There are many heating devices that have high power and can be used to integrate into a heating system. To organize the heating system of a private house, as a rule, gas boilers are used - this choice is not accidental. All sorts of “incidents” periodically happen with centralized heating, so the possibility that you may be left without heat cannot be ruled out. In addition, such heating is not always able to provide people with the necessary heat, and the operating principle of a gas heating boiler allows you to create and maintain coziness and comfortable conditions in the house.
The low cost of fuel also plays an important role in the widespread use of gas-fired boilers, and thanks to the relative accessibility to the gas main, such heating can be installed in any locality.
Although the installation of equipment takes a lot of time, the boilers are practically silent in operation, are capable of heating large areas and can have a long service life.
Types of gas boilers by purpose
According to their intended purpose, the units are produced as single-circuit and double-circuit. And they differ in the number of installed heat exchangers, capable of independently heating water only for heating or both for heating and hot water supply.
In addition, these units are divided according to the heat exchanger material: cast iron, steel and copper.
The most durable is the cast iron option; it resists corrosion processes well, but is considered fragile and is susceptible to water hammer, especially during cold equipment starts.
Copper is used in wall-mounted boilers and has high thermal conductivity. But it is undesirable when installed in conjunction with aluminum radiators, since a galvanic couple is created that destroys aluminum.
Steel heat exchangers are most often used in floor-standing boilers and are inferior in characteristics to the first two modifications.
Modern boilers are grouped according to the degree of condensation of flue gases into condensing-type boilers or non-condensing units.
Double-circuit boilers
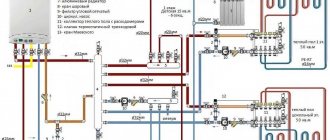
In double-circuit boilers operating on gas fuel, heated water circulates through 2 circuits, one of which is responsible for the functioning of heating, and the second for DHW.
Diagram of a double-circuit boiler
Switching features of a dual-circuit unit:
- Heating. In most modern boilers, the heating circuit starts automatically after the primary temperature sensor gives a signal to the control panel, which increases the gas flow and the speed of the circulation pump for forced coolant circulation systems. The gas is burned in the boiler furnace. Hot flue gases give off their heat through a surface heat exchanger, heating the water, depending on the boiler model, from 75 to 90 °C. A centrifugal pump pumps the heated coolant through the in-house heating system from the boiler to the radiators, and then returns the cooled water to the boiler for a new heating cycle.
- DHW. When the user opens the hot tap on the water supply mixer, the three-way tap on the boiler transfers the coolant from the primary heat exchanger to the secondary one. In this mode, the heating boiler does not work, which is very inconvenient if the family is large. Significant heat consumption for DHW will be required; during this period, the heating system may cool down.
Single-circuit
A single-circuit gas boiler is the simplest in design; it is usually installed in heat supply systems with a small heating area.
They are easy to operate and have the lowest price among gas heating units. Many modern boilers have the design ability to connect an external indirect heating boiler, which is made in the form of a hot water storage tank.
Boiler diagram with one circuit and boiler
At the bottom of the boiler there are special DHW pipes, which are used to connect to an external heat exchanger. This scheme is very effective because it uses the boiler more efficiently.
When the water in the heating system is below the set temperature schedule, the coolant is heated for the heating circuit; when it reaches the desired temperature, the three-way valve switches the coolant to heating water in the storage tank.
At the same time, the DHW water supply will not affect the quality of heating in any way. To reduce heat loss in the heating system, experts advise placing an indirect heating boiler as close as possible to the boiler unit.
Open and closed heating system
Mistake #13
Modern gas boilers cannot be installed on an open heating system.
Indeed, all the latest models are mainly designed for closed systems. They maintain a stable pressure and when it decreases, a sensor is triggered, which turns off the heating device.
A drop in pressure usually indicates a leak. When installing a modern gas boiler on an open system, all you need to do is convey to the sensor the information that the pressure in the system is initially low, and this in no way indicates heating problems.
This is done by simply connecting the sensor wires to each other.
After this, if you do not drain the system and drain the water in the future, the boiler will operate without problems.
Mistake #14
The only caveat is that not all manufacturers consider such a life hack to be a warranty case!
Therefore, check this point with the seller in advance.
Types of gas boilers according to installation method
All gas boilers are grouped according to installation option - floor-mounted and wall-mounted. They all have their advantages and disadvantages; it is important to understand the criteria in which the device will perform best, especially in conditions of shortage of living space.
Wall boilers
These types of gas heating boilers appeared on the climate control market relatively recently, but have already won user sympathy. The modern level of performance of wall-mounted gas units allows them to be used as a mini modular boiler room.
The unit is factory equipped with not only the main but also auxiliary equipment. Typically, its kit includes a circulation pump, two heat exchangers, a fan, a safety group with instrumentation and primary sensors, an air vent and an expansion tank.
These units have a multifunctional mode with 100% automatic combustion process. They are easy to install and have the highest efficiency of up to 92%, since all auxiliary equipment is most carefully matched by the manufacturer to the thermal power of the boiler.
Floor-standing
A floor-standing gas boiler is a traditional option for placing a heating source, which came from a centuries-old Russian stove. These modifications are heavy because, as a rule, they are equipped with a powerful cast-iron heat exchanger. Floor-standing devices are designed for heating houses with a large heating surface.
To increase the thermal power of the heating source, they are equipped with blower fans to organize forced circulation of flue gases.
Depending on the power, the burners are atmospheric up to 80 kW and replaceable inflatable burners with a power of several thousand kW. Such devices are made to be volatile.
Some types of floor-standing units can also be non-volatile, when the heat transfer process is carried out without the need for electrical power, usually these are low-power devices capable of heating an area of up to 200 m2, using natural circulation patterns of the coolant and exhaust gases.
Manufacturer country
Which wall-mounted gas boiler is better - Korean or European? It is between them that the struggle most often occurs in this segment.
Mistake #7
Korean boilers are more economical than European ones.
Mistake #8
European boilers are more economical than Korean ones.
All wall-mounted turbocharged boilers work approximately the same. Yes, their filling is different, but this does not affect the SAVINGS.
The efficiency of both Korean and European models is the same. Here you need to look at another parameter, namely, the availability in your city of a service for maintenance and repair of a specific brand.
Because sooner or later your boiler, no matter how reliable it is, WILL BREAK.
Based on this factor, it is worth making a choice in one direction or another. Remember a simple rule - the further you live from the service, the simpler the units you choose.
Boilers by combustion chamber type
The next important parameter for classifying types of gas boilers is based on the design of the combustion chamber. They come in open and closed types.
The first ones are simpler and cheaper, but have limitations on the heating area of no more than 250 m2. The latter are more expensive, energy-dependent and safe, since they do not burn oxygen in the house.
With open firebox
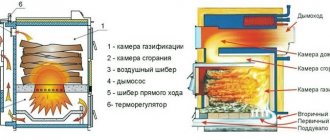
An open firebox means that there is a natural intake of combustion air from the room. This is the simplest design of a boiler unit, in which no electricity is needed to organize the combustion process, as well as the arrangement of air ducts and a blower fan. Boilers of this design are usually low-power and heat a living area of no more than 200 m2.
The disadvantage of this type of boiler units is the high requirements for organizing fresh ventilation in the room where it is located. Legislative requirements for ventilation systems for boilers with an open firebox are to ensure 3-fold air exchange through window and door structures.
Otherwise, the air will become dry and will negatively affect the microclimate in the room. In addition, these boilers often have problems due to imperfect smoke exhaust. If the vacuum level in the firebox drops to zero, carbon monoxide can enter the room, which is deadly for others.
Closed chamber boilers
This is a completely new type of smoke exhaust organization in which the firebox has no contact with the internal air in the room. Oxygen is taken to the burner through closed air ducts from the street.
The supply system is forced through a fan. The air enters through a special channel in which the fan is located. This principle is implemented, for example, in the Turkish Vitopend boiler.
The flue gas removal system in it is organized through a coaxial chimney, which is made of the “pipe-in-pipe” type. Exhaust boiler gases are discharged through the internal pipe, and air from the street is drawn in through the annular space by a fan.
The advantage of this system is that its operation does not affect the climate inside the room; installation of complex smoke ventilation ducts that ensure natural circulation is not required. Low space requirements for installation, allowing installation in standard kitchens.
The disadvantages of this design, users most often include their high cost and dependence on electricity.
Floor or wall?
Mistake #17
There is no clear answer which is better.
In the vastness of our country, it is still believed that floor-mounted ones outperform wall-mounted ones.
At the same time, in Europe they have long been recognized as low-energy efficient devices and are practically banned in all residential buildings.
It's only the beginning