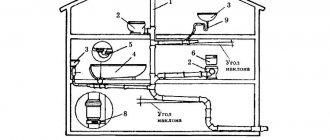
Removing excess moisture from the foundation structure or basement of a building is an important task that the homeowner must solve. To achieve this goal, a drainage system is used, which is a drainage system that can significantly reduce the risks of possible flooding.
Narrative plan:
- Why is drainage needed?
- Classification and features;
- Drainage location methods: Wall or linear;
- Plast;
- Ring;
- Deep;
- Horizontal;
- Vertical;
- Combined;
Why is drainage needed?
When constructing buildings and structures, the project usually provides for the presence of a blind area - a special concrete belt located at a given angle to the surface of the wall. But this drainage structure partially removes moisture.
To ensure that the walls and foundation are not washed away by groundwater, melting snow, and precipitation, a special drainage system is needed for a country house. Drainage in the area around the building helps prevent a number of problems.
- Water stagnation. It passes through the soil layers freely and does not accumulate at one level. This way it is possible to avoid waterlogging of the soil and its heaving when atmospheric temperatures drop. The building settles more evenly.
- Moisture seeping into the structural elements of the house. Any material, from wood to concrete and brick, has microcavities that can accumulate water that penetrates inside. Their main danger is that when frozen, ice crystals begin to burst the structure from the inside.
- Destruction of walls and foundation. When moisture accumulates inside, they crack, lose strength, and the building sags and warps.
- Accumulation of water in the basement, basement. Excessive humidity is dangerous because it creates favorable conditions for the growth of pathogenic microorganisms. Fungus, mold, and corrosion of metal structures will not appear if a drainage system is installed around the house.
- Formation of cold bridges. Because of them, the house becomes less energy efficient, loses heat, and freezes.
Formally, drainage is not a mandatory element of underground communications. But it is necessary in areas with high groundwater levels, as well as in flood zones, at sites in flood zones.
In regions with heavy precipitation, dehumidification helps remove atmospheric moisture from the soil surface, preventing it from spilling and entering the basement.
Classification and features
Drainage sewerage on the site can be surface or buried, with the main communication lines located underground. Each type of such systems has its own characteristics and varieties, used based on the terrain and soil type.
Surface drainage options are used in the following cases.
- Weak filtration capacity of soils. The fertile layer is constantly waterlogged due to the close proximity of the clay layer.
- The natural formation of lowlands in the terrain. Water flows into them without additional effort. The site is constantly located in a flood zone.
- Stagnation of moisture. If the surrounding landscape does not have a natural slope, there is a high probability that after the snow melts, water will remain on the site.
The classification of this type of system involves their division into 3 main groups, according to the characteristics of the device.
Dosing chamber
The dosing chamber will ensure the gradual removal of liquid into the drainage field Source nk.pl
The dosing chamber is a container that has a capacity of up to 1 cubic meter. For construction, a ready-made plastic container corresponding to the required volume can be used.
The bottom of the excavation is leveled, where the container is then loaded. Uninterrupted operation of the system at the outlet of the tank is achieved by installing a siphon, which has a diameter of 100 millimeters and an elbow height of 200 millimeters. As the siphon fills, it will self-charge, then self-empty. Thanks to this, the purified liquid is supplied to the pipelines for distribution.
Drainage placement methods
There are several ways where and how a drainage system can be placed.
Wall or linear
The laying of drainage communications occurs simultaneously with the construction of the blind area and foundation. They ensure the removal of moisture from the above-ground parts of the foundation under the building.
A drainage system is formed in the form of trenches encircling the perimeter of the object, with a depth of about 0.5 m. A prerequisite for laying drains is the creation of a slope that allows water to be naturally evacuated from the soil surface to the inspection well.
Layer
A reinforced version of drainage, organized under the foundation, before its construction or pouring. It is formed on the basis of a sand cushion with a height of at least 300 mm with a continuous gravel backfill or with crushed stone prisms.
The perimeter of the drainage layer must extend beyond the boundaries of the foundation. The final layer in it will be perlite, which helps prevent concrete from leaking when poured onto the drainage system.
Ring
This drying method is applicable both in a country house and directly on the site. It is necessary where groundwater is too high. The ring system is located at a certain distance from the house, with a distance of at least 5 m, at a depth of 30-70 cm.
This is the only type of surface systems that can be installed without additional costs after the completion of the construction phase of a residential building.
Deep
Underground drainage is intended for installation in areas with dense, clayey soil. It makes no sense to build surface systems on them. Here, a complex, multi-level sewer system is formed to remove moisture, with the help of which lowlands and floodplain areas can be drained.
Deep drainage methods are called closed, since they do not affect the appearance of the site and preserve the features of its landscape. This type of communications is required for use if there is a natural body of water in the immediate vicinity - a river, lake, pond.
Areas in lowlands, where the soil is prone to waterlogging, areas where buildings with a usable basement or plinth are erected, are equipped with the deep type of drainage. At the construction stage, it can be wall or trench, after the construction of the house - ring.
Horizontal
Deep horizontal systems have a significant extent. Drainage is carried out using a special pipeline located on the site. Inspection wells are formed at corners and at low-level points, allowing inspection and maintenance.
The water from the drainage system is sent through pipes to storage tanks, from where it is partially evacuated by being discharged into the ground. The remaining liquid is pumped out forcibly using pumping equipment. It is suitable for irrigation and can be used for household needs.
Deep horizontal drainage is laid by analogy with surface drainage:
- ring-shaped;
- wall-mounted;
- layer.
The last option is especially interesting. It involves the formation of an artificial reservoir under the foundation. Inside such an artificial reservoir there is crushed stone and sand backfill with a height of at least 30 cm from the bottom. Moisture is removed naturally and by force.
Vertical
Quite an expensive drainage option. It uses 2 main elements:
- reduction wells;
- water intake wells.
Excess moisture is pumped out forcibly, with the installation of a pumping station. The depth of the reduction wells varies in the range of 20–50 m.
Combined
A compromise solution with elements of vertical and horizontal systems. It is used where it is impossible to make a choice in favor of the only correct option.
Vertical type drains
Such structures are represented by a well in which pumping equipment is located (pumps are used to pump out wells). As a rule, such drainages are used in the agricultural industry, and they are also actively used to drain land during the construction of highways.
When laying this system, wells and trays are used, which, as a rule, are located on a waterproof layer. In addition, such a system must be equipped with deep-well pumping elements. This drainage system is considered the most effective. And if the land on the territory of a particular site has a high coefficient of water resistance, then such a structure will not only be effective, but also quite economical.
A vertical drainage system requires a pump to pump water from wells
The depth of laying vertical drains can be different, since everything in this case depends on the level at which the groundwater is located. It can be 20 or 150 meters, depending on the characteristics of the soil on which the site is located.
Helpful information! The vertical design is represented by different types of pipes: conventional and perforated. Regular ones are located at the top of the structure, and perforated ones are located at the bottom. It is also worth noting that the holes of perforated pipes can be of different shapes.
Such borehole drainages can operate in various modes (the choice of mode is carried out based on the time of year). Do not also forget that such systems require periodic preventive inspections and cleaning of the filter, which consists of sand and gravel.
Preparing for laying a drainage system
The formation of drainage trenches with pipes inside requires accuracy of preliminary calculations. At the preparatory stage, a whole range of surveys of a geological and geodetic nature is carried out. They will allow you to assess how deep the aquifers are located.
Preparation also includes the selection of a drainage structure. Surface ones are laid in moderately loose soils, buried in denser ones. The degree of swampiness of the territory and the depth of soil freezing in winter also matter.
Based on the results of all calculations and surveys, a project is drawn up, linked directly to the site plan. On its basis, the entire complex system of elements will be formed. The designer’s tasks also include determining the goals of the work.
Dehumidification can be performed for:
- lowering groundwater levels;
- redirection of collected rain moisture;
- protecting the foundation and basement from flooding.
In areas with low soil filtration properties, drainage systems are supplemented with storm sewers. During the calculation process, the following is determined:
- exact length of communications;
- the number of elements in their composition;
- the type of materials needed for the job.
Upon completion of the design work stage, you can proceed directly to the purchase of components, and then to the preparation of trenches with their marking at the site.
Features of the drainage system on the site
The simplest solution for removing excess moisture is surface (open) drainage. For it, trenches are dug no more than 0.5 m wide and up to 70 cm deep. The sides of these ditches are placed with a slope of 30 degrees. A sewer network is located around the perimeter, with moisture draining into the drain.
This capacity may include:
- pit;
- common drain;
- autonomous or main storm sewer system.
In areas with a slope towards a road or street, it is enough to simply dig a barrier trench. It is formed in the middle of the slope, across it. Encircles the building around the perimeter. Then, from this trench, additional drains and channels are installed to evacuate wastewater into the ditch.
In areas with a slope in the opposite direction from the road, the drainage process is organized according to a more complex scheme. First, a transverse trench is created in front of the facade of the fence on the site. Behind it, a second one is being dug, this time longitudinal. Towards the end of the section.
Inspection or control hatches, wells are located in each corner or alternating through 1. They are also installed in difficult terrain areas where there are elevation differences. The distance between adjacent inspection wells should not exceed 40 m.
The pipe in such a hatch will definitely burst. If it is solid, when flushing a clogged system under pressure, it will simply burst. During the removal of obstruction, the hose is connected directly at each section from hatch to hatch.
The well at the end of the drainage sewer line is located at the lowest point of the site. From here the water should be discharged to an open reservoir or a regular waste disposal system. In difficult terrain, when it is impossible to direct it by gravity, pumping equipment is used.
In systems with natural drainage, all drainage pipes are laid at a slope relative to the collection collector. When calculating, a level decrease of 20 mm/1 m of the length of underground or surface communications is usually included.
In closed systems, pipes are buried so that they lie below the soil freezing level. Additional insulation is provided by backfill - gravel, sand, small crushed stone. To prevent drains from becoming clogged with fine-grained filler, they are wrapped in geotextiles during installation.
Step-by-step installation of wall drainage
This drainage option is suitable if the construction of the house has already been completed, but moisture stagnates near the foundation. Ground liquids accumulate under the soil-vegetative layer due to the weak permeability of the substrate.
This is a pressing problem for sandy and loamy soils with extremely low filtration capacity. The work process consists of several step-by-step stages.
- Forming a trench around the house. When machine digging, a distance of 1.2 m is made from the foundation or blind area. Manually, you can dig a trench closer, in the range of 0.7–1 m, with the bottom excavated 200–300 mm below the base of the building.
- Connection of the resulting circular ditch with a common drainage system. It is necessary for further removal of collected moisture.
- Filling the bottom. It is covered with a layer of sand along the entire length of the trench on the site. This cushion is then carefully compacted by hand or using tools.
- Preparation of drains. They are unwound, laid next to ditches, and wrapped in geotextiles.
- Lining the bottom of the trench. It is covered with geotextile, like the walls. Drainage pipes are placed inside.
- Installation of storm drainage elements. It is better if both systems are installed in parallel, but at different levels of the trench.
- Filling the ditch with clean, unalloyed sand. It will ensure sufficient filtration of all water coming from the site.
- Connection of linear communications with the collector. A common drainage system is connected to it.
Separately, it is worth considering the requirements for the collector, which takes on the entire drainage load. This well receives discharges from regular sewerage and drainage, from storm containers. Accordingly, its capacity should be enough to receive the maximum possible amount of liquid.
It is customary to carry out calculations with a reserve. So that at maximum load from all systems the collector is filled to no more than 2/3 of its volume. Based on these indicators, the depth of the well and the number of rings in it are selected. A pit is being developed with filter filling along the bottom.
As soon as the rings are installed, the bottom is cleaned and lined with geotextiles. A sand cushion is placed on top of it to filter the water. At the next stage of installation, holes are made in the collector for pipes of each type of drain. They are inserted into holes and are not fixed.
At the final stage, the pit designed for the collector is filled with sand. A trench is dug from it to the main sewerage system or drainage ditch. The pipe is being removed. It is mounted with a bias towards unloading.
Upon completion of this stage, all that remains is to carry out landscaping of the territory. Equip the collector well with a lid and level the area around the house.
How to make a drainage pipe out of a sewer pipe
The drainage pipe for sewerage is a regular perforated pipe.
You can buy it in any store.
But, if you have a PVC sewer pipe for arranging an external sewer system, then you can make a drainage pipe out of it, and do it with your own hands, because sewer and drainage pipes differ only in the presence of holes in their surface.
Drainage pipes for the site
There are two ways to implement this idea. The first is using a circular saw.
In this case, you will need to do the following:
- take the circular saw. The disc must be equipped with carbide nozzles;
- Using this tool, make many cuts in the pipe, distributing them evenly over the entire surface of the product. Their length should be 10-20 cm. You need to make sure that there are not too many cuts, because then the pipe will lose its strength;
Circular saw for cuts in plastic
- remove remaining hangnails with a knife;
- important! The width of the holes should be approximately 5 mm. the distance between the cuts cannot be more than 50 cm. It is desirable that they are located a little more tightly.
You can also make a drainage pipe for sewerage using a drill.
The work will look like this:
Holes in a drainage pipe with a drill
- take a drill and make a large number of holes in the pipe;
- it is necessary to take into account that the diameter of the hole should be smaller than the size of the crushed stone fractions used to arrange the drainage. This will prevent the drain pipe from clogging. The optimal hole diameter is 5 mm. The distance between them should be a maximum of 10 cm.
Drainage pipe with holes
We looked at how to make a drainage pipe from a sewer pipe. You can decide which method to choose based on the available tool.
Useful tips
When arranging drainage communications in an area where a specific type of soil predominates, it is important to adapt the selected drainage method to real conditions. Sandy soils are strengthened with gravel pads and several layers of geotextile in the backfill.
In dense soils, sand filtration is sufficient. If the soil crumbles easily and does not allow drains to be secured well, lighter, plastic pipes are chosen. They will create less load on the surrounding layers of the earth during operation.
For year-round operation of the system for collecting and draining water on the site, it is necessary to place pipes at a depth below the freezing point of the soil. Each region has its own. In a sharply continental climate zone, the trench is additionally equipped with a heating cable.
You can achieve the desired slope when installing drains in a ditch by adding fine crushed stone. The curvature of the installation is measured with a building level. It is important to maintain a one-dimensional slope throughout the entire length of the pipeline to avoid stagnation of water in the communication line.
The cross-section of the pipes in the places adjacent to the well is always larger than on the opposite side. This is necessary to prevent blockages.
Video description
How to choose pipes for a drainage septic tank:
All drainage pipes for the drainage field of a septic tank must have an equal laying slope - the slope of a drainage pipe per 1 meter, the slope is 1.5 centimeters. Every 6 meters, a riser is installed for ventilation.
Sand, with a fraction of up to 10 millimeters, as well as crushed stone with a fraction of 30 millimeters, is used for laying pipelines. In addition, geosynthetics are used, namely geotextiles, which are intended for thermal insulation of pipelines. The material provides additional purification of water waste.
The pipes are “wrapped” in geotextile, sand and crushed stone - these materials trap all large inclusions and additionally protect the pipes from freezing Source infourok.ru