The first in the circuit is the central circuit breaker. In this case, single-pole circuit breakers are used.
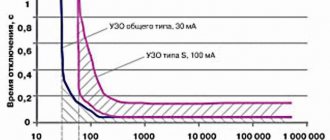
I hasten to assure you: the residual current device really works, so for the sake of your own safety and to prevent accidents associated with electric shock, everyone should install such a device. They cannot protect against electric shock - only against fire.
Before applying voltage after completing installation, be sure to ensure that no one in your household or colleagues touches live elements. Connecting heating elements to a three-phase network. Part 2
It should be remembered that in no case should zeros of different groups from different residual current devices be connected between.
Features of connection with and without grounding Individual experts sometimes express the opinion that connecting an RCD without grounding is impossible or such a circuit will be inoperative. That is, it turns out that the zero is connected bypassing the switch, and the load current will be perceived by it as a differential RCD will be turned off.
The current transformer is made on a toroidal ferromagnetic core.
The grounding device is connected only to the protected objects through a separate grounding bus.
Three independent groups of electrical receivers can be connected to a three-phase ouzo. Scheme with one common RCD This diagram looks like this: electric meter - RCD common for all groups - circuit breakers for each group of consumers. Connection diagram for a four-pole RCD in a three-phase network without using a neutral
Purpose and scope of RCD
The RCD is designed to compare the amount of electric current flowing in the phase and neutral wires. During normal operation of electrical appliances, this value is the same and the counter currents in the RCD windings compensate each other. As soon as an emergency situation occurs - the insulation is broken somewhere with the subsequent flow of charged particles to the ground, bypassing zero, the differential currents will differ and the protection will turn off the power.
In practice, this can be represented as follows: if the electrical wiring breaks down on the body of a washing machine or water heater, their body will be at potential. As soon as the potential begins to flow from the body to the ground, the protection will react and the person will not be harmed. It is most important to connect an RCD to a circuit of powerful appliances in the kitchen or bathroom, because of the release of condensation on their surface and metal body, which is a potential conductor.
But this does not mean that other equipment does not require similar devices for protective shutdown: the same lamps, sockets and other connected loads can also pose a threat to humans. Therefore, it is also important to connect them to the RCD on the panel, both common for all electrical wiring, and separately for any devices or their groups. Features of the use of electronic and electromechanical RCDs directly depend on the power supply circuit and the location of their installation.
Operating principle
Since the RCD is a device for protecting people from electric shock, the principle of operation is based on the neutralization of the dangerous potential of the equipment body. The upper terminals of the device are connected to phase and zero directly from the energy generator, and to the lower terminals - phase and zero from the load. Thus, the pattern of current flow through the circuit is in the order from the source of electricity through the RCD on the wire to the electrical appliance, and then in the reverse order returns to the network.
In the circuit, the device acts as the main controller of the current that enters and exits it, respectively. If the difference is non-zero, a leak is detected, a signal about which is sent to the RCD and in less than a second the electrical circuit is turned off.
In a stable and healthy network, there is no noticeable difference between the incoming and outgoing voltage, so the controller does not operate and all connected equipment works normally. In emergency situations with current leakage, the entire electrical network stops working, preventing fire or direct contact with a person. The principle of operation is aimed primarily at safety, so the RCD does not react in any way to emergency situations that are not accompanied by current leaks, for example, to an overload of the electrical network or a short circuit in it.
Connection diagrams for RCDs in a single-phase network
Most household consumers are powered by a single-phase circuit, where one phase and neutral conductor is used to supply them with electricity.
Depending on the individual characteristics of the network, single-phase power supply can be provided according to the following scheme:
- with a solidly grounded neutral (TT), in which the fourth wire acts as a return line and is additionally grounded;
- with combined neutral and protective conductor (TN-C);
- with separated zero and protective grounding (TN-S or TN-CS; when connecting devices indoors, you will not find any difference between these systems).
It should be noted that in the TN-C system, in accordance with the requirements of clause 1.7.80 of the PUE, the use of differential circuit breakers is not allowed, except for the protection of individual devices with the obligatory combination of zero and ground from the device to the RCD. In any situation, when connecting an RCD, the characteristics of the supply network should be taken into account.
Without grounding
Since not all consumers can boast of having a third wire in their wiring, residents of such premises have to make do with what they have. The simplest circuit for connecting an RCD is to install a protective element after the input circuit breaker and the electric meter. After the RCD, it is important to connect circuit breakers for different loads with the corresponding shutdown current. Please note that the operating principle of RCDs does not provide for disconnecting current overloads and short circuits, so they must be installed together with circuit breakers.
Rice. 1: Connecting an RCD in a single-phase two-wire system
This option is relevant for apartments with a small number of connected devices. Since if there is a short circuit in any of them, shutting down will not bring any noticeable inconvenience, and finding the damage will not take much time.
But, in cases where a sufficiently branched power supply circuit is used, several RCDs with different operating current values can be used.
Rice. 2: connecting an RCD in a branched single-phase two-wire system
In this connection option, several protective elements are installed, which are selected according to the rated current and operation current. As general protection, an incoming 300 mA fire protection RCD is connected here, followed by a neutral and phase cable to the next 30 mA device, one for sockets, and the second for lighting; a pair of 10 mA units are installed for the bathroom and nursery. The lower the response rating is used, the more sensitive the protection will be - such RCDs will operate at a significantly lower leakage current, which is especially important for two-wire circuits. However, it is also not worth installing sensitive automation on all elements, since it has a high percentage of false positives.
With grounding
If there is a grounding conductor in a single-phase system, the use of an RCD is more appropriate. In such a scheme, connecting the protective wire to the device body creates a path for current leakage if the insulation of the wires is broken. Therefore, the protection will operate immediately in the event of damage, and not in the event of electric shock to a person.
Rice. 3: Connecting an RCD in a single-phase three-wire system
Look at the figure; the connection in a three-wire system is made in the same way as a two-wire system, since only a neutral and phase conductor are required for the device to operate. The grounding device is connected only to the protected objects through a separate grounding bus. Zero can also be connected to a common zero bus; from the zero contacts it is routed by wires to the corresponding devices connected to the network.
As in a two-wire single-phase circuit, with a large number of consumers (air conditioner, washing machine, computer, refrigerator and other amenities of civilization), an extremely unpleasant option is the freezing of all of the above electronic circuits with loss of data or disruption of their functionality. Therefore, several RCDs can be installed for individual devices or entire groups. Of course, connecting them will result in additional costs, but will make finding damage a more convenient procedure.
How to properly connect wiring to machines
There are a large number of devices that will make it easier to connect contacts to automation. In order to choose the appropriate option, we will consider them in detail.
Flexible wire lugs
In order to connect elements of an electrical panel, flexible wires with many wires are often used, because even a beginner can cope with connecting such contacts. But there is a nuance here too.
As we have already discussed above, many craftsmen fix the wire with a clamp without termination , which is why the fragile wires begin to break off and the contact weakens .
If stranded wire is used during installation, then do not forget about the lugs
double tips were invented for this purpose . They are best suited when you have to install a lot of jumpers.
Special tip for forming bridges
Arched bend
Usually, to connect the conductors to the clamps, it is necessary to remove 10 millimeters of the insulating layer - this is enough to form an arc on the messenger, which is then placed in the terminal. As practice shows, most electricians, in the absence of tips, use this method.
As a result, it is possible to obtain reliable contact that will not weaken over time. This method is suitable if there is a monolithic core at the end.
Thanks to this connection, the area of interaction between the contact and the clamp expands, this will avoid problems with the operation of the machine
Unbreakable jumpers
When you have to connect several machines with one wire, it becomes necessary to use a comb (bus) . However, it is not always at hand, so you can form a homemade comb from wire of any cross-section.
You should bend the wire so that you get a comb. Then, at the bend site, you need to strip the wires.
Method for forming a continuous comb
Connecting an RCD in a two-phase network
Two-phase power refers to non-standard connections, where a converted old-style 127 V transformer was reconnected into a triangle for modern 220 V consumers, which are powered by linear voltage from it.
Rice. 4: Connecting an RCD in a two-phase system
To connect a residual current device to a two-phase circuit, it is necessary to disconnect both wires at the input to the panel, since each of them is under potential. Then each of the phases is connected to the corresponding phase terminals and neutral terminals, further observing their polarity. Unlike a single-phase system, circuit breakers at the output of the RCD must be installed for each line, or they can be replaced with one two-pole one.
Installation location
Typically, the installation location of the RCD is in the electrical panel. It contains various devices for metering and distributing electrical energy of voltage up to 1000 V. In the electrical panel, along with the RCD, there are automatic circuit breakers, an electric meter, distribution terminal blocks, and other electrical devices.
If you have an installed electrical panel, then to install the residual current device you will need a minimum set of electricians. It will include pliers, side cutters, a set of screwdrivers, and a marker.
In rare cases, you may need a set of socket wrenches and an electrical tester. The RCD is installed on a DIN block. If there is no space on the existing block, you will need to install an additional one.
Connecting an RCD in a three-phase network
Protection of devices powered by three phases at once is carried out according to a similar principle, with the difference that the RCD is selected for four outputs. An example of connection is shown in the figure below:
Rice. 5: Connecting an RCD in a three-phase system
As you can see, in this case, the protective device is also connected after the electric meter and the introductory packet. Individual circuit breakers that respond to phase short circuits are already connected behind it, and, if necessary, more sensitive RCDs are connected to create selective operation for certain groups of consumers.
Since installing a separate device for each phase is too expensive, group RCDs are used in three-phase circuits, which work with all elements of the line at once.
Carrying out work by professional services
Theoretically and practically, also with the participation of specialists, installing an RCD involves taking measures to determine the device’s response threshold.
Instructing the installation of protective devices from the RCD series always requires a certain installation sequence. The first element in the sequence is usually a circuit breaker. Then come the electric meter, RCD and other network elements (+)
There are established rules - a kind of instruction, where the entire sequence of actions in such cases is noted.
Work progress:
- First of all, the load circuit in phase and zero is disconnected from the device, for which an automatic switch is used.
- Next, a diagram of connecting measuring equipment and adjustment elements (potentiometer) to the RCD is used.
- By changing the resistance of the potentiometer, the device is activated and the current readings are recorded on the measuring device.
The marked value of the measuring device at the moment of operation is the differential current of the RCD. The recorded current reading must be within the specified range.
If the condition is not met, installation of a protective device in the circuit is prohibited. It is necessary to select another copy that matches the parameters.
Setting up an already installed device is a classic phenomenon for professional services. Thanks to precise tuning, optimal protection is set, which significantly affects overall safety
When connecting protective devices such as RCDs with grounding, the rules also require work aimed at measuring the leakage current within the boundaries of the device’s protection zone.
Typically, such measures are required for installation of electromechanical devices:
- The load is connected to the protection device through the circuit breaker.
- According to the test circuit, a measuring circuit consisting of a resistance store and an ammeter is connected to the device.
- By changing the resistance store, the device is activated and the ammeter readings are recorded.
- The leakage current is calculated using the formula: Iу = I – Ia, where I is the circuit breaking current, Ia is the ammeter reading.
The resulting value of Iу should not exceed the rated value of the differential current of the RCD by more than one third.
The setup is accompanied by measurements of currents in various modes. Ammeters with a high degree of reading accuracy are used for measurements. Only specialists can do this kind of work.
If such an excess is recorded, this is a clear sign that there is a defective area within the protection zone of the device. For such cases, the rules of the PES require the implementation of the necessary measures aimed at eliminating the leakage current.
Basic mistakes when connecting an RCD
When connecting an RCD, many people make common mistakes that can have very serious consequences for a person. To avoid them, follow these rules:
- the input terminals of the residual current device must be connected only after the corresponding circuit breaker; direct connection to the network is unacceptable;
- observe the correspondence of neutral and phase contacts, their designation is specifically indicated on the housing;
- when installing wiring, carefully follow the diagram, especially for objects with branching, a large number of connected objects and several RCDs for them;
- if there is no grounding conductor in an apartment or house, then it should never be replaced with a wire thrown over heating radiators or water pipes; grounding must be made in accordance with the rules;
- pay attention to the performance characteristics of the purchased devices (rated operating current and shutdown current) and their compliance with the network parameters, for example, if a current of 50A can flow in the line, then the device should be selected at least 63A.
To protect yourself during connection, follow basic electrical safety rules.
How does a three-phase residual current device work?
The design of a 3-phase RCD provides a current transformer, the primary winding of which is formed by four wires: three phase and one neutral. In the absence of leaks, the total magnetic flux is zero and no current flows in the secondary winding of the transformer. If a leak occurs on the grounded body of electrical equipment, the total magnetic flux receives a certain value other than zero. It induces a current in the secondary winding, which leads to operation of the electromagnetic relay. By acting on the RCD tripping mechanism, the relay disconnects the load circuit from the supply network.
Safety regulations
If you decide to connect the RCD yourself, the success and safety of the work performed will depend on your compliance with the safety rules:
- Before starting installation operations, be sure to remove the voltage from the area (after disconnecting it would be a good idea to check the presence of potential with an indicator);
- Take care of the marking of the wires - this will make it much more convenient to connect the device so as not to confuse the leads;
- Be sure to use factory terminals and clamps, and never allow twisting, soldering or other connections with poor contact;
- After installation, check the reliability of the connections and the presence of sufficient insulation on all current-carrying elements;
- When commissioning, be sure to check the functionality by pressing the test button;
- When you first apply voltage to a newly installed device, it may fly apart due to manufacturing defects or installation defects, so it is better not to stand nearby or take measures to protect your eyes.
Before applying voltage after completing installation, be sure to ensure that no one in your household or colleagues touches live elements.