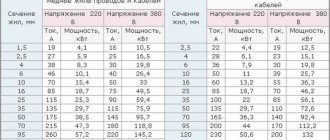
When carrying out electrical installation work, it is often necessary to lay electrical wiring in an open way. To ensure protection of the electrical cable from mechanical influences, precipitation and other factors, to make a neat and aesthetic installation of power or low-current networks, a corrugated tube or, as it is also called, corrugation is used.
How to properly lay cables in the floor
You should remember the basic rule: when installing a cable in a concrete floor, ordinary corrugation is used, and when installing in a wooden floor, metal is used.
Laying wiring without any protection is prohibited by all regulatory documents. What you should know when starting to install electrical wiring on the floor:
- All connections must be made only in junction boxes. The presence of twists in the floor, without additional protection, is unacceptable. Also, other types of connections cannot be left open: using sleeves or terminal blocks, bolted connections, etc.
- It is very convenient to place the junction box on the floor surface. This allows you to quickly identify and eliminate the problem without compromising the integrity of the floor covering.
- The corrugation should not be filled more than half with cable. This should be taken into account and a corrugation of the appropriate diameter should be selected. Only then, to replace the wire, can it be completely removed from the floor.
- You should not install too long lines - 20 m is enough. If the use of longer conductors is required, then special transit boxes must be used.
- There should not be more than two bends on one cable, the angles of which are 90 degrees or higher. This will have a detrimental effect on the further operation of the electrical network and, if necessary, the conductor will be impossible to get.
- When laying a cable in a wooden floor, you should not attach it to the joists; in this case, special holes are made in them, through which the corrugation is then passed. The presence of such holes will not affect the stability of the floor covering in any way. For additional safety, all wooden floor elements must be treated with a special composition that prevents combustion.
- When starting to pour a concrete floor, you must remember that the thickness of the cement screed above the wiring should be approximately 30 cm. For better stability (but not for electrical safety purposes), reinforced mesh is also placed in the screed.
- The corrugation with conductors should not intersect; all cables should run parallel to each other. When crossing them, it will be necessary to raise the floor level, which implies additional consumption of building material.
Recommendation from practice
If you use a tying wire to secure the cable to the cable, be careful not to over-tighten it so as not to accidentally cut the insulation or strands. To eliminate such situations, you can place a strong gasket made of insulating material between the bandage and the cable.
At all attachment points, you must adhere to the same winding pattern - at least 7 turns of the bandage. If plastic clamps are used, make sure that their operating parameters comply: they must withstand low and high temperatures, otherwise they may dry out and fall apart.
For additional line protection and cable insulation, it is recommended to use corrugated pipes. This will reduce the negative impact of bad weather conditions, reduce the financial costs of operation and subsequent possible restoration of the route.
Carrying wires through the air in a corrugated pipe
If it is not possible to collect the line from above, you can try to do it on the ground. You should attach the cable to the cable right there, and then pull it between the supports.
Installation technology
We suggest you familiarize yourself with the basic requirements for installing wiring in corrugated pipes, common mistakes and simple ways to stretch cable ties through the corrugation.
Requirements and errors
When laying wiring in a corrugated pipe, ensure that the following conditions are met:
- the length of one section without transit elements (couplings, tees, splitters) should not exceed 25 m, the number of turns - up to four;
- A one-piece corrugated hose cannot be installed at an acute angle;
- avoid close proximity of two or more turns of the route;
- the rotation angle should be more than 90 degrees, the radius should preferably be larger;
- two corrugated pipes should be located at a distance of at least 200 mm from each other;
- do not connect pipes using electrical tape - it is advisable to use connecting accessories, placing them in the middle of the section, turns and corners;
- one corrugation – one cable network;
- power and low-current lines should be separated from each other (standards are prescribed in the PUE).
How to stretch a cable inside a corrugation
To pull the wiring through the corrugation, you need to use a stiff wire. It is much easier to thread through long lines. The cable is then attached to the end of the wire. If you plan to thread a group of wires, then they are combined into a strong bundle, wrapped with a tie or PVC tape along the entire length. The second option is better, since this product has the necessary smoothness to avoid additional obstacles. If the cable is single, then electrical tape is not needed.
When the harness is ready, you will need to connect it to the broach (wire) using one of the following methods:
- Wrap the bundle with wire and crimp with pliers. There should be several similar twists.
- Simply place the wire parallel to the bundle and wrap strong electrical tape tightly. This option can be used as an addition to the first.
- If you are laying a single cable, then make a hole in its insulation at a distance of 40-50 mm from the edge, and thread the wire through it.
Regardless of the method chosen, if a tourniquet is used, the edge should be carefully wrapped with electrical tape, creating a smooth cone.
The last stage is pulling the harness through the corrugation. Ideally, the procedure should be performed together with a friend: one person holds the broach, the other pushes the tourniquet. Without an extra pair of hands, proceed as follows:
- Attach the free edge of the wire to some stationary object.
- Hold the corrugated product with one hand, providing tension, and with the other, push the tourniquet inside. Do not apply too much force, otherwise the broach may come off the harness. If this happens, cut the corrugation in the area to which the cable was threaded, then repeat the procedure with connecting the wire and the bundle. However, it is not necessary to completely remove part of the corrugation - the joints can be connected with electrical tape. If increased protection from moisture or fire is required, then this option is inappropriate.
The main purpose of the corrugation is to protect cables and wires from mechanical damage, exposure to high and low temperatures, moisture, ultraviolet radiation, chemicals and other environmental factors.
No product can guarantee absolute wiring protection, so it is important to learn how to choose the right tubes based on your specific needs.
Air duct maintenance rules. The need to replace the corrugated pipe for the hood
Smooth-walled plastic pipes are easy to clean, especially if the air duct design consists of several sections of short length and a corrugation diameter of 100 mm (so that a hand can easily pass inside). The sections are disassembled, cleaned of dirt, and then installed in their original place. The situation is more complicated with aluminum corrugation, which has a relief surface. Fat, soot, carbon deposits and dirt accumulate in the folds of the structure over a long period of time. They are very difficult to remove, so it is easier to purchase a new corrugated ventilation duct and install it. We discussed in detail how to do this in the article.
Errors and rules for installing corrugated cables
do not create sharp corners when designing routes
To increase the length of a single piece of corrugated tube, use special transit boxes, tees and couplings
Do not connect the tubes to each other using electrical tape. Install connecting accessories at turns, corners and closer to the middle of the entire area.
You cannot stretch several cable lines in one corrugation at once
power networks and low current must be separated from each other, maintaining appropriate distances
if you are not running a cable in a corrugated pipe, but individual wires, here is a table for selecting the maximum cross-section of conductors and their number, depending on the diameter of the tube:
Recommended corrugation diameters for different networks:
Corrugation d=16mm is usually used on the lighting line
for power sockets with a diameter of at least 20mm
for coaxial cable for video surveillance – no less than 25mm
for low current (telephone, internet, TV cable, alarm) D=16mm
The most common violations of the PUE requirements
The most serious mistake made at home during the installation of a power line is when the electrical network is laid without paying attention to the locations of various communication pipelines taking into account the perspective. This applies to the location of cable wiring, interior accessories located on the ceiling.
Other errors:
- laying telephone and television cables inside one corrugation along with a power cable line;
- the electrical wiring project involves calculating the load for each room without taking into account the simultaneous inclusion of electrical appliances;
- electrical wiring is calculated without reserve;
- a cable or corrugation of insufficient cross-section has been selected.
To create a reliable, safe cable line on the ceiling, it is better to avoid such mistakes.
Electrical installation with wiring along the ceiling Source profi220.ru
Professional advice on choosing
Despite the absence of strict rules for the color marking of corrugated pipes, the specific material of manufacture can usually be determined by the color of plastic products:
- blue – polypropylene;
- gray – polyvinyl chloride;
- black – low-density polyethylene.
On the other hand, you can focus on the international coloring standard, when the color indicates the purpose of the cable line:
- white corrugation or wire – computer network;
- gray or black – general purpose;
- green – telephone network;
- red – street wiring.
Laying a cable in a corrugated cable does not cause any particular difficulties; with certain skills, anyone can handle it. As for the intricacies associated with connecting and organizing the electrical network, if you do not have the necessary knowledge, entrust this work to qualified electricians.
Read more: Press for fuel briquettes, how to make a sawdust pressing machine with your own hands
In houses and apartments, as a rule, hidden wiring is carried out. In this case, it is placed in grooves prepared in advance for this purpose, onto which plaster is then applied. An alternative to this method could be external wiring, which is hidden under plasterboard or suspended ceilings.
When laying central wiring lines, the cable is pulled into the corrugation before it is laid. As for the branches for sockets and switches, the wiring can be done later.
Fasteners
For external wiring, special clips are used, the size of which is selected to match the diameter of the corrugation. In the case when the wiring is mounted in a channel or inside a box, clamps are used for fastening. In the groove, fastening to quickly hardening solutions, for example, alabaster, is allowed.
Cable corrugation mounted on a clip
- When installing wiring, sharp corner connections should be avoided whenever possible.
- If the length of the wiring is too long, the corrugated joints must be reinforced with transit boxes.
- Metal sleeves for wiring are fixed to the metal frame before pouring concrete. In this case, the wires are pulled after the concrete has set.
Corrugated protection can be laid in grooves in the wall and plastered
Helpful information! You can lay electrical protection in concrete walls in grooves. It is secured to wooden structures using clamps or metal brackets.
In the distribution panel, the corrugation must be firmly fixed in the holes
Over time, the material may “sag” a little and tighten, so fastening at the joints is very important
Fastening corrugated protection in the distribution board
Note! Metal protection for electrical wiring must be grounded
Step by step laying
Below are step-by-step instructions for installing electrical wiring under drywall trim.
Step 1. Preparation
Assemble the metal profile, but do not rush to install the plasterboard sheets. Decide where to place the wiring: under the ceiling or along the walls. It all depends on the specific situation. If you have a suspended or suspended ceiling, it is better to hide the wires at the top and then lower them vertically to sockets, switches and other boxes.
If the ceiling in the house is made of concrete or wood, and only the walls are plasterboard, then the wiring should be placed in them, closer to the top. The distance from the ceiling must be at least 10 cm. Remember: when choosing places to install sockets and other equipment. Once you have your diagram on a piece of paper, transfer it to the wall. Calculate materials and proceed with installation.
Step 2. Installation of the box
Place distribution boxes. There should be one of these in every room of the house. Attach the component to the wall or ceiling using self-tapping screws.
Step 3. Laying the wires
Prepare the necessary materials and tools, and then proceed with installation. Secure the clips along the cable route. The distance between the fastening elements must be at least 30–40 cm. It is possible to use plastic clamps, which will speed up the work, but will increase the likelihood of damage to the corrugation due to the sharp ends of the profile.
Before pulling the corrugation through the metal frame, drill holes of a suitable diameter. You can buy a profile with holes already made. A similar method is used to connect the junction box and the points where sockets and switches will be installed. Mark on the drywall where the corresponding component will be, and then sew the sheet to the frame.
Step 4. Switching electrical installation products
All that remains is to install sockets and switches. They are usually called electric points. Using a drill, make holes in the places where they should be located. Install the socket boxes into the drywall. You need to make holes in the bottom to thread the wiring through. Pull out the cable and place the socket box in the groove. When everything is done, check the electrical circuit by supplying power to the apartment or house from the distribution panel.
Types and types of corrugated pipes
Cable corrugation is distinguished according to the following parameters:
- Diameter.
- Wall thickness.
- Materials used.
- Blossom.
- Resistant to loads.
The flexibility of the corrugation and its stability depend on the thickness of the walls and the material from which it is made. The conditions under which it can be used depend on the materials used.
Classification by material and its main characteristics:
- PVC is the most common option. Non-flammable and relatively cheap corrugation for wiring. When exposed to UV radiation, it is destroyed, which imposes restrictions on outdoor use.
- Polyethylene and polypropylene (PPR). There are corrugated pipes made of low-pressure polyethylene (LDPE) and high-pressure polyethylene (LDPE). Operated in a temperature range from -40 to +45 degrees Celsius. Resistant to UV rays, acids, oils and solvents. They are distinguished by color: black and two-layer red - polyethylene, and blue - polypropylene.
- Metal corrugation. It is also called a metal hose. They provide good cable protection from mechanical damage. Resistant to active substances and oils.
Interesting!
The marking of metal hoses is deciphered as follows: RZ-Ts, RZ-TsKh, RZ-TsA - made of galvanized steel; RZ-SL and RZ-SL-X - made of tinned steel tape; RZ-CP – with PVC insulation, for sealing.
Based on the number of layers, they are distinguished:
- Single layer. PVC sleeves most often consist of just one layer, and its thickness can be different.
- Double layer. An example is a double-wall HDPE pipe.
Load resistance:
- Lightweight (up to 320 N/5 cm2) – the walls are thin and flexible. They are installed on suspended ceilings and in plasterboard structures.
- Medium (up to 750 N / 5 cm2) - placed in a groove.
- Heavy (withstand up to 1250 N/5 cm2) - the toughest, laid in concrete screeds.
- Extra heavy reinforced (up to 4000 N/5 cm2 and above). They are laid underground or suspended on supports for outdoor installation.
Another factor is the types of corrugation in color. This is not fixed by regulation, but usually gray and white corrugations are made of PVC, red, black and blue are made of polyethylene. There are also colored models, it depends on what dye is added to the mass during production. You can use specific colors for each line type:
- White – lighting and internet.
- Gray or black – sockets, general purpose circuits.
- Green – information cables and telephony.
- Red – for external use.
In practice, such a division does not occur often.
The thickness of the corrugated wall is in the range of 5-15 mm. The outer diameter for PVC corrugation is in the range of 16-50 mm. Below is a detailed table showing the size range of cable corrugations.
Outer diameter Inner diameter 16 10.7 20 14.1 25 18.3 32 24.5 40 31.5 50 39.6
Size range of metal hoses:
Outer diameter Inner diameter 9.8 5.1 11.0 7.7 13.5 9.7 15.6 11.7 19.0 14.7 22.0 18.0 38.0 31.5 45.0 37.5 58.0 49.5 71.5 62.5 87.5 78.0
There are also options with and without a probe. The probe is often called a wire puller. This is a thin steel wire to which wires are tied and with its help the wiring is pulled into the sleeve. This is especially convenient when using conductors with flexible stranded cores.
Technical characteristics of corrugated pipe for ventilation
Before purchasing corrugated exhaust pipes, you should carefully study their technical characteristics and properties. Air ducts for domestic use are flexible and semi-rigid (semi-flexible). The first type of device withstands bending and tensile deformation well with the ability to restore its original state. Using a flexible pipe, you can build an air duct of any configuration and a large number of angles.
The basis of flexible corrugation is a spiral-type wire frame onto which aluminum foil, polymers, or combinations of these materials are stretched.
The main characteristics include:
- device diameter – 100−500 mm,
- resistance to temperatures up to +100°C,
- bending amount equal to half the diameter.
Flexible air ducts come with or without thermal insulation. Filler (glass wool, mineral fibers) is used to suppress the noise level in the house during operation of the hood.
Table 2. Technical characteristics of semi-rigid corrugated pipes
| Device Parameter | Image | Description |
| Material | For the manufacture of semi-rigid air ducts, galvanized or stainless steel, as well as aluminum, are used. | |
| Permissible bending value of the product | This indicator directly depends on the diameter of the air duct. It indicates the degree of bending of the product (for example, the bending radius must be at least 0.6 of the corrugation diameter). | |
| Corrugation internal dimensions (diameter) | Air ducts for use in domestic and industrial purposes with a diameter of 50−400 mm are widely available on sale. | |
| Temperature indicators | When choosing corrugated pipes, you should take into account the temperature characteristics of the products. Thus, devices made of stainless steel can withstand thermal loads up to +800°C, with a galvanized surface up to 700 mm, and those made of aluminum - 250-300 mm. |
What is corrugation and where is it used?
An electrical installation corrugation is a corrugated pipe for laying an electrical cable for the purpose of protecting it or protecting structures. Laying electrical cables in corrugated tubes is used in various situations with open or hidden electrical wiring.
Hidden gasket
Hidden installation is the installation of electrical wiring inside the structures of walls, floors and ceilings, behind finishing materials. It is conventionally divided into the following types of installation:
Laying inside non-combustible structures is carried out in grooves of walls and ceilings, in floor screeds or simultaneously with the installation of load-bearing structures (for example, when concreting). In this case, corrugation is used for ease of installation, protection from cable crushing and the ability to replace electrical wiring without disturbing the finishing material, chipping or dismantling wall, ceiling or floor structures. When laying corrugated cables inside structures made of non-combustible materials, the PUE allows the use of any type of corrugated tubes.
Laying behind finishing materials or in false spaces has purposes similar to laying in non-combustible structures (protection from mechanical damage, the ability to replace wiring if necessary), but with the installation requirements being met, as when laying over combustible materials. The fact is that finishing materials often contribute to combustion, so the requirements for such installation are quite strict
It is important to use flame retardant or metal corrugations during this installation.
Underground installation is carried out during landscaping work for wiring electrical power lines to lighting fixtures and various equipment (sprinkler pumps, gate and door opening systems), when laying low-current networks for security systems or telephone lines, and in other situations. The main requirement for such installation of corrugated electrical cables is water resistance and high resistance to mechanical deformation (rigidity).
Open gasket
Open laying is carried out over load-bearing and enclosing structures, finishing materials and when installed outdoors to building facades or through the air.
Laying structures over flammable materials involves installing corrugated electrical wiring to ceilings and walls with flammable finishes or made of wood, plastic and other materials that promote combustion. For fire safety reasons, non-flammable (metal) corrugated tubes are used. For such installation, according to the PUE, it is prohibited to use plastic corrugation made of self-extinguishing and flame retardant materials.
Laying over non-flammable structures and materials is carried out using any flame retardant corrugated plastic tubes. It is possible to use metal corrugations to improve the aesthetics of installation or when used in special conditions (aggressive environments, likelihood of mechanical damage).
Laying outside buildings and structures is used for installing lighting or laying power and low-current networks for various purposes along the facades of buildings and fences, as well as through the air between buildings. The corrugation used in this case should also not spread fire and should be resistant to precipitation, ultraviolet radiation and be durable.
Cable laying in fire or explosive areas is carried out exclusively using metal corrugated pipes in combination with a flame retardant electrical cable.
Why do you need a corrugated hose?
Installing electrical wiring is a responsible matter that does not tolerate mistakes. The safety of staying in electrified premises directly depends on its quality.
The benefits of civilization in the form of glowing light bulbs and numerous household appliances, by definition, cannot work without being connected to the power grid.
And any live electrical cable is a source of damaging current that is dangerous to humans.
It is recommended to use corrugated cables for electrical wires everywhere (for hidden and open installation methods, for installation outdoors and indoors). If this is not possible for aesthetic reasons, then it should be replaced with a decorative cable channel
The first protection against electric shock is the insulating braid of the cable itself. Regardless of the material used, it reliably protects a person from the current flowing through the veins.
However, insulation does not last long. These aluminum or copper wires can last 15–25 years, but the outer braid on them is often damaged within 3–4 years after the wiring is put into operation.
The service life of electrical wire insulation is greatly reduced due to:
- high humidity (outdoor or room);
- overheating under increased loads;
- ultraviolet radiation and other factors.
The result is a breakdown, short circuit, fire and electric shock to a person. To minimize risks, electricians lay wires in a corrugated sleeve.
On the one hand, it serves as an additional barrier between electric current and a person, and on the other hand, it serves as protection for the cable.
If the need arises to replace the old wire in the corrugation, it is simply pulled out of the sleeve, and a new one is inserted in its place - and it does not matter whether this channel is located under the finishing or in a concrete screed
A cable laid in a corrugated pipe receives protection from:
- compression and other mechanical damage;
- ultraviolet radiation and precipitation (when laying wires outdoors);
- exposure to moisture.
And the last thing is fire safety. All corrugated hoses for electrical cables are made of non-flammable or self-extinguishing materials.
This reduces the likelihood of exposure to an open flame on the wire inside the corrugation, and also prevents the spread of fire during short circuits and fires of the plastic cable braid.
How to stretch a wire
Scheme of pulling wire into corrugation
You can route electrical cables along walls or ceilings using special clips. Their diameter is selected in accordance with the cross-section of the corrugation. This method is more common because it securely fixes the pipes and has an attractive appearance. In hidden places it is preferable to use dowel screws or metal staples.
When laying pipes, the joints are connected using a low-cost connecting element - a coupling. If the wires in this section are not insulated, the place of attachment to the pipe coupling can be sealed with sealant. To pass through the walls, special perforated sleeves are used, which, if necessary, are also treated with sealant.
Mounting method
rule
By securing it in this way, you influence it mechanically in any way. If at first glance nothing seems to happen to it, then over time, this method of fastening can play a cruel joke on you.
Even without using ties, but using special expensive fasteners, you still make the cable sag under its own weight.
Such fasteners negatively affect its insulation. This is not a SIP, which was originally manufactured taking into account sagging under its own weight.
And this, in a few years, will certainly lead to false alarms of the differential protection.
As you can see, all the methods that are presented by installers as simple and fast do not really fit into the definition of “durable installation”.
Color and type of corrugation
The first thing to note is the color of the corrugation. No one ever paints a corrugated sleeve on purpose, except in isolated cases of its decorative use.
Moreover, each color indicates the material from which the product was made.
- gray color is PVC - polyvinyl chloride. To ensure that it looks perfectly smooth and beautiful when mounted on the ceiling, experienced electricians advise buying it not in twisted coils, but in whips.
- black and orange color is HDPE - low-density polyethylene
- blue color PP – self-extinguishing polypropylene
Technical characteristics of PVC, HDPE, PP corrugated pipes:
PVHPNDPP PP
Many have probably come across beautiful photos and videos where black and orange corrugations spread across the ceiling. Everything looks beautiful, no doubt about it. And HDPE corrugated material itself, although it costs a little more, is much stronger than PVC. Although it all depends on the brand. This simplifies its installation and eliminates the possibility of accidental damage. However, such beauty is a ticking time bomb.
The danger is that both orange and black corrugations support combustion very well. In this case, a fire in an apartment may not start due to a short circuit or overload in the electrical wiring. And now imagine that your entire ceiling is simply covered with such material.
It is enough for one tube to catch fire and the fire will be of such a scale and category that there will be nothing left of the apartment or house. Your main task will not be to put out the fire, but at least to get out of there safe and sound. And the chances will be slim, given the fiery rain of burning molten polyethylene.
In addition, it is this corrugation that will cause the fire to move from one room to another. In those places where the wiring passes through a concrete wall into another room, the flame can easily penetrate there by spreading the combustion of the HDPE corrugated hose. There will be no problems with PVC.
Because as long as it is exposed to fire, it burns. As soon as the fire is removed, it immediately goes out, because... does not support combustion.
Therefore, gray PVC corrugation should be used in apartments and houses. Multi-colored can be used for embedding into walls and concrete, but not for open laying.
Black HDPE corrugation can and should be used outdoors. Not gray, but colored.
It was created to provide protection from ultraviolet radiation. PVC will crack over time and will not provide protection. But don’t listen to all sorts of stories from installers that it’s ideal to use colored marks to wire low current and power circuits. For the installer, this may be convenient during the work process, but you will have to live with this fire-hazardous material for the rest of your days.
Increased cost of work
Let's figure out whether corrugated installation really leads to a significant increase in the cost of repairs.
For ease of installation of electrical wiring, many use round NYM cable, including VVGng with a round cross-section. At the same time, they tighten it into the corrugation d=16mm.
After which you need to prepare a 20mm*20mm groove. If you have a wall chaser, the width of the groove when installing the disks does not particularly affect labor costs.
Many people initially set the cutting depth to 25mm to make it easier to cut the middle of the furrow. The shallower the cutting depth, the harder the core chips.
Therefore, in order to lay the bare cable in the groove, you will still have to cut a strip approximately 20mm deep. Or work very hard with a hammer drill, which will ultimately lead to no less labor costs. At the same time, do not forget one important nuance - gating in load-bearing walls in panel houses and hollow-core slabs is prohibited.
And where the cutout is not made in load-bearing walls, firstly, the integrity of the reinforcement should not be compromised, and secondly, the depth of the cutout should not exceed 20mm.
Therefore, when we talk about cutting a groove in a wall, in 90% of cases we mean cutting a groove in the plaster. The problem is that not everyone wants to apply 2.0-2.5 cm of mixture to the walls, just because of the wiring.
However, there is still an increase in cost when working with corrugation, and for many it can be critical. When working with this material you need:
special fasteners and nails. Using a mounting gun, on average it takes 3 shots per 1 meter of corrugation.
more junction boxes. If you use boxes with 4 separate inputs, then without corrugation you can place a much larger number of cables there. But when working with corrugation, there are only four!
Therefore, the total number of boxes, although not significant, will increase. It was already said above that the gating itself does not increase costs so significantly, but if we talk about drilling through holes through the walls, then everything can change significantly.
If you drill one hole d=32mm, you can easily pass 4 bare cable lines through it. But for the same quantity, but already in a corrugation, you will need to drill at least 4 holes.
When working in an apartment with soft partitions, this point is not critical. But if you try this in a private house, or in a panel high-rise building with high-quality concrete walls, your labor costs will increase many times over.
For many electricians working alone, it can take a whole day of work just to punch through holes. Therefore, yes, in some cases, depending on the working conditions and the specific object, the increase in the cost of laying cables in corrugated cables can be at least 30%. And for some, this is a significant difference in the total cost of repairs.
But can corrugation, on the contrary, help save a lot? Surprisingly yes. Here is a very original use of it for securing a cable in a groove. Thanks to it, you can completely eliminate the cost of dowel clamps. In this case, you can even use the remains of corrugated hoses, which are no longer needed anywhere.
Homemade sliding suspension
Construction stores sell a variety of hangers for cable wiring. However, with a small amount of work, you can do it on your own by creating a homemade fastener.
For this you will need:
- wire cutters;
- round nose pliers;
- galvanized steel wire (preferably more flexible);
- a rod whose diameter is higher than the given value of the cable being installed.
Using wire cutters, create several pieces of wire 25-30 cm long. Take the pliers and make an air loop in the middle of each of them. Its diameter should be equal to the size of the cable being laid, since the next step is to thread it through the “rings”.
Wrap the wire around the rod to create the components to secure the cable to the cable. First, wind one end, then the other end. The pitch of the resulting spiral should be about 20 mm. With these steps you will create a homemade cable hanger.
To lay the cable through the air, secure the cable, then place the hangers at intervals of 50-80 cm and thread the cable through them. After this, the free end of the cable is fixed to the second building.