Today, few people doubt that a heat pump for heating a home is the most effective means of all existing ones. It is also the most expensive and difficult to implement. For this reason, many home craftsmen have taken to solving this problem on their own. But due to its high complexity, achieving positive results is very difficult; you need to have enthusiasm, patience and, in addition, study the theory well. Our article is for those who are taking the first step towards introducing such an alternative energy source as a homemade heat pump into their home.
Instructions for assembling a pump from an old refrigerator
Before you start assembling the unit, decide on its type and operation scheme. On the drawing, indicate the exact dimensions of the device, the distances between the elements and the connection points of the nodes.
The second step in assembling the pump is to remove the compressor from the old refrigerator, which will pump water and refrigerant through the pipeline. The main element of the heating system must be in good working order. If it was previously repaired, then it is unknown whether the assembled equipment will work.
To assemble and install the heat pump, purchase the following parts:
- sealed stainless steel container with a volume of at least 120 l;
- copper pipes of various diameters (3 pcs.);
- plastic tank, volume – 90 l;
- metal-plastic pipes;
- L-shaped brackets (length – 30 cm). With their help, the compressor is attached to the wall.
Next, assemble the condenser, which is located at the back of the refrigerator:
- cut the steel container in half with a grinder;
- place a coil in one part;
- Using a welding machine, weld the container. A durable frame will allow you to retain heat well and withstand high temperatures;
- In order for the condenser to act as a heat exchanger, wind a copper tube around the tank and secure its ends with slats.
The plastic tank will serve as an evaporator. Also install a coil on it and attach it to the wall with brackets.
After preparing the main components, select a thermostatic valve. Remove it from the same device as the capacitor, or buy a similar one. This will make it easy to combine system elements with each other.
Fasten all pump elements together and connect the heat exchanger to the system with PVC pipes.
From tubes with a rarefied medium
This method of heating liquid can be used not only in summer, but also in winter; it is one of the most complex. The installation location of the device made of vacuum tubes should not be shady, directed to the south. Overheating is not allowed, fluid circulation should be from top to bottom.
You will need the following tools:
- Adjustable wrench.
- Screwdrivers.
- Device for welding plastic pipes.
- Drill.
First, build a frame and place it in the intended installation location, the best option is the roof, then secure it, for example, with anchor bolts. Then connect the temperature sensor and air vent. Connect the water line using materials that are resistant to freezing temperatures.
Let's start installing the heating element, take a copper pipe and wrap it with sheet aluminum, insert it into the glass vacuum pipe. Place a fixing cup and a rubber boot on the bottom of the tube. Secure the metal end into the brass condenser (you may see sticky grease on the tube, do not wipe it off).
Close the fixing bowl and install the remaining elements in a similar manner. Install the mounting block and supply 220V electricity to it. Connect a temperature sensor and an air vent to it, although they are moisture-resistant, it is better to install a protective screen for them, then we connect the controller, with its help the operation of the system is monitored, and that’s the whole process of installing a solar boiler with your own hands. Program the system to the required parameters and start.
DIY manufacturing algorithm
Rules for manufacturing the unit:
- Decide on the source from which the heating circuit will operate. In areas with a harsh climate, it is recommended to use sources located underground; in regions with a warm climate, energy can be obtained from the air.
- Calculate the power of the unit. It depends on the quality of insulation of the house. If the building is not sheathed with insulation, then the recommended power of the device is 70 W/m2. Only such a unit will create a comfortable microclimate inside the building. For houses insulated with modern materials, a power of 45 W/m2 is suitable. A building insulated using a special technology does not use a powerful unit. It is recommended to use a power of 25 W/m2. If the power is increased, the temperature inside the room will be too high.
- Prepare basic and additional equipment.
- Install the components and assemble the system. After that, connect it to the source.
Also useful for repairs:
- Foam sphere houses
- Samsung TV does not turn on, indicator light is red
- Idle air control device
Bivalent heating scheme ↑
Using such a scheme will help save money at the stage of manufacturing and installation of the pump. The fact is that the heat pump power is calculated based on the minimum possible temperature. But the peak low temperatures outside only last for a very short time, which means that for most of the year the heat pump will use only part of its power potential.
In order to be able to install a less powerful pump, an additional heat source is connected in parallel with it - an electric boiler. Then, in severe frosts, you can additionally “heat” the room. Considering that there are few such days a year, such heating will not hit your wallet hard, and you can save significantly on the cost of the pump.
It is also possible to use a solid fuel boiler as additional equipment. In this case, a bypass must be included in the heating system.
Using an old refrigerator
Refrigerator heat pump device
So, to assemble a heating system in a country house, you need to have a heat pump.
Today, such units are not cheap, this is explained by high technical characteristics and painstaking work on their assembly. But, if you wish, you can assemble the heat pump yourself.
You can build a simple heat pump from a household refrigerator. The peculiarity of the technique is that it has two main components of a heat pump - a condenser and a compressor. This will significantly speed up the assembly of the heat pump with your own hands.
So, assembling a pump from an old refrigerator is as follows:
Capacitor assembly. The element is made in the form of a coil. In refrigerators it is most often installed at the back. This well-known grille is the condenser through which heat is transferred from the refrigerant. The capacitor is installed in a container that is highly durable and can withstand high temperatures. To avoid damaging the coil during installation, experts recommend cutting the container and installing a capacitor in it. After this, the container is welded. Next, a compressor is attached to the container. It is almost impossible to make a unit at home. Therefore, it is better to take it from an old refrigerator
At the same time, you should pay attention to ensure that it is in good condition. You can use a regular plastic barrel as an evaporator. After all elements of the system are ready, they are connected to each other. Plastic pipes are used to connect the unit to the heating system.
Thus, you can build a heat pump from an old household refrigerator. If you need to pump freon into the system, you need to call a specialist. This work can only be done with the help of special equipment.
The first channel will let air into the freezer, and the second will release it. In this case, physical processes occur that cause the capacitor to heat up.
You can read about Igor Savostyanov’s Henk System heat pumps here.
Refrigerator and its circuits
For reference. Household refrigerators are single-circuit and double-circuit. If there is only one cooling circuit, then it “serves” both the refrigerator and freezer compartments. Plus, each refrigerator is assigned from 0 to 4 snowflake stars. The more there are, the lower the temperature can be set in the freezer.
So, for models with single-circuit cooling and a 4-star freezer, the temperature is set depending on the refrigerator compartment. This is where the temperature sensor is located. And this compartment heats up much more slowly than the freezer.
To maintain the “cold weather” in the freezer at an optimal level, heating elements artificially increase the temperature in the refrigerator compartment. In this case, the sensor triggers the cooling process faster.
It turns out that you first need to heat something in order to freeze something else.
Manufacturing and installation
The pump is manufactured according to the following algorithm:
- the compressor is mounted on the wall;
- a coil is made from pipes (to make it, you need to wrap the pipes around a container of a suitable shape);
- the tank is cut in half, a coil is placed inside it and brewed;
- several holes are left in the container through which the coil pipes are led out;
- to make the evaporator, a plastic barrel is used, identical in size to the tank, and internal circuit pipes are inserted into it;
- PVC pipes (installation diagrams for warm water floors in the apartment) are installed, transporting heated water;
- It is not recommended to fill the unit with freon yourself; it is better to entrust this action to a specialist.
The cost of work in different regions of our country can vary dramatically. In addition, the cost of operation and the pump depend on its type and heating system.
- In St. Petersburg, installation of a heat pump, regardless of its type, will cost the Customer from 35,000.00 rubles;
- In Moscow, installation organizations, regardless of the type of heat pump, are ready to perform turnkey work for an amount over 45,000.00 rubles;
- In Krasnodar, installation of a heat pump will cost from 40,000.00 rubles.
- If we talk about the installation of heating systems using heat pumps, then the average prices for a set of works, taking into account the cost of equipment, are as follows:
READ MORE: Motoblock Patriot Ural TOP-3 rating of the best models of 2020, distinctive characteristics of the device, instruction manual and customer reviews
A) Installation of geothermal domestic heat pumps:
- Power – 4-5 kW (50 – 100 m²) – from 130,000.00 to 280,000.00 rubles;
- Power – 6-7 kW (80 – 120 m²) – from 138,000.00 to 300,000.00 rubles;
- Power – 8-9 kW (100 – 160 m²) – from 160,000.00 to 350,000.00 rubles;
- Power – 10-11 kW (130 – 200 m²) – from 170,000.00 to 400,000.00 rubles;
- Power – 12-13 kW (150 – 230 m²) – from 180,000.00 to 440,000.00 rubles;
- Power – 14-17 kW (180 – 300 m²) – from 210,000.00 to 520,000.00 rubles.
B) Installation cost of air source heat pumps:
- Power up to 6.0 kW (50 – 100 m²) – from 110,000.00 to 215,000.00 rubles;
- Power up to 9.0 kW (80 – 120 m²) – from 115,000.00 to 220,000.00 rubles;
- Power up to 12.0 kW (100 – 160 m²) – from 120,000.00 to 225,000.00 rubles;
- Power up to 14.0 kW (130 – 200 m²) – from 127,000.00 to 245,000.00 rubles;
- Power up to 16.0 kW (150 – 230 m²) – from 130,000.00 to 250,000.00 rubles;
- Power up to 18.0 kW (180 – 300 m²) – from 135,000.00 to 255,000.00 rubles.
How the device works
Those who have come into contact with issues of cost-effective heating are familiar with the name “heat pump”. Especially in combination with terms like “earth-water”, “water-water”, or “air-water”, etc.
Such a heat pump has practically nothing in common with the Frenette device. Apart from the name and the end result in the form of thermal energy, which is ultimately used for heating.
Heat pumps operating on the Carnot principle are very popular both as a cost-effective way to organize heating and as an environmentally friendly system.
The operation of such a complex of devices is associated with the accumulation of low-potential energy contained in natural resources (earth, water, air) and its conversion into thermal energy with high potential.
Eugene Frenette's invention is designed and works completely differently.
The heat-generating system developed by E. Frenette cannot be unconditionally classified as a heat pump. Based on its design and technological features, this is a heater. The unit does not use geo- or solar energy sources in its operation. The coolant oil located inside it is heated by the friction force created by the rotating metal disks. The working body of the pump is an oil-filled cylinder, inside of which the axis of rotation is located. This is a steel rod equipped with parallel disks installed approximately 6 cm apart. Centrifugal force pushes the heated coolant into the coil attached to the device. The heated oil leaves the device at the upper connection point. The cooled coolant returns back from below. Appearance of the Frenette heat pump. Heating of the device during operation. Main design components. Actual dimensions of one of the models.
The operating principle of this device is based on the use of thermal energy, which is released during friction. The design is based on metal surfaces located not close to each other, but at some distance. The space between them is filled with liquid.
Parts of the device rotate relative to each other using an electric motor, the liquid located inside the housing and in contact with the rotating elements heats up.
The resulting heat can be used to heat the coolant. Some sources recommend using this liquid directly for the heating system. Most often, a regular radiator is attached to a homemade Frenette pump.
Experts strongly recommend using oil rather than water as a heating fluid.
During operation of the pump, this liquid tends to heat up very strongly. Water in such conditions can simply boil. Hot steam in a confined space creates excess pressure, and this usually leads to rupture of pipes or housing. It is much safer to use oil in this situation, since its boiling point is much higher.
To make a Frenette heat pump you will need a motor, a radiator, some pipes, a steel butterfly valve, steel discs, a metal or plastic rod, a metal cylinder and a nut set (+)
There is an opinion that the efficiency of such a heat generator exceeds 100% and can even be 1000%. From the point of view of physics and mathematics, this is not an entirely correct statement.
Efficiency reflects the energy loss spent not on heating, but on the actual operation of the device. Rather, the phenomenal claims of the incredibly high efficiency of the Frenette pump reflect its efficiency, which is truly impressive. The energy consumption for operating the device is negligible, but the amount of heat generated as a result is very noticeable.
Heating the coolant to the same temperatures using a heating element for heating, for example, would require significantly more electricity, perhaps tens of times more. A household heater wouldn’t even heat up at this level of electricity consumption.
Why aren’t all residential and industrial premises equipped with such devices? The reasons may vary.
Firstly, water is a simpler and more convenient coolant than oil. It does not heat up to such high temperatures, and eliminating the consequences of water leaks is easier than cleaning up spilled oil.
Secondly, by the time the Frenette pump was invented, a centralized heating system already existed and was functioning successfully. Dismantling it to replace it with heat generators would have been too expensive and would have caused a lot of inconvenience, so no one seriously considered this option. As they say, the best is the enemy of the good.
Refrigerator pump
Heat pump from a refrigerator
The main part of the system is the compressor. It is better to buy it ready-made in the store or use what is available from the refrigerator or air conditioner. All other components - evaporator, condenser, pipeline - can be assembled yourself. Such a device will consume energy only for compression and heat transfer, while generating 5 times more.
Some craftsmen went further and made a heat pump from a refrigerator, placing radiators inside it, heated by the heat of the earth. A positive temperature is constantly maintained inside, which forces the refrigerator to constantly work, heating the radiator located behind it. Using a native radiator, they make a heat exchanger out of it (or make a homemade one), and take away the heat it generates.
The efficiency of such a heat pump is more suitable for demonstrating the operation of the device, since its efficiency is very low. In addition, the refrigerator is not designed for this operating mode and can quickly fail.
Features of device installation
When installing the unit, it is important to take into account the location of the external circuit, depending on which one or another type of installation is carried out. So:
- for air-water pumps, the external circuit with pipes is located on the wall or roof of the building, and the device itself is located indoors;
- if a geothermal pump is installed, then the unit can be positioned vertically (a well is dug up to 100 meters deep, where the probe is placed) or horizontally (pipes are laid parallel to each other in a trench or pit one and a half meters deep).
- When installing water-to-water pumps, the external circuit is located in a reservoir, at its bottom.
Self-installation of an alternative heating system for a private home using a heat pump, made by yourself, is a sure way to save money and provide yourself with comfortable conditions. Heat pumps can cope with heating a swimming pool and garage, a house and a greenhouse.
How to make a Frenette heat pump at home, watch the video.
Types of pumps
There are different types of heat pumps, but they are all based on the principle of producing heat or cold by separating thermal energy and transferring it. Only one TN Frenette is different. The cavitation method of obtaining thermal energy using a hydrodynamic generator is a type of heat pump.
The thermal energy that is used to heat the building is a consequence of energy conversion carried out using a heat pump. Moreover, they obtain heat without burning fuel, but by cooling the external environment and releasing thermal energy indoors, that is, in this case, the law of conservation of energy is observed: how much thermal energy is taken from the external environment, the same amount is released inside the building. Most of these household devices use heat from the sun, which is accumulated by the surface of the earth, water or air.
Therefore, according to the type of primary circuit, all structures can be divided into air, ground and water.
Based on the type of coolant (W - water, G - soil) in the circuits, pumps can be divided into eight types:
- B—B;
- G-V;
- G—air;
- air—B;
- air—air;
- To the air;
- refrigerant—B;
- refrigerant - air.
They can also use the heat of the exhaust air, heating the supply air, that is, operate in recovery mode.
Air-to-air
The principle of operation of a heat pump is similar to that used in an air conditioner in heating mode, but has the only difference. The heater is set to heating, and the air conditioner is set to reduce the temperature in the room.
The principle of operation of the B-B installation is as follows: the air, even at low temperatures, has a certain amount of energy. Only at absolute zero is there no thermal energy. Most HPs are capable of receiving heat at a temperature of –15 °C. Currently, some manufacturers produce stations that retain heat extraction at –30 °C. Heat is collected through the evaporation of freon, which circulates through the internal circuit. For this purpose, an evaporator is used in which the refrigerant is converted from liquid to gaseous state. This absorbs heat.
The next block, which is located in the B-V heating system, is the compressor, which converts freon from a gaseous state into a liquid. This generates heat. The efficiency of the V-V installation directly depends on the ambient temperature. The lower it is, the lower the station’s productivity.
Air-water
Air-to-water HP is the most universal model. It is very effective in the warm season, but in the cold season the performance drops significantly. Simple installation is an advantage of the system. Suitable equipment can be installed anywhere. The heat that is removed from the room in the form of gas or smoke can be reused.
A water heat pump takes heat from groundwater, which is pumped through the evaporator. Such a pump is distinguished by good efficiency and increased stability: efficiency is the result of significant heat transfer from water.
Of course, to use an installation of this type, there must be sufficient groundwater in the area. It is advisable that the water is no deeper than 30 meters.
Water-water
With such a system, an easily evaporating liquid, such as freon, circulates in the internal circuit. The indoor circuit can be water pipes, registers or radiators filled with water.
Any body of water with a sufficiently large amount of water can act as an external contour. This could be a river, lake or pond. In this case, the coolant takes heat from the external circuit and transfers it to the internal circuit.
Geothermal
The HP uses the stored thermal energy of the earth as a heat source. Such pumps are considered the most efficient because the ground temperature remains constant throughout the year.
These systems are divided into horizontal and vertical. But this method requires a fairly large area for horizontal pipes, and for vertical systems it is necessary to perform significant excavation work.
Prices for different types of heat pumps
Heat pump
What is geothermal heating?
This is heat extracted from the earth or water. At certain depths of the soil, a constant positive temperature is maintained, and there are no differences even in severe frosts, the same with water. A person’s task is to take heat from the earth or water, sending it to ensure comfort in living rooms.
Geothermal heating is like a regular refrigerator, but in reverse - the system produces heat, not cold. The pump algorithm is built on the transfer of heat from a source with a small potential of thermal energy to the coolant, and soil or water act as active heat sources.
Advantages and disadvantages of the system
Geothermal heating has several advantages:
- The release of thermal energy is many times higher than the cost of electricity consumed by the pump.
- Environmental cleanliness and safety. The system does not emit harmful substances, there are no emissions or slag after fuel combustion.
- There is no need to purchase fuel or gas; the entire structure is built without the use of chemicals or other substances, so heating with earth or water heat is considered the safest.
- If the installation and operation technology is followed, the equipment and the entire heating system will last without technical support for at least 50 years.
- The heat pump operates silently, there are no acoustic effects.
Maximum economic benefit is achieved without additional investments. The user needs to purchase all the equipment once, configure the design and no longer have to interfere with the operation of the system. An additional advantage is the location of all elements outside the building - heating from earth or water does not require the placement of large installations in the house, so the method of extracting and supplying heat is suitable for houses of any size.
The disadvantage is the large amount of one-time costs for purchasing equipment, installing and putting the system into operation. To form the structure, a pump, a certain amount of materials, installation of an external manifold and an internal circuit are required.
How to make a unit from a refrigerator
A refrigerator is one of the most suitable units for creating a heat pump. This is explained by the fact that the device comes with a compressor.
Preparation of diagrams and drawings
Before starting to build the device, choose the location of the source. Then a well or trench is dug to install the pipes.
The design of the unit is the same for any heat source. The device circuit is ordered from a professional or chosen on the Internet. A drawing is made on its basis. It indicates all distances, node points and dimensions.
Selection of necessary parts
The main part that ensures the operation of the structure is the compressor. If it fails in the refrigerator, a new device is purchased. Such devices are sold by specialists specializing in refrigerator repair. Repairing an old compressor is not recommended.
In addition to the compressor, prepare:
- thermal control valve;
- L-shaped brackets, 30 cm in size;
- a sealed container made of stainless steel with a volume of at least 120 liters;
- plastic container, volume 90 liters;
- copper pipes of different diameters in the amount of 3 pieces;
- several metal-plastic pipes;
- grinder for cutting materials;
- welding machine for connecting pipes;
- standard set of tools.
Installation of system components
- Use a grinder to cut the metal tank into two equal parts.
- Make a coil from a copper pipe. To do this, screw the pipe onto the cylindrical formwork in a spiral, without applying much effort, and remove it.
- Securely fix the coil in one of the tank halves.
- Weld the parts of the metal tank to each other and make threaded holes in the tank.
- Wind a copper pipe onto a steel tank with a volume of 120 liters and secure the ends with slats.
- Connect plumbing transitions to the terminals.
- Wind a coil onto a plastic tank and secure the ends with slats.
- Hang the plastic tank, which serves as an evaporator in the heating system, on the wall using brackets.
After this, assemble the system according to the prepared diagram and pour freon inside. It is recommended to approach the choice of fluid responsibly, otherwise big problems will arise when filling it and during operation of the system. Experts advise using the composition of the brand R 422 or R 22.
Connection to the intake device
When the system is ready, it is connected to the intake device:
- For devices operating on the “water-soil” principle, the collector is immersed in the ground, where the temperature is above +1 °C. Pipes are installed at the same level.
- For devices operating on the water-to-water principle, the collector and pipes are immersed in the center of the heat source.
- Air powered units are installed outside the building.
Design
The industry produces models with different performance characteristics, but they include equipment that performs the typical tasks described above.
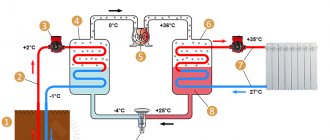
As a design option, the figure shows a heat pump for heating a house.
Here, heat from geothermal sources is received through input pipelines, and on weekends it is transferred to the home heating system.
The operation of the heat pump is ensured by:
- system for monitoring circuit parameters and control, including remote methods via the Internet;
- additional equipment (washing and filling units, expansion tanks, safety groups, pumping stations).
Ground structures
They use three heat exchanger designs to take energy from the source:
- superficial location;
- installation of vertical ground probes;
- deepening of horizontal structures.
The first method is the least effective. Therefore, it is rarely used for heating a home.
Installation of probes in wells
This method is the most effective. It provides for the creation of wells to depths of about 50÷150 meters or more to accommodate a U-shaped pipeline made of plastic materials with a diameter of 25 to 40 mm.
Increasing the cross-sectional area of the pipe, as well as deepening the well, creates improved heat removal, but increases the cost of the structure.
Horizontal collectors
Drilling probe holes is expensive. Therefore, this method is often chosen as it is cheaper. It allows you to get by with digging trenches below the soil freezing depth.
When designing a horizontal collector, the following should be taken into account:
- thermal conductivity of soil;
- average soil moisture;
- geometry of the site.
They affect the dimensions and configuration of the collector. Pipes can be laid:
- loops;
- zigzags;
- snake;
- flat geometric shapes;
- helical spirals.
It is important to understand that the area of the site allocated for such a collector usually exceeds the dimensions of the foundation of the house by 2–3 times. This is the main disadvantage of this method
Water collectors
This is the most economical method, but it requires the location of a deep reservoir near the building. The assembled pipelines are placed and secured with weights at its bottom. For efficient operation of the heat pump, it is necessary to calculate the minimum depth of the collector and the volume of the reservoir capable of providing heat removal.
The dimensions of such a structure are determined by thermal calculations and can reach a length of more than 300 meters.
The picture below shows the preparation of lines for assembly on the ice of a spring lake. It allows you to visually assess the scale of the work ahead.
Air method
An external or built-in fan blows air from the street directly onto the evaporator with freon, like in an air conditioner. In this case, there is no need to create bulky structures from pipes and place them in the ground or reservoir.
A heat pump for heating a house operating on this principle is cheaper, but it is recommended to use it in a relatively warm climate: frosty air will not allow the system to work.
Such devices are widely used for heating water in swimming pools or rooms located next to industrial devices that are constantly involved in the technological process and release heat into the atmosphere with powerful cooling systems. Examples include power autotransformers, diesel stations, and boiler houses.
Operating principle of heat pumps
The operating principle of a device for heating a house is based on the fact that a substance (refrigerant) can give off thermal energy or take it away during a change of state. This idea is the basis for the functioning of the refrigerator (because of this, the back wall of the device is hot).
Thermal pump for heating functions as follows:
- The incoming agent is cooled by 5 degrees in the evaporation section based on the energy from the coolant.
- The cooled agent enters the compressor, which, as a result of operation, compresses and heats it.
- The already hot gas enters the heat exchange compartment, in which it transfers its own heat to the heating system.
- The condensed refrigerant is returned to the start of the cycle.
Device
A heat pump for heating a house consists of several main circuit elements:
- a coolant circuit that transfers energy from the heat source;
- a circuit with freon, which periodically evaporates, taking thermal energy from the first circuit, and again settles as condensate, transferring heat to the third;
- a circuit where a liquid circulates, carrying heat for heating.
Operating a thermopump for heating a home is profitable from a financial point of view. The reason for this is that the device does not require high power (accordingly, the electricity consumption is no more than that of a standard household appliance), but it produces 4 times more heat compared to the electricity consumed.
There is also no need to create a separate wiring line to connect the pump.
Advantages and disadvantages
Before deciding whether to use a heat pump or not, you should familiarize yourself with the advantages and disadvantages of its operation. The main advantages of a heat pump include:
- low electricity consumption for heating the house;
- no need for regular inspection and maintenance, which makes the cost of operating a heat pump for heating minimal;
- Installation in any location is allowed. The pump can work with thermal energy sources such as air, soil and water. Therefore, it becomes possible to install it almost anywhere where it is planned to build a house. And in conditions of remoteness from the gas main, the device is the most suitable heating method. Even if there is no electricity, the compressor can operate using a gasoline or diesel drive;
- The house is heated automatically. There is no need to add fuel or carry out other manipulations, as, for example, in the case of boiler equipment;
- absence of environmental pollution with harmful gases and substances. All refrigerants used are completely safe and environmentally friendly;
- fire safety. Home occupants will never be at risk of explosion or damage due to heat pump overheating;
- possibility of operation even in cold winter conditions (down to -15 degrees);
- A quality heat pump for heating a home can last up to 50 years. Compressor replacement is required only once every 20 years.
Watch the video pros and cons
Like any device, heat pumps have certain disadvantages:
- If the ambient temperature drops below 15 degrees, the pump will not be able to operate. In this case, installation of a second heat source will be required. At very low temperatures, the boiler, generator or electric heater turns on;
- High cost of equipment. It will cost approximately 350,000-700,000 rubles, and the same amount will have to be spent on creating a geothermal station and installing the device. Additional installation work is not required only for a heat pump using air as a heat source;
- It is best to install a heat pump in combination with heated floors or fan convectors, however, in old buildings, redevelopment and possibly even major repairs will be required, which will entail additional time and money. If a private house is built from scratch, there is no such problem;
- When the heat pump operates, the temperature of the soil located around the coolant pipeline decreases. This causes the death of some microorganisms involved in the functioning of the environment. Thus, some damage to the environment is still caused, but it is significantly less than the damage from gas or oil production.
Primary circuits and system functionality
To operate the heat pump, a source of thermal energy is required, which can be any medium, provided that in winter its temperature stably exceeds +1°C. Thus, it is practiced to install units that receive thermal energy from water, air and earth (from soil or deep rocks).
Water
Any natural or artificial reservoir is suitable for laying the primary circuit, provided that it does not freeze to the bottom. The length of the pipeline submerged to the bottom is determined when calculating the power of the heat pump - one meter of pipeline mounted with a snake or rings allows you to obtain up to 30 W of thermal energy. That is, a heat pump with a pipeline 500 meters long is capable of heating a house whose heat demand is 15 kW.
Horizontal pipeline circuit laid with rings
The principle of operation of a water-to-water heat pump is that the resulting heat is used to heat the coolant liquid in a radiator heating system or a heated floor circuit. The functionality of a water-to-water heat pump is sufficient to provide stable underfloor heating, as it allows you to maintain the coolant temperature at 45-60 degrees. For full-fledged radiator heating with such a temperature regime, the house needs to be seriously insulated.
Air
For a water-to-water heat pump, the conversion coefficient is on average 1.5-2.2. While an air-to-air or air-to-water heat pump exceeds this figure approximately twice - the conversion factor is more than 4.
Air-to-air heat pumps are widely used because they do not require the installation of large circuits. Any inverter air conditioner or split systems that heat a room are essentially heat pumps with low efficiency.
Operating principle of an air source heat pump
An air heat pump has a significant drawback - in frosty weather it has nowhere to get heat. Some models of units are designed to operate at -20°C, in other cases the limit does not fall below -10°C.
In addition to air-to-air units, there is an air-to-water heat pump. Its difference is that the resulting thermal energy does not heat the air in the room, but the coolant in the heating circuit.
The operating principle of an air-to-water heat pump is standard. In this case, the evaporator, additionally equipped with a fan, is installed outside the house, and the compressor and condenser are installed inside. By connecting a water circuit to the heat exchanger, you can arrange underfloor heating of the room.
Earth
The most stable natural source of heat is rocks at a depth of over 20 meters, as they are constantly heated by heat from the earth's core. But to install a U-shaped pipe circuit, you have to drill deep wells, which affects the installation price. Geothermal installations are effective, but they pay for themselves only after 10-15 years of operation, provided that the house is properly insulated.
Heat pump "Earth-Water"
A cheaper installation option involves laying the circuit half a meter below the ground freezing level. Laying pattern - snake or circles. Installation of such a system requires a large amount of excavation work, in addition, the external circuit may be damaged during operation.
Features of heat pumps
To obtain thermal energy, HP does not use energy carriers, and therefore does not harm the environment. Such an installation produces more thermal energy than it consumes electricity.
Principle of operation
The operation of HP is based on the principle of heat transfer from a colder source to a warmer one. That is, it makes colder things even colder, and warmer things even warmer. This means that the idea of a perpetual motion machine is not incorporated here, because in total the amount of heat remains unchanged, and electricity is spent only on the separation and transfer of heat.
Results
Undoubtedly, the cost of a heat pump from an air conditioner is several times lower than ready-made factory options, even those made in China. But there are a lot of nuances here: you need to take care of the source and amount of heat supplied, correctly calculate the length of the heat exchangers (coils), install automation, ensure guaranteed power, etc. But if you are able to solve these problems, then it is undoubtedly beneficial. Let us give you some advice: in the first year it is very advisable to have backup heating, and it is better to carry out tests and trial runs in the summer, so that there is time to finalize the unit before the start of the heating season.
Types of heat exchangers
In the designation of the type of heat exchanger of a heat pump, the first indicator determines the method of constructing the external circuit of the heat supply system, and the second - the design of the internal circuit.
"Water - water"
In heat exchangers of this type, heat is taken from water bodies (well, river, lake, etc.), solar energy or other objects. A coolant—water or another liquid—circulates in the primary circuit. Circulation is carried out by creating pressure through the installation of a pump.
The circuit can be closed or open; which option to choose is determined by the type of coolant. In the heat pump, in the internal circuit, freon circulates, which, receiving energy from the external circuit, evaporates, enters the condenser, where it transfers the resulting heat to the consumer’s coolant.
"Water - air"
In heat exchangers of this type, the energy collected in the external circuit, in which liquid (water or other energy carrier) circulates, enters the heat exchangers of the heat pump, where it is transferred to the indoor air.
"Air - air"
In this type of heat exchanger, the external circuit is located on the outside of the building; it is the evaporator in this pump design. The heat from the outside air heats the refrigerant, which evaporates. Then, passing through the compressor, it is compressed and supplied to the indoor unit - a condenser, which is located inside the building. The condenser gives off heat to the air inside the room in which it is located, and the refrigerant is again supplied to the evaporator.
"Air - water"
In this type of heat exchanger, thermal energy is taken from the outside air. The air enters the compressor, where its temperature rises under the influence of pressure, after which it enters the heat exchanger. In the heat exchanger, the supplied air is condensed and energy is transferred to the energy carrier of the consumer’s heating system.
"Earth - Water"
Heat exchangers of this type are based on receiving energy from the earth and transferring it to consumers. Brine (antifreeze) circulates in a closed external circuit located below the freezing level. Circulation is carried out by installing a pump. The brine enters the heat pump's condenser, where it transfers the resulting energy to the refrigerant, which in turn transfers it to the consumer's heating system by condensation in the pump's heat exchanger.
"Earth - Air"
In heat exchangers of this type, the thermal energy obtained by the brine circulating in the external circuit, which is located under the surface of the earth, is transferred in the heat exchanger chambers to the air inside the room.
Application
A self-assembled heat pump is suitable for the following cases:
- if you want to save on fuel to heat your home;
- if it is impossible to supply gas to the house or it is too troublesome, then buying bottled gas is not a solution to the situation;
- there is no desire or ability to heat with coal, wood, electricity, or other fuel;
- if the owner of the house is a supporter of the use of environmentally friendly alternative energy. The device is quite practical even if it has the ability to use other energy sources.
A do-it-yourself heat pump is made for the home, based on technologies for collecting heat from the ground, water, and air. It is used for heating, water heating and even indoor air conditioning.
Characteristics
Most thrifty owners want to save money on heating and water supply for a private home. A heat pump is suitable for such purposes.
It is quite possible to build it yourself, while saving a lot of money - a factory-made device is very expensive.
Properties and device
The device has an external and internal circuit along which the coolant moves. Components of a standard device: a heat pump, a device for intake and a device for heat distribution. The circuit from the inside consists of a mains-powered compressor, an evaporator, a throttle valve, and a condenser. The device also uses fans, a pipe system, and geothermal probes.
Advantages of the heat pump:
- does not emit any harmful substances, absolutely environmentally friendly;
- there are no costs for the purchase and delivery of fuel (electricity is spent only on moving freon);
- no need for additional communications;
- absolutely fire- and explosion-proof;
- full heating in winter and air conditioning in summer;
- A self-built heat pump is an autonomous design that requires minimal control effort.
Operating principle of an air-water pump
As already mentioned, the main source of thermal energy for installations of this type is atmospheric air. The fundamental basis for the operation of air pumps is the physical property of liquids to absorb and release heat during a phase transition from a liquid to a gaseous state, and vice versa. As a result of the change in state, temperature is released. The system works like a refrigerator in reverse.
To effectively use these properties of the liquid, a low-boiling refrigerant (freon, freon) circulates in a closed circuit, the design of which includes:
- electric compressor;
- fan-driven evaporator;
- throttle (expansion) valve;
- plate heat exchanger;
- copper or metal-plastic circulation tubes connecting the main elements of the circuit.
The movement of the refrigerant along the circuit is carried out due to the pressure developed by the compressor. To reduce heat losses, pipes are covered with a heat-insulating layer of artificial rubber or foamed polyethylene with a protective metallized coating. Freon or freon is used as a refrigerant, which can boil at subzero temperatures and does not freeze down to -40°C.
The entire work process consists of the following sequential cycles:
- The evaporator core contains liquid refrigerant whose temperature is lower than that of the outside air. During active blowing of the radiator, thermal energy from low-potential air is transferred to the freon, which boils and turns into a gaseous state. At the same time, its temperature rises.
- The heated gas enters the compressor, where it heats up even more during the compression process.
- In a compressed and heated state, the refrigerant vapor is supplied to a plate heat exchanger, where the heating system coolant circulates through the second circuit. Since the coolant temperature is significantly lower than that of the heated gas, freon actively condenses on the heat exchanger plates, releasing heat into the heating system.
- The cooled vapor-liquid mixture enters the throttle valve, which allows only cooled, low-pressure liquid refrigerant to pass to the evaporator. After which the whole cycle repeats.
To increase the heat transfer efficiency of the tube, spiral fins are wound onto the evaporator. Calculation of the heating system, selection of circulation pumps and other equipment must take into account the hydraulic resistance and heat transfer coefficient of the installation's plate heat exchanger.
Video overview of the system design and its operation
Inverter heat pumps
The presence of an inverter as part of the installation allows for a smooth start-up of the equipment and automatic control of modes depending on the outside temperature. This allows you to maximize the efficiency of the heat pump by:
- achieving efficiency at the level of 95-98%;
- reducing energy consumption by 20-25%;
- minimizing loads on the electrical network;
- increasing the service life of the installation.
As a result, the indoor temperature is stably maintained at the same level, regardless of weather changes. At the same time, the presence of an inverter complete with an automated control unit will provide not only winter heating, but also the supply of cooled air in summer when the weather is hot.
At the same time, it should be taken into account that the presence of additional equipment always entails an increase in its cost and an increase in the payback period.
Advantages and disadvantages
The advantages of using a heat pump include:
- Possibility of use in remote villages where there is no gas pipeline.
- Economical consumption of electricity only for the operation of the pump itself. Costs are significantly lower than when using electrical appliances for space heating. A heat pump consumes no more energy than a household refrigerator.
- Ability to use a diesel generator and solar panels as an energy source. That is, in the event of an emergency power outage, the heating of the house will not stop.
- The system is self-contained and does not require adding water or monitoring its operation.
- Environmentally friendly installation. During operation of the pump, no gases are generated and there are no emissions into the atmosphere.
- Work safety. The system does not overheat.
- Versatility. You can install a heat pump that operates for heating and cooling.
- Durability of use. The compressor requires replacement once every 15–20 years.
- Releasing the premises that were intended for the boiler room. In addition, there is no need to purchase and store solid fuel.
Disadvantages of heat pumps:
- Installation is expensive, although it pays for itself within five years;
- In the northern regions, the use of additional heating devices will be required;
- The ground installation, although slightly, disturbs the ecosystem of the site: it will not be possible to use the territory for a garden or vegetable garden, it will be empty.
Manufacturing of geothermal installation
It is quite possible to make a geothermal installation with your own hands. In this case, the thermal energy of the earth is used to heat the home. Of course, this is a labor-intensive process, but the benefits are significant.
Calculation of the pump circuit and heat exchangers
The circuit area for HP is calculated at the rate of 30 m² per kilowatt. A living space of 100 m² requires about 8 kilowatt/hour of energy. This means the contour area will be 240 m².
The heat exchanger can be made from a copper tube. Inlet temperature 60 degrees, outlet 30 degrees, thermal power 8 kilowatt/hour. The heat exchange area should be 1.1 m². Copper tube with a diameter of 10 millimeters, safety factor 1.2.
Circumference in meters: l = 10 × 3.14 / 1000 = 0.0314 m.
Quantity of copper tube in meters: L = 1.1 × 1.2 / 0.0314 = 42 m.
Necessary equipment and materials
In many ways, success in the manufacture of heat pumps depends on the level of preparedness and knowledge of the contractor himself, as well as on the availability and quality of everything necessary for installing a heat pump.
Before starting work, you need to purchase equipment and materials:
- compressor;
- capacitor;
- controller;
- polyethylene fittings intended for assembling manifolds;
- pipe to the earth circuit;
- circulation pumps;
- water hose or HDPE pipe;
- pressure gauges, thermometers;
- copper tube with a diameter of 10 millimeters;
- insulation for pipelines;
- set of seals for sealing.
How to assemble a heat exchange block
The heat exchange block consists of two components. The evaporator must be assembled according to the “pipe-in-pipe” principle. The inner copper tube is filled with freon or other rapidly boiling liquid. Water from the well circulates through the outside.
Construction of the soil contour
In order to prepare the required area for the soil contour, a large amount of excavation work is required, which should preferably be carried out mechanized.
You can use 2 methods:
- With the first method, it is necessary to remove the top layer of soil to a depth below its freezing. At the bottom of the resulting pit, lay the free part of the outer pipe of the evaporator in a snake and reclaim the soil.
- In the second method, you first need to dig a trench across the entire planned area. The pipe is laid in it.
Then you need to check the tightness of all connections and fill the pipe with water. If there are no leaks, you can fill the structure with earth.
Refueling and first start
After installation is completed, the system must be filled with refrigerant. It is best to entrust this work to a specialist, because special devices are used to fill the internal circuit with freon. When filling, you need to measure the pressure and temperature at the compressor inlet and outlet.
After refueling is completed, you need to turn on both circulation pumps at the lowest speed, then start the compressor and monitor the operation of the entire system using thermometers. When the line warms up, frosting is possible, but after the system is completely warmed up, the frosting should melt.
Types of heat pumps for home heating
There are compression and absorption heat pumps. Installations of the first type are the most common, and this is the type of heat pump that can be assembled from a refrigerator or an old air conditioner using a ready-made compressor.
You will also need an expander, evaporator, and condenser. For the operation of absorption units, an absorbent refrigerant is required.
Heat pumps are most often assembled from units of air conditioners and refrigerators. Such homemade designs are simple, effective, and if the master has the skills to do such work, they can be made in just a few days
Depending on the type of heat source, installations can be air, geothermal, or using secondary heat (for example, waste water, etc.). One or two different coolants are used in the input and output circuits, and depending on this, the following types of equipment are distinguished:
- "air-to-air";
- "water-water";
- "water-air";
- "air-water";
- "ground-water";
- "ice-water".
A system can only be efficient if it consumes less energy than it produces. This difference is called the conversion factor. It depends on many factors, but the most significant is the temperature of the coolant in the input and output circuits. The greater the difference, the better the system works.
Image gallery Photos from The source of heat is air from the street. The units are connected to water heating systems. They are able to work effectively as long as the outside air temperature is above -25 degrees. The water temperature in the heating system can reach 63 degrees
The equipment is designed to heat buildings using water resources. It is installed in areas located near natural bodies of water. Horizontal heat pumps of this type take energy from the bottom layers of water, and vertical ones are designed to extract heat from underground and groundwater
Professional installation of a geothermal pump is an expensive service, but the cost is recouped through low operating costs. The installations are characterized by increased reliability and safety. They are weather-sensitive and designed for connection to low-temperature heating systems, which include heated floors
The installations generate heat while freezing water. By turning 100-200 liters of water into ice, you can get enough energy to heat a medium-sized house for 1 hour. For the system to function, solar collectors and a tank with a large amount of clean water are needed.
Air-to-water heat pump
Block diagram for multiple heat pumps
Geothermal heat pump for home
Ice-water heat pump
There are no reliable formulas for calculating the performance of heat pumps, because... their work depends on many factors.
When you assemble a heating system yourself, you cannot expect it to be as efficient as industrially produced equipment, but it is quite enough to create an economical additional heating system.