- About thermal conductivity and energy efficiency
- Types of insulation for a wooden frame house
- Layer scheme
- Technology for insulating a frame house using various types of insulation materials
- Insulation of the roof and ceiling in a frame house
- Floor insulation
The very concept of “frame house” implies the use of insulation, which is an integral part of the “pie”. In this case, the use of various types of insulation of both synthetic and organic origin is allowed.
About thermal conductivity and energy efficiency
Frame houses are among the warmest, which is why they are so popular in Canada and Scandinavia. The use of an extensive layer of insulation placed inside hollow walls makes it possible to achieve revolutionary thermal conductivity indicators of 0.02 W/(m K). For comparison: the thermal conductivity of walls in houses made of timber or rounded logs is 0.15 W/(m K), of foam blocks - 0.45 W/(m K), of brick - 0.58-0.81 W/ (m·K). The lower the thermal conductivity, the warmer the house in winter and the more comfortable (cooler) in the summer heat.
Features of the technology for insulating the walls of a frame house also make it energy efficient, allowing you to reduce the amount of energy consumed required for heating. Thanks to the low thermal conductivity achieved through the use of porous, “air” insulation, a frame house can be easily warmed up to a comfortable temperature in a few hours, even if it has not been heated for a long time in the cold season.
Insulating a frame house with 150 mm thick cotton wool insulation will provide a thermal resistance of the structure of 3.25 m²C/W, while according to SNiP II-3-79* “Building Heat Engineering”, for Moscow and the region the required thermal resistance is lower - 3.15 m²C/W . And again, to comparison. If, to achieve the mark of 3.25 m²C/W, it is enough to insulate the walls of a frame house with insulation 150 mm thick, then to achieve the same thermal resistance indicator, the wall of a brick house should be no narrower than 200 mm, a wall made of expanded clay concrete blocks should be no narrower than 500 mm , and from dry wood – 550 mm!
Types of insulation for a wooden frame house
Basalt insulation in slabs
More than 75% of all timber-frame houses in Canada, the USA and European countries are insulated with basalt slab insulation. It is considered one of the best materials for low thermal conductivity and high energy efficiency. Therefore, when thinking about how to insulate the walls of a frame house, first of all, take a closer look at basalt wool. Being a type of mineral wool, basalt slabs are characterized by a high thermal insulation coefficient - and this is the main criterion for all insulation materials.
Basalt insulation is produced from rocks (which is why it is also called stone wool), which melt at t ≈ 1500 ⁰C and form thin fibers that form the basis of the wool. Essentially, this is the same glass wool, but made from gabbro-basalt, and not from quartz.
Main advantages:
- low thermal conductivity – 0.03-0.05 W/(m K)
- ensuring good waterproofing of the walls of a frame house due to hydrophobicity (does not absorb moisture, water absorption by volume - no more than 2%)
- 100% non-flammable material, which increases the fire safety of wooden buildings (the maximum temperature that basalt insulation can withstand is 1114 ⁰C!)
- high vapor permeability - 0.3 mg/(m h Pa), therefore, insulating the walls of a frame house with basalt wool allows you to maintain not only temperature, but also optimal humidity conditions
- good sound insulation: stone wool can muffle vertical sound waves traveling inside the walls
- very durable and resistant to mechanical deformation: with a deformation of 10%, basalt insulation has compressive strength limits from 5 to 80 kilopascals
- environmentally friendly, biologically and chemically inert (does not emit any harmful substances, resistant to fungi and microorganisms)
- important for those who insulate a frame house with their own hands: unlike glass wool, stone wool does not irritate the skin, does not prick, and does not cause allergic reactions
- 50 years - average service life depending on the declared characteristics
It is basalt insulation (mineral wool), in particular Rockwool LIGHT BUTTS and Rockwool LIGHT BUTTS SCANDIC, that the PNR company uses. These are the most modern Rockwool products, designed specifically for use in private housing construction. Among the key advantages of LIGHT BATTS and LIGHT BATTS SCANDIC insulation, the following can be noted:
- guarantee of absence of drafts: the material fits tightly into the frame of the house, does not form cracks or “cold bridges”
- does not shrink throughout the entire period of operation, which is at least 50 years (subject to compliance with the manufacturer’s recommendations related to installation technology and operating conditions)
- not only keeps out the cold in winter, but also the heat in sultry summers
- biostability: Rockwool insulation is not suitable as food for rodents, does not contribute to the emergence and spread of bacteria
- ease of installation due to the ability to combine slabs of different sizes and the implemented “flexion” technology, thanks to which one edge of the slab is springy, which facilitates the process of installing insulation into the frame
- vacuum compressed packaging, allowing you to save on delivery.
Glass wool
Everyone probably knows that glass wool pricks and causes severe irritation on the skin from childhood. But the disadvantages of glass wool do not end there. Once installed, it is inferior in its performance characteristics to modern cotton insulation.
The main disadvantage! Glass wool is subject to shrinkage, which over time leads to the formation of cracks, forming channels for constant heat leakage. And if you do the insulation of a frame house with your own hands, then know that you most likely will not be able to compensate for this phenomenon. The fact is that the thermal conductivity of compressed glass wool becomes higher, its energy efficiency decreases, and living in such a house becomes less comfortable.
Main advantages:
- low cost (sometimes the low price becomes the determining factor when choosing insulation)
- When packaged, it takes up very little space, which greatly facilitates and reduces the cost of transporting the material to the site. Moreover, after unpacking, the compressed glass wool quickly restores its original volume
- biological and chemical inertness (does not emit substances harmful to health and is not afraid of rodents)
- light weight, and therefore less load on the structure
- glass wool fibers are 2 times longer and 2 times thinner than basalt insulation fibers. This property allows the material to be used on uneven surfaces and in structures with complex geometries.
- fire resistance: glass wool does not burn and does not support combustion, withstanding temperatures from 400 to 700 ⁰С depending on the declared characteristics and type of material
- good sound insulation
- 15-20 years – service life
Ecowool
Videos about insulating a frame house with natural insulation – ecowool – are becoming increasingly popular online. It is equally suitable for insulating walls both inside and outside. In addition, spraying technology allows the use of ecowool, including for insulating the ceiling in a frame house.
Main advantages:
- low thermal conductivity – 0.03-0.04 W/(m K)
- environmental friendliness and hygiene. The insulation is made of cellulose impregnated with brown and boric acid - antiseptics that are harmless to humans.
- does not shrink
- quick and easy installation. Thanks to the spraying method, the thermal insulation is monolithic and seamless.
- high vapor permeability – 0.31 mg/(m h Pa)
- low density – 30-58 kg/m³ (the lower the density, the higher the thermal insulation properties of the material)
- good sound insulation
- 50 years is the average service life. In Finland, this thermal insulation material has been used for almost a century. There are many houses there that were insulated with ecowool more than 70 years ago, and the question of changing the insulation has not yet been raised.
Expanded polystyrene
To insulate external walls, polystyrene foam (also known as extruded foam) is also used. When deciding to insulate a frame house with your own hands, choose special fire-resistant types of polystyrene foam.
Inferior to cotton insulation in terms of sound insulation, extruded foam has other advantages:
- thermal conductivity is better (lower) than that of mineral wool. Averaged 0.037 W/(m K) versus 0.046 W/(m K), depending on the declared characteristics, which means that your home will always be warm
- resistant to significant loads for a long time, which allows the use of polystyrene foam as a full-fledged element in building structures
- high vapor permeability: from 0.005 to 0.023 mg/(m h Pa)
- manufacturability: a polystyrene foam board weighs so little that the wind can pick it up, so installation of insulation can be done by one person
- it's inexpensive
- practically not subject to shrinkage (to a lesser extent than other insulation materials)
- biologically passive: it is not afraid of either mold or mildew
- 40 years - average service life depending on the type and type of material
Foam insulation
The technology for insulating the walls of a frame house allows the use of foam insulation, which has not yet become widespread in our country. The essence of all foam insulation comes down to the fact that they are literally blown into the voids of the frame like foam. This method clearly improves the connection between the insulation and the frame itself. However, insulating the ceiling of a frame house with your own hands in this case will be very difficult, because the foam will simply pour out before it has time to harden.
But, despite the presence of controversial issues, foam insulation is gaining popularity, having a number of unique advantages. The latter include the ability to fill even the smallest cavities and the ability to provide insulation in hard-to-reach places.
Video instructions for do-it-yourself thermal insulation
More information about the technology of home insulation is described in the video.
Korovin Sergey Dmitrievich
Master of Architecture, graduated from Samara State University of Architecture and Civil Engineering. 11 years of experience in design and construction.
Frame houses have earned popularity due to their cost and reliability
It is important to know that depending on the period of operation, there are differences in the design of walls and roofs. Frame houses intended for winter living must be sufficiently insulated
This is the only way to ensure the comfort of permanent residence in them.
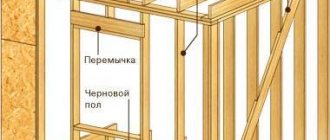
Layer scheme
Regardless of what materials are used to insulate a frame house, the layer diagram necessarily includes:
- frame (PHR company uses original I-beams)
- thermal insulation
- steam and waterproofing, wind protection
- internal and external lining
- external cladding
Steam and waterproofing of the walls of a frame house are a mandatory step in insulation. The frame with insulation is sheathed with a windproof membrane, and the inside is covered with a layer of vapor barrier that protects the insulation and frame from moisture, condensation, “dew points” and the unpleasant consequences of all this.
Technology for insulating a frame house using various types of insulation materials
Insulation with mineral wool
Basalt insulation and glass wool are types of mineral wool.
Vertical frame posts are usually attached in increments of 60 cm, which corresponds to the width of the mineral wool slabs. The thickness of the slab is 5 cm. This allows you to navigate the number of layers according to the location, taking into account climatic conditions. Most often, 3 layers of mineral wool (15 cm) are laid, which are fastened together with wooden posts from the inside. Another layer (5 cm) is attached to the outside, covering the frame beams and thus eliminating the possibility of “cold bridges” occurring.
It is very important to install the insulation correctly! The material should be placed tightly between the posts, adhering to the entire surface. In this case, the insulation should not sag. A layer of vapor barrier should be placed on top of it. The joints of the vapor barrier membrane can be fixed with special construction tape - reinforced adhesive tape. If there is a layer of vapor barrier on the outside of the house, then there is no need to do it from the inside.
Ecowool insulation
The technology for insulating a frame house with ecowool allows for three options: dry backfilling, spraying with water and spraying with glue.
The most inexpensive method is the first one - dry backfill. Pressed ecowool briquettes are delivered to the construction site, which are subsequently loosened with an electric mixer. After loosening the briquettes, the volume of insulation triples! This must be taken into account when making estimates and purchasing material.
Insulation or OSB boards are pre-attached to the vertical posts of the frame. A gap is left at the top, through which ecowool is poured until it fills the entire space. But the work on insulation does not end there. Having filled in the ecowool, you need to manually compact it as tightly as possible.
Wet methods of insulating walls with ecowool are usually used by professionals, as they require the use of special equipment, in particular, a spraying unit in which the wool is wetted (either in water or in glue) and softened. The prepared insulation is “sprayed” onto the wall under pressure, filling the sheathing sections one after another. The thermal insulation applied to the walls is left to dry for a day, after which work on the installation and finishing of the walls can continue.
Insulation with polystyrene foam
The construction of walls using polystyrene foam will require the installation of profile strips - vertical suspensions with a pitch of 60-70 cm. Their presence will show where to remove excess material and in which places to add glue.
In the video about insulating the walls of a frame house, you can see that to improve adhesion, a kind of primer is applied to the sheets of expanded polystyrene - weakly diluted glue. After this, the insulation is pressed tightly against the pre-prepared (leveled) wall. If necessary, it can be additionally secured using dowels or screws with wide heads. Subsequent rows are laid by analogy with brickwork - staggered. As soon as the thermal insulation is completed, the polystyrene foam boards should be reinforced with reinforced mesh and puttied. Professionals recommend applying putty in two layers.
A variety of methods for using ecowool
The second most popular material for thermal insulation of frame buildings is ecowool. But here it is better not to experiment and entrust the work to professionals. Mechanized backfilling will ensure the required density and uniformity of laying. There are three methods of using ecowool:
- dry "spray";
- wet application;
- glue method.
The dry method is applicable for horizontal surfaces, inclined closed cavities, filling interfloor ceilings and non-demountable structures. The packing density of ecowool using this method is 45-65 kg/cubic meter. m depending on the slope.
Wet technology is suitable for vertical open walls. Ecowool flakes are moistened and applied to the surface under pressure. The density of the thermal insulation layer is about 65 kg/cu.m. m.
The adhesive method is similar to the previous one, but instead of water, an adhesive component is added. Advantages of the technique: high adhesion of the insulation to the wall, elasticity of the material and low deformation after drying. The adhesive method is indispensable for thermal insulation of flows from below; this option is also suitable for treating walls.
The issue of insulating a house needs to be thought through at the construction stage. This is more profitable from a financial point of view and technically correct. Structural elements are insulated as the building is erected, and there is no need to carry out major repairs to the building after commissioning.
Insulation of the roof and ceiling in a frame house
As thermal calculations show, the greatest heat loss in frame houses built using Canadian technology occurs on the roof and lower floors. And if insulation in the walls can be laid in one layer, then the ceiling of a frame house, or rather the rafter system, is insulated with a one-and-a-half layer.
If you insulate the roof of a frame house with your own hands, then after insulating the walls there should be no difficulties, since the roof is insulated according to the same principle. Thermal insulation material is laid into the rafter system, which is lined with a vapor barrier on the inside, reinforced with slats, and on the outside with wind protection. Between the roof and the insulation, as well as between the insulation and the waterproofing, it is necessary to provide an air “cushion” to freely remove the resulting moisture.
Answering the question of how to insulate the ceiling of a frame house, we add that directly for the ceiling you can use reflective thermal insulation, which is a thin sheet of polyethylene foam, on top of which aluminum foil is glued. Such insulation is simply glued to the ceiling (or stapled to wooden floors), trapping heat under the ceiling and “reflecting” it, keeping it indoors.
Floor insulation
The technology of floor insulation largely depends on the foundation on which the frame house is built. But, nevertheless, there is a certain number of activities that must be performed regardless of the type of foundation:
- the subfloor boards should be laid close to each other (this way there will be noticeably fewer drafts)
- it is necessary to install a wind barrier that is laid on the joists and subfloor. After all, to prevent the boards from rotting, the underground must be ventilated. Additionally, OSB boards can be laid on top of the wind barrier, which will eliminate even the slightest drafts
- insulation is placed between the joists (by analogy with insulation of walls and ceilings)
- A wind barrier is laid on top of the insulation, which is nailed to the joists using a stapler.
- the installation of a finishing plank flooring completes the stage of floor insulation work.
To summarize, we note: in order for the insulation in a frame house to last as long as possible and perform its functions properly, choose high-quality, reliable materials. Control the installation process, do not be lazy to check the seams and connections - this will ensure a comfortable microclimate.
On the website you can study various frame house projects, or discuss an individual project by simply leaving a request in the form below.
Calculation of material thickness
The thermal insulators listed in the previous paragraph have approximately the same thermal conductivity values, which means that their thermal insulation abilities are also comparable. A frame house for long-term living must be properly insulated, and for this you will need to select the thickness of the heat insulator. The value depends on the climatic region. For most of the country, a layer of 100 mm can be used.
In order to live in a house with maximum comfort, a full thermal calculation is performed. To do this, it is not necessary to study mountains of regulatory documentation and delve into the principles of calculation.
Now there is a simple program “Teremok”, which performs a full calculation based on regulatory documentation. With its help, the thickness is selected in a few minutes. You can install the program on your computer (free and open access) or use the online version.
To calculate you will need:
- thickness of all layers except insulation;
- thermal conductivity of all materials.