The basis of any heating is a boiler. Whether the house will be warm depends on how correctly its parameters are selected. In order for the parameters to be correct, it is necessary to calculate the boiler power. These are not the most complex calculations - at the third grade level, you will only need a calculator and some data on your possessions. You can handle everything yourself, with your own hands.
There are several ways to calculate the power of a heating boiler
What is boiler power and how to find it out
The thermal power of a boiler is the maximum amount of thermal energy transferred to the coolant during fuel combustion (measured in kilowatts/hour or simply kW). This means that a boiler with a power of 20 kW, when continuously operating at maximum power, will generate and transfer 20 kW of thermal energy to the coolant in an hour.
The boiler power can be determined in several ways:
- look for a list of technical characteristics on the boiler body;
- find the value in the model data sheet. If the documentation has not been preserved, you can look for an electronic version or study the offers of online stores, which must indicate its rated power in the description of the model;
Location of technical specifications on the boiler body - if we are talking about a gas boiler, you can find out the approximate heating output by gas consumption, for which you need to check and record how many cubic meters the boiler consumes during continuous operation at maximum power. The specific heat of combustion of gas is a constant value and is equal to 9.3 kW. It is also important to take into account the efficiency of the boiler (it can also be found in the list of technical characteristics), for old Soviet models these values are in the region of 70-85%, for new models the efficiency is in the range of 86-94%. Total, maximum power = 9.3 kW (specific heat of combustion of natural gas) * 0.8 (if efficiency is 80%) * 2.5 cubic meters. m/hour (resulting gas consumption per hour) = 18.6 kW. In a similar way, you can calculate approximate values for a solid fuel, liquid fuel or electric boiler.
It is impossible to increase the heating output of a domestic boiler without serious unsafe changes to its design, therefore the choice of the minimum required power must be approached responsibly. If it is not enough, you will have to install an additional boiler unit or insulate the walls, floor and ceiling, replace windows and doors in order to reduce heat loss.
Why is there high gas consumption in the house?
High gas consumption from a home heater can have various reasons. It is known that a floor-standing unit is more wasteful. It is much inferior to wall-mounted options. In addition, the situation can be worsened by an incorrectly designed smoke removal system (for example, made of brick, ferrous metals or uninsulated stainless steel pipes). You can find out more about the places through which heat leaves the house using a special thermal imaging device.
Also read with this article: Checking gas equipment
Methods for selecting the minimum required boiler power
In order to maintain a comfortable temperature in each room, the heating capacity of the heating system (and, accordingly, the boiler) must ensure the heat loss of the house, which is also measured in kW. That is, the heat output of the boiler unit = the total heat loss of the house through the walls, floor, ceiling, foundation of windows and doors + reserve in case of more severe frosts.
A visual representation of heat loss in a private home.
Calculation of heating boiler power by area of the house
The simplest and most common method. Based on practice, for an average private house in the climatic zone of the Moscow region, with a masonry of 2 bricks and a ceiling height of 2.7 m, 1 kW of thermal power is required for every 10 m2 (this is the ratio that corresponds to the average heat loss). We also recommend keeping a power reserve of 15-25%.
For example, for the house described above with an area of 100 square meters. m. minimum boiler power = 100 m2: 10 * 1.2 (20% reserve) = 12 kW.
Also, when calculating the power of a heating boiler based on the area of the house, adjustments can be made taking into account the insulation of the house. So, for a moderately insulated house (the presence of a 100-150 mm layer of thermal insulation or a wall made of timber), for every 10 m2 there may be 0.5-0.7 kW of heat loss. For a well-insulated house with a small glazing area, the norm is 0.4-0.5 kW for every 10 m2.
Therefore, if your case is radically different from the average house described above, it is worth calculating the boiler power using a more accurate method, taking into account all the features, it is described one point below.
How to choose a room thermostat and save up to 30% per month on heating
Calculation by room volume
Another fairly simple method, based on SNiP and usually used for apartments. The initial value is not the area, but the cubic capacity of the heated premises. According to the methodology specified in SNiP 23-02-2003 “Thermal protection of buildings”, the rate of specific heat energy consumption is:
- for a brick apartment building – 0.034 kW/m3;
- for a panel apartment building – 0.041 kW/m3.
Knowing these standards, the area of the apartment and the height of the ceilings, you can use the method of calculating the power of the heating boiler by the volume of the premises.
For example, for an apartment in a panel apartment building with an area of 150 square meters. m. and a ceiling height of 2.7 m (without external and internal wall insulation), minimum heating capacity = 2.7 * 150 * 0.041 = 16.6 kW.
From the principle of calculation, again, it is clear that all accounting for heat loss comes down to average values and thermal conductivity of walls made of various materials. This means that it is rational to use it if the external walls are not insulated, the apartment has no more than 4 standard windows, the radiators are connected in the most efficient way, and the neighboring apartments are heated.
We calculate taking into account all the main features of the house
The detailed formula is based on the area of the premises, but takes into account all possible heat losses, the method of connecting radiators, which affects the efficiency of the heating system, as well as the climatic conditions in which the private house is located.
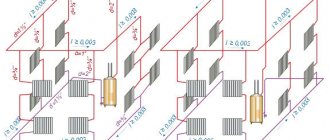
The calculation is made for each room separately, which is more correct. The values obtained for each room can later be used to select the power of heating radiators. By summing up the heating capacity required for each room, you will get the value for the entire heating system of the house, which means for the boiler, which must provide its power.
The exact formula for calculation:
Q = 1000 W/m2*S*k1*k2*k3…*k10,
- where Q is the thermal performance indicator;
- S – total area of the room;
- k1-k10 – coefficients that take into account heat loss, climate and features of radiator installation.
Show coefficient values k1-k10
k1 – number of external walls in the premises (walls bordering the street):
- one – k1=1.0;
- two – k1=1.2;
- three – k1-1.3.
k2 – room orientation (sunny or shady side):
- north, northeast or east – k2=1.1;
- south, southwest or west – k2=1.0.
k3 – coefficient of thermal insulation of room walls:
- simple, non-insulated walls – 1.17;
- masonry with 2 bricks or light insulation – 1.0;
- high-quality design thermal insulation – 0.85.
k4 – detailed accounting of the climatic conditions of the location (outdoor air temperature in the coldest week of winter):
- -35°C or less – 1.4;
- from -25°С to -34°С – 1.25;
- from -20°С to -24°С – 1.2;
- from -15°С to -19°С – 1.1;
- from -10°С to -14°С – 0.9;
- no colder than -10°C – 0.7.
k5 – coefficient taking into account the ceiling height:
- up to 2.7 m – 1.0;
- 2.8 - 3.0 m - 1.02;
- 3.1 - 3.9 m - 1.08;
- 4 m or more – 1.15.
k6 – coefficient taking into account heat loss from the ceiling (what is located above the ceiling):
- cold, unheated room/attic – 1.0;
- insulated attic/attic – 0.9;
- heated living space - 0.8.
k7 – accounting for heat loss from windows (type and number of double-glazed windows):
ordinary (including wooden) double windows – 1.17;- windows with double glazing (2 air chambers) – 1.0;
- double glazing with argon filling or triple glazing (3 air chambers) – 0.85.
k8 – accounting for the total glazing area (total window area: room area):
- less than 0.1 – k8 = 0.8;
- 0.11-0.2 – k8 = 0.9;
- 0.21-0.3 – k8 = 1.0;
- 0.31-0.4 – k8 = 1.05;
- 0.41-0.5 – k8 = 1.15.
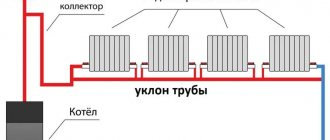
k9 – taking into account the method of connecting radiators:
- diagonal, where feed is from above, return from below – 1.0;
- one-way, where feed is from above, return from below – 1.03;
- double-sided bottom, where both supply and return are from below – 1.1;
- diagonal, where feed is from below, return from above – 1.2;
- one-way, where feed is from below, return from above – 1.28;
- one-sided bottom, where both supply and return are from below - 1.28.
k10 – taking into account the location of the battery and the presence of a screen:
- practically not covered by a window sill, not covered by a screen – 0.9;
- covered by a window sill or wall projection – 1.0;
- covered with a decorative casing only on the outside - 1.05;
- completely covered by a screen – 1.15.
For greater convenience, below is a calculator where you can calculate the same values by quickly selecting the appropriate source data.
Calculator for accurate determination of thermal power
Weather-compensated automation
You can adjust the power level of a gas boiler using weather-dependent automation. A special feature of the delivery set is the presence of external and internal temperature sensors. Thanks to the automatic mode, you can make changes to the power without overheating the indoor air.
The most popular manufacturers today produce high-precision and modern weather-dependent automation kits for most models of gas boilers. However, the basic supply of equipment, as a rule, does not include such systems, so they must be purchased separately.
Performance reserve depending on the type of boiler
For a standard single-circuit boiler, regardless of the type of fuel used, we always recommend a power reserve of 15-25%, depending on the temperature in the coldest decade and the insulation of the house. However, in some cases a slightly larger margin is required:
- 20-30% reserve if the boiler is double-circuit. Most models operate on the principle of DHW priority, which means that at the moment the hot water consumption point is activated, the boiler does not heat the heating circuit; to operate on two circuits, higher performance is required;
- 20-25% of the reserve if supply and exhaust ventilation without heat recovery is organized or planned in the house.
A scheme with the connection of an indirect heating boiler is also often used (especially in conjunction with solid fuel boilers). In this case, excess capacity may exceed 40-50% (the figure is calculated according to the situation). It is worth understanding that in any of the cases, the provided reserve is not “idle”, but is used whether for the purpose of heating hot water, replenishing higher heat losses, or heating a buffer tank.
The tall white tank to the right of the boiler is an indirectly heated storage boiler that constantly maintains a large volume of hot water.
Gas boilers Buderus for 250 sq.m.
Buderus Logamax U072-24
- Power, kWt:
24 - Number of circuits:
1 - Type:
wall - Network phasing:
1 - Circulation pump:
yes - Expansion tank:
yes - Rating:
4.0
Advantages:
- economical
Flaws:
- often produces errors
Buderus Logamax U072-24K
- Power, kWt:
24 - Number of circuits:
2 - Type:
wall - Network phasing:
1 - Circulation pump:
yes - Expansion tank:
yes - Rating:
3.5
Why you shouldn’t choose a boiler with too much power reserve
With a lack of heating performance, everything is very clear: the heating system simply will not provide the desired temperature level even with continuous operation. However, as we have already mentioned, excess power can also become a serious problem, the consequences of which are:
- lower efficiency and increased fuel consumption, especially on one- and two-stage burners that are not able to smoothly modulate productivity;
- frequent clocking (on/off) of the boiler, which disrupts normal operation and reduces the burner life;
- simply a higher cost of the boiler unit, given that the performance for which the increased payment was made will not be used;
- often greater weight and larger dimensions.
When excessive heat output is still appropriate
The only reason to choose a version of the boiler that is much larger than needed, as we have already mentioned, is to use it in conjunction with a buffer tank. A buffer tank (also a heat accumulator) is a storage tank of a certain volume filled with coolant, the purpose of which is to accumulate excess thermal power and subsequently distribute it more rationally for the purpose of heating a house or providing hot water supply (DHW).
For example, a heat accumulator is an excellent solution if the performance of the DHW circuit is insufficient or when a solid fuel boiler cycles, when the fuel, when burned, releases maximum heat, and after burning out the system quickly cools down. Also, a heat accumulator is often used in conjunction with an electric boiler, which heats the tank during the period of a reduced night electricity tariff, and during the day the accumulated heat is distributed throughout the system, maintaining the desired temperature for a long time without the participation of the boiler.
InstructionsBoilers
Oasis gas boilers for 250 sq.m.
Oasis BM-20
- Power, kWt:
20 - Number of circuits:
2 - Type:
wall - Network phasing:
1 - Circulation pump:
yes - Expansion tank:
yes - Rating:
5.0
Advantages:
- price
- simplicity
- bimetallic heat exchanger
Flaws:
- No
Oasis RT-20
- Power, kWt:
20 - Number of circuits:
2 - Type:
wall - Network phasing:
1 - Circulation pump:
yes - Expansion tank:
yes - Rating:
5.0
Advantages:
- electronic control
- powerful
- safe
- reliable
Flaws:
- few functions
Oasis BM-18
- Power, kWt:
18 - Number of circuits:
2 - Type:
wall - Network phasing:
1 - Circulation pump:
yes - Expansion tank:
yes - Rating:
5.0
Advantages:
- price
- Ease of use
- safety
- compact
- frost protection
Flaws:
- No
Oasis RT-16
- Power, kWt:
16 - Number of circuits:
2 - Type:
wall - Network phasing:
1 - Circulation pump:
yes - Expansion tank:
yes - Rating:
5.0
Advantages:
- price
- electronic control
- safety
- compact
- powerful
- silent
Flaws:
- No
Oasis BM-16
- Power, kWt:
16 - Number of circuits:
2 - Type:
wall - Network phasing:
1 - Circulation pump:
yes - Expansion tank:
yes - Rating:
4.0
Advantages:
- price
- support for heated floors
- availability of display
- protective functions
- autodiagnostics
- economical
- silent
- presence of thermometer and pressure gauge
- auto ignition
Flaws:
- noisy
- loud start
- common mistakes
- quick failure
Oasis RT-24
- Power, kWt:
24 - Number of circuits:
2 - Type:
wall - Network phasing:
1 - Circulation pump:
yes - Expansion tank:
yes - Rating:
3.5
Advantages:
- design
- compactness
- multi-level security system
Flaws:
- price
- build quality
- noise
- chinese pump
- heat exchanger is leaking
- frequent problems with the board
- loud start
Navien gas boilers for 250 sq.m.
Navien DELUXE 24K
- Power, kWt:
24 - Number of circuits:
2 - Type:
wall - Network phasing:
1 - Circulation pump:
yes - Expansion tank:
yes - Rating:
4.0
Advantages:
- price
- remote control
Flaws:
- noise
- cold and hot shower
Navien SMART TOK 24K
- Power, kWt:
24 - Number of circuits:
2 - Type:
wall - Network phasing:
1 - Circulation pump:
yes - Expansion tank:
yes - Rating:
4.5
Advantages:
- wi-fi
- remote control with thermometer included
- phone app
Flaws:
- remote control with defective
Navien DELUXE 13K
- Power, kWt:
13 - Number of circuits:
2 - Type:
wall - Network phasing:
1 - Circulation pump:
yes - Expansion tank:
yes - Rating:
4.5
Advantages:
- price
- quality
Flaws:
- noisy
Gas boilers Vaillant for 250 sq.m.
Vaillant atmoTEC pro VUW 240/5-3
- Power, kWt:
24 - Number of circuits:
2 - Type:
wall - Network phasing:
1 - Circulation pump:
yes - Expansion tank:
yes - Rating:
4.0
Advantages:
- copper internal hydraulic connections
- separate heat exchangers
Flaws:
- noise
- complex controls
Vaillant turboTEC pro VUW 242/5-3
- Power, kWt:
24 - Number of circuits:
2 - Type:
wall - Network phasing:
1 - Circulation pump:
yes - Expansion tank:
yes - Rating:
4.5
Advantages:
- reliability
- compactness
- design
- silent
Flaws:
- post-warranty service
- lack of parts for repair
- high cost of repairs
- complex menu
- no water heating sensor
- need good water pressure
Leberg gas boilers for 250 sq.m.
Leberg Flamme 24 ASD
- Power, kWt:
20 - Number of circuits:
2 - Type:
wall - Network phasing:
1 - Circulation pump:
yes - Expansion tank:
yes - Rating:
4.5
Advantages:
- easy installation
- brass heat sink
- fan at the top
- price
- build quality
- auto diagnostic system
- double-circuit
- high efficiency
Flaws:
- weight
- frequent breakdowns
Kentatsu gas boilers for 250 sq.m.
Kentatsu Nobby Smart 24–2CS
- Power, kWt:
23.8 - Number of circuits:
2 - Type:
wall - Network phasing:
1 - Circulation pump:
yes - Expansion tank:
yes - Rating:
4.5
Advantages:
- silent
- quality assembly
- easy setup
- heat exchangers
- branded pump and cooler
Flaws:
- No