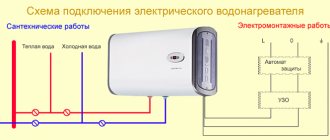
To ensure comfortable living in the cold season, even at the stage of designing a private house, you need to take care of the calculation and installation of heating. Correctly performed thermal calculations will allow you to determine the optimal and cost-effective heating system. Any error can lead to you freezing or the building becoming hot and stuffy.
Independent calculations will not be a problem for people with technical education. However, not everyone has physical and mathematical skills, so an online calculator will be a good guide to calculations. It will help identify heat losses at home and calculate the power that the boiler should have. It will also determine the number of radiators needed and how many sections it should have. It will calculate heating costs for you, which will be useful for choosing a suitable heat source. Collect the necessary data for the calculation.
Determine heat losses. To do this, you need to know what material the external walls and floor coverings are made of, how they are insulated and their thickness. Measure the area of the house, windows and exterior doors. High intensity of heat loss from ventilation and sewerage. They also need to be taken into account in the calculations.
The climatic conditions of the location of the house play an important role in the choice of heating system. Find out the average annual and minimum temperatures in your area, as well as the average wind speed.
What calculation options are there?
To make the right choice of gas equipment, we suggest using three calculation options:
- Accurate thermal technology is not suitable for ordinary consumers, it is complex and requires the use of a thermal imager.
- On an online calculator - to get the result, the user enters the initial data into a special program: the number of windows, doors, wall thickness and other information. Based on them, the program produces the result.
- Manual calculations. The most accessible way to find out the optimal heating performance of a heater is to use the elementary ratio of area and power. The formula used is: 10 m² = 1,000 W. This simple option is correct for buildings characterized by an average degree of thermal insulation and having ceilings with a height of about 2.7 m.
When calculating the power characteristics of heating devices, developers often take into account the volume of the premises. In the technical documentation of imported models, the parameter “heating in m³” is often found.
Calculation of boiler power with one circuit
Having performed the simplest calculation for a single-circuit wall-mounted or floor-standing boiler using the ratio: 10 kW per 100 m², you need to increase the calculated value by 15–20%.
Let's give an example of calculations. It is necessary to equip a house with an area of 80 m². To heat it, you will need a device with 9,600 W = 8,000 W + 20%. If there is no exactly suitable option on sale, you should take a modification with greater performance. This method of calculation is only suitable for devices with one circuit, without an indirect heating boiler.
Calculation of boiler power with two circuits
The calculation is based on the following ratio: 10 m² = 1,000 W + 20% (reserve) + 20% (water heating). If the house has an area of 200 m², then the required value will be: 20,000 W + 40% = 28,000 W.
Determining the power of a model with a boiler
First, the required volume of the boiler is determined so that it can satisfy the needs of the household for hot water. Water consumption is calculated taking into account the operation of all water intake points:
- bath - 8–9 l/min;
- shower - 9 l/min;
- toilet - 4 l/min;
- washing - 4 l/min.
The technical documentation for the boiler indicates what boiler performance is required to ensure water heating. For a boiler with a capacity of 200 liters of water, a heater with a power of approximately 30 kW is suitable. Then the performance required for heating is calculated. The results obtained are summarized. At the end of the calculations, you need to subtract 20% from the result obtained, since water heating for hot water supply and heating occurs simultaneously.
Calculation of boiler power for typical houses, taking into account the climate zone
For houses built according to standard designs, the formula is used: M = S*UM/10, where
- M/UM - design/specific power, kW;
- S—area, m².
PA depends on the region, kW:
- south - 0.7–0.9;
- middle band - 1.0–1.2;
- Moscow region - 1.2–1.5;
- North - 1.5–2.0.
Let's perform calculations for a house with an area of 300 m² located in the Moscow region: 300 * 1.3/10 = 39 kW. This result is suitable for installing single-circuit models. To calculate the power of a dual-circuit device, you need to increase the final number by 25%.
Valtec “Sputnik” equipment configurator
Configurator software is a modular configurator for various metering devices and equipment. Allows commissioning of the Valtec “Sputnik” automated energy metering system.
- The configurator includes the following modules:
- polling of metering devices via radio channel using radio modem VT.WRM.MASTER.0
- module for reading data from VT.WRM hubs
- module for configuring wireless pulse counter-recorder GSM/GPRS VT.WLR.GSM
- module for configuring a wireless pulse counter-recorder with a radio channel (LoRAWAN 868 MHz) VT.LR
- module for configuring pulse counter-recorder SIPU (RS485/M-Bus) VT.MB/ VT.RS
What to look for when choosing
Depending on the manufacturer, the design of boilers and their technical characteristics may vary. When selecting a product, a number of factors must be taken into account. This will allow you to choose an installation with high efficiency and cost-effectiveness.
Type of fuel
Modern boiler systems can operate either from a centralized gas supply system or from cylinders. In the second case, liquefied propane-butane is used. Connecting heating from cylinders is possible at facilities where there is no centralized gas supply system.
It should be taken into account that boilers designed for connection to gas pipelines and cylinders differ in their design. Some manufacturers produce models that, if necessary, can be converted from gaseous fuel to liquefied fuel and vice versa.
Power
Before choosing a unit for heating a private house of 200 square meters. m, it is necessary to correctly calculate its power characteristics.
After determining the minimum permissible power of the installation, a number of factors must be taken into account:
- Using DHW. Heating hot water requires additional thermal energy. Lack of power will not allow you to simultaneously warm the room to a comfortable temperature and supply hot water. As a result, the installation will constantly operate at maximum power, which will negatively affect its service life.
- Presence of heat loss. When choosing products, you should consider whether the walls, ceiling and floor of the building are insulated. Large heat losses require additional energy consumption. In the absence of insulation, you should choose a unit for heating a 200 m2 house on models with an increased power rating.
- Climatic conditions. Depending on the region, heat loss during the winter season differs. This must be taken into account when choosing.
Correct calculation of the power of a gas boiler for 200 sq. m will provide a comfortable room temperature regardless of weather conditions.
Price
The price of a boiler for a house of 200 square meters differs depending on the design of the product, manufacturer, number of circuits and degree of automation.
The choice of model is made based on the personal preferences of the owners of the premises. Products from foreign manufacturers have a higher price. Domestic boilers have a low cost.
Taking into account the technical characteristics of the boiler installation, it will be possible to choose a gas boiler with a good price-quality ratio.
Economical
To reduce fuel consumption, products with a high efficiency are selected. Such models make it possible to make maximum use of the thermal energy generated as a result of gas combustion. Depending on the design and equipment, boilers heat the coolant in different ways.
How to more correctly assess the degree of thermal insulation of the walls of a room?
As promised above, this section of the article will help the reader with assessing the level of thermal insulation of the walls of his residential properties. To do this, you will also have to carry out one simplified thermotechnical calculation.
Principle of calculation
According to the requirements of SNiP, the heat transfer resistance (which is also called thermal resistance) of building structures of residential buildings must not be lower than the standard value. And these standardized indicators are established for the regions of the country, in accordance with the characteristics of their climatic conditions.
Where can I find these values? Firstly, they are in special appendix tables to SNiP. Secondly, information about them can be obtained from any local construction or architectural design company. But it is quite possible to use the proposed map-scheme, covering the entire territory of the Russian Federation.
Diagram map for determining the normalized value of the thermal resistance of building structures
In this case, we are interested in the walls, so we take from the diagram the value of thermal resistance specifically “for walls” - they are indicated in purple numbers.
Now let's take a look at what this thermal resistance consists of, and what it is equal to from the point of view of physics.
So, the heat transfer resistance of some abstract homogeneous layer x is equal to:
Rх = hх / λх
Where:
Rx - heat transfer resistance, measured in m²×°K/W;
hx is the layer thickness, expressed in meters;
λx is the thermal conductivity coefficient of the material from which this layer is made, W/m×°K. This is a tabular value, and for any building or thermal insulation material it is easy to find on Internet reference resources.
Conventional building materials used for the construction of walls, most often, even with their large (within reason, of course) thickness, do not reach the standard indicators of heat transfer resistance. In other words, the wall cannot be called fully thermally insulated. This is precisely why insulation is used - an additional layer is created that “makes up for the deficit” necessary to achieve standardized indicators. And due to the fact that the thermal conductivity coefficients of high-quality insulation materials are low, you can avoid the need to build very thick structures.
You may be interested in information about what a hydraulic arrow is, how it works, its purpose and calculations
Let's take a look at a simplified diagram of an insulated wall:
Wall diagram with insulation layer and finishing
1 - in fact, the wall itself, which has a certain thickness and is built from one material or another. In most cases, “by default” it itself is not able to provide the normalized thermal resistance.
2 - a layer of insulating material, the thermal conductivity coefficient and thickness of which should ensure “covering the shortage” up to the normalized R value. Let’s make a reservation right away - the location of thermal insulation is shown on the outside, but it can also be placed on the inside of the wall, and even located between two layers of the supporting structure (for example , laid out of brick according to the “well masonry” principle).
3 - external facade finishing.
4 - interior decoration.
Finishing layers often do not have any significant effect on the overall thermal resistance rating. Although, when performing professional calculations, they are also taken into account. In addition, the finishing can be different - for example, warm plaster or cork slabs are very capable of enhancing the overall thermal insulation of the walls. So, for the “purity of the experiment,” it is quite possible to take both of these layers into account.
But there is also an important note - the façade finishing layer is never taken into account if there is a ventilated gap between it and the wall or insulation. And this is often practiced in ventilated facade systems. In this design, the external finishing will not have any effect on the overall level of thermal insulation.
So, if we know the material and thickness of the main wall itself, the material and thickness of the insulation and finishing layers, then using the above formula it is easy to calculate their total thermal resistance and compare it with the standardized indicator. If it is not less, there is no question, the wall has full thermal insulation. If it is not enough, you can calculate which layer and which insulating material can fill this deficiency.
You may be interested in information about how heating is calculated in a private house calculator
And to make the task even easier, below is an online calculator that will perform this calculation quickly and accurately.
Just a few explanations about working with it:
- To begin with, using the map diagram, find the normalized value of heat transfer resistance. In this case, as already mentioned, we are interested in the walls.
(However, the calculator is universal. And it allows you to evaluate the thermal insulation of both floors and roofing coverings. So, if necessary, you can use it - add the page to your bookmarks).
- The next group of fields indicates the thickness and material of the main supporting structure - the wall. The thickness of the wall, if it is built according to the “well masonry” principle with insulation inside, is indicated as the total thickness.
- If the wall has a thermal insulation layer (regardless of its location), then the type of insulation material and thickness are indicated. If there is no insulation, then the default thickness is left equal to “0” - move on to the next group of fields.
- And the next group is “dedicated” to the external decoration of the wall - the material and thickness of the layer are also indicated. If there is no finishing, or there is no need to take it into account, everything is left by default and moved on.
- The same applies to the interior wall decoration.
- Finally, all that remains is to choose the insulation material that you plan to use for additional thermal insulation. Possible options are indicated in the drop-down list.
After clicking on the “CALCULATE MISSING INSULATION THICKNESS” button, the result in millimeters will be shown. Here are the possible options:
— A zero or negative value immediately indicates that the thermal insulation of the walls meets the standards, and additional insulation is simply not required.
— A positive value close to zero, say, up to 10÷15 mm, also does not give much reason to worry, and the degree of thermal insulation can be considered high.
— Insufficiency of up to 70÷80 mm should already make the owners think. Although such insulation can be classified as average efficiency, and taken into account when calculating the thermal power of the boiler, it is still better to plan work to enhance thermal insulation. What thickness of the additional layer is needed is already shown. And the implementation of these works will immediately give a tangible effect - both by increasing the comfort of the microclimate in the premises and by reducing the consumption of energy resources.
— Well, if the calculation shows a shortage of more than 80÷100 mm, there is practically no insulation or it is extremely ineffective. There cannot be two opinions here - the prospect of carrying out insulation work comes to the fore. And this will be much more profitable than purchasing a boiler with increased power, part of which will simply be spent literally on “warming up the street.” Naturally, accompanied by ruinous bills for wasted energy.
You might find the heating diagram for a two-story house with forced circulation useful
Calculator for assessing the effectiveness of wall thermal insulation
Go to calculations
We will conclude the publication with a video, also dedicated to taking into account heat losses when calculating the power of a heating system. Compression fittings for metal-plastic pipes you will find the answer in the link.
What power reserve should be
The power for selecting a heating source with an indirect heating boiler with simultaneous operation of heating and hot water supply is determined by the formula:
M k= (Mo+Mgvs)*Kz,
Where:
- Mk-combined power, kW;
- Mo - source power sufficient to provide the heating load of the house, kW;
- Mgvs - source power required to compensate for the load on hot water supply, kW;
- Кз - safety factor.
In the case of alternating operation of heating and hot water systems:
Mk = Mgvs * Kz
Very important! When calculating the performance of heating and hot water equipment, it is necessary to take into account that the power of the BKN does not in any way exceed the same indicator in the boiler. For this reason, it must be selected with a heating capacity in kW so that it can cover the load of both heating and domestic hot water with a margin.
The performance reserve is calculated depending on the design of the heating equipment.
For single-circuit modifications, the margin is 20.0%; for dual-circuit - 20.0%+20.0%.
For the above examples, the heating output of the boiler will be equal.
When heating and hot water systems operate simultaneously:
Mo = 24 kW. Mgvs = 24 kW. Kz= 1.4.
Mk= (24+24)* 1.4= 67.2 kW.
When operating heating and hot water systems alternately:
Mk=24*1.4= 33.6 kW.
Thus, performing an initial calculation of the power of a gas thermal energy source is not a difficult process. It may be used for preliminary selection of boiler equipment.
If the subscriber lacks an approximate calculation of the efficiency of gas boilers, and it is necessary that the heat loss of the building, the DHW load and the boiler performance be determined more accurately, he will need to contact qualified specialists to carry out a comprehensive home heating project with the development of a diagram and selection of equipment . Calculations
Valtec “Sputnik” software package
The Valtec “Sputnik” software package is intended for use in the housing and communal services sector (management companies, homeowners' associations) and industry. The intuitive interface makes it easy for users to quickly learn. A number of special reports for management companies (homeowners associations, resource supply organizations) and integration with accounting programs (1C) make it easy to generate payment receipts. The control center includes reports that allow you to track emergency situations, unauthorized access to resources, and requests from subscribers from your personal account.
Integration into the Housing and Public Utilities GIS has been introduced to simplify reporting in organizations.
- Main features:
- Collection of readings from metering devices, event sensors, remote resource limitation
- Online emergency monitoring
- Data storage
- Generating special reports
- Integration with related software products used in the organization’s business processes (1C, video surveillance, POS, etc.)
- Open API
- Recommendations for saving resources
To familiarize yourself with the program's capabilities: Login: demo Password: demo
In the case of a comprehensive supply of metering devices and dispatch systems, a license file that allows you to fully work with the program is issued free of charge. The server is formed on the customer's side.
As an additional paid service, it is possible to use a Valtec remote cloud server.
For commissioning, commissioning of a facility or testing of dispatch system equipment, a free test license file valid for 1 month is provided.
For details on obtaining a test license, please contact the managers working in your region.
Reserve for heating tap water
If you want to use your gas boiler for hot water supply, then you should decide how exactly you will prepare hot water for the water supply. This determines what reserve for hot water supply you will need to include in your calculations.
If you use a double-circuit boiler, then to reliably heat tap water in instantaneous heater mode, you need to set at least 30 percent of the power.
That is, for our case this is a minimum of 6 kW, and the total power is at least 26 kW. And that is not all.
If you use two water points in the bathrooms, one point in the kitchen, a bath, a shower, and also heat water for the bath with a boiler, then you will have to spend not 30, but 50 percent on hot water.
That is, at the output we already have 10 kW for DHW or 30 kW of total power.
However, if you decide to use a single-circuit boiler and an indirect heating boiler, then you should set the minimum power for hot water supply in the region of 2-3 kW.
Of course, if you install a standard 100 liter 24 kW boiler, then for quick heating it can take on all 20 kW.
But in the case of using only 3 kW of reserve, it will also heat the water. Only it will take about 4 times longer to do this.
Although, with a reserve of 3 kW, water in the BKN of 100 liters is heated to +55 degrees Celsius in just 40-50 minutes.
System installation
First of all, we need to install sectional radiators. They must be placed strictly under the windows; warm air from the radiator will prevent the penetration of cold air from the window. To install sectional radiators, you do not need any special equipment, just a hammer drill and a building level. It is necessary to strictly adhere to one rule: all radiators in the house must be mounted strictly on the same horizontal level; the overall circulation of water in the system depends on this parameter. Also ensure that the radiator fins are vertical.
After installing the radiators, you can begin laying pipes. It is necessary to measure the total length of the pipes in advance, and also count the number of various fittings (elbows, tees, plugs, etc.). To install plastic pipes you will need only three tools - a tape measure, pipe scissors and a soldering iron. Most of these pipes and fittings have laser perforations in the form of notches and guide lines, which makes it possible to carry out installation correctly and evenly on site. When working with a soldering iron, you should adhere to only one rule - after you have melted and joined the ends of the products, under no circumstances twist them if you did not manage to solder smoothly the first time, otherwise a leak may occur in this place. It’s better to practice in advance on pieces that will go to waste.
Reserve for severe frosts
When thinking about which gas boiler to choose for heating a house of 200 square meters, you should not forget about the climatic features of your area.
How cold is the weather in winter? How strong do the winds blow in winter?
This is surprising, but the heat loss from your home at -10C with wind may be greater than in calm weather and -20C.
How many kilowatts should be put into reserve “just in case” - taking into account extremely low temperatures and strong winds? It depends on the characteristics of your place of residence.
The standard “reserve” is approximately 20 percent of the required minimum power of the heat generator. If our minimum power is 20 kW, then the reserve will be 4 kW.
So, we end up with a minimum required power of 20 kW, a DHW reserve of 3 or 6 kW (depending on the DHW scheme) and a cold reserve of 4 kW. The final power is around 27-29 kW.
Radiator calculations
In our case, we will use standard aluminum radiators with a height of 0.6 m. The power of each fin of such a radiator at a temperature of 70 ° C is 150 W. Next, we will calculate the power of each radiator and the number of conventional fins:
- room 1: 28 m3 · 40 W · 1.2 = 1344 W. We round up to 1500 and get 10 conventional fins, but since we have two radiators, both under the windows, we will take one with 6 fins, the second with 4.
- room 2: 28 m3 · 40 W · 1.2 = 1344 W. We round up to 1500 and get one radiator with 10 fins.
- room 3: 56 m3 · 40 W · 1.2 = 2688 W We round up to 2700 and get three radiators: 1st and 2nd with 5 fins each, 3rd (side) with 8 fins.
- hallway: 22.4 m3 · 40 W · 1.2 = 1075.2 W. We round up to 1200 and get two radiators with 4 fins each.
- bathroom: 11.2 m3 · 45 W · 1.2 = 600 W. Here the temperature should be a little higher, you get 1 radiator with 4 fins.
- toilet: 8.4 m3 · 40 W · 1.2 = 403.2 W. Round up to 450 and get three edges.
- kitchen: 43.4 m3 · 40 W · 1.2 = 2083.2 W. We round up to 2100 and get two radiators with 7 fins each.
As a final result, we see that we need 12 radiators with a total capacity:
- 900 + 600 + 1500 + 750 + 750 + 1200 + 600 + 600 + 600 + 450 + 1050 + 1050 = 10.05 kW
Based on the latest calculations, it is clear that our individual heating system can cope with the load placed on it without any problems.
Number of heating circuits
The issue of hot water supply in the house must be resolved at the stage of arranging the heating system. You have two options:
- Single-circuit boiler. Equipment of this type heats the coolant only for heating residential premises. To provide your family with hot water, you need to connect an indirect boiler and two pumps to the heat generator. The coolant will be directed from the heating system to the boiler, where it can heat water for domestic purposes. Double-circuit boiler. Such equipment has a separate unit for heating water, which will be supplied to the taps in the kitchen and bathroom. Thanks to this system, you do not have to purchase a separate boiler and install equipment for hot water supply.
It would seem that the choice is in favor of a double-circuit boiler for a house of 200 square meters. meters is obvious. Firstly, it will save you from the need to purchase additional expensive equipment for hot water supply. Secondly, such a system takes up much less space than a combination of a single-circuit boiler and an indirect heating boiler.
However, not everything is so simple. It is important to understand that heating coolant and hot water for domestic use requires a lot of power and high fuel consumption. Moreover, the longer the heating line inside the house, the less economical the heating equipment will be. In small cottages, the coolant circulates relatively quickly through a closed system and does not have time to cool down.
In houses with an area of 200 sq. meters, it is advisable to use a single-circuit boiler with an additional boiler of 200-250 liters - this option is considered to be the most economical and practical.
VALTEC CO 3.8. Heating system design software
VALTEC CO is a calculation and graphic program for designing radiator and underfloor heating systems using VALTEC equipment, developed by SANKOM Sp. z oo based on the latest version of the Audytor CO program – 3.8. The product allows you to design and regulate heating systems, and perform a full range of hydraulic and thermal calculations. The program is certified for compliance with the current construction standards of the Russian Federation and the requirements of the Voluntary Certification System of NP "ABOK" (
).
Installation method
When choosing a heating boiler for 200 sq. meters, pay special attention to the place where the equipment will be located:
- Wall-mounted models
are usually compact in size and light in weight. All key components of the heating system - expansion tank, pumps, pressure gauges, additional components, etc. - are already located inside the housing. Most often, wall-mounted boilers operate on gas and electricity. Such devices do not require a special boiler room - they take up minimal space and can be conveniently placed in any room of the house, for example, in the kitchen. - Floor-standing models
require more free space and are often installed in a separate boiler room. They are often distinguished by impressive dimensions and significant weight. All heating boilers operating on wood and coal are available only in a floor-standing version. High-power models are also most often installed on the floor.
Boiler for a house 100 sq. m
A standard house with an area of 100 m² without enhanced thermal insulation measures requires a boiler with a power in the range of 10-12 kW. It is important to understand that the operating time of a heat generator on one fuel load will depend not so much on its performance as on the type of design. At the moment, there are three types of boilers, which are most often installed in small private houses. The first is standard direct combustion boilers, which are capable of maintaining continuous combustion for no more than 6 hours. Their advantage is that the cost of the heat generator itself is low, but the imperfection of the design has a number of disadvantages.
Classic solid fuel direct combustion boilers have to be filled with fuel 4-5 times a day in the cold season. This is a rather labor-intensive task that not all family members are always ready to do. Often this situation becomes the reason that the owner of the house has to be constantly on the spot. If you miss the moment when all the fuel in the boiler burns out and do not update the loading chamber in time, then the temperature in the house will inevitably fall below comfortable values.
The optimal model in this case is a long-burning bottom layer boiler. Firstly, such a heat generator can continuously operate on one load several times longer, and secondly, its efficiency is much higher, which has a positive effect on fuel consumption. And thirdly, given the peculiarity of the boiler’s operation, adding fuel to it is extremely simple. Combustion occurs only in a limited space at the bottom of the loading chamber, which allows the fuel supply door to be freely opened during operation.
In Ukraine, at the moment, the most technologically advanced model is the Thermiko long-burning mine boiler. It takes into account all the shortcomings of similar designs that were released at various times over the past decades. By eliminating the main shortcomings of similar devices, Termico engineers managed to produce a heat generator with very high performance. An efficiency of 90% guarantees minimal fuel consumption, and, as a result, significantly reduces the budget for the heating season in the cold season. Since the recommended boiler power for a home is 100 sq. m is 10-12 kW, then the best choice would be the Termico KDG 12 kW mine boiler.
If your budget allows, you can also pay attention to the Termico EKO-12P pyrolysis boiler. This model has an even higher efficiency and guarantees the maximum possible savings in wood or coal. The process of burning pyrolysis gases allows you to extract maximum heat from processing a certain volume of fuel. Unlike coal-fired gas generators in mines, in which pyrolysis combustion is used only partially, in Thermico pyrolysis boilers the entire volume of heat is obtained entirely in the process of combustion of pyrolysis gases. This boiler is for a house of 100 sq. m in power should be no more than 12 kW to avoid overheating of the heating circuit.
Boiler for a house 150 sq. m
Among the three main types of solid fuel boilers, long-term bottom burning mine boilers have the optimal price-performance ratio. It is the heat generator of this model that you should first pay attention to if you do not want to go to the boiler loading chamber 4-5 times a day to replenish it. The optimal power of a mine solid fuel boiler for a house is 150 sq. m will lie between 14 and 16 kW. The average power of the heat generator, depending on the area of the building, is taken at the rate of 1 kW per 10 m². Based on this standard, 14 kW can only be installed in a house with very good thermal insulation, located not in the coldest regions of the country. A more rational choice would be a 16-kilowatt boiler from a good src=”https://ProUteplenie.com/images/wp-content/uploads/2017/05/p-bn-pa.png” class=”aligncenter” width=”360 ″ height=”350″[/img]
Among all the long-burning solid fuel boilers on the Ukrainian market today, we recommend paying attention to the Termico KDG 16 kW mine boiler. A special separate air supply system, combined with an extremely reliable design made from high-quality materials, makes this device a leader in its price segment. The introduction of a number of engineering solutions resulted in the high efficiency of this heat generator, which, according to numerous reviews from users of the device, can significantly reduce fuel consumption.