Walls made of timber create an optimal microclimate in terms of temperature and humidity indoors, since wood has a special structure that ensures microcirculation of air flows.
In addition, a house made of timber for permanent residence must guarantee all sanitary requirements for heating, water supply and energy supply.
What are year-round cottages?
These are buildings constructed from wooden beams, which contain one or more residential sections intended for long-term stay of citizens on the right of private ownership or rental:
- separate mansions;
- townhouses;
- cottages.
Auxiliary outbuildings that do not contain living rooms, attached to existing residential buildings, garden sheds, terraces, utility rooms, gazebos and detached garages or sheds cannot be recognized as residential buildings.
, a separate winter house made of timber for year-round use is considered as a set of residential and non-residential rooms contained in one building, intended for long-term living and providing a normal sanitary environment.
Such facilities are electrified and have all the life support conditions for the citizens living in them: cooking, bathing/showering, heating and water supply systems.
Is it worth building them from this material?
Russian town planning standards allow the use of wooden beams as wall material. These are mainly coniferous trees or larch.
Several varieties are used for the construction of winter cottages.:
Glued is a typesetting element made from glued lamellas made from coniferous trees.- Profiled from solid wood with a complex configuration of connecting elements.
- Regular, having a square or rectangular cross-section with dimensions from 40 mm to 300 mm.
It can be used in different humidity levels, but the developer should be aware that the variety with natural humidity is susceptible to :
- deformations;
- shrinkage;
- cracking.
Dry is obtained through the process of chamber drying, practically devoid of the above disadvantages, but has a significantly higher cost.
The most
popular today are glued and profiled modifications of wall timber. They are produced with a tongue-and-groove system, which speeds up the assembly process and allows you to create reliable and heat-protective connections. Such a house does not require additional external or internal finishing, with a thickness of over 270 mm.
Wooden houses have proven themselves well over many centuries. Houses made of timber are a modern interpretation of a classic wooden house; they can and should be built in modern conditions, the requirements of which they fully comply with.
Logeco stacked timber
The material is a hollow type of thermal timber: the cavities between the boards are filled with vapor-permeable fibrous insulation (mineral or cellulose wool) during the construction process. In this case, the internal space of the beam is divided by longitudinal partitions, and the transverse wooden connections between them are arranged in a checkerboard pattern, which avoids the appearance of cold bridges. The wooden elements of the beam are not only glued together, but also connected with transverse brackets for greater strength. During construction, a traditional flax-jute or fibrous synthetic sealant is laid between the crowns.
The parts of a house kit, as a rule, do not need adjustment and fit tightly to each other, but as a result of uneven shrinkage, the gaps may increase. Photo: Yeti Architects
Building requirements and parameters
The most important parameter that distinguishes the seasonal and winter versions of a house is the heat resistance of wall structures, which is determined by the thickness of the walls.
For summer cottages, external load-bearing walls are installed with a beam thickness of at least 150 mm, and for winter home ownership, the thickness should be at least 270 mm . In the event that a house for permanent residence is being built from timber of a smaller thickness, a multi-layer construction of external walls is provided with the installation of insulation of at least 100 mm.
A house with permanent residence also differs in its level of comfort. SNiP establishes not only the thickness of the walls, but also the size and functionality of the rooms in the house, as well as the mandatory engineering systems that must be installed in it.
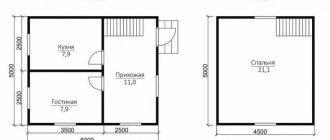
The standards establish the smallest areas of living rooms:
living room at least 12 m2;- each sleeping room from 8 m2;
- kitchen from 6 m2;
- shower/bathroom from 1.8 m2;
- hallway from 1.8 m2;
- toilet approximately 1 m2;
- ceiling height from 2.5 m;
- width of stairs and passages over 0.9 m;
- water supply and sanitation;
- heating system with a source: solid fuel, gas or electric boiler;
- power supply systems;
- ventilation and air conditioning systems;
- telephony.
Attic floors may have rooms with a smaller area, for example, for a bedroom a reduction of 1 m2 is allowed.
A winter home must be provided with the minimum acceptable comfort. Utility networks or their equivalents must be connected to it. So, as a drainage system, it is allowed not only to connect to the central water supply system, but also to install cesspools . In this case, filters and cleaning systems for toilets must be provided.
Water supply can be central through an in-house system of plastic or metal water pipes. It is allowed to install individual sources of water supply - artesian wells or wells in the local area.
The heat supply must provide at least + 18 C during the coldest period of the year. The heating system is determined by the project according to the customer’s specifications; it can be either central heating or individual heating with a gas, solid fuel or electric boiler.
Internal heating devices can be either radiator or convector type. Their thermal power is calculated based on the conditions of 10 W per 1 2 total area. For the arrangement of the boiler room, a separate room of at least 5 2 with increased conditions for ventilation and fire protection is allocated.
The ventilation system in such houses is natural-supply, provided by window units. They also provide the required level of illumination. If shower rooms and toilets do not have natural ventilation due to the lack of windows, forced ventilation is installed.
Gasification of timber cottages is carried out from the boiler room or kitchen . The use of gas cylinder units with liquefied gas is allowed with a volume of no more than 12 liters, which are installed in separate non-residential premises in metal boxes.
The supply of electricity, as a rule, is carried out with the installation of overhead power distribution lines. Electrical wiring in the house is carried out in fire-resistant steel pipes.
Fire safety requirements for such houses are complex and begin to apply even at the moment of timber production, when it is treated with fire-resistant solutions. Further, the requirements are divided into functional engineering systems: gas, electricity and heating with a boiler.
Check-in to the site in winter
Everything is very simple here - we often encounter problematic drives in winter or summer, but we always stop by! If the road to your site is filled up, hire equipment and clear the entrance and place for unloading - it’s a cheap question. If there are difficulties - the house is on a hill or in a lowland, inform your manager about this in advance, and also, just in case, have the telephone number of special equipment (tractor, walkable manipulator, etc.) on hand. In summer, due to rain, we encounter problem runs more often than in winter, but we always overcome the situation.
What types of wood are suitable for permanent residence buildings?
A permanent home must first of all be reliable and warm. In this regard, it is not better to find a beam with a cross-section of 270 mm for this purpose .
However, for the northern and eastern regions it will also need to be insulated with a layer of at least 100 mm.
In this case, the most preferable option would be glued and profiled timber, which has a low percentage of shrinkage, not higher than 2-3%, respectively.
In order to build a warm house, when choosing, the developer will need to pay attention not only to the cross-section of the material, but also to a number of other conditions:
The timber must be made of softwood . Such varieties are more resistant to temperature changes because they have a large amount of resin substances.
They are also natural antiseptics and are able to heal minor cracks, thus reducing the wood’s ability to crack, which means less heat loss from the walls. It is made from wood cut down in winter. During this period, it has only natural humidity, since the movement of moisture through the structure is slowed down, and its remains are simply frozen out naturally.
Single “mini-beam”
This simple and reliable design is essentially one of the options for facade insulation. The basis of the wall is a frame made of dry boards with a section of 50/70 × 120/140/180 mm. From the outside it is covered with a vapor barrier, and then a sliding sheathing is installed from bars 50 × 100 or 50 × 150 mm, depending on the required thickness of the insulation (mineral wool boards). The insulation is covered with hydro-wind protection, and then the house is sheathed with imitation timber (you can use other options for façade boards, as well as composite and vinyl siding). The corners are decorated with wooden overlays, which protect the insulation from moisture and give the house a finished look.
To avoid the risk of uneven shrinkage, it is advisable to build walls made of “mini-timber” no higher than 3 m; Projects with an attic or semi-attic floor are preferred. Photo: Yeti Architects
Construction of a fence based on a single “mini-beam”
1 - beam; 2 - vapor barrier; 3 - insulation; 4 - frame; 5 — wind and moisture protection; 6 - sheathing; 7 - imitation timber. Photo: Homgart
The construction of “mini-timber” walls does not use vapor barrier or windproof materials. The wall releases moisture to the outside air, and a comfortable microclimate is maintained in the rooms
Construction rules
A box of such lumber is erected by alternately laying the crowns on top of each other , securing them in the corners and ends with locks cut into the body of such elements. These are recesses of a specific shape that organize their mutual adhesion and horizontal fixation.
They are stacked on top of each other, connected vertically with dowels made of wood or metal, helical ties or compensating spring mechanisms. Such a house has a fairly resistant wall structure that can withstand, including earthquakes.
The difference between wooden houses is their high percentage of shrinkage. This is due to the drying of the product body with a decrease in cross-section. The percentage of shrinkage directly depends on the timber production technology; for traditional timber this figure reaches 8%.
In other words, a wall made of beams with a height of 2.7 m after shrinkage will become lower by 0.21 m. Usually, a log house built from such material is left without movement for 1 to 2 years , and only then windows and doors are installed and finishing work is carried out.
The shrinkage time mainly depends on humidity and the manufacturing technology of timber for glued and profiled timber; it is minimal from 0.4 to 3%, so many specialists in such houses almost immediately begin to carry out finishing work.
An important element in timber house construction is the angles, which affect the thermal resistance of the building. These places are considered the most vulnerable to temperature changes, receiving cold and moisture first. For this reason, winter buildings made of glued or profiled timber have corner joints with the “remainder” or “into the bowl”, and the “straight” corners will freeze and rot.
Weak spots
Problem areas of walls made of any insulated timber are openings and corners. In the corners it is necessary to cover the insulation and decorate the ends of thin boards. When ordering a house kit, the necessary parts must be glued into the timber, and additional end caps or sliding strips must be installed. Sometimes you have to make camouflage structures yourself. It is more difficult to properly design the openings. Some builders ignore the shrinkage of the walls and rigidly fix the rough frames without leaving compensation gaps above them. This is a gross mistake, especially since it is not difficult to manufacture and install traditional casing. To do this, you need to remove part of the insulation at the ends of the walls and insert sliding slats in its place, and nail the rough frame boards to them. Above the upper lintel of the latter, it is necessary to leave a gap insulated with fibrous material of about 4% of the height of the opening.
When building from insulated timber, the speed of work and proper storage of the house kit are very important. Wet boards begin to lead, the crowns do not stick together well, and parts may break along the adhesive seam or insulation
Thanks to locking and tongue-and-groove connections, a wall made of vertical timber has high strength and is not blown through. Photo: Naturi
Step-by-step instructions: how to build?
The installation of a log house begins with pouring the foundation; there are no particular difficulties here, since the walls of such a building do not create high loads on the foundation of the house.
After the foundation work is completed and the concrete has acquired the required characteristics, before laying the initial row of beams, the foundation is waterproofed by laying horizontally 2 layers of roofing felt on bitumen mastic. Under the first crown you need to place a backing board made of larch 50 mm thick.
Before laying, the backing board and the first crown are treated with antiseptics and fire retardants.
Technology for laying the walls of a winter house:
Each subsequent crown is laid only after tape insulation has been laid on the previous element and secured with a stapler.- The beams are fastened with wooden dowels. To do this, holes are drilled on them at intervals of 1.5 m: the upper one is fully drilled, and the lower one is 1/2 of the thickness. A dowel is inserted into the holes 10 mm deep.
- Regardless of the chosen method of laying the main elements, the first crown is mounted in a “half-tree”, and a “half-tree” is also made at a corner connection using a root tenon.
- After assembling the 1st and 2nd crowns, they begin installing the logs to create the floor in increments of 50-60 cm with a board thickness of 30-40 cm. If the plinth design is possible, then the logs can be laid on it. Otherwise they are cut into the first crown.
- Skull bars are attached to the sides of the logs and shingle boards are placed on them.
- After this, you need to lay out the waterproofing layer surrounding and directly the logs.
- Insulation is placed in the gaps of the logs on the bevel boards and hydraulic layer, and a layer of vapor barrier is placed on top and a subfloor is placed on top.
- Temporary supports made of unedged boards are installed in technological openings for windows and doors.
- Internal partitions are made after the box is built; they are cut into load-bearing walls.
- Roofs are most often gable or sloping, and as
- Mauerlat use the last crown.
- After the completion of the shrinkage processes in the house, the cracks that have appeared on the walls must be well leveled with mastic or caulked.
- After this, they install window units and doors, install utility networks and begin finishing work.
Advantages and disadvantages
Modern winter houses made of timber have retained all the advantages of classic wooden houses . All the shortcomings of outdated technologies have been replaced by modern advances in the field of wooden house construction.
Log buildings are not only beautiful, but also have a modern level of environmental safety. The former problem of old wooden buildings - fire hazard, today has also been practically eliminated, thanks to high-quality fire retardant treatment in the factory.
New production lines are capable of creating high-quality timber with a minimum percentage of humidity and shrinkage, and the external processing of the material with precise geometry and smooth surfaces does not require additional wall finishing, which significantly saves the family budget during construction.
The main positive properties of houses made of timber:
- no adjustment of material is required during installation and assembly operations;
- the reliability of the fastening does not contribute to the creation of cracks that can become cold bridges in the house;
- the construction time for an average house of 100 m2 does not exceed 30 days;
- lightweight wall structures do not require a heavy foundation;
- buildings made of laminated and profiled timber give the smallest shrinkage than similar buildings made of other modifications of lumber.
Some users call the disadvantage of such a house a high fire hazard, but rather this is only possible for houses whose wall material has not been treated with appropriate impregnations in the factory. Other disadvantages can only appear if the conditions of construction and operation of winter log houses are violated.
How to prepare a laminated timber house for winter
First of all, pay attention to the roof, namely the pitched roof. During the winter, there is a lot of rainfall, and if the roof is not able to protect the house, then many problems will arise later.
Check the roof. Inspect it carefully for any defects or damage. Especially carefully inspect the weakest points in the structure - cornices and ridges, because there is the greatest likelihood of leakage.
After successfully inspecting the outer covering, move on to the inner side. The most convenient way would be to go out into the attic or climb into the attic. If you notice elements starting to rot, immediately treat these areas with special solutions. You don't want the roof to collapse, do you?
As for autumn, the first step is to remove fallen leaves from the roof. Leaves have an ability to retain moisture that is not very pleasant for coatings, which can have a detrimental effect on materials in the future. Cleaning is a rather scrupulous process; treat it with caution so as not to damage the roof. Very minor scratches are not dangerous, but beware of serious damage. After some time, the roof may use up its resource. To prevent corrosion, damaged areas on the metal surface should be painted over.
Let's go down a little lower and move on to checking the timber and logs. Materials should be inspected for cracks and damage once every six months. Rot most often forms in places of damage and cracks, so if you don’t take care of this, repairs can cost a pretty penny.
The easiest way to protect timber from mold and mildew is to use an antiseptic. Just don’t think that after using this product once, you can forget about caring for your home - regularity is needed here. Without it, relative air humidity in the range of 75–100% will easily provoke the development of fungus.
Also, do not forget about ventilating the house. This simple step will help you avoid damaging the timber. Places that have already rotted must be promptly removed and treated so that the damage to the timber does not continue. We strongly recommend that you pay close attention to protecting your home from fire. To feel completely safe, use special substances that prevent combustion - fire retardants.
Checking your windows shouldn't be an afterthought. It is their serviceability that will determine how the house will retain heat and protect its owners from precipitation. When inspecting, take a good look at window frames made of solid wood.
Window seals and fittings also require careful inspection. All moving parts of the window - handle, turning mechanisms, locks - must be lubricated several times a year using lubricant or special sprays. When choosing a treatment product, choose one that does not contain resin or acid. Machine oil or technical Vaseline is best. Special products for processing window fittings are also available for sale.
To clean elastic window seals, which keep your home airtight and warm, use products that do not contain solvents or oily substances. After processing, apply a product that will preserve the flexibility of the material.
The foundation is a fairly expensive part of the house, so unless you want to spend a lot of money on fixing it, then it should be looked after like the rest of the house. There is nothing complicated about it. The first step is to avoid foundation flooding - this most often occurs due to cutting off the soil near the foundation. Don't forget that planting plants will adversely affect your foundation due to excessive watering.
Let's move to the bathhouse. Inspect stoves and associated tanks for water. If excess water is found, remove it.
And one of the main rules: if you do not live in the house all year round, then before leaving, be sure to drain all the water from the pipes, tanks and radiators. Otherwise, when frost sets in, the water will turn to ice and your pipes will become unusable. Moreover, ice can tear not only plastic pipes, but also metal. Therefore, do not forget to drain the water to avoid unpleasant situations.
If you have a well on your property, then do not forget about caring for it. Use chlorinol - it will help treat the well. The remaining water must be pumped out. After these steps, you will receive clean water in the spring.
Reviews
The dream of a country house, warm winter house made of timber, has become an obsession for many Russians, some of them have come quite close to realizing their dream and have already begun to select a project for construction or are planning to purchase a finished building.
In order not to make a mistake in their choice, to know the real advantages and disadvantages of such houses, they study the opinions of experienced owners through online forums.
Many owners of log houses are happy to share their construction experience and the intricacies of operation, noting the real problems of such buildings for year-round residence :
The timber tolerates frost well and does not crack.- Stylish appearance of the house.
- Possibility to do without interior decoration.
- Warms up quickly and holds heat well
- Individual projects of houses made of timber may contain errors; it is better to choose proven ready-made projects.
Reviews can be read here and here.
Average prices
Prices for these types of houses depend on the stage at which the project is being completed: “turnkey” or “shrinkage”. You need to pay attention to this when concluding a contract. If with the “shrinkage” option, everything is more or less clear, a box is erected and the roof is built according to the customer’s wishes. But the term “turnkey” in such a house does not mean that the owner can immediately move in and live in it.
In the “key-to-key” version of a dwelling made from professional timber, the customer will receive:
- Floor, window and door packages.
- Walls prepared for interior and exterior finishing work.
- Engineering communications, without instruments. The maximum is temporary lighting in the form of a light bulb.
Average price for turnkey work on a 100 m2 premises:
- for shrinkage from edged timber 150x200 mm with a foundation - 830,000 rubles;
- for shrinkage from professional timber 200x200 mm with a foundation - 930,000 rubles;
- for shrinkage of laminated veneer lumber 200x200 mm with a foundation - 990,000 rubles;
- finishing work - 650,000 rubles;
- heating - 150,000 rubles;
- water supply - 50,000 rubles;
- electricity - 100,000 rubles;
- ventilation - 30,000 rub.
Total:
- turnkey from edged timber 150x200 mm with a foundation - 1,810,000 rubles;
- turnkey made of professional timber 200x200 mm with a foundation - RUB 1,910,000;
- turnkey made of laminated veneer lumber 200x200 mm with a foundation - RUB 1,970,000.
Unusual orientation
In the story about new designs of timber walls, one cannot fail to mention the technology of construction from vertical timber (Austrian brand Naturi).
Actually, the elements from which such a house is built can hardly be called timber; rather, they are profiles of complex cross-section, made by milling from solid dry timber. The profiles are installed vertically and fixed using guide pins and a shaped locking connection. Interventional spacers as well as insulating films and membranes are not used when assembling the box at home. It also does not need cladding: the outer elements have a smooth surface and are connected to the wall with the same locking connection. A wall made of vertical timber does not shrink, can withstand heavy loads from floors and roofs and allows excess moisture to leave the premises. Due to the presence of closed air chambers, it is slightly superior in thermal insulation capacity to a structure made of laminated veneer lumber (according to the manufacturer, a 200 mm thick fence has a heat transfer resistance of 2.05 m2 • °C/W).
To avoid the need to adjust the pillars supporting the balcony, it is best to build the latter on consoles. Photo: “Angarsk House”
This technology is associated with high costs of energy and timber (up to 50% of the volume of wood goes into shavings and sawdust) and belongs to the elite category: a standard cubic meter of vertical timber costs 35–40 thousand rubles. (for 1 m2 of wall you will have to pay at least 7 thousand rubles).
Photo
Options for houses for permanent residence can be seen in the photo: