Laying an internal pipeline is one of the important stages of work after the construction of individual housing. In the absence of a plan or self-installation, you often have to solve the problem of what pipe diameter to choose for water supply in a private house.
It is worth noting that to accurately determine pipe diameters, it is necessary to take into account a wide range of factors and use tabular data or formulas for calculations. On the other hand, the task is not so difficult if you use standard methods for determining pipe sizes according to repeatedly proven recommendations of specialists.
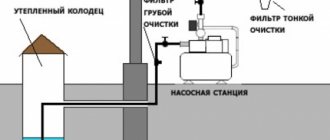
Rice. 1 Options for installing internal water supply in the house
Requirements for water supply pipes and their types
In individual houses, several types of pipes are used to supply hot and cold water. Their physical parameters ensure a long service life at the given temperature and pressure characteristics of the working environment.
Basic requirements for pipelines according to SNiP 2.04.01-85:
- They must withstand a network operating pressure of at least 4.5 bar at a cold water temperature of 20 °C for 50 years of operation.
- At a constant hot water temperature of about 75 °C, the estimated operational life of the pipeline should not fall below 25 years.
SNiP 2.04.01-85 also establishes what the internal water supply system should be like. It allows the use of polymer pipes made of low-density polyethylene (HDPE), polypropylene (PP), polyvinyl chloride (PVC), polybutylene (PB), metal-plastic, fiberglass, other plastics and their composite compounds.
From metals, it is allowed to lay pipelines made of copper, bronze, brass, steel with external and internal anti-corrosion coating.
When used in hot water supply, not all pipes satisfy these conditions, so hot and cold water pipelines are often installed from different materials.
Despite the wide range of pipes permitted for laying internal water supply systems, their use is limited by the following important factor.
The internal pipeline must have the lowest thermal conductivity to prevent heating of cold and cooling of hot water.
As a result, the list of pipes from which water supply can be made should not include all metal products. Metal-reinforced polymers - polypropylene with an aluminum shell and metal-plastic - are also not suitable.
If we exclude from consideration rare and therefore little-used pipes made of polybutylene, fiberglass, and adhesive polyvinyl chloride, then the answer to the question of which pipes are best to choose for water supply will become obvious.
Two types of pipes will remain in use, and these are PP polypropylene and HDPE low-density polyethylene. Each of these materials, due to their thick walls, has low thermal conductivity - 0.25 W/m°C for polypropylene and 0.32 W/m°C for low-density polyethylene.
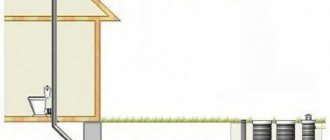
Rice. 2 Examples of laying an external water main
What diameter is specified for measurements?
Since each pipe casing has an outer and an inner diameter, it can be confusing to specify them. Any user closely involved in laying water pipes should know that pipes made of metals and plastics are measured differently.
The diameter of metal pipes is determined by their internal passage channel; it is called nominal or conditional. This is due to the fact that it is tied to the nearest value from the standardized series and does not correspond to the real value. An example of a standard numerical series of nominal diameters of steel pipes: 10, 15, 20, 25, 32, 40, 50, 65 mm.
Sometimes the diameters of steel pipelines are indicated in inches with fractions, correlating them with dimensions in millimeters: 1/2 - 15 mm, 3/4 - 20 mm, 1 - 25 mm, 1 1/4 - 32 mm, 1 1/2 - 40 mm.
The dimensions of all polymer pipes are specified by their outer diameter in millimeters. They must correspond to the standard number series, its fragment: 20, 25, 32, 40, 50, 63, 75, 90, 110 mm.
This indicator exactly corresponds to the dimensions in millimeters and is not specified in inches.
The markings of polypropylene pipes always indicate the wall thickness, making it easy to calculate the diameter of the passage channel. This may be important when carrying out hydraulic calculations.
Sometimes they are marked with the SDR symbol, which is equal to the result of dividing the outer diameter by the wall thickness. The lower the SDR, the thicker the wall the plastic pipe is considered to be.
It is worth noting that, unlike steel pipes, the dimensions of copper and stainless steel pipes are determined by their outer diameter.
| Pipes PN10 for cold water, operating temperature 20 ºС pressure 10 atm., lengths 4 m | |||
| Size mm | Outer diameter mm | Wall thickness mm | Water capacity l/m |
| 20 x 1.9 | 20 | 1,9 | 0,206 |
| 25 x 2.3 | 25 | 2,3 | 0,327 |
| 32 x 3.0 | 32 | 3,0 | 0,531 |
| 40 x 3.7 | 40 | 3,7 | 0,834 |
| 50 x 4.6 | 50 | 4,6 | 1,307 |
| 63 x 5.8 | 63 | 5,8 | 2,075 |
| 75 x 6.9 | 75 | 6,9 | 2,941 |
| 90 x 8.2 | 90 | 8,2 | 4,254 |
| 110 x 10.0 | 110 | 10,0 | 6,362 |
Heating systems
To correctly calculate the diameter of the pipes, you need to take into account the wiring diagram. Resistance affects the parameters of heating equipment and the characteristics of parts (section, material). The cottage uses 2 types of heating systems.
Two-pipe
The heating option with a vertical riser for the placement of pipes can be either upper or lower. Two elements are connected to each radiator: for supplying hot moisture and removing cold moisture. Horizontal wiring is:
- dead end;
- parallel;
- radial (collector).
Features of polypropylene pipes
Polypropylene pipes occupy a leading position in terms of the breadth of use in water supply systems of private houses and communal apartments. They have no worthy competitors in terms of cost, ease of installation and practicality when laying cold water supply (CW) mains. The main disadvantage of polypropylene is the high coefficient of linear expansion when heated, which is not an important factor in this case.
In hot water supply (DHW) pipelines, ordinary polypropylene is not used due to insufficient heat resistance and high linear elongation coefficient.
There it is better to use co-extruded material, which is a polypropylene pipe with an internal fiberglass shell. Fiberglass increases the heat resistance of the entire pipe and reduces its thermal expansion.
Polypropylene pipes are connected by soldering; if two sections of the same diameter are joined, a coupling, elbow or tee is placed on top of them, depending on the unit being mounted. This connection method is called socket connection. Thanks to this method, the flow area of the polypropylene pipeline remains unchanged in all sections. Thanks to the large number of different polypropylene fittings, almost any assembly can be soldered. When joining pipe sections of different diameters, transition couplings are used.
With the same external dimensions, the diameter of the passage channel of PP pipes is much smaller than that of metal or polymer analogues made of cross-linked polyethylene.
As for pressure characteristics, ordinary polypropylene can withstand pressure from 10 (PN10) to 20 (PN20) bar throughout its entire service life. A fiberglass-reinforced pipeline can operate for a long period at a working fluid pressure of up to 20 (PN20) or 25 (PN25) bar at elevated temperatures.
Rice. 3 Dimensions of polyethylene pipes
Where can I get the tables?
Everything is simple here. Usually, all detailed tables with all the necessary data can be viewed (or downloaded) on the websites of pipe manufacturers. But it happens that there are still no tables.
You can get out of this situation as follows. If there are no tables for the outer diameter, then take the one for the inner diameter and calculate according to it. Yes, there will be inaccuracies, but, as experience shows, for forced circulation they are completely insignificant and acceptable.
Having analyzed a huge number of already installed and perfectly working systems, experts noticed a certain pattern in the choice of pipe cross-section. It is mainly suitable for small-sized autonomous systems.
In private houses, the pipes that come out of the boiler are most often one-half and three-quarters in size. This diameter of the pipe for heating a house is used until the first fork, and at each subsequent fork the cross-section is reduced by exactly one step.
But this method is applicable only for apartments and one-story houses; for high-rise buildings, alas, everything will have to be calculated very carefully.
If we have a private house or apartment, autonomous heating for no more than 5-8 radiators and 2-3 forks, we can easily calculate everything ourselves. We need to know how powerful each heating point is, the heat loss in the room and a good table for selecting the pipe diameter.
However, as has already become clear, trust experienced specialists to calculate a complex multi-level system with numerous junctions and forks. Well, if you still decide to do everything yourself, then at least read articles like ours and consult with experts.
Source: eurosantehnik.ru/kak-vybrat-diametr-truby-dlya-otopleniya-doma.html
Low pressure polyethylene pipes
HDPE pipes are used for external laying of water pipes. They are produced in lengths and coils of diameters corresponding to the standard number series.
There are several grades of polyethylene depending on its internal structure; pipes are made from PE-80 and PE-100, the latter being the best.
Unlike polypropylene pipes, the wall thickness of HDPE pipes can vary within wider limits. For them, the dimensional ratio of the outer diameter to the wall thickness SDR is also established, and it can vary in the range from 2.5 to 41.
HDPE pipes are designed to transport water with a temperature not exceeding 40 °C. It is clear that they are used only in cold water supply systems.
As for the pressure characteristics, the pressure that a HDPE pipe can withstand ranges from 2.5 to 25 bar and directly depends on the SDR.
HDPE pipes are connected using external compression couplings, so that their internal diameter remains unchanged throughout the entire pipeline.
Related article:
What is HDPE pipe
A separate article explains what HDPE pipe is - the production process, application, joining methods, installation.
Rice. 4 Installation of polypropylene and polyethylene pipes
Required data for calculation
The main task of heating pipes is to deliver heat to the heated elements (radiators) with minimal losses. We will build on this when choosing the correct pipe diameter for heating a house. But to calculate everything correctly, you need to know:
- pipe length;
- heat loss in the building;
- element power;
- what kind of pipe layout will be (natural, forced, single-pipe or two-pipe circulation).
The next point, after you have all the above data in your hands, will be necessary to sketch out a general diagram: how, what and where it will be located, what thermal load each heating element will carry.
Then you can begin to calculate the required cross-section of the diameter of the pipe for heating the house. You should also be careful when purchasing:
- metal-plastic and steel pipes are marked by the size of the internal diameter, there are no problems here;
- but polypropylene and copper - by outer diameter. Therefore, we need to either measure the internal diameter ourselves using a caliper, or subtract the wall thickness from the external diameter of the pipe for heating the house.
Don’t forget about this, because we need exactly the “inner diameter of the pipe for heating the house” in order to calculate everything correctly.
Factors influencing the choice of pipe diameter
The water supply pipeline is designed to transport cold and hot water of the required temperature and pressure to the points of collection. If the temperature parameters depend on the properties of the source and the thermal conductivity of the pipes, then the pressure characteristics are determined by the pipe dimensions. That is, the smaller the cross-section and the longer the length of the pipeline, the lower the water pressure will be at the end of the line.
Taking into account the above, the following factors influence the choice of water pipe diameter:
- Pressure at the inlet of the internal water supply. For individual water supply, it is set by automatic devices (pressure switches).
- Pipeline length.
- Required pressure at water points.
- The number, type and cross-section of passage channels of shut-off and control valves, metering devices, pumping equipment along the water route. Any narrowing of the passage along the watercourse path significantly increases hydraulic losses.
- The number of turns and bends in the highway. Every turn and bend creates resistance to water flow and increases hydraulic losses.
- Volumes of water consumption. The factor is directly related to the number of connection points for plumbing fixtures - the more there are, the larger the cross-section of pipes will be needed.
- Pipeline layout diagram. If the line approaches each device in series, its diameter is made larger. When using a collector line, the internal cross-section of the pipes is taken smaller.
The sequence of calculating the cross-section of heating lines
For communications with circulation pumps, you will need to take into account the volume of coolant in the system, the total length of the heating main, the reference flow rate, heating heat transfer, equipment power, resistance value and pressure without a pump.
To find out the size of the products, you will need to make an adjustment for a decrease in efficiency - resistance to turns, bends and fittings. Calculations can be carried out using the formula H = λ(L/D)(V2/2g), where:
- H – height of zero pressure without pressure in m;
- λ – pipe resistance coefficient;
- L – line length;
- D – internal diameter of the pipe in mm;
- V – flow velocity in m/s;
- g – gravitational acceleration equal to 9.81 m/s2.
In the process of calculating the minimum heat loss, you need to check several diameter options for minimum resistance.
What pipe diameter to choose for water supply in a private house
As shown above, the pipe diameter is specified by fixed values from a standardized number series with a significant variation. This makes accurate calculation using formulas, tables and online calculators a meaningless procedure in the vast majority of cases. Even the simplest option of determining the diameter based on the throughput of pipes and summing up the water consumption of simultaneously turned on plumbing equipment (Table 3.) is not worth the time spent and was carried out long ago by specialist installers.
Outside
If an individual water supply system is installed for a private house, then water from a submersible or surface electric pump enters it through an underground pipeline made of low-density polyethylene HDPE.
The outlet pipes of most pumps are designed to accept pipes with a diameter of 1 or 1 1/4 inches, that is, outer diameters of 25 and 32 mm. Since the pipeline from electric pumps is prohibited from being narrowed, installers have no choice which pipes to use.
Sometimes, if the outlet of the electric pump has a 1-inch (25 mm) outlet pipe, and the distance to the house is too great, a larger diameter 1 1/4-inch (32 mm) pipeline is used to reduce hydraulic losses.
The same applies when connecting from a centralized water main. In the vast majority of cases, installers do not face the question of which pipe to choose. It is enough to use two types - 25th or 32nd HDPE pipes.
Rice. 5 One of the options for manifold wiring and corresponding pipes made of thin-walled metal-plastic (for PP, all diameters should be increased by one standard size)