Laying electrical wiring is one of the most important stages of home renovation. If you select the wrong current-carrying cable, the wiring may overheat and melt, and in some cases lead to a fire. We will tell you about the most popular types of cables used for wiring and explain how to choose the right wire cross-section. In this article, we will consider exclusively wire with copper conductors, since aluminum is falling out of popularity due to its low electrical conductivity compared to copper.
Classification of cables for wiring
Each cable consists of several copper cores of a certain cross-section. In turn, the cores in the cable can be single-wire monolithic or multi-wire. Each core is enclosed in a protective sheath made of rubber, polyethylene or PVC plastic. Note that any cable used for electrical wiring has at least two layers of insulation: the first envelops the core, and the second collects all the conductive wires into a bundle.
The most popular types of wires for wiring in a house and apartment are:
- VVG
- NYM
- PUNP
Let's look at what these types of cables are and where they are used.
Do-it-yourself electricity supply to the house
Electricity is introduced into the house at the earliest stages of construction, as soon as the need to use power tools arises.
Before properly supplying electricity to a private home, you need to familiarize yourself with the safety requirements, as well as recommendations for installing overhead lines and laying underground cables. Below we will talk about how to supply electricity to the house (several options) and how to arrange an internal electrical network, and not about how to connect an extension cord, since everything is simple with this, but about how and in what way (open or hidden ) install permanent electrical wiring. Let's look at everything in order. So, before you properly introduce electricity into the house, decide how you will connect to the 220 V street electrical network - through an overhead line or by laying an underground cable.
VVG cable
The VVG cable is used for wiring in networks with voltages up to 1 kV. The number of cores in the bundle can be from 1 to 6. The letters VVG are deciphered as follows:
- B - the first layer of PVC insulation.
- B - second layer of PVC insulation.
- G - insulation without an additional protective layer (armor).
Additionally, some types of VVG wire may have the designation “ng”. These letters mean that the wire is flame retardant. Thus, if a high temperature occurs due to a short circuit, the wire will melt, but will not burn. We recommend using this type of VVGng wire for installing electrical wiring in an apartment.
There are also VVG types with the designations “P” and “Z”.
- P means that the wire in the wire is flat;
- 3 - that the space between the cores and the outer insulation is filled with PVC plastic.
Here is an example of a flat flame retardant cable REXANT VVG-Png-LS 3x2.5:
The advantage of the VVG cable is the ability to use it in conditions of low and high temperatures from -50 to +50 degrees. Also, in comparison with other types, it is much cheaper. For example, VVGng 3x2.5 costs on average from 35 - 40 rubles per 1 m, and NYM 3x2.5, which has similar characteristics, costs about 55 - 60 rubles. If the house is large, the difference in wiring costs can reach a couple of thousand rubles.
VVG wire cores can be single- or multi-wire. Multi-wire ones are more flexible than single-wire ones, but they are also a little more expensive. Single-wire ones have a cross-section from 1 to 50 mm2, and multi-wire ones from 16 to 240 mm2. It is worth noting that for residential wiring, cables with a cross-section of 1.5 to 6 mm2 are usually used.
The bending length of the VVG wire (at turns in the groove) is equal to the cross-section of the entire bundle multiplied by 10. That is, if you have a wire with a cross-section of 5 mm, then the bending radius should be at least 50 mm.
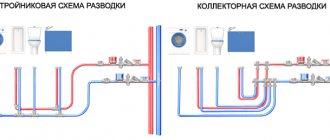
Single-core or stranded wire: which is better for home wiring?
Each wire seems to conduct current well and withstand the load, but they have significant differences. Which one to choose for installing home wiring? A professional electrician shares his experience in our article.
To simply say that one wire is better than another would be a grave mistake: after all, each is used in a specific area. For example, overhead power line networks are installed only with multi-core wire, and underground cable networks only with single-core wire. Both types can be used in home wiring. Which is better for hidden wiring in an apartment: single-core or multi-core? Let's explain with specific examples.
NYM cable
The NYM cable is applicable in networks with voltages up to 0.66 kV. The number of conductors in the bundle is from 2 to 6. In addition to the current-carrying conductors, there may be a yellow-green grounding conductor. Although the cable is mostly used for indoor wiring (it is afraid of ultraviolet radiation), it can also be used for outdoor installation if it is placed in a protective sleeve (plastic pipes, boxes, etc.). NYM stands for as follows:
- N - standard type wire (German classification).
- Y - sheath of cores made of PVC plastic.
- M - there is an outer shell (most often also made of PVC).
Additionally, the wire may have the symbol “J”, which indicates the presence of a grounding conductor in the harness. It is worth noting that NYM is initially manufactured with insulation that does not support combustion, so you should not look for the letters “ng” in the marking. However, unlike VVGng, the NYM cable can withstand lower temperature loads, so it is better to use it for single installations rather than for group installations. It is manufactured with a cross section from 1 to 35 mm2.
The advantage of this cable is its durability - German-made wire can last up to 40 years (VVG is about 30 years). But the Russian analogues of NYM are not as durable, no matter how the manufacturers convince them of this. NYM can be used in rooms with high humidity up to 98%, so it is convenient for wiring in baths and saunas.
The bend radius length for NYM wire will be four cross sections. Thanks to this, passing “turns” while laying cables in ditches will be easier than with VVG. However, this and other factors significantly influence the high cost of the wire (compared to other types). Here is a relatively inexpensive two-core wire Pan Electric NYM 2×1.5 (100 m):
Key Rules for Electrical Wiring
FORUMHOUSE has a section where they will help you choose the optimal electrical wiring diagram in a private house for a specific project. But any electrical wiring diagram in a private home must be drawn up in compliance with the key rules prescribed in regulatory documents:
- electrical wires and cables can only be laid strictly vertically or strictly horizontally;
- the angle of rotation of the wire should not be obtuse or sharp, only straight, and the wire should also extend from the switchboards and junction boxes strictly at a right angle - it is forbidden to lay it diagonally, no matter how much you would like to save material or wall space;
- according to PUE-6, you cannot lay a wire or cable next to communication pipes, you must retreat at least 100 mm, and from gas pipes - at least 400 mm. The distances of wires and sockets from heating radiators are not regulated by the rules, but it must be taken into account that heating devices will additionally heat the cable, so the distance should be such that the air temperature around the sockets and cable does not exceed +25 ° C. To do this, you need to retreat a distance of about half a meter.
To plan other indents, you can use this cheat sheet:
There are rules provided not by regulatory documentation, but by considerations of personal comfort: sockets on both sides of the bed, switches at a height of 80-90 cm, on stairs and in halls - pass-through switches (also known as duplicate or changeover switches), which allow you to control one from different places light source.
Amikta FORUMHOUSE user
When going up to the second floor, you can turn on the light below so as not to climb in the dark, and turn off the light on the first floor from the second.
All objects that are connected to power lines must be grounded using the third core of the cable - a wire in yellow-green insulation.
PUNP cable
This is a budget type of cable for electrical wiring. It is a flat two or three-core wire with a core cross-section from 0.75 to 6 mm2. PUNP stands for as follows:
- P - wire.
- UN is universal.
- P - flat shape.
Also in the abbreviation the letter “G” is sometimes found, which means that the wire is flexible. Its main advantage is its low cost compared to VVG and NYM.
There is an opinion among electricians that PUNP wire is prohibited for manufacture and use. Indeed, on June 1, 2007, a ban was introduced on the use of TU 16.K13-020-93 by members of the Elektrokabel association. However, manufacturing plants continue to produce and sell PUNP. In Russia they can be purchased freely.
Concerns about the use of PUNP are well founded. Statistics of fires caused by electrical wiring fires showed that in 60% of cases the source of fire was the PUNP cable type. The reason for this is that TU 16.K13-020-93 states that during the manufacture of wires, a deviation of 30% from GOST 22483-77 in the cross-section of current-carrying conductors is allowed. This means that, for example, a wire with a nominal cross-section of 4 mm2 may well be 2.9 mm2 or even less.
In general, whether to buy PUNP or not is up to you. In any case, if you have the means, it is better to purchase a wire of good quality once and not be afraid of a fire.
How to choose a wire cross-section?
There is a table of correspondence between wire cross-section and load (shown below). It indicates what maximum load corresponds to what cross-section of copper conductor.
| Core cross-section, mm2 | 1.5 | 2.5 | 4.0 | 6.0 | 10.0 | 16.0 | 25.0 | 35.0 | 50.0 |
| Current load, A | 19 | 27 | 38 | 50 | 70 | 90 | 115 | 140 | 175 |
So, suppose you need to select a wire for wiring in the kitchen. For example, the kitchen has a 1.6 kW boiler, a 0.4 kW refrigerator, a 1.8 kW microwave and a 1.2 kW toaster. In this case, the total current load will be as follows:
(1600+400+1800+1200)/220=22.7 A
It is also necessary to multiply the current load by a power reserve factor of 1.5, since the number of electrical appliances may increase in the future. In total we get:
22.7x1.5=34.05 A
Now we look at the plate and see that our load corresponds to a wire with a cross section of 4 mm2 .
Using the same principle, the wire cross-section is selected for all other rooms and for the input cable.
Selection of conductor cross-section by power and length
The length of the conductor determines the voltage supplied to the end point. A situation may arise when the voltage at the point of consumption is insufficient to operate electrical appliances.
In household electrical communications, these losses are neglected and a cable is used ten to fifteen centimeters longer than necessary. This surplus is spent on switching. When connected to a distribution board, the reserve is increased, taking into account the need to connect circuit breakers.
Cable laid in a closed way Source kadetbrand.ru
When laying long lines, one should take into account the inevitable voltage drop. Everyone has their own resistance, which is influenced by three main factors:
- Length measured in meters. As this indicator increases, losses increase.
- Cross section, measured in square millimeters. If this parameter is increased, the voltage drop decreases.
- The resistance of the conductor material, the value of which is taken from the reference data. They show the reference resistance of a wire with a cross-section of one millimeter and a length of one meter.
The product of resistance and current numerically represents the voltage drop. This value should not exceed five percent. If it exceeds this figure, then it is necessary to take a conductor with a larger cross-section.
Total: how to choose a cable for wiring?
- We decide on the type of cable. NYM would be a better choice, but this wire is quite expensive. If your budget is limited, you can take VVG. For wiring in wooden houses, it is better to use the “ng” type, that is, non-flammable.
- We decide on the number of cores . If you have a single-phase network with grounding, you need three wires: phase, neutral and ground. Without grounding - two. For a three-phase network, cables with four cores (three phases and zero) are used.
- We calculate the cable cross-section. We calculate the maximum load from consumers, multiply by a safety factor of 1.5 and look at our plate.
Briefly about the main thing
A cable for laying in the ground for 15 kW of network power must be taken with protection or laid in a pipe. The cross-section of such a wire should be from 10 mm².
Cables are available for overhead and underground installation.
The cable must be routed through the wall in a metal pipe at a slight angle.
The cross-section of the cable directly depends on the method of its entry, as well as the material from which it is made.
For a 15 kW network with a voltage of 380 V, it is necessary to install an additional three-way circuit breaker.
Ratings 0