Hi all! The range of thermal insulation materials is constantly expanding. At the same time, new developments appear that are noticeably superior to their predecessors, as well as competitors. New insulators include Tepofol insulation.
I would like to talk about what kind of material this is, what its features are, as well as how it is produced and in what industries it is used.
We will also touch on the topic of tepofol or penofol - which is better, since both materials are often compared with each other.
Comparison of insulation for balconies and loggias
A balcony, according to Wikipedia, is “an unheated room in the form of a fenced area protruding from the plane of the façade of a building.” It's nice and cool in the summer, but in the winter? There comes a time when there is a desire for the balcony to please even during the long winter months of our harsh winter.
A modern balcony, if you apply a little imagination, desire, materials and material investments, is an additional room that can be used at any time of the year. This is also a room for receiving friends, where you can drink a cup of tea or a glass of wine and chat.
This is a study room with a small bookcase and computer accessories, and a relaxation room. where you can read, knit, daydream, or a playroom for children. This means that in order to use the balcony in winter, you need to insulate it.
Which insulation material to choose
There is a large selection of thermal insulation materials on the modern market. How to understand them and make a decision in favor of a certain material? What parameters are important?
Parameters of thermal insulation materials
Weight . The less weight of the insulation, the less weight the balcony structure will take after installation.
Material thickness . The thinner the material used, the more free internal space the balcony has.
Thermal conductivity . The lower the thermal conductivity, the higher the retention of internal heat in the room.
Moisture permeability . The lower the moisture permeability, the lower the effect of moisture on the material and the lower the thermal conductivity.
Soundproofing. Protection of the interior space from excessive noise from the street.
Fire safety. The material must be non-flammable and, when exposed to elevated temperatures, must not emit toxic fumes.
Environmental friendliness. The material used must be environmentally friendly for both human health and the health of the environment.
Economical. Must be economically accessible to a wide range of consumers.
Durability. The longer the period of use of the material, the cheaper it costs the consumer.
Easy to use during installation. This point is important for people who like to do their own repairs.
Insulation of interior walls
To prevent the walls from becoming covered with fungus and mold from moisture entering from outside, you need to insulate them using foil foam. It is better to use penofol types A, B and C. The choice depends on the installation method and the expected result. Type A
used as an additional layer of insulation.
Attached to the main insulation to protect against moisture. Type B
is used as the main thermal insulation material.
Type C
can be mounted on a wall base.
To fasten penofol indoors, use a stapler. The thickness of the material is 4–5 mm. If the house is very cold, you first need to insulate the walls with polystyrene foam and cotton wool.
Carrying out installation work:
- A frame is first made on the wall using wooden slats. The slats should be no more than 15–20 mm thick. Leave an air space of about 2 cm on both sides of the foam foam for the material to work effectively. The frame beams are attached at a distance of 1 m from each other.
- Check the condition of the electrical wiring and apply additional insulation if necessary. Aluminum foil material has good electrical conductivity. Penofol should not be allowed to come into contact with exposed wires.
- Attach penofol to the wooden frame using a furniture stapler. Cut the strips and lay them end to end, sealing the seams with aluminum tape. Make sure there is no overlap at the edges. Condensation may drain when steam is formed.
- A frame with an air “cushion” of 2 cm is mounted on penofol and fastened with plasterboard panels, plywood boards, sheets that can be puttied, painted or wallpapered.
Ceiling insulation
. We fasten the first cut strip along the wall in the middle of the ceiling. We begin to lay penofol from the strip to the corner. Having reached the corner, nail the edge of the last strip. Do this procedure on the other side of the strip and nail the edge. Do not forget to constantly smooth the foam foam on the ceiling.
The wall surface does not need to be pre-prepared; it does not need to be processed.
What is the difference between penofol and isolon?
Penofol and the like Teplofol, Energofol (foil insulator based on foamed polyethylene)
This insulation consists of several layers of polyethylene foam, having unequal density, thickness and different porous structure. The insulation also has a layer of foil for a reflective insulation effect.
Penofol has a thickness of only a few millimeters, which is on average 10 times thinner than conventional mineral wool insulation. It reflects about 97% of thermal energy and is very light and thin. Penofol is used for internal and external thermal insulation, vapor barrier, sound insulation, waterproofing, has a long service life, is not particularly difficult to install and is relatively inexpensive.
Izolon, Penolon (foil insulator based on foamed polyethylene)
This material has the structure of foamed cross-linked (physically and chemically) polyethylene and is used for thermal insulation, sound insulation, vapor barrier, and moisture insulation. Penolon (izolon) is an ideal option for insulating balconies and loggias. It does not compact after a long time, does not create dust and does not emit substances harmful to the body.
Externally, Penolon is an elastic, mostly white, sometimes with a yellowish or grayish tint. The canvas is produced in rolls and sheets. The surface of Penolon has a slight roughness. It is used for both internal and external thermal insulation, sound insulation, waterproofing, vapor barrier, is not subject to wear, and is easy to use. The price is affordable.
This thermal insulation insulation is made using steam foaming of polystyrene. Polystyrene foam has very low weight and low thermal conductivity, is resistant to dampness, is easy to cut with a sharp knife, has low compressibility, and is easy to use during installation. Due to its low cost, it is in priority demand for insulating balconies.
Differences between Isolon PPE and NPE
The differences between these two types of Izolon are visible to the naked eye, and they also have different areas of application. Externally, Izolon NPE has larger cells and is less elastic to the touch. It is undesirable to use it under point loads, since air-filled cells can burst, depriving the material of its noise-absorbing and heat-insulating properties. Large cells contribute to the formation of a rather uneven surface of the material, which can complicate the process of gluing it and subsequent leveling of the surface.
Most often, this type of Isolon is used when carrying out packaging work, as well as when it is necessary to create a shock-absorbing pad. Thanks to a simpler production method, NPE is an order of magnitude cheaper than polyethylene foam with a cross-linked molecular base.
PPE costs a little more, but its technical characteristics benefit in many ways. It is stronger and more elastic, better adapted to changes in ambient temperatures and mechanical stress, and it is also more durable. This material has a perfectly smooth surface, making it easier to install. When gluing the material, several times less glue is used than when installing NPE.
Penofol: what is it and why is it needed?
Various building materials are used to insulate residential and non-residential buildings. Penofol is also used as insulation. Let's consider what this material is, what its advantages and disadvantages are.
What it is?
Penofol is a two-layer heat-insulating building material, which can be made from one or 2 layers of foil applied to a base layer of polyethylene foam. Depending on the type of product, the density and thickness of the foam may vary. Utilitarian and inexpensive insulation is in great demand among buyers, because it has high performance characteristics.
A layer of foil, the thickness of which is 20 microns, provides penofol with excellent heat-reflecting qualities.
This insulation is used in everyday life and industry as the main insulating material or as an auxiliary thermal insulation layer.
Penofol is used as the main insulating material in cases where it is necessary to insulate a room with normal heat loss and where there is a powerful heating source (bathhouse, sauna, underfloor heating system in a wooden house). As an additional insulating building material, penofol is used to create complex heat insulation in residential and industrial premises, and such premises must be equipped with vapor barrier and waterproofing.
Areas of application of foil penofol
Penofol is available in rolls. The thickness of the material is 2-40 mm. At the same time, the same indicator of foil varies between 12-30 microns, which ensures good heat-reflecting qualities of the material. The thickness of the foil layer directly affects the price of penofol per m2. The thinner the thermal insulation material, the lower its price. The most popular insulation is 5 mm thick. The price of foil penofol is 120 rubles/m².
Foil penofol is used for steam, sound, moisture and heat insulation
This material has a wide range of uses. It is used for thermal insulation of residential single- and multi-storey buildings, industrial and administrative buildings, saunas and baths, cold and heated hangars, warehouses, refrigerators, permanent, stationary and mobile trade kiosks and shops, railway cars, refrigerators, vans, pipelines of various types. purpose, heating, air conditioning, ventilation and water supply systems, and is also intended for technical insulation of equipment.
It can be safely used for waterproofing attics, basements, attics and basements. This is reliable heat and sound protection for loggias and balconies. Penofol can be used for finishing external and internal surfaces of walls, ceilings, floors, and ceilings above cold rooms in basements. The material is used to shield heating radiators, insulate and seal window and door systems.
Foil penofol is in great demand among motorists. Using this material, you can perform high-quality noise and sound insulation of the body of a car and truck.
Advantages and disadvantages
The use of penofol has its advantages:
- The small thickness of the material allows you to create reliable thermal insulation of the room.
- Installation of building materials does not require special skills or special tools. Working with this material is much easier than with other types of insulation.
- The material is environmentally friendly, which makes it possible to use it for storing food.
- Fire safety. This building material belongs to the class of fire-resistant materials.
- Ease of transportation. The thickness of the product allows the insulation to be rolled up, which allows it to be transported in the luggage compartment of a car.
- Excellent sound insulation. Mounting penofol on top of the frame of building structures provides good insulation of extraneous sounds.
Penofol has not only positive qualities. There are also disadvantages to using this building material:
- The insulation is soft. Because of this, this product is not used for finishing plastered walls. When lightly pressed, the material bends.
- To fix the insulation you will need special adhesives. It is not recommended to nail it to the surface, because in this way penofol loses its thermal insulation qualities.
What to glue it with?
A correctly selected adhesive solution for foil material does not yet guarantee a successful installation. For a quality connection of materials, it is necessary that the surface to be glued be carefully prepared. All defects, irregularities, and various debris must be eliminated.
To improve adhesion, materials made of metal, concrete and wood can be treated with a special primer solution.
Concrete floors and walls are leveled, cracks are sealed, and metal products are treated with an anti-corrosion agent.
Adhesive for foil insulation can be either specialized or universal. You can also use liquid nails, double-sided tape, or a thin layer of foam. The choice of glue depends entirely on the purpose of the surface and its further use.
The adhesive composition must correspond to the performance indicators of the insulating material:
- permission for indoor use;
- the toxicity of the solution should be 0;
- high resistance to adhesion;
- the glue must withstand temperatures in the range of -60 to +100 degrees.
If insulation is carried out externally, then the adhesive solution must be resistant to water vapor and liquid.
In order for penofol to be reliably glued to the surface, the glue must be applied to the side that does not have a foil layer. The adhesive solution is applied evenly, without gaps. The edges of the panel are carefully coated with glue so that the foil material does not come off during operation.
Before you start fixing the penofol, you need to wait 5-60 seconds for the glue to dry slightly. This ensures better adhesion to the products. Penofol is pressed to the surface, holding it, and smoothed out with special care.
If the insulation is glued in pieces, then the joints are additionally glued.
Which material is better?
As you know, heat is transferred from product to product in 3 ways:
- heated air;
- thermal conductivity of materials;
- radiation - heat transfer from one product to another occurs using electromagnetic waves in the infrared spectrum.
Let's look at some differences between penofol and other thermal insulation materials.
Most thermal insulation building materials (mineral wool, isolon, penoplex, tepofol) interfere with one type of heat transfer. A distinctive feature of foil material from other types of insulation is that it has a complex effect: foamed polyethylene is an obstacle to convection, and thanks to aluminum foil, the thermal reflection rate reaches 97%.
Penofol can be compared with only one group of thermal insulation materials - isolon. Comparing isolon and penofol, there is no significant difference in the quality and method of their use. To determine the winner, you need to look at the availability and price category of a particular building material. The only advantage of Izolon is that the range has been expanded with sheet building materials, the thickness of which ranges from 15 to 50 mm.
Penofol is mounted using glue, and the penoplex is fixed using fungal screws. Also, foil insulation does not accumulate heat, but rather reflects it.
Mineral wool is attached only to vertical slats. The price category of penofol is significantly lower than that of mineral wool.
Properties of penofol
Foil penofol is an insulating material with a reflective effect, which has a multilayer structure.
The main purpose is to remove drafts or wind currents from building structures, eliminate condensation or moisture, steam that rise up the tiers. The material also isolates external noise or sounds. It is a universal type of insulator, as it increases sound insulation, vapor barrier, protects against moisture and retains heat. Such features are due to the structural organization of the material and the technology used in production. The main part of the material is foamed polyethylene . At the same time, the pores formed on it are closed and filled with air. This polyethylene foam is used in the form of skeins with different densities, thicknesses and different internal structures. Either on one or both sides, based on the purpose of the material, polyethylene is covered with aluminum foil. Before application, it is processed and polished to a shine with a maximum reflectivity coefficient (up to 97% and even more). More often, foil is applied using heat welding, which provides better adhesion of the material.
The thickness of penofol is from two to ten millimeters, the foil is only from 12 to 30 microns. The thickness of the material can be increased to 40 mm if it is necessary to create particularly powerful thermal insulation, for example, in arctic climate conditions.
The operation of penofol is based on the “Dewar vessel” principle known in physics. At the beginning of the last century, James Dewar established that every substance has a certain resistance to heat transfer. Whatever this indicator, the material can only stop or make the movement of heat slower, but not stop it altogether. At the same time, heat waves are collected in the substance and energy accumulates inside the substance; after some time, supersaturation is created, after which any material itself becomes a source of heat.
Experimenting further, Dewar isolated several substances that did not absorb thermal energy, but reflected it. Among these were all precious metals (platinum, silver and gold), as well as polished aluminum. In this case, heat rays are reflected from surfaces almost 100%. These reflectors themselves are excellent heat conductors and should be used together with heat absorbers.
A common thermos works in approximately the same way, and Dewar's research became the basis for the creation of space suits and materials for thermal insulation with a reflective effect.
The use of both double-sided and single-sided insulators reduces the cost of heating rooms in winter, and in warm summer weather they prevent the house from heating up too quickly.
Penofol
About the manufacturer
Penofol is a brand produced by LIT Plant, which was founded in 1979. The company was the first in Russia to begin applying a reflective layer of foil to the surface of foamed polyethylene. Thanks to this fact, the Penofol trademark is widely known in the Russian market.
Very often, the consumer calls penofol any insulation made of foamed polyethylene with a reflective surface. And this despite the fact that in Russia there are about 30 similar manufacturers with their own brands.
The main activities of the enterprise are:
- production of energy-saving materials based on polished aluminum foil, operating on the principle of reflecting heat flow (reflective thermal insulation), intended for insulation of enclosing structures of residential and industrial buildings;
- production of materials from foamed polyethylene intended for technical thermal insulation of heating and water supply, ventilation and air conditioning systems, for use in “warm floor” systems, as well as for protecting thermal insulation from mechanical damage, atmospheric influences and ultraviolet radiation.
The company is successfully developing and producing products for various purposes under the trademarks: PENOFOL®, TILIT®, ARMOFOL®, TITANFLEKS®, used in construction.
About products
A distinctive feature of Penofol is its blue color. In principle, only foil is used as a reflective layer. Excellent quality material with an adhesive layer, one of the best on the market, if not the best.
Since 2015, LIT Plant began producing the updated Penofol material with additional protection against counterfeiting - a hologram, which is printed on both sides on polished aluminum foil.
Characteristics of regular and self-adhesive penofol
Depending on the manufacturing technology of the heat insulator, there are three main types of penofol: A, B and C. The first group is represented by a polymer insulating material with one-sided foil. It can have a thickness from 2 to 40 mm. The width of penofol is 40-120 cm. This type of insulation is often combined with other material options in the form of mineral wool or glass wool; it is often used for thermal insulation of floors.
Penofol type B has double-sided foil, which achieves a higher insulation effect. The thickness of the material is 2-10 mm, width - 58-200 cm. This version of the reflector is used for thermal insulation of load-bearing structures of walls, floors, waterproofing of the attic and basements.
Helpful advice! Laying insulation B under the roof will create an obstacle to hot air entering the premises in the hot summer.
The most popular types of penofol include products of types A, B and C
Penofol type C is a self-adhesive version of insulation, which is covered with polished aluminum foil on one side, and on the back there is a moisture-resistant adhesive composition, covered with a protective film, which prevents adhesion. This material can be used for thermal insulation of any surface, which makes it possible to significantly save time. Penofol C is especially preferable for finishing inconvenient areas of the structure. Before use, the material is cut into elements of a certain size.
Helpful advice! For conventional insulation, the base is white, but for penofol 2000 type C, A or B it is blue, which indicates a cheap analogue of the standard material with lower characteristics.
Other types of polymer insulation with foil
There are other types of penofol that are in less demand. Type R material has one-sided foil on which a relief pattern is applied. This option can be used not only as insulation, but also as a decorative element to decorate the structure, as demonstrated in the photo of the foam foam used to decorate the walls of the premises.
SML panels: a modern and multifunctional analogue of drywall
Description of the material, advantages and features. Scope of application, prices and customer reviews. Painted magnesite plate.
Insulation grade M also has one-sided foil coating. The other side of the material has a relief surface. It is advisable to use penofol insulation of this type for finishing places where it is necessary to create an air layer, which is often required when arranging a loggia or balcony. In this case, the ribs on the surface should be located vertically, due to which a good level of ventilation of the structure will be achieved.
Products of type R are equipped with a relief pattern and one-sided foil
Highly specialized types of penofol include materials such as ALP and NET. The first option has a coating of polyethylene laminated film, which ensures high reflective properties of the material, increased corrosion resistance and good dielectric properties. This type of insulation is typical for finishing incubators, and is also ideal for a “warm floor” system.
Helpful advice! You can check the quality of the insulation by looking through it into a bright light, which should reflect all the spots, stripes and unevenness of the material.
Penofol type NET is similar to option B, but is produced in narrow roll strips, making it convenient to use as an insulator for pipelines, heating mains and air vents.
Among the new products we can highlight perforated penofol. A distinctive feature of the material is its ability to “breathe”, which is achieved due to the presence of a large number of micro-holes. This option is most appropriate to use for thermal insulation of wooden structures.
Penofol type M is suitable for insulating loggias and balconies
Tepofol
About the manufacturer
Tepofol is a brand, a registered trademark also belongs to Tepofol LLC. The manufacturing company was founded in 2004 and began its activities by designing and putting into practice a laminator for applying a reflective layer to a polyethylene foam surface.
“Tepofol” is the founder of a completely new thermal insulation material made of non-crosslinked polyethylene foam and seamless insulation technology based on it. Currently, Tepofol is not only the first and leading domestic manufacturer, but also the only company in Russia and in the world in the segment of production of insulation in rolls (thickness over 50 mm) with a patented technology for interlocking the material.
Unlike Penofol, the production company specializes only in foamed polyethylene and products made from it.
About products
A distinctive feature of Tepofol is the edge of the locking connection at the top and bottom of the roll.
Foil or metallized Mylar film is used as a reflective layer. Tepofol is used for basic (20-150 mm) thermal insulation of residential premises and construction sites. Tepofol for additional thermal insulation
Additional thermal insulation (2-10 mm) is used as a supplement to the main insulation when insulating a house structure, as well as in other design solutions for vibration, hydro, and noise insulation of residential premises and construction sites.
Tepofol for basic thermal insulation
Tepofol (20-150 mm) is widely used as the main and only (without insulating membranes) thermal insulation instead of traditional types of insulation (foam plastic, mineral wool, expanded polystyrene, etc.). Insulation of an object based on Tepofol and seamless technology is simple, easy to install, reliable, and does not require replacement for many years. Not only foil is used as a reflective layer, but also metallized lavsan film is used for use in a humid environment to avoid corrosion of the foil.
In addition to the production of thermal insulation material, we have extensive practical experience in insulating various objects, on the basis of which unique technologies have been developed and patented that guarantee high insulation results for many years, namely:
- insulation of industrial buildings, warehouses, hangars (frame, frameless, tent);
- insulation of private residential premises (walls, roofs, floors, foundations, attics) and frame houses;
- insulation of balconies, loggias;
- thermal insulation of sports facilities, including facilities where it is necessary to maintain snow or ice cover;
- insulation of objects in the Arctic zone;
- and others.
Application and installation
This material can be used as an independent insulation material or in combination with other materials. You can simply glue it to wooden walls under the finishing and in this way you will significantly increase the thermal insulation characteristics of the building.
Penofol can be used not only for insulating walls; it can be used to insulate warm floors and ceilings. Installation can be done by yourself without the involvement of specialists.
To attach to a wooden wall, you can use glue, a stapler or nails; the seams must be taped with aluminum tape so as not to violate the integrity of the insulation layer. The reflective side of the material should be directed towards the room.
Foil penofol is used to insulate hoods and air ducts; this is easy to do, as it is very elastic. Another advantage is that installation can be carried out at any time of the year. To carry out installation you do not need to have special equipment.
Between penofol and other finishing materials, it is necessary to leave a gap for ventilation so that moisture does not accumulate. If we talk about the service life of this insulation, we must remember that it is based on polyethylene foam, and its service life is more than 200 years, so penofol will last for decades.
Advice: for insulation you can also use the “old-fashioned method”, namely, an environmentally friendly and economical method.
Mineral wool and polystyrene foam are often used for thermal insulation.
Despite the fact that this material has many advantages, like any other insulation, it also has some disadvantages:
- it does not have sufficient rigidity, so it cannot be glued with wallpaper or plastered;
- some people nail penofol with staples, but in this way its thermal insulation characteristics deteriorate; it is better to use special glue or rolls with a self-adhesive base;
- For complete wall insulation, the use of penofol alone will not be enough; it must be used in combination with other materials.
If during the installation of the specified insulation you accidentally cut it, then it’s not a big deal. The specified place must simply be sealed with aluminum tape.
This material is also suitable for installing heated floors; for this you need to use penofol A-LP or regular A-03, but you need to lay a film under it.
I know that penofol is a good insulation product, but I still have questions for the experts.
I would like to know about its use as insulation under linoleum in an old wooden country house. There is simply no point in buying something expensive... the house is quite old, we only use it in the summer and autumn, but still the floor is always cold. Insulating building materials are becoming increasingly popular nowadays. Their scope has expanded significantly. When you come to a store or market, it is difficult to understand the assortment of samples offered. In this article we will talk about modern insulating material - foil foam.
Insulation Penofol
In the insulation department of any construction supermarket there is a place allocated for penofol. Thin rolled material with a foil surface attracts attention, but its appearance does not always answer the question of where it can be used.
However, it successfully occupies a whole niche in the field of home insulation, where conventional insulation materials, such as mineral wool or expanded polystyrene, will not help adequately cope with the task.
How to lay penofol with your own hands
The best insulation effect is achieved if you adhere to the following rules:
- Between the structural element and the insulation itself, you need to leave some distance for the sake of ventilation, no more than a couple of centimeters.
- If you install one-sided penofol, the layer with foil should be directed in the direction where the heat will come from.
- It is better to connect sheets of material joint to joint, which gives uniformity in heat reflection. But if, for example, a loggia is insulated, joining using the overlapping method to a width of up to 10 cm is also acceptable.
- When sealing joints between sheets of materials, tape, also foil, should be used.
It is very important to remember that this material must be attached taking into account the fact that the reflective aluminum foil conducts current. Therefore, if there is wiring nearby, it is necessary to insulate the wires well.
An example of using penofol for insulating walls and floors
Once a material suitable for the operational requirements has been selected, additional waterproofing, protection from steam or heat can no longer be used. It will also be possible to save on the installation process and materials necessary for high-quality insulation and insulation of surfaces. You can also watch several videos on this topic.
What is Penofol
Penofol is a practical and inexpensive insulation made of non-crosslinked polyethylene foam with aluminum foil applied on one or both sides of the material. Gas-filled cells are sealed and closed, which provides high compressive strength, but does not interfere with the bending of the material. The cell size is usually from 0.5 to 2 mm.
Its advantage is its dielectric properties - it does not allow electric current to pass through , which is especially important when installing electric heated floors.
The insulation stands out from the rest due to its affordable price and simple installation method, however, due to thickness limitations, it is used in a fairly narrow number of cases where it is only necessary to supplement the existing enclosing structures, increasing the overall resistance to heat loss.
Penofol has found its main area of application in air conditioning and thermal insulation systems, where the bulk of the heat is transferred using infrared radiation.
Three types of penofol are produced:
- Type A - with one-sided foiling;
- Type B – with double-sided foil;
- Type C – foil on one side and self-adhesive surface on the other side.
The choice of a suitable option is determined by the direction of propagation of the target thermal radiation. For example, one-sided penofol, when installed on the wall of a living space, when the foil surface is facing inward, protects against heat loss from inside the house to the outside. This means the house will be warmer in winter.
Double-sided penofol can not only prevent heat loss from the house to the street, but also the flow of heat from outside. So it will be warm in winter and not hot in summer, since the heat from the walls irradiated by sunlight will not overheat the air inside the room.
Varieties
See also:
What is the best way to sheathe a frame house: a review of materials for the facade
In addition to the type of coating made of foil or sprayed metal, tepofol is divided into several categories.
- Type
A. This is a rolled material made of foamed stitched polyethylene. On one side it is covered with a metallized film. Suitable for pitched roofs, ceilings, walls, floors and attics. Can be used as a reflector for heating radiators. Tepofol type A is also used to insulate pipes; - Type
B. There is a double-sided reflective layer in the form of aluminum foil. There is polyethylene foam between them. This structure provides maximum protection against heat loss. Used for insulation of floors, walls, pipelines. They also install air ducts, an attic, and a roof. And not only for heat protection, but also for noise and moisture protection; - Type
C. The structure includes a metallized film, polyethylene foam, an adhesive layer and a protective coating. Can be used on roofs and attics. It insulates well and protects walls from noise and moisture. Can be used in baths and saunas.
Based on what needs to be isolated and where, you can select the appropriate type of tepofol.
Specifications
A significant part of the thermal energy is distributed in the form of radiation, and therefore the heat-reflecting surface of penofol allows not only to slow down heat loss, but to turn the heat back into the room in winter or prevent it from coming from outside in the hot summer.
The layer of foamed polyethylene acts as a strong and durable base for the aluminum screen, and at the same time copes with thermal insulation in the usual way, increasing the thermal resistance of the fences. That is why it is difficult to compare penofol with traditional insulation using a simple calculation.
Aluminum, even of this thickness , does an excellent job of reflecting up to 97% of thermal radiation , while foamed polyethylene provides thermal insulation in the classical way, preventing convection heat transfer.
| Characteristic | Unit. | Type A | Type B | Type C |
| Operating temperature | ºС | -60..+100ºС | ||
| Thermal reflection coefficient | % | 95-97 | ||
| Coefficient of thermal conductivity | W/m*K | 0,037-0,049 | 0,038-0,051 | 0,038-0,051 |
| Water absorption by volume | % | 0,7 | 0,6 | 0,35 |
| Specific gravity at 4 mm thickness | Kg/m3 | 44 | 54 | 74 |
| Dynamic modulus of elasticity under load 2kPa | IPA | 0,26 | 0,39 | 0,26 |
| Vapor permeability | Mg/m*h*Pa | 0,001 | ||
| Compressive strength | MPa | 0,035 | ||
| Specific heat | J/kg*K | 1,95 | ||
To compare penofol with other materials, it is more clear to use the value of the total heat transfer resistance R under equal operating conditions and a difference between external and internal temperatures of 40ºС.
For example, penofol 3 mm thick Type B (double-sided foil) according to tests creates a resistance equal to 1.173-1.064. Similar resistance is provided by:
- 1.7 m of concrete;
- 77.40 cm of expanded clay concrete;
- 11.70 cm wooden beam (oak);
- 55.0 mm mineral wool (stone);
- 42.2 mm EPS;
- 36.0 mm polystyrene foam;
- 31.7 mm polyurethane foam.
The numbers are impressive, but such results can only be achieved if operating rules are followed and provided that the main source of heat transfer is radiation. Simply put, in the absence of active convection air flows in a heated room.
Ceiling and roof covering
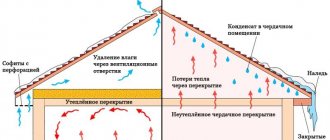
It is proposed to do preliminary insulation of attic roof slopes according to the following scheme (shown above in the drawing):
- Waterproofing - a diffusion membrane - is laid horizontally on top of the rafters, with a minimum overlap of 100 mm. The order of fastening the canvases is from bottom to top.
- The membrane is pressed against the beams with counter-lattice bars, and horizontal boards of the main sheathing are nailed to them. A roofing covering is mounted on top - metal tiles, slate, profiled sheets, and so on.
- From the inside, horizontal beams 50-60 mm thick are attached to the rafters, the installation step is 60 cm.
- Three-layer “Penofol” type B with two foil surfaces is applied to the bars. Note that the thin insulation goes around the rafters so that there is a gap on both sides.
- The internal lining - lining, moisture-resistant plasterboard, chipboard panels or other finishing materials - is vertically screwed to the ends of the bars.
Attention! The Penofol roll is rolled out vertically on the surface, adjacent sheets are laid end-to-end, not overlapping. We carefully seal the seams with aluminum tape.
To seal the joints, use a mounting tape with a width of at least 50 mm.
In this case, the insulation reflects heat flows on both sides, which is very useful in the summer, when the metal roof gets very hot. The inner layer remains unventilated, moisture from the external air is removed through the membrane. Since Penofol serves as a vapor barrier, it is necessary to organize natural exhaust in the attic using a separate ventilation duct.
Please note that there is an inaccuracy in the drawing above - there is no external counter-lattice that creates a ventilation duct above the superdiffusion membrane. In the next version of the diagram, which shows the thermal insulation “pie” of the attic roof, the frame of the sheathing is clearly visible. What is different about this cladding method:
- Between the rafters there is a thick layer of basic insulation - 120-200 mm of mineral wool.
- The bottom of the mineral wool is lined with two-layer “Penofol” type A right along the ends of the beams. The aluminum faces the inside of the attic room, the canvases are turned horizontally.
- A gap of 2-3 cm is left between the polyethylene and mineral wool insulation, and about 4 cm on the foil side.
- We nail the bars for interior finishing to the ends of the beams directly through the layer of polyethylene.
The foil surface faces the inside of the room, a gap is provided between it and the lining.
The section clearly shows that Penofol plays the role of an additional insulator and vapor barrier - traditional film is not used from the inside. The moisture formed in the mineral wool is removed through the upper vent and the waterproofing membrane. Vapors from human activity are removed by supply and exhaust ventilation.
Advice. When working with Penofol, it is important to understand the essence: we always leave a layer in front of the foil, and lay the polyethylene base close to the building structures. We connect the canvases only end-to-end.
Ceilings are insulated according to a similar principle:
- If on the attic side the wooden floor is covered with expanded clay, sawdust or reeds, it is enough to lay 1 layer of “Penofol” type B, creating gaps using lathing.
- Type C material can be glued directly to a concrete ceiling, with the foil facing down. Next, mount the frame for attaching the gypsum board or other finishing.
- When major insulation of the ceiling is necessary, use the attic scheme, only without a membrane and external sheathing. Install a frame of beams or galvanized profiles, insert the main insulation between them, then hem the bottom with type A polyethylene foam.
If Penofol is the only insulator of heat flow (which is not always correct), choose the maximum thickness of the material - 8...10 mm. In tandem with other insulation materials, a sheet with a thickness of 3-4 mm works well.
About the thickness of Penofol
The thicker the insulation, the more expensive it is. And the price and technical characteristics of foil Penofol are influenced by the number of layers of aluminum foil: there can be one or two. As for thickness, its standard sizes are: 10, 8, 5, 4 and 3 millimeters. You can understand that centimeter-thick material with a double layer of foil will be the most expensive. By the way, it not only stores heat better than anyone else, but also protects well from noise.
In terms of optimal price-quality ratio, Penofol with a thickness of 0.5 centimeters came out on top. If maximum thermal insulation, as well as protection from noise and moisture, is required, then it is better to opt for a centimeter layer of Penofol. As for the other parameters of the insulation, they also depend on the thickness of its layer, as well as on its type.
About Penofol's heat conductivity
Since this insulation is combined, combining heat reflection and absorption, it is difficult to compare it with traditional heat insulators. Penofol insulation helps reduce convection due to the polyethylene foam layer, and the foil layer on the outside can reflect up to 97% of heat rays. The result is comprehensive insulation.
And yet, let’s try to compare, if not the thermal conductivity coefficient, but the heat transfer resistance of Penofol and other insulation materials. If we take this material with a thickness of 4 to 5 millimeters, covered on both sides with aluminum foil, we get a heat transfer resistance of 1.2 to 1.23 square meters-degrees Celsius per watt. To achieve the same result, the layer of mineral wool should be no less than 8 or 8.5 centimeters. Data are calculated according to SNIP II-3-79.
About the material's absorption of water
Penofol almost does not absorb moisture, and it does not matter what humidity the air has indoors and outdoors. This does not depend on the change of season or change in temperature. This distinguishes this insulation from most modern heat insulators.
About the vapor permeability of Penofol
There is no need to lay a vapor barrier film when using Penofol. After all, its vapor permeability coefficient does not even reach 0.001 milligrams per meter-hour-Pascal. We can say that this insulation is an excellent barrier to fumes.
Sound resistance
Speaking about the sound absorption of Penofol, we can name the following number: 32 decibels. This is precisely the sound absorption that class “A” material has. It is mounted not inside the frame of the building structure, but on top of it, with no seams. Therefore, it allows you to protect yourself from various noises: both acoustic and structural. This versatility is a definite plus.
Fire protection
According to the standards, this material is classified as substances that are difficult to burn and do not support combustion. The Research Institute of Construction Physics issued Penofol a certificate of conformity confirming that the material is not a fire hazard. When burned, polyethylene releases water and carbon dioxide. True, if there is not enough oxygen, carbon monoxide may appear.
Service life and safety
One of the cleanest materials in terms of ecology is polyethylene foam. Therefore, it is this that underlies Penofol. By the way, in terms of durability (200 years) this substance can be given the highest score. At the same time, you will be able to protect yourself from the harmful effects of electromagnetic radiation. They can be reduced by two or even ten times.
What is it needed for
The main feature of penofol is the presence of a heat-reflecting screen. It is indispensable for insulation:
- walls and ceilings as part of multilayer enclosing structures;
- balconies and loggias;
- pitched roofs, attics and attics;
- utility rooms and outbuildings;
- greenhouses;
- heat-reflecting screen as part of a heated floor system;
- niches with an installed heating radiator;
- air conditioning systems for freezing units;
- pipes and lines with refrigerant or coolant within the permissible operating temperatures.
Covering all the advantages, penofol is ideal for arranging insulated heat-efficient rooms: greenhouses, incubators, vegetable stores, for protecting basements and semi-basements.
Thanks to the hermetic closed structure of polyethylene foam, penofol has good soundproofing properties. Basically, it absorbs shock sound and vibration well, but is less resistant to high-frequency sounds and noise.
As an underlay for flooring, as well as under a thin screed, it will absorb the sound of footsteps or impacts on the floor.
Floor insulation. Under the screed
When insulating floors, penofol is used as a substrate for all types of screeds, wet, semi-dry, dry, bulk or made with any sheet material, as well as as a substrate for all types of floor coverings.
This is facilitated by the high compressive strength of the material and the dynamic modulus of elasticity is much higher than that of any other insulation.
Floor insulation scheme
Polyethylene ensures the strength of air bubbles, which in turn provides uniform shock absorption to any distributed loads.
Taking into account the horizontal distribution of penofol, it is not necessary to attach it additionally to the base.
Balcony insulation
For insulating a balcony, penofol is an ideal thermal insulation material. In conditions of extremely limited space, it will be necessary to subtract only 20 mm from each fence in order to insulate the room with penofol, taking into account the required gap between the insulation and the finishing to form a closed air chamber.
Two installation options are used:
- Uniform laying of the material end-to-end over the entire insulated surface and installation of sheathing for further finishing on top of it;
- First, a sheathing made of 40x40 mm timber is attached, and then insulation is distributed in each cell, extending onto the sheathing elements.
Balcony insulation scheme
In both options, there is no need to use adhesives or a large number of fasteners. In the first case, the insulation will be securely pressed to the base by the sheathing, and in the second case, it is enough to attach the penofol under the very base with a stapler to the same sheathing.
The choice of the optimal option is determined based on the required load capacity of the sheathing and the weight of further finishing.
How to properly lay foil insulation on the floor
To lay foil insulation on the floor, you must first prepare the base, on which all irregularities, defects and cracks must be eliminated. Then the surface is treated with a soil solution.
Helpful advice! To achieve better thermal insulation properties, many experts recommend laying foam plastic 7-12 cm thick under foil insulation on a concrete floor.
When using a type A heat insulator, a thin, uniform layer of penofol adhesive is applied to the base. Particular attention is paid to the edges of the material, which must be carefully treated with adhesive. Next you should wait 10-60 seconds. for the glue to dry, which will contribute to its better adhesion. After this, the insulation is fixed with little force, performing careful smoothing.
For indoor floor insulation, a more convenient option is penofol C 10 mm. To install the material, it is enough to remove the protective polyethylene film from its inner surface. The insulation must be laid in such a way as to ensure that it overlaps the walls by 5 cm. Penofol strips should also not overlap. Protruding areas should be removed using a construction knife. The joints must be sealed with insulating aluminum tape.
Foiled penofol is suitable for the “warm floor” system
Important! When deciding which side to lay the foil insulation on, you should remember that the foil part of the insulation should face the inside of the room, while the opposite side is glued to the floor. In this case, reliable vapor and noise insulation is ensured.
How to lay insulation for a “warm floor” system and on the ceiling
To install a “warm floor” system, two methods of laying penofol are used. The first involves installing joists on the insulation. This option is advisable to use if a wooden floor is mounted on a heat-insulating material. The logs should be laid along such a base on top of the heating elements.
When installing a heated floor under the tiles, the base is covered with foil foam, which is fixed to the concrete surface with glue. Heating elements are mounted on it, which are covered with reinforced mesh and then filled with concrete mixture. For this option, it is recommended to use foil penofol "Leroy Merlin" type ALP.
The laying of electrical cables over foil foam is carried out in a protective corrugation. This also applies to radio cable and telephone wire. This safety measure is explained by the fact that foil is a good conductor.
Foil penofol types A and B are suitable for insulating ceilings
Let's consider how the ceiling is insulated using such material. First of all, self-adhesive foil penofol 5 mm is fixed to the base surface. Wooden slats are screwed onto it to create a frame for type B insulation. It is attached to the bars using screws or a construction stapler. If it is necessary to install a third layer, the process is performed in a similar way.
How to attach
The basis for penofol is polyethylene, which, unfortunately, has very weak adhesion to construction adhesive solutions.
Mechanical methods are used for fastening: self-tapping screws with a press washer, stapler brackets, clamping strips, fixation under the sheathing. When laying on a horizontal surface under a screed, fastening is not necessary at all.
All joints and fastening points where the material has been stitched through are sealed with special tape made from thick aluminum foil or a polymer base coated with aluminum. This will restore the tightness of the insulation layer and give additional strength to the insulation.
Foil self-adhesive
As an additional fastening, double-sided tape can be used along the edges of the penofol strip.
However, manufacturers provide an even better option. The self-adhesive surface of foam foam “type C” makes installation on any clean, prepared surface extremely simple. One side of the material is completely covered with an adhesive composition with the same properties as regular tape, covered with a protective film.
It is enough to prepare the surface, clean, degrease and, if necessary , prime it so that it does not accumulate dust.
Insulation technology
It's time to tell how reflective thermal insulation is installed on the ceiling in a private house. To install insulation on a self-adhesive base, you do not need to construct a sheathing on the base. The base needs to be well prepared - cleaned of old finishes, putty on defects and uneven surfaces. The insulation is glued to the primed surface. To do this, remove the protective film from the adhesive layer.
The heat insulator without an adhesive base is mounted between two battens. Moreover, the insulation is laid in two layers - the first is fixed directly to the main ceiling, after which the sheathing is mounted with other heat-insulating material embedded in its cells, and then another layer of penofol or isolon is attached to the sheathing from below. Next comes another lathing to create an air gap between the insulation and the finish. This ventilation gap will prevent condensation from accumulating.
Tools and materials
To insulate the ceiling with isolon from the inside, you will need the following tools and materials:
- perforator;
- drill;
- wooden slats for sheathing;
- wood hacksaw;
- self-tapping screws and dowels for fastening the sheathing;
- laser level;
- roulette;
- ruler;
- pencil;
- ladder;
- foil insulator (taking into account two-layer laying);
- primer;
- reinforced tape;
- putty;
- rollers and spatulas;
- solution container;
- cutter or scissors;
- stapler and staples for it.
Installation of foil insulator on the ceiling
Installation of penofol on the ceiling is carried out in the following order:
- We remove the old finish from the base ceiling, eliminate all defects with putty, and level the surface with mortar. After the putty mixture has dried, the surface is primed twice.
- We install the first layer of reflective insulator on the ceiling. For initial fixation, we use double-sided tape (if there is no self-adhesive base), then we press the covering with the lathing slats. We install the slats in increments of 500 mm. We tape all the joints of the reflective insulation with tape.
- If necessary, we place another heat-insulating material (mineral wool, foam plastic) between the slats, but you can do without it. Next, we attach strips of foil insulation to the slats. We lay the material end to end and shoot it with staplers. All joints are sealed with reinforced tape.
- We install another sheathing of wooden slats 2 cm high.
- After this, we attach the selected finishing material (plasterboard, plywood, MDF, PVC panels, lining, etc.) to the installed sheathing.
Izolon or penofol: which is better?
Penofol can be compared with only one group of thermal insulation materials of the Izolon brand, namely “heat-reflecting insulation IZOLON”.
The ISOLON company offers insulating materials based on polyethylene foam (ISOLON 100) or cross-linked polyethylene foam (ISOLON 500) with aluminum foil or lavsan applied on one side.
When comparing Isolon 100 and penofol, there is no significant difference in properties and method of application, so the final winner will have to be determined by availability and cost. The only advantage of Izolon is that the range has been expanded with sheet material with a thickness of 15 to 50 mm.
Thermal reflective insulation based on Isolon 500 is made from cross-linked polyethylene foam, which gives it much greater strength and a slightly lower thermal conductivity coefficient. Depending on the frequency of foaming (5-40 times), the compressive strength at 10% deformation ranges from 0.011 to 0.15 MPa.
In most cases, it is enough to use penofol, however, Izolon makes it possible to use heat-reflecting screens in cases where the performance characteristics go beyond the limits permitted for penofol.
Types of penofol
Manufacturers offer different penofol options for different functionality. The generally accepted classification divides it into three varieties:
- A type – one-sided penofol (aluminum film is applied to one side of the polyethylene after foaming). This type is used more often as an additional heat insulator with foam;
Penofol type A - B type – penofol foil-coated on both sides, has universal use, including for autonomous insulation;
Penofol type B
- C type – self-adhesive. On one side there is a layer of reflector on aluminum, on the opposite side there is a moisture-resistant adhesive on polyethylene foam, which is protected by a sticker. This penofol is more convenient for finishing areas that are difficult to reach. No special installation tools are required during installation.
Penofol type C
In addition to these standardized types, the developers have also prepared modifications that occupy a separate niche in the building materials market:
- ALP type - penofol with lamination, on the foil side there is a plastic film. This type of material is used for insulation of agricultural buildings operated in a not too aggressive environment;
- M or R types – one-sided foil with a corrugated “top”;
- AIR – penofol used to prepare air exhaust structures;
- Super NET (from the word “Network”) - the main task of this type of penofol is insulation and steam protection for air vents, pipelines or heating mains.