Autonomous heating allows you not to depend on established consumption standards, the pricing policy of heat suppliers and their mood. This makes it possible to independently control the heating process and maintain the most comfortable temperature in the house, while saving resources.
And if you wire your heating boiler with your own hands, then it will last longer and will take up less financial resources, isn’t it? But have you never engaged in tying, and the word itself seems incomprehensible to you at first glance?
Don’t be intimidated by the abundance of pipes, devices and technological steps - after reading the article, you will be up to the task. Here we consider piping schemes for floor and wall types of heating equipment, select illustrative photos and recommendations from specialists for piping at home.
What is boiler piping with polypropylene
Polypropylene pipes are designated according to the international classification PPR. Piping is carried out to connect radiators or other types of heating devices with the boiler room and auxiliary heating equipment, which includes a pump, fan, primary sensors of the automation system, vents, expansion tank, water purification filter and sump.
The heating boiler piping scheme with polypropylene can be performed in a circuit of any complexity. It is necessary to weld heating network components using a special welding machine - a soldering iron for PPT or PPR fittings. The second option is less preferable, since over time such connections begin to leak.
When starting the assembly, the mechanic must first think through the executive circuit in such a way that it has the least number of connections.
A complex network not only leads to increased heat losses and a decrease in the overall efficiency of the installation, but also increases the possibility of leaks.
Likewise, you need to worry about ensuring smooth transitions, since they contribute to an increase in the speed of movement of the medium and, as a result, increase heat transfer and performance of the system as a whole.
When piping a floor-standing boiler, it is necessary to comply with the requirements of SNIP, gas and fire safety. When piping the gas line, steel gas pipes must be used.
They are connected to the boiler using “American” or metal pipes. There is also a limitation for installing gaskets on such connections - they must be paronite. Made from heat-resistant material, they do not lose their protective properties even at steam temperatures and high pressure drops, which ensures the tightness of the assembled line.
The use of rubber and fum tape in such an assembly is strictly prohibited.
The connection of the in-house heating system to the boiler along the supply and return lines is made with a section of steel pipes, the length of which is established by the manufacturer and is indicated in the technical documentation for the boiler. Usually the size should be at least 1 m. Then the strapping is done with polypropylene.
When can systems be combined?
It is permissible to install a combined heating system in premises of any purpose. The main thing is to choose the finishing product and the type of heated floor in accordance with the requirements. The combined design is ideal heating for a two-story private house.
When laying a heated water floor on the first floor, warm air masses, rising, will warm up the floors of the second floor, where only radiators can be installed. For the finishing material on the first floor it is better to choose tiles, and for the second floor any material is suitable.
It is not possible to build a combined system in apartment buildings, since it is prohibited to connect hydrofloors to the heat supply source for the entire house. The solution is to install a heat exchanger.
Advantages and disadvantages of polypropylene pipes
Recently, PPR heating pipes, which have excellent performance parameters, have gained particular popularity in the building materials market.
The advantage of using them is the fact that the installation can be done independently at home. This will provide real savings to the family budget.
Advantages of PPR pipes compared to steel:
- Long service life.
- Strength, the material is distinguished by its hardness and resistance to wear by abrasive particles, which move at speed in the hot coolant of the heating circuit.
- High thermal insulation qualities of PPR pipes for heat supply, which significantly reduce heat loss.
- Anti-corrosion, the material is absolutely not susceptible to negative corrosion processes.
- Affordable price.
- Insignificant specific gravity.
- Increased sound insulation qualities. PPR material can muffle the sounds of moving water.
- Frost resistance, permissible indoor conditions at temperatures up to - 15 C, in the absence of constant heat supply in the house intended for temporary stay of residents.
- Chemical resistance.
- Ease and convenience of installation.
- Protection against stray currents, the material does not conduct electricity.
- The smooth heating surface prevents scale formation, and the pipes are able to maintain good permeability.
- Environmental safety, pipes are absolutely harmless to human health and the environment.
- No increased requirements for operation and maintenance.
- High aesthetic appearance, fits well into any interior.
Disadvantages of polypropylene pipeline heating systems:
- The low melting point of the material is +160/170 C, which does not allow their use in systems with high-temperature coolant, in the absence of automation and protection systems in heating sources.
- They are also a fire hazard.
- A relatively high coefficient of thermal expansion, which can cause ruptures in the connecting nodes of the system when starting the system from a cold state.
The simplest and most effective option for solving the problem caused by thermal expansion of pipes is their reinforcement.
There are 2 key methods of reinforcing PPR pipes that are suitable for heating systems: using aluminum foil and fiberglass. The first option reduces the linear expansion by 2 times, and the second - by 5 times.
Temperature balancing
To balance the system by temperature, we will need the already familiar balancing valves (or thermal heads with presetting) and an electronic thermometer for non-contact measurement of surface temperature.
Balancing begins with the balancing valves on the last and penultimate radiator being fully opened. The coolant flow rate on the first, as well as on subsequent radiators from the boiler, is set to minimum values (with an increase in flow rate as the radiators move away from the boiler).
For example, if there are 8 radiators installed in the system, and the balancing valve screw is adjusted within 4.5 turns, then the first radiator from the boiler is first completely closed, then its balancing valve is unscrewed by 1.5 turns. The regulator of the second radiator is unscrewed by 2 turns, the third by 2.5, and so on. The coolant flow on the last and penultimate radiator in most cases remains maximum. If possible, adjustments are made only on those radiators that are closest to the boiler (the distance is measured from the beginning of the supply line).
It is not recommended to unscrew the regulator less than 1.5 turns. After all, if you turn down the throttle opening of the valve too much, the device will quickly become clogged with scale or other debris.
Fine adjustments are made according to the readings of the thermometer. The main goal of balancing in this case is to achieve approximately the same temperature difference at the inlet and outlet of each radiator.
If the temperature difference at the inlet and outlet of a single radiator reaches 10ºС, it is not recommended to close its balancing valve even more.
And one more thing: noise in the radiator during operation of the heating system indicates that the coolant flow should be reduced.
Which boiler to use: wall-mounted or floor-standing
When considering the question of which boiler is better for using PPR pipes, one must proceed from two parameters - the operating temperature of the coolant and the presence of safety automation.
For boiler units with a coolant temperature above 80C, which do not have automatic temperature maintenance systems in the heating circuit, polypropylene pipelines are not recommended.
Mounted boilers operating on gas fuel, both in double-circuit versions for heating and hot water supply, and in single-circuit versions for heating, are quite acceptable to be connected to an intra-house system using PPR pipes.
To simplify installation, the specialist first draws up a drawing of the installation of heating devices, taking into account all the features of the location of the premises and the furniture located.
If the heating system is complex, has a floor breakdown and different types of heating - radiator and “warm floor”, you will need to create separate temperature circuits and connect them through hydraulic manifolds on the supply and return. Professionals recommend using average pipe diameters for installation in such a system - 20x3.4.
For floor-standing boilers operating on gas fuel, there are no special recommendations for installing PPR pipes; they are the same as for a mounted unit.
With regard to floor-standing solid fuel boilers, everything is much more complicated; when choosing such boiler equipment, you will need to pay attention to the recommendations given by the manufacturer on the use of acceptable pipe material for piping the boiler.
Typically, complete protection systems install a minimum permissible section of steel pipe on the coolant supply and outlet pipes of at least 1 m, but more precise installation recommendations will depend on the automation system adopted by the manufacturer.
Connection features
Installing an electric boiler does not involve complicated work, but it is worth considering the installation recommendations. If the boiler is wired correctly, it can be placed anywhere in the house and still work efficiently.
Electric boilers are suitable for use in different circulation systems. The equipment and supply pipeline must be placed at the lowest point of the heating system, which contributes to better heating of the radiators.
The boiler also needs to be grounded. The use of the zero phase is excluded, since the automation detects this as a short circuit.
In addition to the correct installation of the boiler and the selection of high-quality components, it requires professional installation. If the piping is done according to the rules, it will ensure a minimum temperature difference between supply and return.
Materials and tools for work
When starting to piping a gas-fired heating boiler, you need to have a design and executive diagrams. Without these documents, the owner will not be able to put the heating boiler into operation.
Each project has an equipment specification section, which contains a detailed list of all elements of the thermal circuit by standard sizes, assortments and quantities.
Therefore, using the specifications, even a non-professional will not have much difficulty purchasing spare parts and components in the retail chain.
The key components of the intra-house heating network are:
- Coolant circulation pump.
- Expansion tank to compensate for the expansion of water in the circuit.
- Vents for removing air from the heating circuit.
- Mud trap for cleaning the water of the internal heating circuit from suspended particles.
- Hydraulic arrow or manifold on the supply and return for distributing coolant through the heating circuits.
- PPR pipes PN 25, for the heating circuit, reinforced with foil for systems with a working pressure of 2.5 atm and temperatures up to +95 C.
- PN 20 for piping a double-circuit boiler unit with temperatures up to +80 C and pressure up to 2 atm.
- PN 10 - thin-walled PPR - products, used if the unit supplies water to the “warm floor” system. Working temperature no more than +45 C and pressure up to 1 atm.
- Fittings for connecting PPR pipes in quantities according to the design diagram.
- Soldering kit for welding PPR pipes.
Polymer pipeline systems can be used in both open and closed circuits, taking into account the coefficient of thermal expansion. Usually, compensation loops are installed for this purpose.
Security group
The security group consists of three elements connected in series or to one housing:
- An emergency safety valve that allows you to discharge excess coolant when the pressure in the system increases. The discharge can be placed in a transparent container (for example, a plastic bottle). This will make the device safer and will notify you that an emergency has occurred (even if no one was home).
- Automatic air vent - removes air from the coolant, which, if present in the heating system, can render it inoperative.
- Pressure gauge - allows you to visually monitor the coolant pressure in the supply line.
The safety group crashes into the supply line immediately at the outlet of the heating boiler. This is done in order to primarily protect the boiler, which has the highest temperature.
If it is possible to install protection directly on the boiler body, then this feature of the heating device should be used.
The safety group is installed strictly vertically, and it must be located above the level of the heating boiler.
There should be no shut-off valves between the safety group and the boiler. After all, if you accidentally close the tap, thereby isolating the protection from the rest of the heating, you can cause a rupture of the boiler or other elements of the system.
Evgeniy FORUMHOUSE user
Ignorance, inattention, haste, fatigue and other human factors can lead to accidents. For example, I changed the pressure gauge, but forgot to turn the tap, etc.
An additional automatic air release valve should be installed at the highest point of the system. Air will definitely enter the system during its refueling (refueling), and this device will help stabilize the operation of the system, avoid stagnation of the coolant due to air accumulation and extend the life of the circulation pump.
krim FORUMHOUSE user
We install the air vent at the top point of the system. It doesn't have to be on the security group.
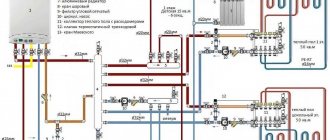
Boiler piping schemes with polypropylene
Efficient and safe operation of the boiler unit can only be achieved if it is properly tied. There are differences for schemes with natural and forced circulation, both in the number of elements and in the maximum coolant pressure.
Natural circulation
This is the simplest scheme, it can be done independently. The operating principle is non-volatile. A pump is not required to move the coolant along the circuit; the process uses the gravitational principle, due to the temperature difference between cold and hot water.
This scheme is most preferable for heating small-sized and low-rise residential buildings. The advantages of schemes with natural circulation of heating include:
- Simplified installation and strapping;
- non-volatility, operation without power supply, it is allowed to use rechargeable batteries for the operation of safety automatics;
- compactness of the boiler and auxiliary equipment;
- low cost of system maintenance;
- high maintainability;
- reliable operation, since there is no equipment in the thermal circuit that can break.
Forced circulation system
This heating system is used in houses with large and multi-level heating loads. It allows you to control each circuit separately, for example, in a hot water supply system, high-temperature heating in radiators and low-temperature heating in a “warm floor” system.
This option is the most expensive, but its payback period does not exceed 4 years, since the system operates with increased efficiency in the power range from 20 to 100%, which can provide annual fuel savings of up to 30%.
The disadvantages of such boilers include:
- The need to have a reliable source of electricity.
- The need to balance heating circuits.
- A complex executive heat supply circuit requires additional expensive elements in the form of a hydraulic arrow, circulation pumps for each circuit and shut-off and control valves.
- Complex installation and commissioning requires the participation of a qualified installation organization.
- High price.
Emergency circuit
Protective equipment is installed in the volatile circuits of a double-circuit boiler, which should protect the boiler structure in the event of a sudden power outage. In practice, several effective protective schemes are used:
- An uninterruptible battery-powered power source used to operate the circulation pump, fan and security systems.
- Installation of a gravity circuit that provides additional heat removal of thermal energy when the circulation pump is stopped.
- Hybrid circuit with installation of an uninterruptible current source and a protective gravity circuit.
Scheme with a wall-mounted boiler
The wall-mounted design of a gas boiler is most suitable for small residential buildings. For large objects, to increase the range of modulation of the object's heat supply modes, it is possible to install several such units, each of which can carry the load along the heating and hot water circuits.
This scheme is especially preferable when the floor heating scheme is made of heating devices operating in different temperature conditions: “warm floors” and bimetallic radiators.
In a house in which there is a large load on the hot water supply, an external indirect heating boiler is integrated into the thermal circuit with a wall-mounted single-circuit gas boiler.
Such schemes make it possible to remove the high temperature of the coolant and the pressure of the medium in the circuit, established by the rules for the operation of polypropylene pipes.
Pumping and mixing unit
It is possible to construct a heating system according to a combined scheme in a private house using a pumping and mixing unit. The design with it is the most effective, but will be more expensive compared to using a 3-way valve, although the operating principle is the same.
Cooled water from the return pipe dilutes the hot coolant, and the presence of balancing taps allows this to be done in the required proportions.
This unit comes in different configurations. It depends on the purpose and cost of the equipment. The standard device includes:
- thermostatic valve;
- immersion temperature sensor;
- balancing valve with fixing spring valve;
- circulation pump;
- immersion thermometer;
- threaded sleeve;
- bypass and shut-off valve;
- drain and ball valve;
- air vent;
- bypass bypass.