November 23, 2021 Stroyexpert Home page » Foundation » Types and types
Diagram of a slab foundation with stiffeners
The most important structural element of the future building, on which its strength, reliability and durability depends, is the foundation. There are many types of foundations used for private housing construction. One of the most reliable foundations for any type of soil, as well as at any level of groundwater, is a slab foundation with stiffeners.
Slab foundation with stiffeners
Scheme of a slab foundation with stiffeners
The most important structural element of the future building, on which its strength, reliability and durability depends, is the foundation. There are many types of foundations used for private housing construction. One of the most reliable foundations for any type of soil, as well as at any level of groundwater, is a slab foundation with stiffeners.
- Types of foundation slabs
- Advantages of a slab foundation
- Slab foundation technology
- Preparation
- Formwork
- Concreting
- Conclusion
Types of foundation slabs
- Stiffening ribs down: when the strip base is placed under the base of the slab;
- ribs up: the tape is poured around the perimeter of the slab;
- combined production option: ribs are placed in two ways on one plate.
The ribbed slab reduces the amount of concrete used, without reducing the strength index.
Tapes on a monolithic slab are laid around the perimeter of the slab, under the supporting structures. If the building area is large, then transverse slabs (FBS) are laid for strength. The height of the tape is determined in accordance with the calculated data. The upper ribs - protrusions - act as a base. Insulation is installed in the opening. If necessary, communication cables and heated floors are laid.
Design features
Essentially, this design is a combination of strip and slab base
The slab base in the form of a continuous monolithic structure under the house is itself quite strong. But in some cases it is necessary to give the structure additional rigidity. This is achieved through the use of stiffening ribs, which are located along the perimeter of the slab and sometimes stand at a certain pitch along the longitudinal side (if the slab is very long).
Important: among all types of foundations, it is the monolithic slab that ensures sufficient stability of a heavy building on any type of soil, since it has the largest supporting area.
Essentially, this design is a combination of strip and slab base. Imagine that a solid monolithic slab was placed on a monolithic strip or, conversely, a monolithic strip was installed on a solid slab base. This is what a slab foundation looks like, equipped with stiffening ribs.
In this case, the slab is a single monolith with a rib structure. This gives the entire structure additional strength, resistance to soil movement and rigidity.
Attention: stiffeners must be installed along the perimeter of the slab part and under all load-bearing walls of the building.
If the building area is large, then the ribs can be located not only across the long side, but also along it, thereby forming a lattice-like structure. The thickness of the slab structure and the height of the strip part are determined by calculations taking into account all loads and soil characteristics.
Scope of use
Such foundation designs can be used on soils of any complexity, but it is especially advisable to choose this type of foundation in the following cases:
- On soft soils, a slab structure with stiffening ribs will be a good alternative to a deep strip foundation.
- In the northern regions, due to the large depth of freezing, the cost of installing a deeply buried strip structure increases significantly, so it is better to use a slab with increased rigidity.
- Also, such structures are indispensable on bulk soils.
It is worth knowing: when groundwater is deep, as well as when building on rocky, dense soils, installing a foundation slab is not practical from an economic point of view.
Foundation slab with stiffeners
Slab foundation with stiffeners 2014 Postroj-sam.ru
As mentioned earlier in my articles, a slab foundation is a monolithic slab poured under the entire house. But the technologies for laying this type of foundation are slightly different, and one of these types is precisely a slab foundation with stiffeners.
This type of foundation is a monolithic slab with additional stiffening ribs around the perimeter; in some cases, for example, if the building is long, additional ribs are constructed along the long side of the house.
It is a good alternative to a deeply buried strip foundation on soft soils and in northern regions, where the cost of laying a strip foundation is quite high due to the large freezing depth. In such cases, it will be more appropriate to use a slab foundation with stiffeners.
Depending on the purpose, a slab foundation with stiffeners is used in two different versions:
- with stiffening ribs downwards with stiffening ribs upwards
Now let's take a closer look at both of these types.
Slab foundation with downward stiffening ribs
It is mainly used instead of a conventional slab foundation to save material, that is, the slab is made thinner, and the strength is compensated by stiffening ribs that strengthen the slab along the perimeter (usually under load-bearing walls), where the maximum load is concentrated.
This type of slab foundation is somewhat reminiscent of a shallow strip foundation. monolithically poured over the slab. The stiffeners and the slab must be a single whole, that is, a monolith. The reinforcement of this type of foundation must be treated with extreme care.
The technology for laying such a foundation is simple. The soil is excavated according to the dimensions of the future foundation, then a trench is dug where there will be stiffening ribs near the slab. If necessary, formwork and a sand cushion are constructed, then reinforcement is tied together and the whole thing is filled with concrete of a grade not lower than M200. Well, don’t forget that concrete gains most of its strength 28 days after pouring.
Slab foundation with stiffening ribs up
It is used in the same way as the previous type - to save material. The technology itself of laying a slab foundation with upward stiffening ribs will not bring any savings compared to the foundation discussed a little earlier, but in the future it will allow saving on the construction of the base, since the upward-directed stiffening ribs will perform its function.
This type of foundation, like the previous one, is preferably laid as a monolith. This is where some difficulties may arise. As can be seen from the diagram, it is necessary to construct formwork for these same ribs, but since it is advisable to fill the slab together with the ribs at one time, part of the formwork will have to be constructed “in weight”.
Not only must the formwork “hang” at a certain height from the ground, it must be secured in such a way that during pouring the concrete will not push it upward, thereby violating the geometry of the foundation and increasing costs.
In addition, it is necessary to pour concrete into the formwork with some caution, since the rule of communicating vessels may work. Following the laws of physics, the level of concrete in the main slab will try to equal the level of concrete in the formwork, “pulling” it away from there
Stages of constructing a monolithic foundation with your own hands
Foundation layout diagram
- digging the foundation along strictly marked lines and with a calculated immersion depth;
- filling the base with a sand and gravel cushion;
- creation of a special pipe or drip drainage system along the perimeter of the future foundation or along the external contour of the foundation;
- It is recommended to create an expensive layer of footing in the sand cushion, which protects the basement from water ingress.
That's it, the preparatory work is completed. The pit is ready, a drainage system is provided, the load on the corners of the foundation, as well as the main load points, are correctly calculated. Now it's time to build the foundation itself. And this procedure also consists of a number of stages, because only then will everything work out as correctly and reliably as possible:
- Foundation reinforcement. Depending on the type of building and its mass, horizontal and vertical reinforcement can be considered popular. There is also corner reinforcement using seal welding, but this is popular in the construction of high-rise prefabricated buildings.
- Installation of wooden formwork. It should be slightly wet to ensure optimal adhesion to the concrete mortar. It is also taken into account that mesh formwork always protrudes beyond the width of the foundation. But this is not a problem, because all popular monolithic foundations are buried, so the external contours are subject to waterproofing. The arrangement of formwork is done depending on the type of soil and its characteristics, therefore it is selected individually in each case.
- The main stage is concreting. There are several options here. If it is possible to use several concrete mixers at once, then it is better to simultaneously pour concrete in layers. But if the budget does not allow this, then you can fill the fragments with concrete and connect them with reinforcement. But this technology is a little more expensive.
- Dismantling the formwork and checking the monolithic base for strength. This is the climax.
Bases with ribs down
Slab structures with downward ribs are commonly used in place of traditional slab foundations.
Slab structures with downward ribs are commonly used in place of traditional slab foundations. This makes it possible to reduce the height of the monolithic slab, which significantly reduces material consumption. In other words, the decrease in strength due to a decrease in the thickness of the slab is compensated by stiffening ribs that strengthen the structure around the perimeter and under the load-bearing walls.
This type of foundation is very similar to a shallow-buried strip structure with a monolithic slab on top. All parts of the base must form a single whole, that is, be a solid monolith. That is why the reinforcement of a slab foundation with stiffening elements should be treated with special attention.
Important: the rigidity of a slab structure with a downward-pointing frame depends on the characteristics of the soil on the site and the load on the foundation.
The advantages of such designs:
- No interference when constructing a basement, since the top surface of the slab is quite smooth.
- Easier installation technology.
- Since the base under the slab must be carefully compacted, it is necessary to use expensive high-quality formwork for the stiffening elements. Otherwise, the geometry of the box may be disrupted.
- Filling with mortar is carried out in stages (first - tape, and after a week - slab). This can lead to a violation of the integrity of the structure due to cracking of the protective layer of concrete. As a result, the durability of such a foundation will be short.
- In order to lay communications under the slab, you will have to arrange special channels by laying capsules and casings. If this is not done, then repair work on utility networks will not be possible without opening the monolithic slab.
Advice: if the house is planned to have a basement, then it is better to lay utility lines directly on the floor.
Classification
There are three types of ribbed slab bases:
- with ribs pointing down (in this case, the monolithic slab rests on a frame in the form of a continuous strip);
- with ribs directed upward (a continuous strip of stiffening elements rests on a monolithic slab on top);
- combined version of the frame arrangement.
The ribs turned upward additionally serve as a base. They must be insulated. Utilities can be laid between them, as well as underfloor heating systems installed. The monolithic tape located on the top of the slab serves as a support not only for load-bearing walls, but also for the materials cladding the facade, as well as roof structures and ceilings.
A foundation with stiffening elements turned downward resembles a shallowly buried strip base, which is rigidly connected to a monolithic reinforced concrete slab laid above. The only difference is that the cross-section of the tape is trapezoidal rather than rectangular.
The technology for constructing a base with ribs pointing down is somewhat simpler than in the second option. The thing is that in this case there is no need to erect hanging formwork. Also, when pouring stiffeners, there is no need to monitor the level of the concrete mixture, which, according to the laws of physics, can begin to rise in the area of contact with the slab.
Plate with stiffening ribs down
The structural features of a foundation slab with downward stiffening ribs are that the design resembles a shallow strip foundation combined with elements of a concrete slab. The so-called inverted bowl. The ribs are trapezoidal in shape. Depending on the type of base on which they will be located, the shape of the ribs is poured. When constructing a building on combined types of soil, several types of slabs with different rib shapes and technical indicators can be combined. In each specific case, it is necessary to carry out calculations, since the manufacturing technology does not provide templates. This can be independent calculations using available literature or the involvement of a qualified team.
The more correctly the calculations are carried out and the desired shape of the ribs is selected, the more concrete can be saved. However, we should not forget about the safety and strength of the building. For many designers, the “inverted bowl” causes an ambiguous opinion for the reason that it is necessary to incur costs at the stage of constructing the trench. Due to the design features, an increased width will be required, and the cost of binding wire for tying with the reinforcing mesh will be required. However, these are the costs only at the initial stage; subsequently they are compensated by a minimum layer of concrete when pouring.
Slab installation cost
The relatively new technology of using a profiled PVC membrane under the base makes it possible to simplify and speed up the installation of the foundation slab. Due to its excellent mechanical strength and water resistance, it serves as waterproofing and allows you to do without concrete.
Let's consider what the cost of such a foundation slab for an aerated concrete house with an area of 150 m² is at the beginning of 2021. Slab thickness 250 mm, section of plinth walls 600*400 mm:
| Name of materials and works | Unit change | Quantity | Price, rub. | Amount rub. |
| Work to bring the project to the site | complex | 1 | 3730 | 3730 |
| Soil development without removal | complex | 1 | 11220 | 11220 |
| Installation of embedments for sewerage from PVC pipes d110 mm: work | complex | 3730 | 3730 | |
| —“— materials | complex | 1 | 4270 | 4270 |
| Installation of mortgages for water supply from HDPE pipes d32 mm: work | complex | 1 | 7221 | 7221 |
| —“— materials | complex | 1 | 11220 | 11220 |
| Construction of a geotextile separating layer: work | roll | 3 | 749 | 2246 |
| —“— materials | roll | 3 | 2500 | 7500 |
| Sandy base with compaction thickness. 300 mm: work | m³ | 60 | 749 | 44928 |
| —“— materials with delivery | m³ | 60 | 850 | 51000 |
| PVC membrane Planter-standard: work | m² | 120 | 31 | 3744 |
| —“— materials | m² | 145 | 120 | 17400 |
| Built-up horizontal waterproofing: work | roll | 11 | 749 | 8237 |
| —“— materials | roll | 11 | 1565 | 17215 |
| —“— gas cylinder | PC | 2 | 1200 | 2400 |
| Consumables: board and timber for formwork | m³ | 2 | 11000 | 22000 |
| AIII fittings | tn | 2,1 | 50000 | 105000 |
| knitting wire | kg | 42 | 110 | 4620 |
| clamps | PC | 250 | 10 | 2500 |
| technical polyethylene | m.p | 500 | 50 | 25000 |
| Layout of foundation axes | m³ | 21 | 150 | 3150 |
| Installation of a volumetric frame with a cell 200*200 mm | m³ | 21 | 1872 | 39312 |
| Cutting and bending of reinforcement | m³ | 21 | 1495 | 31395 |
| Assembling the slab formwork | m³ | 21 | 299 | 6279 |
| Formation of a slab of B22.5 concrete with delivery: work | m³ | 21 | 2392 | 50232 |
| —“— materials | m³ | 21 | 5100 | 107100 |
| Dismantling the slab formwork | m³ | 21 | 76 | 1596 |
| Formwork for basement walls (lumber) | m² | 42 | 800 | 33600 |
| Removal of the axes of the stiffening ribs (base) | m³ | 6 | 150 | 897 |
| Installation of the plinth frame | m³ | 6 | 1872 | 11232 |
| Cutting and bending of reinforcement | m³ | 6 | 1495 | 8970 |
| Installation of plinth formwork | m³ | 6 | 299 | 1794 |
| Formation of a plinth from concrete B 22.5 with delivery: work | m³ | 6 | 2392 | 14352 |
| —“— materials | m³ | 6 | 5100 | 30600 |
| Dismantling the plinth formwork | m³ | 6 | 75 | 452 |
| Overhead and transportation costs | ||||
| Rent and transportation of a cabin | PC | 2 | 13500 | 27000 |
| Backhoe loader | shifts | 1 | 15500 | 15500 |
| Delivery of fittings | cars | 1 | 13500 | 13500 |
| Delivery of piece materials and boards | cars | 1 | 14000 | 14000 |
| Concrete pump | cars | 2 | 21000 | 42000 |
| Rigging and fastening | 15% | 65614 | ||
| TOTAL ESTIMATED: | 873760 |
Thus, 1 m² of a foundation slab with stiffening ribs pointing upward, and with a profile membrane instead of a footing, costs 5,825 rubles.
The foundation is ready, all that remains is to dismantle the formwork
Types of slab foundation
Initially, for heavy buildings, this foundation was made in the form of a rectangular reinforced concrete structure of the same thickness in all areas. However, such a slab has a maximum construction budget due to excessive consumption of reinforcement and concrete mixture. Therefore, modifications have been created for different operating conditions of the following types:
ribbed slab - the foundation is much thinner in the central part (10 - 15 cm instead of 35 cm), under the load-bearing walls there are stiffening ribs directed downwards or upwards
insulated “Swedish” foundation – has a warm water floor integrated into the upper part, poured with stiffeners on top of a heat-insulating layer (high-density extruded polystyrene foam)
coffered slab – has a basement under one/several rooms, poured in three stages
Attention: For cottages with basement usable levels, two foundations can be used - a recessed strip or a slab. The first option is 10 - 20% cheaper, so buried slab foundations are used extremely rarely
The depth of the slabs is 40–70 cm, and the arable layer of soil, rich in organic matter, will have to be completely removed in any case. If this is not done, in a few months the organic matter will rot, and the building will inevitably sag below the design level.
Our works (all our works are here)
Kirpolye village Slab foundation according to the customer's design. Area 180 m2, thickness 15 cm, concrete B25.
For a client from Vsevolozhsk, complex construction work on the construction of the foundation was completed. The foundation was poured with dimensions
Price
| Thickness 200 mm | Thickness 250 mm | Thickness 300 mm |
| from 3200 RUR/m2 | from 3800 RUR/m2 | from 4200 RUR/m2 |
| The cost of work includes: | ||
- Geodetic works
- Digging a foundation pit (30 -40 centimeters deep)
- Laying the bottom of the pit with geotextiles
- Construction of a sand-crushed stone cushion with layer-by-layer compaction (20 cm sand, 10 cm crushed stone)
- Installation of formwork from boards
- Installation of windows for utility networks and laying of pipes
- Double reinforcement with a pitch of 250x250mm
- Pouring concrete M300
- Foundation waterproofing
A slab foundation with stiffeners is a “lightweight” version of a conventional flat slab. Thanks to the presence of reinforcing ribs, the thickness of the slab part can be reduced by 2–2.5 times without reducing the strength of the structure. This saves concrete, but requires more complex foundation work and increases the consumption of reinforcement.
Design and types of slabs with stiffeners
There are three types of such foundation:
- with stiffening ribs upward (concrete “ribbon” poured on top of a flat slab);
- with ribs down (with a strip part under the slab);
- combined (ribs are directed both up and down).
The first type is described in detail in the article “Do-it-yourself slab foundation with a grillage.” Here we will consider the second type - a slab with stiffening ribs directed downward. First, about its design.
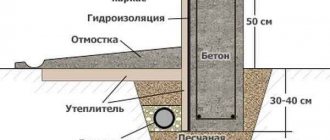
Stiffening ribs are protrusions resembling a concrete strip (up to 80 cm deep), but not with a rectangular, but with a trapezoidal cross-section. This shape reduces the soil pressure on the foundation (the loads in this case are tangential). The ribs are located under the slab along the perimeter of the house and inside the perimeter:
- under load-bearing walls;
- along the slab at a certain distance from each other;
- along and across the foundation (like a lattice).
Types of slab foundation
There are several options for making a foundation slab. Most often it is a monolithic slab, the thickness of which is the same over the entire area. The advantages of such a base include ease of installation; the disadvantage is that the upper edge is close to the ground surface - in this case, the base of the walls may be exposed to moisture, which is harmful to building structures. To ensure that the edge of the slab is located higher above the ground surface, you should not increase its thickness - this will significantly affect the cost of the foundation. A more practical option would be to install a slab with stiffeners.
The foundation is a monolithic slab with ribs up
The monolithic structure is a flat base with reinforcing ribs protruding above the surface - it looks like a strip foundation on top of a slab.
The ribs are located around the perimeter and under future load-bearing walls inside, if this is provided for by the project. A foundation slab with upward stiffening ribs allows the construction of a building with a basement or ground floor. In this case, the monolithic structure must be buried in the ground and grillage ribs of a suitable height must be designed. Subsequently, a layer of waterproofing is laid over the ribs and wall structures are mounted.
Slab foundation with ribs down
To increase the load-bearing capacity of the slab foundation without deepening it, a monolithic structure is made with stiffeners directed downwards.
There are two options for making a monolithic slab with downward stiffening ribs:
- Stiffening ribs are formed by trenches dug in the ground below the level of pouring the reinforced concrete slab. A reinforcing frame is installed in the pits for the ribs, made as a single unit with the frame of the slab itself, after which the concrete mixture is poured.
- A pit with a flat bottom is being prepared for the slab. Polymer slab insulation is laid on the waterproofed base - stiffening ribs will form in the spaces between the “islands” of the heat insulator and the walls of the pit. Before pouring the concrete mixture, a reinforcement cage is installed.
Stiffening ribs should be located under load-bearing walls and capital internal partitions. If the project does not include partitions, but it is necessary to increase the rigidity of the slab, the downward-facing ribs should be located parallel to the short side of the building in increments of up to 3 meters.
Laying a heat insulator, including extruded polystyrene foam, under the foundation slab not only allows you to install stiffeners of the required size, but also helps to insulate the foundation base and reduce the cost of heating the house. This type of foundation is called a “Swedish slab”. It is often supplemented with a water heating circuit.
Prefabricated slab base
Instead of a monolithic slab foundation, in some cases a precast concrete foundation is used.
Finished structures are laid close to each other. But this option can only be used on rocky soils that are not prone to heaving. In other cases, the base may deform over time under uneven heaving loads due to the lack of a rigid connection between the slabs. A foundation made of ready-made reinforced concrete slabs is used only in the case of the construction of outbuildings, bathhouses, and small light houses. A screed is made on top of the laid slabs. The technology for installing a prefabricated foundation requires the use of special equipment for transporting and laying slabs.
Height of floating slab above surface
According to the standards SP 21.13330, a slab foundation can be buried to any distance, focusing on the groundwater level and soil composition.
However, the higher the slab is located above the surface, the longer the lifespan of the wall materials. For example, the maintainability of the lower crowns of a log house is much higher if they are located above the ground. Therefore, for timber and log buildings, slabs with stiffeners are usually used:
- cup-shaped - a slab is cast, after the concrete has gained strength, formwork is installed, reinforced concrete beams are made under the load-bearing walls
- inverted bowl - the outer formwork panels are higher, the inner ones remain under the concrete structure for the entire period of operation, the inner perimeter is filled with sand or polystyrene foam is laid to insulate the structure
On heaving soils, it is necessary to calculate the cross-section of the reinforcement, the mesh cells of the lower and upper chords. It is forbidden to rigidly connect foundations to a sidewalk or blind area with a floating slab. Various loads and uneven freezing of soils under these structures can lead to the opening of cracks in reinforced concrete.
In this case, the calculation is made for the tensile strength of the sole from prefabricated loads, the upper surface of the slab when heaving forces occur.
Attention: The lower mesh can be made from rods 10 – 16 mm, since prefabricated loads are always present. The bottom mesh is knitted from rods 8 - 14 mm, since swelling is partially balanced by the weight of the house
Thus, the slab foundation for outbuildings has a thickness of 10 cm. To support the cottage, a load-bearing capacity calculation will be required. The choice of thickness is influenced by the size of the protective layer of concrete and the minimum permissible distance between the reinforcing mesh.
The foundation is a “monolithic reinforced concrete slab” 200mm thick.
Vibrating rammer with a 4-ton roller
A few words about the construction of this type of foundation. First you need to remove the fertile layer. After this, it is necessary to pour in ASG (sand and gravel mixture) and be sure to compact it. Briefly about the main types of compaction of ASG: copious spilling of water for 1-3 days; layer-by-layer compaction of 200 mm with a vibrating rammer weighing 50–300 kg; compaction with a roller weighing about 4 tons with vibratory compaction (punches up to a meter at a time). It is best to compact it with a roller; it is ultimately cheaper and faster; now for $100...200 you can order a roller with delivery. Next, it is necessary to separate all underground communications, lay down a film so that the cement laitance does not escape, and pour concrete into a pre-installed formwork with reinforcement. It seems nothing complicated, but in reality there are many nuances. Once again I was recently convinced when I was building a similar foundation
foundation stiffeners
your future home. I draw your attention to the fact that if the concrete is grade 400, then there is no need to do waterproofing, because... In this case, concrete does not allow moisture to pass through.
And a few words about a common analogue - USP (insulated Swedish stove). In my opinion, a very risky and expensive decision. Firstly, the insulation is located directly on the sand-
foundation reinforcement
gravel mixture and it is unknown what will happen to this material in 10 years. Moreover, under such a considerable load. Secondly, the sand can be compacted unevenly, and then a hole will form under the slab: the insulation will shrink together with the sand and there will no longer be proper thermal conductivity. Thirdly, there is too much excess insulation, it is three times more than necessary and sufficient. It should be taken into account that there will be no
Characteristic advantages and disadvantages
- Despite the widespread use of the slab type, it has a significant drawback in the form of a number of channels for laying communication cables and heated floors. Communications must be laid in advance and ensure that they are not damaged before pouring. This is not always practical, since there are many objective factors. If there is a basement, the laying is done along the floor of the structure;
- the need to construct two formworks: one in the form of a trapezoid at the bottom, the second at the top in the form of a rectangle;
- non-standard scheme for structural reinforcement. In each specific case it is necessary to draw up a calculation;
- the need to install waterproofing, since the impact will be from moisture;
- single use;
- difficulties in designing load-bearing and secondary walls due to the large area of the foundation pit.
But, despite many minor shortcomings, there are a number of positive aspects, such as:
- an inverted slab allows you to reduce the thickness of the slab to a minimum of 100 mm, reducing the cost of the estimate;
- flat surface of the basement floor;
- reducing costs for surface leveling;
- the possibility of construction on different types of soil foundations, including heaving ones and with a high level of groundwater.
The quality of the pros outweighs the quality of the cons.