partition separating the kitchen was removed and a partition off the bedroom was installed. As a result, we got a kitchen-living room and a separate lounge room. To make the kitchen separation more obvious, a small partition was placed to delimit this area.
The alteration did not affect the exit to the balcony. It can be glazed and insulated, after which it can be attached to the room. (Read more about connecting balconies here ).
Another method is presented in the following project. The initial layout is not entirely successful: the long narrow kitchen is clearly inconvenient.
Selecting a bedroom in a one-room apartment using a radial partition and connecting a balcony
During the redevelopment process, it is necessary to remove the partitions separating the living room and the kitchen. The layout of the bathroom has been changed. The area was increased due to the kitchen, but there was still room for all the plumbing fixtures and a washing machine. In the hallway there is a small partition that screens off the built-in closet.
The living room area is separated from the kitchen-dining area by a small partition. The separation is supported by an extended dining area, which is an extension of the extensive work surface. A window block was installed at the exit to the balcony from the former kitchen. It lets in enough light to illuminate the kitchen.
The bedroom is separated from the living room by a gypsum plasterboard partition; the separation is completed by a translucent sliding radial partition. To prevent the bedroom from being too small, the loggia is insulated and glazed. The window block with the window sill was dismantled, and a closet was installed in the resulting corner. A workplace is organized against the opposite wall.
And also the layout and its conversion into a three-room apartment. More precisely, there are two rooms left, but a studio is formed - a combined kitchen with a dining room. This idea is radical - the kitchen is moved to the place of the living room. The option can be agreed upon only if an electric stove is installed, as well as the availability of technical capabilities to relocate sewer and ventilation risers.
In this option, the bathroom is combined, the kitchen is moved into the room, and in place of the kitchen there is a children's room. The former living room is divided into a bedroom, a significant part of which goes towards the kitchen. The dressing room was also dismantled - it is also included in the kitchen area. The corridor became larger, which made it possible to make all the allocated rooms separate. An ambiguous option, but possible.
We turn it into a studio (3 options)
Among young people, the idea of transforming a standard apartment into a studio apartment, in which only the bathroom remains enclosed, is very popular. There may also be partitions that partially separate one area from another. They can be from ceiling to floor, but do not completely block the entire passage, leaving the space unified.
Series type of building construction 81. Typical series of houses
When choosing an apartment, we are usually guided by its most obvious characteristics: area, area, view from the window. In fact, the quality and living conditions primarily depend on the residential building: apartment layout, number of floors, sound insulation - these and many other parameters you purchase along with your new home. And the comfort of your stay will depend on how carefully you treat them.
At first glance, all the houses are approximately the same. In fact, there are many types of them, in other words, series. Series of houses are groups of residential buildings, almost or completely identical within each group in appearance, apartment layouts, and materials used in construction. Such houses are the architectural basis for residential areas.
Housing construction began to develop in Russia during the “Khrushchev Thaw”, when for the first time the task of a planned economy was not the development of heavy industry, but the improvement of people’s living conditions. The new course was aimed at building houses with separate full-fledged apartments for each family, as opposed to communal apartments. Many series from the 80s, 70s and even 60s serve well to this day, and, moreover, most people prefer these houses.
Each region is characterized by certain series of buildings depending on the geographical location, climatic and seismic conditions. In Vladivostok you can most often find houses of series 81, 83, 125. About them in order.
81 series - large-block type of house.
Floors - 5, 9.
Apartments - 1, 2, 3 rooms.
Years of construction: 1970s. - Until now.
Such buildings are located on Lermontov, Lugovaya, Trudovaya streets. Sakhalinskaya, 100-letiya Ave (Vtoraya Rechka district), Kotelnikova 16 (Balyaev district), Krasnoye Znamya 125.
83 series - panel type of house.
Number of floors - 5-10.
The years of construction are the same as those of the 81st series.
Most of these houses are in microdistricts 64-71. Streets: Neybuta, Ladygina, Kariernaya, Kuznetsova, Kalinina, Tukhachevskogo 62 (BAM area), Irtyshskaya 30a, Karbysheva 52, 54 and many, many others.
Two-room apartments in houses of this series are the most popular in Vladivostok, due to their layout: a large kitchen of 8 to 10 square meters and a loggia.
125 series - panel type of house.
Number of floors - 5/9-10.
Ceiling height - 255 cm.
Apartments - 1, 2, 3, 4 rooms.
Years of construction: 1970s - 1980s; The 9-story modification is currently being built.
This series includes houses at the following addresses: Davydova 40, Irtyshskaya 40, 40/2, Shoshina 3, 5, 15, 19, 25a (BAM district), Kirova 101; Gulbinovicha 29, Burachka 17 (Churkin); Karbysheva 6; Heroes of Varyag 2, 4, 6, 8, 10; Kiparisovaya 2, 4, 6, 14, 16
Houses of the 125th series are the favorites of Vladivostok residents. They are less common than those listed above and are located on the outskirts and hills of the city. According to residents, the advantage of the layout of this series is the large area of the kitchen and corridor; the rooms have a square shape, and not an elongated rectangular one as in the houses of the 83 series.
Usually, advertisements for the sale of apartments indicate the series of the house, therefore, by taking care of this issue in advance, you can find housing that meets all your wishes.
The majority of housing in apartment buildings in Moscow and the Moscow region are apartments in serial (standard) buildings. A series of houses is a group of residential buildings with identical apartment layouts, engineering structures and building materials used. The layouts in such houses are called standard. You can combine different series of houses based on wall material or time.
Based on the building materials used, three main types can be distinguished:
- Brick houses
are standard series, the external walls of which are built of brick. - Panel houses
are standard series built from prefabricated reinforced concrete panels. - Block houses
are standard series, the external walls of which are built from concrete blocks.
Based on time, four main periods of construction can be distinguished:
- Stalin series are standard series of houses designed in the 1950s. The houses are mostly brick or block. Distinctive features are high ceilings, spacious rooms, large corridors and kitchens.
- Khrushchev series - standard series of houses designed between 1956 and 1964. The houses are mostly panel, sometimes brick. Distinctive features are small kitchens, lack of elevators, combined bathrooms, poor heat and sound insulation.
- Brezhnev series are standard series of houses designed in the USSR from 1965 to the end of the 1980s. There are both brick, panel and block projects. The number of floors gradually increased, first to 9, and then to 17 floors. Later projects are distinguished by a wide variety of designs and successful standard layouts. The most successful Brezhnev series were modified and are still being built today.
- Modern series are standard series of houses designed since the early 1990s. They differ from the previous ones in an attempt to add individual features to standard houses, houses of variable number of storeys and combined houses appear, apartment layouts become more spacious, and the quality of the exterior and interior decoration of buildings increases.
The site features most of the model series of homes built since the 1950s. Those. 90% of all possible options for standard apartments and houses presented on the market in Moscow and the Moscow region.
114-85 or simply 85 is an all-Union standard series of multi-apartment brick residential buildings in the USSR. The series was developed by TsNIIEP Dwellings in 1969 based on the 1-447S series. Series 85 houses were built from 1974 to the mid-2000s. The houses in this series belong to the Brezhnevkas of the late period (“improved” or “new layout”). Five-story modification. Recognizable by the alternation of wide loggias recessed into the facade and protruding small balconies, from the entrances - two paired loggias recessed into the facade
Series:
114-85
House type:
brick
Manufacturer:
The manufacturers of this series of houses are local construction companies.
Years of construction:
1970-2000s
Number of floors:
5 or 9 (10) floors.
Number of rooms in apartments:
The number of rooms in the apartments of this series ranges from 1 to 4, however, in some modifications there are no one- and four-room apartments
Height of living quarters:
2.48 m
Number of apartments per floor:
3 less often 2
Number of sections (entrances):
Multi-sectional houses designed according to the block-sectional principle. The series includes both ready-made houses and block sections - row, corner, rotary block inserts. The block-sectional principle allows you to “assemble” houses of various shapes from sections - straight, angular, curved. Block sections are designated by indexes 85-0хх, ready-made house projects are designated by indexes 114-85-хх.
Elevators:
9-storey modifications have 1 passenger elevator
Stairs:
double-flight from prefabricated reinforced concrete marches and platforms
Ventilation:
natural exhaust ventilation
Garbage removal:
available on each interfloor platform
Loggias:
There is
Balconies:
There is
Baths:
standard (not seated)
Bathrooms:
separate
Load-bearing walls:
Load-bearing walls - external and transverse internal walls
Wall material:
The wall material is brick, most often white silicate; there are houses made of red brick
Floors:
Floors - hollow-core reinforced concrete slabs 220 mm thick
Series 114-85 includes a large number of modifications: standard projects with a height of 5 and 9 floors, as well as small-family and projects for rural construction. Advantages: the apartments have loggias, a variety of planning solutions, separate bathrooms, good heat and sound insulation. Disadvantages: some modifications of the series do not have one- and four-room apartments
Remodeling 2-room apartments
With two-room apartments there are usually more options: after all, there is more space, which means they provide more room for imagination.
Make a two-ruble into a three-ruble
Having a two-room apartment, you often want to turn it into a three-room apartment. In the option proposed below, a distant long and narrow room with a built-in wardrobe is divided into two. Moreover, the partition was made nonlinear, which made it possible to organize two closets for storing clothes.
Convert a 2-room apartment into a 3-room apartment
The alterations also affected the bathroom area. It is enlarged due to the corridor. The area became almost twice as large, which made it possible to install a washing machine. Since the entrance to the kitchen from the corridor was blocked, it was made from the living room.
A different type of initial layout and a different approach. Strictly speaking, there are two rooms left, but two zones have appeared - the living room and the dining room. As a result, the rooms turned out to be separate and both can be used as bedrooms - one for adults, the other for children. At the same time, the family will have a spacious room where everyone can gather.
Turn a two-room apartment into a three-room one
The advantage of this plan for remodeling a two-room apartment is that it is possible to make wall cabinets in both rooms.
Another layout option with widely spaced rooms. The task is the same: to have three dedicated rooms. If you don't bother with a global relocation of the kitchen and bathroom, then there are two possible options.
Not the most comfortable apartment to remodel
In the first case, the partition separating the corridor is removed and the resulting space is divided by partitions (blue) or translucent partitions (green). In the back room there is a closet. The second method is more obvious - they divide a large room into two small ones, dividing the exit to the balcony.
Changing the size of the bathroom and hallway
In many cases, redevelopment concerns the bathroom and hallway. Sometimes the size of the hallway is increased by reducing the bathroom, and vice versa. Such options are presented in the photo below.
Redevelopment of three-room apartments
As in other 3-room apartments, the main idea is to enlarge or combine the bathroom, a more rational use of the available space. Specific solutions depend on the wishes of the owners.
Optimization of space use (due to the corridor)
In the version presented below, the partition separating the living room from the corridor has been dismantled. The result is a spacious room, giving scope for the implementation of various kinds of design ideas. The bathroom and toilet are combined, one door is blocked. This made it possible to slightly increase the area of the second room.
Increasing living space due to the corridor
Another project also reduces the size of the corridor. This area is part of the living room, but it becomes a walk-through area, which is not critical for this room. The alterations also affected the bathroom - the partition between the toilet and the bathroom was removed, and the area was also expanded a little by moving the wall into the corridor. Due to the same corridor, the kitchen area has been increased - the door block has been placed almost close to the entrance to the bathroom.
Optimizing space use
And the last alteration is the dismantling of the non-load-bearing window sill and the installation of sliding glass doors in the floor instead of the former window block.
Organization of a second bathroom
In four-room apartments, the areas are already large, and quite a lot of people can already live. Therefore, in such cases they often want to make a second bathroom. The main difficulty is whether there are technical capabilities to supply water supply and sewerage. Also, they will not be allowed to install a bathroom above residential premises - only above technical ones. In these redevelopment projects, the second bathroom is planned in place of the closet, which is possible.
Changing the corridor area
All major changes relate to the use of the hall area, as well as the size of the second bathroom. The purpose of the rooms (all except the kitchen) may also change.
Architectural educational program. 10 standard series of residential buildings in Kazan
Brezhnevkas, or improved apartments (improved apartments), are a series of houses that were built during the reign of Leonid Brezhnev: from the mid-1960s to the end of the 1980s. In Brezhnev's houses, unlike Khrushchev's, there was a watch, an elevator and a garbage chute. They were taller, with more apartments on the landing (from four to eight) and rooms in the apartments. Four-room apartments appeared in Brezhnevkas and the number of three-room apartments increased. Adjacent rooms are found mainly only in three-room apartments.
Brezhnevkas also include small-family and hotel-type houses. Hotels, as a rule, were built in the 1960s and 1970s as temporary housing for employees of large enterprises. These are panel or brick buildings from three to 16 floors. On each floor there are 10-40 apartments - small one-room apartments (include a living room, kitchen, hallway, bathroom) and tiny rooms with a kitchen niche in the hallway and a combined bathroom. A striking example of a hotel of the second type is the house on Musina, 59b.
Small families are an intermediate type of housing between dormitories and individual apartments, which were built in the 1960s–1990s. The houses consist of one-room apartments, their height is five, nine or 12 floors. The walls are made of brick or reinforced concrete panels. On each floor of the house there are from 10 to 20 apartments, the entrance is a corridor type. A small family consists of a living room with an area of 11 to 20 square meters, a kitchen with a street window, a small hallway, and a combined bathroom; rarely - storage rooms and balconies.
After the decree “On the Elimination of Excesses in Design and Construction” was issued, the country abandoned Stalinist buildings, but party workers and the elite did not want to live in panel houses. And since 1963, the USSR began to build tsekovsky houses (or tsekovkas) - buildings made of strong brick according to individual designs. “Elite” houses were externally different from standard high-rise buildings, but did not have their own architectural image.
In the 1970–1980s, the USSR also used the term “Leningrad layout” (Leningradki) - apartments built according to an experimental design by Leningrad architects (apartment area - 32-85 square meters; windows face one side; apartments have a large separate bathroom; kitchen area - 8-10 square meters; the houses have an elevator and a garbage chute. - Note "Inde"). More spacious homes built in the 1980s were called "new floor plans."