Efficient and economical heating or cooling of the working environment in modern industry, housing and communal services, food and chemical industries is carried out using heat exchangers (HE). There are several types of heat exchange units, but plate heat exchangers are the most widespread.
The article will discuss in detail the design, scope and operating principle of a plate heat exchanger. Particular attention will be paid to the design features of various models, operating rules and maintenance features. In addition, a list of leading domestic and foreign manufacturers of plate heat exchangers, whose products are in high demand among Russian consumers, will be presented.
Design and principle of operation
The design of a gasketed plate heat exchanger includes:
- a stationary front plate on which the inlet and outlet pipes are mounted;
- fixed pressure plate;
- movable pressure plate;
- package of heat exchange plates;
- seals made of material that is heat-resistant and resistant to aggressive environments;
- upper supporting base;
- lower guide base;
- bed;
- set of coupling bolts;
- Set of support feet.
This arrangement of the unit ensures maximum intensity of heat exchange between working media and compact dimensions of the device.
Design of a gasketed plate heat exchanger
Most often, heat exchange plates are made by cold stamping from stainless steel with a thickness of 0.5 to 1 mm, however, when using chemically active compounds as a working medium, titanium or nickel plates can be used.
All plates included in the working kit have the same shape and are installed sequentially, in a mirror image. This method of installing heat exchange plates ensures not only the formation of slot channels, but also the alternation of primary and secondary circuits.
Each plate has 4 holes, two of which provide circulation of the primary working fluid, and the other two are isolated by additional contour gaskets, eliminating the possibility of mixing working fluids. The tightness of the connection between the plates is ensured by special contour sealing gaskets made from a material that is heat-resistant and resistant to active chemical compounds. The gaskets are installed in the profile grooves and secured using a clip lock.
Operating principle of plate heat exchanger
The effectiveness of any plate maintenance is assessed according to the following criteria:
- power;
- maximum temperature of the working environment;
- bandwidth;
- hydraulic resistance.
Based on these parameters, the required heat exchanger model is selected. In collapsible plate heat exchangers, the throughput and hydraulic resistance can be adjusted by changing the number and type of plate elements.
The intensity of heat transfer is determined by the flow regime of the working medium:
- with laminar flow of the coolant, the intensity of heat transfer is minimal;
- the transition regime is characterized by an increase in the intensity of heat transfer due to the appearance of turbulence in the working environment;
- The maximum intensity of heat exchange is achieved with turbulent movement of the coolant.
The performance characteristics of the plate heat exchanger are calculated for a turbulent flow of the working medium.
Depending on the location of the grooves, there are three types of heat exchange plates:
- with “soft”
channels (grooves are located at an angle of 600). Such plates are characterized by slight turbulence and low heat transfer intensity, however, “soft” plates have minimal hydraulic resistance; - with “medium”
channels (corrugation angle from 60 to 300). The plates are a transitional option and are distinguished by average turbulence and heat transfer rates; - with “hard”
channels (corrugation angle 300). Such plates are characterized by maximum turbulence, intense heat transfer and a significant increase in hydraulic resistance.
To increase the efficiency of heat exchange, the movement of the primary and secondary working fluid is carried out in the opposite direction. The heat exchange process between the primary and secondary working fluids occurs as follows:
- The coolant is supplied to the inlet pipes of the heat exchanger;
- When moving the working media along the corresponding circuits formed from heat-exchange plate elements, intense heat transfer occurs from the heated medium to the heated one;
- Through the outlet pipes of the heat exchanger, the heated coolant is directed to its destination (heating, ventilation, water supply systems), and the cooled coolant again enters the working area of the heat generator.
Operating principle of a plate heat exchanger
To ensure efficient operation of the system, complete tightness of the heat exchange channels is necessary, which is ensured by sealing gaskets.
What types are on the market?
Devices are classified according to the type of fuel they burn to produce heat. It can be:
- Alcohol . Heat exchangers that operate on alcohol are distinguished by their compactness. However, they are not able to warm the fisherman in severe frost. Most often used as an additional means of heating.
- Solid fuel (firewood) . Heat exchangers operating on solid fuel (wood, briquettes) are the most common among fishermen, because... it can be found in any forest. The main disadvantage of contraction is its large weight and size.
- Gasoline . Liquid fuel devices are compact. However, they have not become widespread due to the explosive properties of gasoline.
- Gas . Fish use devices that operate on gas quite often. Their distinctive feature is their small size and safety of use. Gas enters the burner from the storage facility through a special hose. The fuel supply is regulated by a valve.
Electric heat exchanger
Note! There are devices on sale that operate on electricity.
Each person decides which option to choose based on personal preferences.
Requirements for gaskets
To ensure complete tightness of the profile channels and prevent leakage of working media, sealing gaskets must have the necessary heat resistance and sufficient resistance to the effects of an aggressive working environment.
The following types of gaskets are used in modern plate heat exchangers:
- ethylene propylene (EPDM). Used when working with hot water and steam in the temperature range from -35 to +1600C, unsuitable for fatty and oily environments;
- NITRIL gaskets (NBR) are used for working with oily working media, the temperature of which does not exceed 1350C;
- VITOR gaskets are designed to work with aggressive working environments at temperatures not exceeding 1800C.
The graphs show the dependence of the service life of seals on operating conditions:
As for attaching the sealing gaskets, there are two ways:
- on glue;
- using a clip.
The first method is rarely used due to the complexity and duration of installation; in addition, when using glue, maintenance of the unit and replacement of seals is significantly more complicated.
The clip lock ensures quick installation of plates and ease of replacement of failed seals.
Design Features
The main purpose of any type of plastic heat exchanger is to convert heated liquid into a cooled environment. The design of the plate heat exchanger has collapsible parts, and the device consists of the following elements:
- set of plates;
- movable and fixed plates;
- rounded upper and lower guides;
- fastening elements that combine the slabs into a common frame.
Frame sizes of different products can vary significantly. They will depend on the heat transfer and power of the heater - with a large number of plates, the productivity of the equipment increases and, naturally, the weight and dimensions increase.
You can control the power on the heat exchanger - increase or decrease
Advantages of plate devices:
- low production and investment costs;
- highly efficient heat transfer;
- small dimensions;
- self-cleaning effect using high turbulent flow;
- the ability to increase efficiency by adding plates;
- high degree of reliability;
- ease of washing;
- small weight;
- ease of installation;
- minimal surface contamination;
- impossibility of mixing liquids due to a special seal configuration;
- high corrosion resistance;
- minimal heat transfer surface due to high efficiency;
- insignificant pressure losses due to the optimal choice of plates with different types of profiles;
- effective temperature regulation due to the small volume of coolant.
In this video you will learn how hot water is generated thanks to a heat exchanger:
Specifications
As a rule, the technical characteristics of a plate heat exchanger are determined by the number of plates and the way they are connected. Below are the technical characteristics of gasketed, brazed, semi-welded and welded plate heat exchangers:
| Operating Parameters | Units | Collapsible | Soldered | Semi-welded | Welded |
| Efficiency | % | 95 | 90 | 85 | 85 |
| Maximum operating temperature | 0C | 200 | 220 | 350 | 900 |
| Maximum working pressure | bar | 25 | 25 | 55 | 100 |
| Maximum power | MW | 75 | 5 | 75 | 100 |
| Average period of operation | years | 20 | 20 | 10 — 15 | 10 — 15 |
Based on the parameters given in the table, the required heat exchanger model is determined. In addition to these characteristics, one should take into account the fact that semi-welded and welded heat exchangers are more suitable for working with aggressive working environments.
Choosing material
The coil is traditionally made from a pipe, the length and diameter of which are determined by the desired level of heat transfer. The efficiency of the structure will depend on the thermal conductivity of the material used. The most commonly used pipes are:
- copper with a thermal conductivity coefficient of 380;
- steel with a thermal conductivity coefficient of 50;
- metal-plastic with a thermal conductivity coefficient of 0.3.
Copper or metal-plastic?
With the same level of heat transfer and equal transverse dimensions, the length of metal-plastic pipes will be 11, and steel pipes will be 7 times longer than copper ones.
That is why it is best to use annealed copper pipe to make the coil.
Such a material is characterized by sufficient plasticity, and therefore it can easily be given the desired shape, for example, by bending. The fitting is easily connected to the copper pipe with a thread.
We are looking for improvised means
Considering the high cost of materials, it would be appropriate to consider the possibility of using products that have already served their purpose, but have not yet fully exhausted their service life. This will not only reduce the cost of manufacturing the heat exchanger, but will reduce the time for installation work. As a rule, preference is given to:
- any heating radiators that do not leak;
- heated towel rails;
- radiators from cars and other products of similar design;
- instantaneous water heaters.
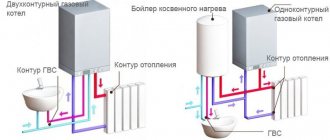
Why is a heat exchanger needed in a heating system?
Explaining the presence of a heat exchanger in a heating system is quite simple. Most heating systems in our country are designed in such a way that the temperature of the coolant is regulated in the boiler room and the heated working environment is supplied directly to the radiators installed in the apartment.
If there is a heat exchanger, the working medium from the boiler room is released with clearly defined parameters, for example, 1000C. Once in the primary circuit, the heated coolant does not enter the heating devices, but heats the secondary working medium, which enters the radiators.
The advantage of this scheme is that the temperature of the coolant is adjusted at intermediate individual heating stations, from where it is supplied to consumers.
Model types
The devices differ in the installation method. And this directly affects the efficiency of the entire system. Very often a boiler design is used that already has a heating heat exchanger inside. Heat losses in such devices are practically reduced to zero. And for productive work all you need is proper configuration.
External structures are much less efficient. Because their position does not allow the coolant to heat up well. But they are used where there are no individual heating boilers. For example, in houses using centralized heating.
Advantages and disadvantages
The widespread use of plate heat exchangers is due to the following advantages:
- compact dimensions. Due to the use of plates, the heat exchange area significantly increases, which reduces the overall overall dimensions of the structure;
- ease of installation, operation and maintenance. The modular design of the unit makes it easy to disassemble and wash elements that require cleaning;
- high efficiency. PHE productivity ranges from 85 to 90%;
- affordable price. Shell-and-tube, spiral and block installations, with similar technical characteristics, are much more expensive.
The disadvantages of the plate design are:
- need for grounding. Under the influence of stray currents, fistulas and other defects can form in thin stamped plates;
- the need to use high-quality working environments. Since the cross-section of the working channels is small, the use of hard water or low-quality coolant can lead to blockage, which reduces the intensity of heat transfer.
What is so attractive about a potbelly stove?
Although in this case half of the thermal energy evaporates through the direct-flow pipe. But no one writes off even a heating source that has rusted over time as scrap.
Such a temporary stove can be easily made in a day or two. But first, make your own drawings of the potbelly stove. Much of what is stored in the closets of rural houses and dachas is used. These are milk and water metal (not duralumin) cans, barrels for diesel fuel, vegetable oils, pipes, boxes, corners.
Nothing expensive, including tools - in villages every owner has them at hand. High-quality assembly using gas or electric welding.
But neighbors who have units will help with this. Welding machines provide greater reliability and rigidity of the assembly. Below are step-by-step instructions on how to make a potbelly stove with your own hands.
Plate heat exchanger piping diagrams
There are several ways to connect a PHE to a heating system. The simplest is considered to be parallel connection with a control valve, the circuit diagram of which is shown below:
PHE parallel connection diagram
The disadvantages of such a connection include increased load on the heating circuit and low efficiency of water heating at a significant temperature difference.
Parallel connection of two heat exchangers in a two-stage scheme will ensure more productive and reliable operation of the system:
Two-stage parallel connection diagram
1 – plate heat exchanger; 2 – temperature regulator; 2.1 – valve; 2.2 – thermostat; 3 – circulation pump; 4 – hot water flow meter; 5 – pressure gauge.
The heating medium for the first stage is the return circuit of the heating system, and the heated medium is cold water. In the second circuit, the heating medium is the coolant from the direct line of the heating system, and the heated medium is the preheated coolant from the first stage.
Where to use a homemade furnace for mining
Since during the combustion process engine oil, especially used one, does not emit the most pleasant odor, and from a health point of view it is not very useful, it is better not to use stoves of this kind in residential premises. If there is no other way out, high-quality removal of combustion products is mandatory.
Typically, stoves are installed in non-residential premises - utility rooms, garages, sheds, workshops, and so on - where constant heating is not required, but only warming up the air for a relatively short time.
Due to the fact that even the simplest designs of such a “garage stove” make it possible to regulate the intensity of fuel combustion, it is possible to ensure either an economical mode of its use and gradual heating of the premises, or increased consumption with very fast heating of the air volume.
User manual
Each factory plate heat exchanger must be accompanied by detailed operating instructions containing all the necessary information. Below are some basic provisions relevant to all types of VET.
PHE installation
- The location of the unit must provide easy access to the main components for maintenance.
- The fastening of supply and discharge lines must be rigid and airtight.
- The heat exchanger should be installed on a strictly horizontal concrete or metal base with sufficient load-bearing capacity.
Commissioning works
- Before starting the unit, it is necessary to check its tightness according to the recommendations given in the technical data sheet of the product.
- During the initial startup of the installation, the rate of temperature increase should not exceed 250 C/h, and the pressure in the system should not exceed 10 MPa/min.
- The procedure and scope of commissioning work must clearly comply with the list given in the unit’s passport.
Unit operation
- When using PHE, it is not allowed to exceed the temperature and pressure of the working medium. Overheating or increased pressure can lead to serious damage or complete failure of the unit.
- To ensure intensive heat exchange between working media and increase the efficiency of the installation, it is necessary to provide for the possibility of cleaning working media from mechanical impurities and harmful chemical compounds.
- Regular maintenance and timely replacement of damaged elements will significantly extend the service life of the device and increase its performance.
We increase the efficiency of the furnace
door to the firebox and ash pan; it is advisable to provide a damper; side metal screens
Potbelly stove in casing
Round furnace with afterburner and casing with heat gun
A stove with elbows for a chimney,
the throughput of the chimney, blowing the chimney with a fan firewood in the stove with slots and a valve, strips of metal buckets or a metal box with sand, sand backfill or a heat accumulator made of stones
Scheme of a potbelly stove with sand backfill, the stove is made of a pipe with a diameter of 500 mm, its length is 650 mm,
lined with 1-2 layers of brick
Brick screen
area of its walls bricks or metal sheet Video on the topic: Do-it-yourself potbelly stove stove
Flushing the plate heat exchanger
The functionality and performance of the unit largely depends on high-quality and timely washing. The frequency of washing is determined by the intensity of work and the characteristics of technological processes.
Methodology for cleaning work
Scale formation in heat exchange channels is the most common type of PHE contamination, leading to a decrease in heat exchange intensity and a decrease in the overall efficiency of the installation. Descaling is carried out using chemical washing. If, in addition to scale, other types of contamination are present, it is necessary to mechanically clean the heat exchanger plates.
Chemical washing
The method is used for cleaning all types of PHE, and is effective with minor contamination of the working area of the heat exchanger. To carry out chemical cleaning, disassembling the unit is not required, which can significantly reduce the work time. In addition, no other methods are used for cleaning brazed and welded heat exchangers.
Chemical washing of heat exchange equipment is carried out in the following sequence:
- a special cleaning solution is introduced into the working area of the heat exchanger, where scale and other deposits are intensively destroyed under the influence of chemically active reagents;
- ensuring circulation of detergent through the primary and secondary maintenance circuits;
- flushing heat exchange channels with water;
- draining cleaning agents from the heat exchanger.
During the chemical cleaning process, special attention should be paid to the final rinsing of the unit, since chemically active components of detergents can destroy seals.
The most common types of contamination and cleaning methods
Depending on the working media used, temperature conditions and pressure in the system, the nature of the contaminants can be different, so for effective cleaning it is necessary to choose the right detergent:
- cleaning from scale and metal deposits uses solutions of phosphoric, nitric or citric acid;
- inhibited mineral acid is suitable for removing iron oxide;
- organic deposits are intensively destroyed by sodium hydroxide, and mineral deposits by nitric acid;
- fatty stains are removed using special organic solvents.
Since the thickness of the heat exchange plates is only 0.4 - 1 mm, special attention should be paid to the concentration of active elements in the detergent composition. Exceeding the permissible concentration of aggressive components can lead to destruction of plates and sealing gaskets.
The widespread use of plate heat exchangers in various sectors of modern industry and public utilities is due to their high performance, compact overall dimensions, ease of installation and maintenance. Another advantage of VET is the optimal price/quality ratio.
Determining the volume of fuel fill
For the potbelly stove to operate efficiently, it is important to load the optimal amount of fuel into it, and for each type of fuel it is necessary to find its own indicator.
If you overload the furnace, there will be too many combustion products and they will block circulation; if you underload, there will be few of them, which also makes circulation impossible. The bookmark volume is selected as follows:
- fuel is collected in a bucket;
- they take a handful from the bucket and, placing it in the firebox, set it on fire;
- add fuel in small portions until the initial section of the hog is cherry red hot. Now they estimate how much fuel is taken from the bucket - this is the minimum volume of the stowage;
- continue to add fuel (the portions must be increased) until the dimensions of the hot section reach 80%-85% of the length of the “hog”. At this moment, the volume of fuel taken from the bucket will correspond to the maximum fuel load.
The test is carried out in moderate lighting: if during the day, then in cloudy weather (winter); If it’s clear outside, it’s closer to evening. When loading high-calorie fuel (pellets, anthracite), the hot area sometimes takes the form of a ring with different widths, occupying different positions along the length of the hog.
Then the volume of the bookmark is determined as follows:
- maximum: the section of the hog farthest from the furnace is hot for 1/3 of its length;
- minimal: the hot zone is located in the middle and is 3-4 palms long.