We carry out the construction of turnkey foundations at a price of 6,000 rubles per m/p. The minimum period is 7 days. We will purchase the materials and deliver them ourselves. We use professional formwork, tools and equipment. We carry out the installation of foundations in strict accordance with the structural calculations. We use reinforcement with a diameter of 14 and 16 mm, concrete not lower than grade M350.
We guarantee:
- strict adherence to deadlines;
- an officially concluded agreement;
- online observation or photo and video reports every week;
- benefit up to 20% on materials through purchasing at the wholesale price list.
We carry out a range of works on site marking, pit digging, and relief planning. We do not engage in subcontracting - SBC employs only full-time specialists. During the pouring process we use up to 4 deep vibrators simultaneously. We moisten the concrete daily during the period of strength gain. We remove the formwork carefully, without knocking off the corners.
TYPES AND COSTS OF FOUNDATIONS FOR A PRIVATE HOUSE
The price depends on the type of base, the amount of concrete and reinforcement required. Approximate calculations can be found in the table below on the page. We carry out the construction of foundations for private houses of all types:
- monolithic-tape
– universal type of base, suitable for clay, sandy, heaving soils; - pile-grillage
- used in areas with deep levels of freezing, complex terrain and weak-bearing soil; - monolithic slab
- has a high load-bearing capacity, suitable for the construction of houses of any type; - insulated Swedish plate (USP)
– due to insulation, the foundation reduces heat loss by 30-60%; - prefabricated foundation made from FBS blocks
- easy to install, characterized by high construction speed and relatively low price.
In the Moscow region, soils mainly fall into the “loam” category. Groundwater can be at a depth of 1 meter, so SBC specialists must conduct a geostudy before starting work.
Other Features
In addition to the nuances regarding the depth, type and width of the sole, as well as the elevation on the plan of a strip-type foundation, the drawing must be drawn up in compliance with a number of rules. These include scaling and fragmentary images of individual nodes and elements.
Scaling
Regulatory acts for drawing up a foundation drawing are established by the following documents:
- GOST R 21.1101-2013.
- GOST 2.302-68.
- GOST 21.501-2018.
The requirements applicable to scales reveal the main points affecting the images of the entire structure and its individual elements. The detailed ratio can be found in the table below.
| Applicability | Value, scale |
| Plan of the facade, foundation, roof, basement, floors and ceilings | 1 in 100 or 1 in 200 |
| Separate plan of sections, fragment of foundation, basement, facade | 1 in 50 or 1 in 100 |
| Detailed schematic representation of the unit, product | 1 in 2, 1 in 5, 1 in 10 or 1 in 20 |
Important! These requirements apply only to architectural and construction drawings of residential and public buildings. Different standards apply for commercial and industrial buildings.
MONOLITHIC-BELT FOUNDATION
Used in heaving soils.
This type of foundation can withstand heavy loads; there is the possibility of arranging a basement floor. Turnkey price - from 8,000 rubles per m.p. Load bearing capacity:
from 8.500 ₽/m.p.
work+materials
- Order
- More details
Classification of soils in construction
Choosing a foundation for a house begins with studying the soil on the site, understanding its load-bearing capabilities and features that affect the design of the house’s foundation and the material used to make the walls. Let's look at the main types of soil.
| Soil type | Description | pros | Minuses |
| Rocky | Consist of a rock mass. | Does not shrink under loads; Does not require a buried foundation; The load-bearing capacity is usually sufficient to support a building simply placed on top of them. | They freeze to a greater depth, compared to other types of soil. It is necessary to insulate utility inputs and, using insulation, “cut off” the soil from the building. |
| Sandy | Consist of more or less large sand particles. They vary in size: large, medium-sized, small, dusty, density: dense, medium, loose. | Not prone to frost heaving. Easy to compact. | They crumble easily and require serious work to strengthen the walls of trenches and pits. |
| Peat soils and vegetation layer | almost half consist of humus and plant residues. | None. | They cannot form the basis of structures. Roman Nikonov: If you find such soil at the base of a building, you need to replace it with sand, make the base of the foundation below the layer of such soil, or go through it using a pile foundation. |
| Silty-clayey | Consist of a mixture of sand and clay particles in different proportions - sandy loam, loam and clay | They hold vertical walls, which simplifies excavation work. They are waterproof | They are heaving. |
Only studying the totality of the properties and characteristics of the soil will make it possible to build a strong, reliable and durable foundation.
PILE-GRILLF FOUNDATION
Suitable for houses up to two floors - it is designed for relatively light loads. Cannot be used in moving soils. It will not be possible to arrange the ground floor. The main advantage is the relatively low price - from 6,000 rubles. per m.p.
- Load bearing capacity:
- Device cost:
- Manufacturability:
from 6.000 ₽/m.p.
work+materials
- Order
- More details
The need for a plan
A drawing of the foundation of a building is made so that the structure erected on it is reliable and functions for a certain time. Owners should safely use entrances, elevators and stairwells as... the load from them is provided for when designing the support of the structure.
The foundation design for a house must meet the requirements:
- contain simple technical solutions that are convenient to implement on site;
- provide for advanced construction methods during construction with savings in labor costs and materials;
- include durable structures that do not tip over or slide in the ground;
- contain the required dimensions, tied to the axes of the walls of the house.
Material costs for the construction of the foundation are 10% of the total cost of the building in the absence of a basement and 15% in the case of using a basement floor. The labor intensity of the work is 12–15% of the figure for the entire building.
FOUNDATION - MONOLITHIC PLATE
Suitable for weak and moving soil. Withstands colossal loads. The main disadvantage of this is the high cost - from 6,000 per m2, because... Significantly more reinforcement and concrete are required.
- Load bearing capacity:
- Device cost:
- Manufacturability:
from 6.000 ₽/sq.m.
work+materials
- Order
- More details
Conditions for accurately transferring the plan to the area
Marking the area
The main parts of the drawing are drawn on the same scale, but individual detail units are drawn in enlarged form for better reading. General scaling is performed within 1:100, 1:200, 1:300 and smaller.
To carry out the transfer, the axes of the structure are laid out on the ground. The surveyor maintains right angles and distance between lines. The directions of the axes are marked with a cord; the marking points are placed at a distance that will not be affected when digging trenches.
The laying depth is set by a level, while a ±0.00 mark is placed on adjacent walls, buildings or pillars, which serves as a guide for further height calculations.
INSULATED SWEDISH PLATE
USHP is suitable for any type of soil, can withstand enormous loads, there are no “cold bridges” - you immediately get a warm floor for your home. During its construction, energy-saving technologies are used, which allow you to save on heating in the future. The cost of USP is from 6,500 rubles. per m2.
- Load bearing capacity:
- Device cost:
- Manufacturability:
from 6.500 ₽/sq.m.
work+materials
- Order
- More details
Site layout
When choosing a site for their future home from several options, many developers are guided only by price, area and the presence of utilities. But, as practice shows, one of the decisive factors when choosing a site for future development, and therefore foundation work, should be the possibility of competent planning of the territory.
Andrey Pashukhin. Construction engineer for the company Fundamentally. RF
It is advisable to choose a site for a house in accordance with your understanding of how you plan to use it subsequently, namely, what kind of house and outbuildings will be built on it.
Already at the initial stage, you need to look at whether the site is suitable for your needs, and not try to build a house on a completely unsuitable territory.
If you initially plan to build a large stone house with two or three floors, then the appropriate site must be selected. It should be at least 10-15 meters larger than the boundaries of the house and have soil with good bearing capacity.
You need to clearly understand that the more complex the geology and soils on the site, the more expensive it will cost to build the foundation of the house. The design should be based on a feasibility study of the house design and geological surveys to determine the type of soil.
The main factors that determine what the design will be are as follows:
- Characteristics of the future house and its design features;
- The material from which the house will be built;
- Type of soil and slope of the site;
- Groundwater level and soil freezing depth in winter.
The heavier the house and the more complex its design, the more complex the foundation and the more expensive it will cost.
PREFABRICATED MONOLITHIC FOUNDATION FROM FBS BLOCKS
An ideal solution if you need to build a basement quickly. It has high compressive strength and withstands frost. Suitable for clayey, sandy, low-heaving soils, and for soils with high acidity. Popular due to its simple installation, speed of construction, and relatively low cost - from 8,000 rubles. per m.p.
- Load bearing capacity:
- Device cost:
- Manufacturability:
from 8.000 ₽/m.p.
work+materials
- Order
- More details
Nuances to consider when building a foundation
When designing the foundation of a future home, you need to consider a number of points:
- When developing a pit for the foundation of a house, additional space will be required for the excavated soil. The volume of soil removed can be significant. Then it is necessary to take into account the additional costs of removing soil if its secondary use is not planned.
- The delivery and storage of materials must be planned in advance. It is advisable to place materials near the pit in descending order of its specific gravity. This will save effort when mixing and pouring concrete.
- If you plan to use machinery, then in wet weather you will need to fill the road with crushed stone or construction waste.
- When pouring concrete in several stages, it is necessary to provide additional time at the end of the shift to clean the tools from cement mortars and mixtures. Dried cement will require much more effort and time from you to clean.
- Placing bags of cement will require careful waterproofing of the site. Impermeable material must be laid on the ground and the stacks of cement must be carefully covered. Damp cement very quickly turns to stone and becomes unsuitable for use.
- The last thing you need to do is deliver the reinforcement to the construction site.
- Correctly calculate the required water supply if there is no source nearby. Make a separate point about the supply of drinking water.
- In cramped conditions, digging a foundation pit or trench begins from the most inaccessible edge.
- The easiest way to determine right angles when marking a pit is to compare the diagonals. In a regular rectangle, the diagonals should be equal.
Here in this video you can watch all the most important moments of designing a building foundation online.
Among the main types of foundations that are used in modern construction, several types can be distinguished separately:
- tape;
- monolithic tape;
- columnar;
- pile;
- slab;
- shallow;
- screw;
- floating;
- foundation from scrap materials for small structures (bathhouse, fence, greenhouses).
Various types of foundation construction for a private residential building
SIZES, PRICES AND VOLUME OF CONCRETE
The cost of building a foundation is calculated on the basis of design solutions, where the depth, height, width, volume of materials and work are determined. The most popular foundations are 6x8, 8x8, 10x10, 10x12 meters. The volume of concrete depends on the amount of reinforcement (linking pattern) and the size of the future house. Experts analyzed actual estimates for 2021-2022 and compiled a table where you can see how much a foundation of popular sizes costs depending on the type of foundation. The price includes planning, site marking, and a complex of earthworks. To get an accurate estimate, contact the manager.
- 6 by 6
- 6 by 8
- 6 by 9
- 8 by 8
- 8 by 9
- 8 by 10
- 10 by 10
- 10 by 11
- 10 by 12
Basic calculation parameters
Depth of foundation
The support of the house is designed according to calculations that are performed on the basis of engineering and geological research.
Take into account the following data when choosing a foundation layout:
- design features and purpose of the house, the amount of pressure on the foundation;
- marking the location of adjacent supports and laying adjacent communications;
- relief of the built-up area;
- mechanical and physical properties of the earth, combination of layers, presence of weathering areas, etc.;
- the impact of construction on changes in soil characteristics;
- the likelihood of soil erosion during construction in water bodies;
- the depth of soil freezing and the height of soil liquids.
A rational depth mark is selected after comparing several alternative options. Markings in the plan are carried out along the auxiliary and main axes of the structure, while the elements are detailed and a drawing of a section of the foundation is drawn up.
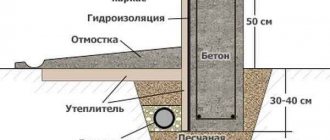
Insulation of a shallow foundation
- The first step is to dig a trench around the perimeter of the base, going deep to the foundation cushion. The width of the trench should be 5 cm greater than the freezing level of the soil.
- The outer part of the base is treated with a bitumen waterproofing compound, applying it in a continuous layer over the entire surface of the foundation wall, including the base. You can also use bitumen-based roll material as waterproofing. It is glued to the wall using bitumen mastic.
- The thermal insulation material is covered with a dense membrane or geotextile. This will give the insulation a flat and smooth surface, which will protect the material from damage as a result of soil heaving.
- Upon completion of these procedures, drainage pipes are laid if necessary. The trench for them is filled with a sand and gravel mixture.
Expanded polystyrene slabs are secured using a gas burner. The waterproofing roll covering is heated in several places, after which the insulation is pressed tightly against the wall.
We recommend:
- How much concrete is needed to construct a strip foundation? In order for the strip foundation to be installed correctly, it is necessary...
- How not to make a mistake when building a monolithic grillage foundation A pile foundation for a grillage during the construction of a house today has enough...
- Building a bathhouse with your own hands: building a foundation Any construction work during the construction of a bathhouse begins with the construction of a foundation….
- Water heating devices: what to choose? During the construction of a country house, much attention is paid to interior decoration...
Video description
To see all the work involved in preparing the site and pouring the foundation, watch the video:
Formwork
Before pouring the foundation for the house, it is necessary to form a strong, reliable formwork. To form removable formwork you can use:
- wood;
- metal;
- plywood;
- plastic.
Permanent formwork becomes part of the structure and avoids the dismantling stage. To form it use:
- expanded polystyrene;
- wood boards;
- fiberboard
Permanent formwork block for strip foundation Source ofacade.ru
Construction of a thermally insulated shallow foundation - TFMZ
The laying scheme and parameters of the thermal insulation layer in the foundations of heated buildings with floor insulation are shown in Fig. 1.
| Fig.1. Layout of thermal insulation in the foundations of heated buildings. 1 - foundation; 2 - wall; 3 - floor; 4.5 - horizontal and vertical thermal insulation; 6 — protective coating; 7 - sand preparation; 8 - blind area; 9 - PGS 10 - drainage; 11 - floor insulation. |
As a thermally insulated shallow foundation (hereinafter referred to as a warm foundation), foundations on a soil cushion (columnar, strip or foundation slabs) are used, the base of which is laid to a depth of 0.4 m in heated buildings and to a depth of 0.3 m in unheated buildings.
Unheated buildings are buildings with indoor air temperatures in winter equal to or below +5 °C.
The bearing capacity and dimensions of the foundation are determined by calculation in accordance with SNiP.
Preparatory work
The preparatory work stage occupies an important place in the process of building a house. First of all, it is necessary to clear the area of construction debris, cut down excess trees and uproot stumps, and remove dry grass.
Preliminary zoning of the site will allow you to effectively use every corner during operation. It is best to level the surrounding area before starting construction work and laying the foundation. This will not only give the site an attractive appearance, but will greatly facilitate construction work at all stages. The terrain with large differences requires stepwise leveling of the territory.
Next, the exact location of the house is determined and the foundation is marked. To do this, pegs are installed in all corners of the future building. If the house is a standard rectangular shape, the result should be a figure with perfectly equal angles of 90°. If the angle is not maintained, it is necessary to achieve this result by moving the limit cord in one direction or another.
Along the future walls, at the same distance from each other, pegs are also installed and a rope or cord is pulled between them. The diagonals drawn between the corners of the building must be exactly equal to each other.
An example of checking angles in markings - if the diagonals are equal, then all angles are 90° Source homeframe.ru
When marking for a strip foundation, it is necessary to retreat from the walls of the house at a distance equal to the width of the foundation. Most often this figure is no more than 20 cm.
You can dig a trench either by hand or using specialized equipment. It is formed at least 20 cm below the freezing point of the ground, characteristic of the area in winter. It is necessary to dig a trench strictly following the markings and forming a flat bottom.
Technology for constructing pile foundations
The technology for constructing pile foundations includes several stages:
- Drilling wells of the required diameter;
- Installation of fittings;
- Subsequent concreting of the well.
The main advantage of a pile foundation is the possibility of using a hand-held construction drill.
The construction of pile foundations always begins with drilling wells, the size and number of which depend on the area and weight of the future building. The parameters of the piles are determined by the loads created by the partitions, roofing and floor. Please note that the maximum diameter of a hand drill should be within 300mm. If you need to drill wells with a diameter of 600 mm, you should use an industrial drill.
At the next stage, it is necessary to carry out high-quality waterproofing of the foundation, for which roofing material is laid along the diameter of the well (a “pipe” is made from the material, which should be approximately 300 mm greater than the depth of the well). When making the upper part of the “pipe”, three layers of roofing material are used, which are pulled together using steel wire (this part will be the formwork).
Technology for laying a pile foundation for a house
If the well is a quarter filled with water, then before pouring concrete, excess liquid must be pumped out. Failure to use roofing felt can be fraught with unpleasant consequences: when the concrete sets, the cement will not gain sufficient strength, and freezing of the soil will have too negative an effect on the condition of the concrete.
Pile foundation arrangement diagram
After preparing the well, it is time to tie the reinforcement for the foundation, for which a frame is made from the reinforcement, consisting of three vertical rods with a diameter of 6 mm. The last stage is to fill the well with concrete, which must be poured in layers 40-60 cm high. During pouring, the concrete is compacted using vibrators.
By type of design
Based on the type of construction, foundations that can be used under a house in our latitudes are divided into five general types.
- Strip foundation - one of the most common for individual housing construction. It can be used on almost any type of soil. It can be used to build not only light wooden or frame houses, but also heavy ones - for example, made of brick. The essence of such a foundation is that it is laid under all the external walls and main partitions of the house. Thus, the entire structure receives maximum rigidity. Strip foundations are convenient because they are suitable for arranging basements - in this case, the basement walls will be the foundation strips (however, this depends on how high the groundwater is). There are several different types of strip foundations depending on the material, method of pouring (or laying), and depth (we will talk about them in more detail in the following articles of the project). In each individual case, a different option is chosen. As we have already said, a strip foundation can be built on different soils, but it is usually recommended to use it on so-called medium-density soils (limestone, shale, sandstone, lime spar, etc.). But if the house is located on “floating” soil (in the case of Tatarstan, this could be, for example, a wetland, clayey soil, loess) - you may have to choose a different type of foundation.
Photo proprofnastil.ru - A pile foundation is another popular option in our area, which, however, has one big drawback: it won’t work as a basement or ground floor. And one more drawback - it cannot be equipped without the use of special equipment. This design consists of piles buried in the ground to the required level and united by a grillage. They are installed in corners and in places of heavy load (for example, where load-bearing walls intersect). Pile foundations are shown on those soils that have the unpleasant ability to “float or go” (the same clay, loess, quicksand, loose sand and other treacherous soils). Such a foundation can be driven (when the supports are loudly driven into the ground with a pile driver to the delight of the neighbors), driven (when they first drill wells under the piles and then simply pour concrete mortar there) and screw (this is a task for cheaters: screw piles with blades on at the end of the working part they are simply screwed into the ground, like a corkscrew). The piles themselves can be made of reinforced concrete or, for example, wood. The pile foundation is considered strong, stable and durable, and it can also be used in coastal areas where groundwater is quite high.
- Columnar foundation - the third most popular option after tape and pile. It can safely be called the cheapest, and it behaves perfectly in freezing soils. But do not think that this is a dream foundation: it can only be used for the lightest houses (for example, for small frames), a grillage is desirable for it (with the exception of those houses whose design already includes a lower load-bearing beam), they do not tolerate side beams well loads, and the basement or basement will also require costs. In addition, the soil under it must have normal bearing capacity - such a foundation cannot be built either on sand or loess. Or rather, it will work, but it’s not worth it. And it is also not recommended to build a columnar foundation in an area with a large difference in heights - uneven soil pressure can topple some supports after installation.
The material for a columnar foundation can be wood, concrete, brick, stone, reinforced concrete or prefabricated blocks. Not only light frame houses are built on such a foundation, but also very often bathhouses, outbuildings, and summer houses.
Photo 1beton.info - Slab foundation is a reinforced concrete slab that is poured under the entire area of the house. This is not the most common type of foundation in our area: it is very expensive. For example, a calculator on the website of one of the construction companies in Kazan shows that a slab foundation with an area of 80 square meters for a residential building will cost 700 thousand rubles.
This solution is chosen if you want a very heavy house (for example, brick or stone), and the soil is fragile, with low bearing capacity. The slab will create a perfectly level foundation for building a house, leveling out soil movements. And even if the soil swells (moves not only to the sides, but also upwards), the slab foundation will simply rise entirely along with the soil. It will not be possible to build a basement under it, but the slab can become the basis for the floor on the ground floor.The slab foundation consists of several layers: in addition to the reinforced slab itself, a waterproofing layer is laid under it, a concrete preparation layer and geotextiles are placed even lower, and a compacted sand base is installed at the very bottom.
- TISE foundation (stands for “technology of individual construction and ecology”) - a technology developed in the mid-90s of the 20th century. It is a kind of hybrid that combines pile and tape technologies. This foundation is formed from bored piles, expanded at the bottom, and a raised reinforced concrete grillage. In order to do this, you need to arm yourself with a special hand drill, equipped with a cutting and expansion nozzle, which creates a dome-shaped expansion at the bottom of the well.
TISE foundation is gaining popularity because it is quite versatile. You can build lightweight houses on it: two-story houses made of timber, foam concrete and frames, and one-story brick houses. Such foundations are well suited for brick and concrete fences; bathhouses, garages, and workshops stand perfectly on them. In terms of soil, there are no special “whims” - the TISE foundation will behave well on clay, and on sandy loam, and on loess, and on sand.In addition to the fact that you cannot build heavy houses on such a foundation, another serious disadvantage is the impossibility of organizing a basement or basement, and a raised grillage leaves ample opportunity for drafts between the subfloor and the ground, so the floors will need to be insulated quite thoroughly.
Different types of foundations are made from different materials. Photo onduline.ru
By build type
And finally, according to the type of assembly, foundations can be:
- prefabricated (made of blocks, slabs or beams connected with cement mortar);
- monolithic (first the formwork is made, then concrete is poured into it) - and this is the most durable option;
- Combined (prefabricated-monolithic, monolithic-prefabricated, whatever).
As you can see, the choice is wide. Each option has its pros, cons and features. Therefore, each individual case requires careful consideration. Let us repeat, with this article we are not closing the topic of foundations, but, on the contrary, opening it up.
Lyudmila Gubaeva
Real Estate Tatarstan