Read the publication about which insulation is best to choose for installation under siding, but for now let’s talk about the rules for fixing basalt slabs.
Stone wool is a fibrous material with high insulating characteristics, due to which it perfectly retains heat and sound. To increase comfort inside the house, you simply need to correctly fix the mini-slabs on the surface. In this article we will look at how to attach basalt insulation to a wall to achieve maximum thermal insulation effect.
Scheme for insulating the walls of a frame house with mineral wool
Scheme of the wall of a frame house with mineral wool insulation.
The scheme of insulation of the walls of a frame building is similar to a pie consisting of separate layers. The basis of the cake is a heat insulator, in our case it is mineral or stone wool.
Pie of walls of an insulated frame house
The wall pie of an insulated frame house consists of the following layers:
- Interior finishing, which is performed using plasterboard, OSB boards or other similar material.
- Vapor barrier layer.
- Thermal insulation layer, mineral or basalt wool. For a frame house, three layers of standard 50 mm insulation are used.
- Waterproofing layer.
- Wind and noise protection.
- Exterior finishing: siding, lining, finishing slabs or any other finishing.
The insulation is located between the frame sheathing, to which the external and internal OSB boards are attached.
Facade insulation
If the house has already been built, but its insulation is not enough, you can use facade insulation or perform external wall insulation, which was already mentioned above. Guides made of wood or metal are placed on the façade in increments equal to the width of the insulation slabs - mineral wool. Then a hydro and vapor barrier is laid. Sheets of mineral wool are placed between the guides and secured with a stapler or glue.
The insulation from the outside is covered with waterproofing and external finishing of the facade. This finishing can be siding, lining or facade slabs.
Finishing
The final finishing after the main stage of laying the insulation consists of painting the already plastered walls. For this purpose, primer paint is used. To improve adhesion between the wall surface and the paint, the plaster is treated with fine sandpaper.
The final stage will allow you to solve two problems at once: protective and decorative. More common are plastered facades, which are applied to insulation secured using the “wet” method. If the basalt wool is installed using the ventilated facade method, I cover it with siding.
How to insulate a frame-panel house for winter living
For complete insulation, in addition to the walls, you need to insulate the floor, ceiling, door and window openings, roof and utility lines into the house.
Scope of work:
- Surface preparation. Elimination of all cracks and cracks by sealing with jute or tow with PVA glue and sealing with waterproof sealants. If repairs have not been carried out for a long time, then it is advisable to open the base of the structures, since existing defects may not be detected by a simple external inspection. Cleaning the walls of dirt, loose old coatings, leveling the surface by plastering, applying a primer.
- When using slab insulation, it is recommended to lay the material in the sheathing. When used for siding facade cladding, standard elements that come with the panels are used. The heat insulator is placed tightly between the sheathing elements, moving in the direction from bottom to top. In the locations of window and door openings, solid slabs are installed, cut to the required dimensions. Thermal insulation of the outer corners of the building is carried out with the obligatory bandaging of the slabs; long vertical joints and cross-shaped joints are not allowed. The slabs are fastened with adhesives and dowels with wide heads. It is imperative to take into account the characteristics of heat insulators. For example, for mineral wool slabs, vapor barrier devices are required, and after the insulation layer there is a ventilation gap and a windproof waterproofing membrane.
- External cladding with cladding materials.
- It is recommended to replace wooden windows with single-chamber double-glazed windows with two glasses. Doors are installed using sealing gaskets.
- Floors and ceilings are insulated using waterproofing and vapor barrier membranes.
When choosing a method, how and with what to insulate a panel house, when living in a dacha only in the summer, it is enough to take care of the strength of the structures. A good option is cladding with environmentally friendly chipboards or plasterboard.
Technical characteristics of basalt wool
The name already tells you what cotton wool is made from. This is the mineral basalt. Additionally, similar rocks from the basalt group are used. Cotton wool is obtained by melting rocks.
And to make thin basalt fibers more fluid, 10–35% of charge or limestone is included in the melt. This transforms the fiber structure and gives it protection from elevated temperatures and the aggressive influence of external factors.
Technical characteristics of basalt wool:
- Biological resistance.
- Vapor permeability. Condensation will not form as the slabs remove moisture. Vapor permeability index 0.3 mg/(m h Pa).
- Fire resistance. Even at a temperature of 1000 ℃, the insulation layer will not melt.
- Over time, the material will not change shape. The compressive strength at a deformation of 10% can be 8–60 kPa. It all depends on the manufacturer.
- Water permeability is only 2–5%.
- The thermal conductivity coefficient is very low - 0.032–0.045 W*/mK.
- The density of basalt wool varies, it all depends on the scope of application. Insulation of pitched roofs with basalt wool is carried out with a material with a density of 100 kg/m3. This way the material will not slip and the fibers will not blow out. In general, the density range is as follows: 40–200 kg/m3.
Ceiling insulation
Ceilings are different. In residential buildings, this can be a concrete slab or a suspended ceiling.
As for the hemmed ceiling, to insulate the ceiling with basalt wool, you can use a material with a density in the range of 40-75 kg per cubic meter .
Insulating the ceiling of a cold attic
In a bathhouse and other small-sized buildings for periodic use or household purposes, the ceiling can also be decked, which means: a thin layer of boards separates the interior from the cold attic. In order to at least somehow protect against the cold in the latter case, insulation is placed or poured on the flooring boards from the attic side. In particular, it is possible to insulate the ceiling of a cold attic with basalt wool.
When it comes to a suspended ceiling, it should be remembered that its load-bearing capacity is not too high, so the insulation should be as light as possible. For example, you can use basalt wool of minimum density - from 15 kg per cubic meter .
As mentioned above, mineral wool cannot be left without protection from moisture, which boils down to the fact that there must be a vapor barrier on the bottom and a one-sided permeable membrane on top.
Thermal insulation technology
The insulation technology includes four steps:
Next, we will consider this process in order.
Frame wall diagram - there must be a vapor barrier on both sides of the insulation
Stage 1: vapor barriers
To protect thermal insulation from moisture, attach a vapor barrier membrane to the inside of the walls as follows:
| Illustrations | Description of actions |
Materials. You will need:
| |
Tape installation:
| |
Membrane installation:
| |
Arrangement of the joint of the canvases:
According to this principle, the frame is completely covered with a vapor barrier on the inside. |
Stage 2: installation of mineral wool
Do-it-yourself insulation of a frame house is done as follows:
| Illustrations | Description of actions |
Preparing mineral wool:
| |
Installation of insulation:
|
This completes the thermal insulation of the walls.
Stage 3: installation of wind and moisture protection
To avoid the penetration of cold air and moisture into the “pie”, a hydro-windproof membrane must be secured to the outside of the walls. The work is carried out like this:
| Illustrations | Description of actions |
Materials. You will need:
| |
Membrane installation. The operation is performed in the same way as installing the membrane from the inside:
|
Stage 4: wall decoration
External wall cladding is carried out as follows:
| Illustration | Description of actions |
Materials. For cladding you will need the following materials:
| |
| Installation of sheathing. Secure the slats over the membrane using self-tapping screws. Make the distance between the screws about 500 mm. | |
| Installation of OSB. Fasten the OSB sheets to the sheathing with self-tapping screws at 250 mm intervals. When installing sheets, observe the following rules:
| |
| Installation of sheathing. To cover OSB walls with your own hands with façade material, you need to secure the slats according to the scheme described above. | |
| Wall cladding. To complete the work, cover the walls with any façade material. The instructions for performing this operation are standard, i.e. the work is carried out in the same way as when finishing ordinary walls, so we will not consider it. |
There is also an economical option for wall cladding. Its essence lies in the absence of OSB boards. As a result, the facade cladding is carried out immediately after the installation of the hydro-windproof membrane and installation of the sheathing.
This technology really allows you to save money, however, the walls are less durable. Therefore, if you are not very limited in finances, it is still better to sheathe the frame with OSB.
Now all that remains is to sheathe the walls from the inside. The work is carried out absolutely according to the same scheme as the exterior cladding:
| Illustrations | Description of work |
| Installation of sheathing. Slats are attached to the racks, which provide a gap between the vapor barrier and the sheathing. The lathing can be either vertical or horizontal. The position of the slats depends on the location of the finishing material. | |
| Wall cladding. The finishing material is attached to the sheathing - it can be plasterboard, OSB, lining or any other covering. |
Here, in fact, is all the information about how to insulate the walls of a frame house with mineral wool.
Application: what is it used for, as insulation and other options
For chimney
The purpose of the chimney is to provide heat to the room. But do not forget that chimneys also need insulation. Basalt materials, which are suitable for insulating stainless, ceramic, asbestos, and brick pipes, are widely used to solve this problem.
Exiting the chimney pipe through the wall. Photo by NZSK
Insulation is important for several reasons:
- fire prevention;
- increase in service life; sudden temperature changes, exposure to alkalis and acids can lead not only to the destruction of the pipe, but also the surfaces and elements surrounding it: ceilings, walls, floors;
- heating the surface of the pipes negatively affects surrounding objects in the room, it also affects humans, thermal insulation prevents an unfavorable effect and ensures normal heat exchange;
- reducing the release of condensate, which can form harmful chemical compounds after reacting with other substances in the pipe.
The choice of type of heat insulator depends on the design of the chimney, its features and the wishes of the owners regarding thermal characteristics.
Cylinders and shells are used in home and industrial heating systems, used for external and internal insulation, at temperatures not exceeding 300 degrees. The cylinders have a longitudinal seam for ease of installation; the products are fastened with bandages made of galvanized or stainless sheet steel or binding wire made of black (diameter 1.2 mm) or stainless steel (2 mm). The joints are insulated with aluminum tape.
Plates and rolls are intended for structures whose contact temperature will be 450-700 degrees; they are recommended for use for pipes with non-standard diameters; they are not very suitable for structures passing through walls. For passage units, it is recommended to choose high-density insulation (more than 100 kg/cub.m.); foil plates are suitable for internal and external insulation of single-wall pipes.
Basalt cardboard is excellent for insulating brick chimneys and can withstand temperatures up to 900 degrees. Foil cardboard is recommended for external insulation.
The chimney pipe passes through wooden surfaces. Photo StroyDom
There are several recommendations that, if followed, will allow you to perform high-quality thermal insulation with your own hands:
- a protective screen is a mandatory design element if materials without foil were used for insulation;
- when laying mats in several layers, the joints must be covered with the following layers;
- passages through wooden surfaces should be insulated with cotton wool no less than 50 mm thick, the distance from the load-bearing beams should be at least one meter;
- when laying insulation in several layers, each subsequent layer should be laid with an offset of 180 degrees around the circumference and by 150-200 mm. by lenght;
- The thickness of the internal insulating layer is no more than 40 mm, the external one - up to 100.
In addition, you should adhere to some rules when working with systems made of different materials:
- Asbestos. Chimneys made of this material require external insulation. Sheets or rolls 30-50 mm thick. secured with special staples.
- Ceramics. The pipes are insulated with materials 30-50 mm thick, fastening is carried out using clamps.
- Steel. To organize the insulation, two pipes with different diameters are used: a larger one for the outer surface, a smaller one for the inner surface. One pipe is placed inside another. The resulting gap is filled with material. The end of the structure is additionally insulated. An alternative to the first three stages is to purchase ready-made sandwich pipes, which are characterized by low weight, high heat resistance and excellent heat-resistant characteristics.
- Brick. For insulation, mats or rolls are used, which are cut into layers with the required dimensions, they are fastened with tape, a protective screen is mounted on top, and, if necessary, the surface is plastered or painted. basalt insulation is also used for insulation in penetrations, the gaps between pipes and structures are filled with stone wool, for the manufacture of fire-resistant grooves, which serve to protect wooden surfaces located nearby.
For furnaces
The stove is a dangerous object, so proper installation and protection of surrounding objects from its heat is important. To solve this problem, various materials are used, including those based on basalt. Some recommendations for organizing a protective screen are presented in the corresponding article.
Insulation, how to insulate
The versatility of basalt wool allows it to be used for insulation of various structural elements of buildings. But each specific case has its own recommendations and features of the work. Isolation of individual premises is of particular interest to Internet users; the specifics of their isolation will be discussed further.
Cold attic ceilings
An uninsulated attic space is the most vulnerable part of a structure . About 20-40% of the thermal energy needed by residents “exits” from the house through the attic floors, the figure varies depending on the materials used in the construction of the rafter frame and roofing. Insulating the ceiling in houses with cold roofs will significantly reduce heat loss and, accordingly, save on home heating costs.
Before you begin choosing insulating materials and performing insulation work, you should decide on the purpose of the attic space. Insulation is carried out if the attic will serve as a non-residential space, for example, as a storage room. If you plan to make the attic heated, then it is necessary to insulate the roof.
Basalt insulation IZBA Standard is suitable for attic insulation. Photo source here
The roofing pie from the inside out will include the following layers: vapor barrier (a vapor-proof film is used), insulation (the vapor permeability of which should be higher than that of the vapor barrier) and waterproofing (since basalt wool does not absorb moisture, a regular waterproof film is suitable here). But this is another task, so let’s return to the insulation of attic floors, which is performed in two ways:
- 1) insulation from the attic side;
- 2) installation of insulation on the ceiling, i.e. from the side of the room.
1) The first method is the most common, since the process does not require special efforts from the performer . In addition, it is possible to save on materials; there is no need to cover the insulation with vapor and waterproofing. The materials dry out on their own when the attic is ventilated.
The insulation technology depends on the type of floor:
Reinforced concrete. The work includes several stages. Firstly, the surface is repaired and leveled. Secondly, a vapor barrier is performed, the canvas is placed with approaches to the walls. Thirdly, the insulation (it is more convenient to use rolls) is laid in two layers, the seams of the lower layer are covered with mats located in the second row - the arrangement is staggered.
Wooden. The process is carried out in several stages. Insulating materials are placed in the space between the joists, or more precisely in the cells between the joists. Before laying the insulation, a vapor barrier material is placed in each cell, extending onto the joists and walls. The insulation is cut, each layer should be 2 cm larger in length and width than the dimensions of the cell. The height of the insulation should be equal to the height of the logs. To insulate the attic space, it is recommended to choose materials with a density of no more than 30 kg/cubic meter.
2) Insulation technology from the room side, i.e. Ceiling insulation is more difficult to implement, but sometimes it is the only one possible, so we will consider it. Cotton materials are extremely rarely used to solve this problem. The installation process is very labor-intensive; it requires the construction of a frame, the presence of which will significantly reduce the height of the ceiling. As a result, there are two development options: either carefully consider ways of additional fixation of materials and their fasteners, or pay attention to other types of insulation.
Ceiling in the bathhouse
Basalt wool is ideal for insulating bathhouse elements. There are baths with and without an attic. In the first case, the quality of the ceiling insulation is not so important, since it is possible to focus on the insulation of the attic and roof. In the second, you need to approach the work as responsibly as possible .
Ceiling insulation is carried out during the construction stage. The choice of insulation also depends on the type of ceiling (floor, hemmed, panel). Basalt wool is suitable for any type of insulation. But flooring is the most popular, as it is budget-friendly. It should be remembered that the vapor barrier is installed closer to the room, and the waterproofing is installed on the attic/roof side. Each type of ceiling is an individual sequence of layers, details here.
False ceiling in the process of installation. Photo StroyDom
A comparison of basalt wool with other thermal insulation materials for ceilings, as well as recommendations for choosing the thickness of the material, are presented in a separate publication.
Many manufacturers offer special insulation for baths, so there will be no shortage of options to choose from. Some options for basalt insulation are presented here.
For facade
Insulation of facades is carried out for several reasons:
- heat conservation, therefore saving energy and money;
- removal of the place where condensate falls and settles from inside the wall material beyond its limits;
- the ability to design facades.
Rockwool insulation Rockfacade 100x600x1000 mm 1.2 sq.m. Photo Petrovich
Insulation of facades with basalt wool is carried out in three ways:
- increase the thickness of the walls;
- construct a ventilated façade by constructing a “pie” of insulation, a ventilation gap and waterproof sheet material;
- to carry out the organization of a non-ventilated facade by installing insulation and plastering the surface, this technology has an alternative name - the “wet” method, which we will consider in more detail in the next paragraph.
The cost of additional materials is higher than the price of insulation, so the first method is not suitable for solving problems. Thus, now we should pay attention to the technology of organizing a ventilated facade.
Preparation includes performing a number of tasks:
- removal of various objects and communication systems;
- cleaning the surface from old plaster and dirt;
- sealing defects: cracks, grooves, seams using foam;
- padding;
- treatment with a special compound to increase adhesion.
Installation of fiber insulation requires the formation of a frame , the distance between the guides of which should be 10-20 mm. smaller, the width and length of the slabs (! in this case, it is preferable to use insulation slabs). The height of the guides should be slightly greater than the thickness of the material to form a ventilation gap.
The stone wool is fastened using dowels with wide plastic rings at the ends (fungal dowels). A windproof membrane is placed on the heat-insulating materials , the sheets of which are overlapped - up to 100 mm, the joints are taped. Then a counter-lattice is formed , to which the finishing trim is attached; siding has been particularly popular lately.
Under plaster
The installation of a non-ventilated façade should be carried out at temperatures from +5 to +30 degrees, without wind or precipitation, in the shade from direct rays of the sun. The process includes the following steps:
- preparing the facade for work, removing old plaster coating, removing stains and soot, covering grooves and seams with adhesive foam, repairing cracks and other defects, removing dust;
- applying a primer, drying the surface;
- installation of the base profile;
- “laying” the insulation (the optimal layer thickness is at least 100 mm) begins with applying an adhesive composition to the materials and gluing the layers of the first row, starting from the end of the building; insulation boards must be placed tightly to each other, avoiding gaps;
Reference. Some experts recommend performing insulation in two layers: the first - soft materials, to level out uneven walls, the second - hard slabs with a density of 130 kg/cub.m., making it easy to apply glue and plaster.
- additional fixation of the insulation with dowel-fungi is carried out after three days; each slab is optimally fastened with 5 dowels, the caps of which must be protected from moisture with a solution;
- priming the surface of the insulation and applying a plaster or adhesive composition;
- location and fastening (by pressing into the solution) of the reinforcing mesh , which is joined with an overlap of 100 mm, profile corners are used for the corners, the result is a so-called “armor”;
- plastering, for this it is necessary to select a plaster that does not chemically conflict with the composition of the insulation and the resulting “armor”; the work is carried out after the reinforcing layer has completely dried;
- surface priming;
- finishing.
For floor
Floor insulation is carried out in several cases:
- insulation of the base above the ground floor, basement, which are most often not heated, and, as a result of the overlap, do a poor job of saving heat;
- for heat and sound insulation of interfloor ceilings;
- for arranging attic floors.
The thickness of the insulating layer varies from 50 to 200 mm . depending on the operating conditions, for example, for insulating the foundations of houses in the southern regions and insulating interfloor ceilings, it is recommended to use a 50 mm insulator; for high-quality floor insulation in a house intended for year-round use - 200 mm.
It is important to choose materials that are optimal in density . Multilayer structures in residential premises are created using rolls with a density of 35-40 kg/cub.m. or slabs no more than 90. Insulation of a wooden floor is carried out in two layers, roll materials are used, the use of a vapor barrier membrane and waterproofing film is mandatory.
To work with a concrete floor on which a screed is planned, you should choose high-density slabs (from 150).
The insulation process begins with dismantling the old coating and cleaning it from debris and dust. If defects are identified in the surface of the rough foundation, a set of works is carried out to eliminate them. Leveling the base is done using a screed, after which it has completely dried, materials for water and wind protection are laid.
For dense and even installation of insulation, it is recommended to install joists/guides , the distance between which should not exceed one meter. The insulation is cut with a small margin (10-20 mm) around the perimeter to eliminate gaps. Then a vapor barrier is performed, the joints of which are closed with tape. Afterwards, using self-tapping screws, a board or plywood is laid , which serves as a substrate for the finishing coating. The next stage is laying the finished floor, it is attached to the joists.
For walls
The effectiveness of the insulation performed depends on the correctly selected materials. The thickness of the insulator layer depends on the climatic zone of the location of the house, apartment and the material of the walls. For central Russia, materials with a thickness of 50 mm are used for internal insulation, for facades - 100, for frame walls - 150-200. Recommended density:
- for frame buildings it is recommended to use materials of 50-75 kg/cub.m.;
- walls with a gap for ventilation are insulated with materials with a density of 80-130;
- the “wet” method requires the use of insulation 130-160;
- concrete facade - 150-175.
Depending on the material of the walls, the technology varies, so we list the stages of work for each case:
Wooden. Basalt wool is laid in a lathing on a previously prepared wall . Preparation involves removing communications, clearing debris, you also need to seal the gaps between logs or beams; sealants, mastics, resins, polyurethane foam, fibrous materials, a mixture of sawdust and PVA glue are suitable for this. to the wall , a sheathing is formed, and windows and doors are tied. Insulation is placed in the cells of the sheathing, which is covered with a vapor barrier film, the structure is covered with plasterboard, then cladding can begin.
There is also a frameless method of attaching insulation; it is carried out by analogy with the “wet” method.
Frame. A distinctive feature is that the insulation is located inside the wall, and not from the inside. As a result, work is carried out in the following order:
- a vapor barrier is attached to the frame posts;
- the film is covered with plasterboard or OSB sheets;
- insulation is placed between the racks, the thickness of which in most cases is 150 mm;
- the structure is covered with a windproof membrane;
- a counter-lattice is formed to create a ventilation gap;
- façade cladding.
Brick. A sheathing is formed, the insulation is placed in the cells, a vapor barrier is attached with the processing of the joint seams, a counter-lattish is filled, onto which the sheathing material is fixed. In accordance with this technology, work is carried out with concrete and block walls.
Sound and noise insulation, acoustic
Stone wool is not a soundproofing material, but has excellent sound-absorbing properties. The most effective for solving these problems is cotton wool with a density of 50-80 kg/cub.m. Leading manufacturers provide special product lines designed for sound insulation, for example, ROCKWOOL Acoustic Butts, Technoacoustic (from TechnoNIKOL). Materials are actively used to fill frames . Basalt slabs eliminate the so-called “drum effect” in frame structures.
Types of basalt wool
The first classification of basalt insulation is related to the form of release. The material comes in rolls, slabs and granules. The first resemble soft mats. The density of wool in them is minimal.
The rolled version can withstand external influences on walls and in attic floors. The maximum amount of air in the rolled wool makes it as warm as possible. Sounds stick best in loose mats. Tile insulation is inferior in heat and sound insulation.
However, you can adjust the indicator by increasing the thickness of the wool layer. In its rigid form, it is useful under floating floor screeds, in the ceilings of high-rise buildings and on facades covered with a wet system.
Insulation boards are divided according to their rigidity. There are soft ones. They are only slightly denser than mats. The second option is semi-rigid slabs. Maximum density for hard ones. There are also lightweight slabs. They differ from rolled cotton wool only in the form of release.
Rolls and slabs are purchased mainly by private traders. On large objects it is more convenient to use granulated wool. It is blown into the walls using pneumatic devices, similar to ecowool produced by recycling waste paper.
The release form also includes the geometry of basalt wool. For chimneys and pipelines, for example, hoses are produced. They have gaps to allow the insulation to stretch while being placed on the pipes. The gaps are called seams. So from the point of view of tailors, sleeves made of basalt fiber are just an unstitched pattern.
Any variety of this material can be foil or not. The additional layer of aluminum, as mentioned, protects the raw material from water. If the humidity around the insulation is constant and high, vapors are trapped between the fibers. Accordingly, the proportion of air in the wool decreases, and the noise and heat insulation properties decline.
Foil, like basalt, is non-flammable. Attaching the metal layer to the wool, like the resins that glue it, is less resistant to fire. Therefore, instead of adhesive between mineral threads and foil, it is recommended to choose wire stitching.
It makes the product more expensive and is less common. You can search in Rockwool basalt wool. Of the Russian manufacturers, the assortment is provided by TechnoNIKOL. Basalt wool, as you can see, can be more or less flammable. This is reflected in the product labeling. The letter “G” is placed, and next to it is a number from 1 to 4. One is the best indicator.
“G4” on the packaging is evidence of the maximum flammability of the insulation. However, on basalt wool there are no “3” and “2”. “G1” is preferably marked with a crossed out letter. This is the designation for absolutely non-flammable cotton wool.
It is difficult to distinguish insulation by the quantity and nature of the bonding resins. There are no special marks on the packages. Sellers rarely have information. You can find out whether the material is made in accordance with GOST, or only with technical specifications. The latter has loopholes that allow you to “play” with percentages and the name of bitumen resins.
Comparison with mineral wool, ecowool and more
Basalt wool is not the only type of mineral insulation; slag and glass also . Types are often compared according to basic characteristics in an attempt to determine which material is better. But the range of products for thermal insulation is not limited only to mineral materials. Therefore, basalt wool is also compared with other insulation materials. Detailed information is provided here.
Types of basalt insulation
Basalt insulation is a fibrous heat insulator, a type of mineral wool. It is produced from volcanic rocks - basalt, gabbro, dolerite. Minerals are melted to a temperature of 1500 ° C in a furnace and passed through a filler feeder with tiny holes. Threads with a diameter of 3-8 microns, hardened under a strong air flow, are formed into a carpet and treated with a binder based on urea, phenol-formaldehyde resins, bitumen or bentonite clays. The content of organic compounds is no more than 2%. The fiber preform is then cut into sheets.
Basalt wool is treated with water-repellent additives - oil and organosilicon compositions that impart water-repellent properties.
The industry produces products with a layered vertical or horizontal structure, spatial shapes, and combined density. To insulate flat surfaces, insulation materials are manufactured in the form of rolls, slabs, and stitched mats; for curved surfaces, cylinders and segments are used. Additionally, the products are covered with aluminum foil, kraft paper, and fiberglass to increase the heat-shielding qualities of the insulation.
GOST 9573-2012 regulates the types and properties of basalt insulation. According to it, slabs are marked by hardness and density:
- Soft PM with a specific gravity of 40-50 kg/m³;
- Semi-rigid PP – 60-80 kg/m³;
- Hard pancreas – 100-140 kg/m³;
- Increased hardness PPZh – 160-200 kg/m³;
- Solid PT – 220-300 kg/m³.
Soft slabs PM - for thermal insulation of unloaded horizontal, inclined and vertical surfaces. In frame houses these are floors, joist floors, pitched roofs, and internal partitions.
Plates of the PP and PZh brands are used to insulate external walls, roofs, and ceilings.
Rigid slabs can be loaded with plaster over a reinforcing mesh and a concrete screed can be installed. They keep their shape well.
The densest products are used in industry for heat and sound insulation of enclosing structures and equipment.
All types of insulation are used as sound insulators.
Insulation of the under-roof space of a pitched roof and attic
There are various reasons why owners insulate the under-roof space of a house or bathhouse. In one case, the temperature inside this space is equalized; in summer it is not so hot, in winter it is not so cold, while the attic itself can remain unheated.
In another case, this is a residential or at least heated space, which is insulated in order to prevent heat loss during the cold season.
In any case, you need to choose the right heat insulator parameters. It seems that above we did not clearly talk about why we do not give specific figures for the thickness of the layer that is used for various structural elements. And it’s not just a matter of thermal engineering calculations, which have definitely already been mentioned. Even if the dew point is shifting, the choice of layer thickness will depend on the specific climatic conditions of the area .
But the right density matters. Since we are talking about pitched roofs and attics, they are considered non-load-bearing surfaces and allow the use of the least dense wool. For roofs this is a density from 25 to 55 kg per cubic meter , for attics the minimum density is 35 kg per cubic meter.
For pitched roofs, you can use basalt wool in rolls.
Installation of slabs on the facade
The whole process is divided into several successive stages
It is important to adhere to them and not miss a single point. This:
- Facade preparation work.
- Fastening basalt insulation to the wall.
And now in more detail.
Preparing the walls
Before sheathing a wooden house, it is important to perform a visual inspection of the facade. Look at the walls, base and roof
What to do:
- Are there visible cracks and damage at the junction of the foundation with the first crown, in the walls, door and window frames.
- Are there any curvatures or bulges in the walls? If necessary, cut them down, lay guide bars on top, with a cross-section of 4x4 cm and a length of 2 m.
- Cover the base and pediment with waterproofing materials. Roofing material is suitable for this as a sheet waterproofing material, or liquid-type coating compositions: liquid glass, bitumen mastic.
- Clean the facade, remove dirt and old cladding, if any.
After all the preparatory work, you can begin installing the basalt insulation.
Installation of slabs
There are two options - dry and wet. When working with wood, it is better to use dry. The idea is to fix the slabs to the wall using dowels with an umbrella.
With wet insulation, the slabs are mounted on a prepared adhesive composition of quartz sand or silicone (this is about wood). Universal adhesives are suitable for cement or brick. Insulation of walls with basalt slabs involves the use of slabs with a density of 90 to 135 kg/m3.
Particular attention is paid to the joints. They need to be well sealed to prevent the formation of cold bridges.
After installing the slabs, you can begin finishing the facade. Wall insulation with basalt slabs and siding are often used. In this case, a frame is created on the surface of the walls along the width of the slab, the mats are installed in the opening, after which the siding is installed.
You can attach basalt slabs without using a frame. This option is used if the façade is to be plastered.
Insulation of walls with basalt slabs, technology without frame:
A horizontal strip is installed along the base. It will allow you to install the bottom row of slabs without allowing them to move. The row will be even. Fixing the insulation to the wall starts from the corner of the house. A row is made around the entire perimeter. In some ways the method is similar to strapping. The first row or belt is formed. Then, according to the same scheme, the second row is fastened using the same dowels or glue
Important! The second row is staggered relative to the first. A layer of vapor barrier material and a mesh for reinforcement are laid on top of the slabs
All that remains is to plaster the surface and paint. Decorative type plaster (bark beetle, fur coat) can also be used.
This completes the work. As you can see, insulating walls with basalt wool can be done independently, without special equipment or outside help. The house will become much warmer, quieter and more comfortable. And to protect it as much as possible, the roof is additionally insulated. In this case, there is no doubt that replacement can be done after half a century or more.
Preparation
Installation of insulation is carried out in two ways. These are the following technologies:
- wet facade;
- on the frame according to the type of ventilated structure.
For work, it is better to take rectangular or wedge-shaped slabs, since they are easier to join together. Preparation includes the following important points:
- removal of various communication systems, objects (nails, fittings);
- cleaning the surface from a layer of plaster and dirt;
- sealing all defects and cracks on the surface using polyurethane foam, tow, and felt;
- if there are differences in the thickness of the facade, it is necessary to adjust them using different thicknesses of low-density basalt insulation;
- priming walls against the development of mold and mildew;
- treatment with a special surface composition to increase adhesion.
Correctly completed preparatory work will help install the thermal insulation system efficiently and quickly. To complete the event, you need to prepare the following products and tools in advance:
- insulation in the form of basalt slabs or cotton wool;
- glassine;
- polyurethane foam;
- wooden slats;
- knife and construction nails;
- grinding float;
- hammer.
How to find out the recommended thickness of the basalt layer
There is a formula by which you can find out the optimal thickness indicators. Then the thermal insulation will fully perform its functions and the funds will not be wasted. To begin with, you should find out the following indicators:
- R – thermal resistance. It is designated m2*K/W;
- λB – thermal conductivity of basalt wool (indicated on the packaging from the manufacturer). Let's choose average values of 0.45 (W/m2 * K).
Index B indicates the possibility of using insulation for rooms with high humidity. R – thermal resistance (the properties of a material to prevent heat from passing through it. The higher this indicator, the better the heat is retained inside.
On average, for walls this coefficient is 3.3 m2*K/W, for a roof – 4.95 m2*K/W. Based on the formula (R* λB), you can calculate the thickness of the wool layer for wall insulation: 3.3 * 0.45 = 1.485 m = 14.85 cm. If we round, we get the optimal thickness of the basalt layer of 15 cm.
For the roof, the indicators are as follows: 4.95 * 0.45 = 2.2275 m. By rounding, you can get a thickness of 22.3 cm. Now that the thickness has been decided, you can insulate the facade with basalt slabs, the roof or walls from the inside.
Subtleties of application
Low-density basalt wool is used for facade finishing, which is due both to its high moisture strength and thermal efficiency, and to the ability to significantly prevent a decrease in the internal area of the building, which inevitably occurs with internal wall cladding. Installation work should be carried out only on a dry, warm day (air temperature from +5° to +25°C), so that the humidity level does not exceed 80%. It is important that during the installation of low-density facade insulation, direct sunlight does not fall on the treated surface. Laying thermal insulation (insulation for a basalt facade) begins with preparatory work.
Insulation for walls of frame houses
The energy efficiency of houses built using frame technology is achieved by using heat insulators with low thermal conductivity. The set of rules SP 31-105-2002 recommends the use of materials in which this value does not exceed 0.1 W/m°C.
In this category:
- Stone (basalt) wool;
- Glass wool;
- Ecowool;
- Polystyrene foam (expanded polystyrene).
Mineral wool
To insulate the walls of frame houses, stone or glass wool is used. These are fibrous materials with a large number of air cavities. The porous structure ensures low thermal conductivity of the insulator, since heat transfer in gases is much lower than in solids.
Mineral wool is produced from the melt of basalt rocks or broken glass. Hydrophobizing (water-repellent) additives are added to the composition. Fibers with a diameter of 6-8 microns are formed in a centrifuge under the influence of a strong air flow. A carpet made of thin threads is treated with an organic binder based on phenol-formaldehyde or urea resins. Then it is cut into sheets 50-2000 mm long and 400-1000 mm wide. The thickness of finished products is up to 200 mm.
Slabs are marked according to density from PM 40 to PT 300. Soft, semi-rigid, rigid and hard insulation materials are used in various fields where the materials are subject to requirements not only for thermal conductivity, but also for strength and heat resistance. GOST 9573-2012 specifies the regulatory characteristics of thermal insulation made from mineral raw materials.
Mineral wool is a non-flammable material, so it is recommended for installation inside the walls of frame buildings.
Foam insulation
Thermal insulation products made from foam plastic - gas-filled plastic - are widely used to insulate the walls of frame buildings. Regulations allow their use for fastening to an external surface, since the initial raw material for production - polystyrene - is a flammable substance. Plaster or non-flammable cladding is a fire safety condition when using such insulation.
Polymer granules are catalyzed at high temperature and pressure with a mixture of freon and carbon dioxide. A mass similar to whipped cream is formed into products with a microporous structure by extrusion - squeezing through molds.
The material has low thermal conductivity and water absorption, durability, biological stability, lightness and strength. Marked depending on density. The lightest are PPS 10 slabs, their specific weight is only 10 kg/m³.
Standard product sizes are 60x120 cm. The construction industry produces slabs with a length of more than 2 m, a width of over 1 m, and a thickness of 20-100 mm. Compressive strength – from 40 to 350 kPa. The thermal conductivity coefficient does not exceed 0.044 W/m°C, self-combustion time is 1-4 s. Technical conditions for thermal insulating polystyrene foam boards are regulated by GOST 15588-2014.
Ecowool
Cellulose insulation received this name due to its external resemblance to cotton wool and economically viable raw materials. 80% of it consists of waste paper, the rest is low-toxic, non-volatile antiseptics and fire retardants.
Ecowool has low thermal conductivity (at the level of mineral wool), is environmentally friendly, and is not afraid of moisture. The capillary structure of the material restores its properties after drying. The density of cellulose insulation is 28-65 kg/m³, flammability group G2 is moderate. A natural polymer treated with brown (sodium salt of boric acid) ignites, but the fire quickly dies out.
In our country, ecowool has been used since 1992. Its production is growing, technological lines include processing of recyclable materials, grinding, mixing with boric acid and borax, and packaging.
There are 3 installation methods:
- Manual laying on horizontal surfaces;
- Dry blowing with a special installation;
- Spraying wet cellulose onto vertical and inclined surfaces.
The latter option is preferable for the walls of a frame house, as it allows you to control the quality of installation. The resulting smooth surface is ready for further finishing after 12 hours.
Other materials
To insulate frames, polyurethane foam is used in the form of sheets with locking edges or spray foam. It is non-flammable, penetrates well into small crevices, has high adhesion, environmental friendliness, and low thermal conductivity.
Cement-bonded fiberboards with a density of 600 kg/m³ are used to sheathe internal partitions, and high-density ones (950-1050 kg/m³) are used to insulate external walls. The material is non-flammable, durable, and lasts up to 50 years. The composition does not contain phenol-formaldehyde resins or other organic compounds that can release substances toxic to humans.
Why insulate a house with basalt filler?
Based on the above listed features and advantages of the material, we can say with confidence that basalt backfill belongs to the category of high-quality insulation materials that maintain their performance characteristics regardless of the type.
The fibrous structure gives the material special elasticity and mechanical strength in use. The thermal insulation properties of basalt backfill remain unchanged over a long period, and the material itself does not shrink.
Requirements for thermal insulation material
The frames of houses built using “Canadian” technology are assembled from OSB boards or wood. To prevent the insulation from causing damage to structures, it must have sufficient vapor permeability - at least 0.32 Mg.
Fiber heat insulators – mineral wool materials – absolutely meet this requirement. Popular synthetic insulation materials, such as polystyrene foam and polymer-based analogues, cannot be used in wooden structures for two reasons:
- Firstly, due to the lack of elasticity, the heat insulator will not be able to adapt to temporary deformations of the wood (shrinkage, increase in volume). The result is the formation of cracks and cold bridges.
- Secondly, polystyrene foam and its analogues do not allow wood to “breathe”. This leads to moisture accumulation, mold and rotting of structural elements.
When choosing how to insulate a frame house, in addition to vapor permeability, you should also take into account the additional properties of the heat insulator. The following indicators are welcome:
- fire safety;
- environmental friendliness;
- low thermal conductivity;
- resistance to shrinkage;
- minimal water absorption.
Wood sawdust
The thermal conductivity of sawdust is 0.07–0.08 W/m*C. Sawdust is rarely used as an independent insulation material, as it is prone to absorbing moisture and further rotting. Therefore, they are mixed with other materials:
- clay;
- expanded clay;
- perlite;
- vermiculite
The ability of these materials to remove moisture prevents sawdust from being blocked even when laid in a thick layer. By the way, you can only use small sawdust, which is obtained when processing wood on modern machines with high speeds.
Having examined all types of bulk insulation, we can conclude that heat insulators made from rocks and clay have proven themselves to be the best. In terms of price/practicality/heat transfer resistance, the best option is penoizol. An outsider in our rating, ecowool is poison in its purest form, nothing less.
Stage five. Installation of insulation
If mineral wool is used for thermal insulation, before starting work, be sure to wear personal protective equipment - a respirator, gloves, safety glasses, and special clothing. If you use polystyrene foam (and this material, as we said, is not very suitable), then such safety measures are not needed. When insulating a frame house, lay the material evenly between the frame posts, not forgetting the ventilation gaps required between the thermal insulator and the sheathing. To cut mineral wool, you can use scissors or a regular knife, but for polystyrene foam you will need an electric jigsaw or a hacksaw with small teeth.
Note! Experts say that it is more effective to lay insulation in two layers. So, first there should be a first layer 10 centimeters thick, then a wooden sheathing should be laid in a horizontal position, on top of which the second layer should be laid (its thickness should already be 5 centimeters)
This little “trick” will help avoid the formation of cold bridges.
Lay a protective film over the insulation (if it is necessary, that is, if the outside of the house was not properly insulated). This will ensure that the material will always be in a dry state, and moisture will not get in from the outside.
Note! For the ventilation gap, which has been mentioned more than once, fill the wooden sheathing with a thickness of 3 centimeters
After this, you can begin installing OSB boards and decorative trim.
Laying basalt slabs
Insulation of the enclosing structures of a frame house with basalt wool is most effective if the installation rules are followed:
- Unloaded surfaces - floors, joist floors, roof slopes - are insulated with loose roll insulation or soft low-density slabs - up to 35 kg/m³;
- PM 40, PM 50 are installed in the internal partitions;
- To protect facades, denser slabs PP 80 - PZH 140 are used, for plaster finishing - PZH 160 and higher;
- To eliminate cold bridges, it is better to replace thick materials with 2 thinner layers, for example, a 200 mm slab with two 100 mm each;
- The layout is carried out with a seam spacing of at least 150 mm;
- The products are mounted in the spacer between the frame posts or floor joists without gaps; for this purpose, an allowance of 10-20 mm is left when cutting;
- Be sure to lay a moisture- and windproof membrane on the outside of the insulation, a film vapor barrier on the room side, and carefully glue the seams;
- Places where rodents have direct access are covered with metal mesh; mice do not eat basalt, but make passages in it and use fiber to make nests;
- If there is a layer of aluminum, the insulation is laid with the foil side facing the room;
- Cut the material with a sharp knife or saw with fine teeth;
- When cutting, installing or moving, mineral wool protects the respiratory system and skin from contact with microparticles of insulation. Use a mask or respirator, gloves with rubber coating on the palms, and clothing made of thick fabrics.
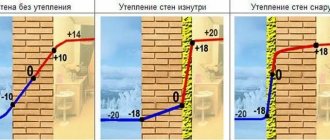
Internal and external insulation - features and nuances
Each insulation option deserves its right to exist, since in some situations it shows better results. The advantages and disadvantages of each method should be analyzed point by point.
Internal insulation has a higher heat retention coefficient, thus energy costs will be minimal.
This is due to the fact that there is no need to warm up the walls; most of the air is retained directly in the room. The situation is twofold, since walls can also collapse due to a shift in the dew point. So the moisture from the cold air will be transformed into droplets almost in the room itself.
Comparison of insulation methods
Also, the internal insulation option is easier to install; you can reach the wall using a simple stepladder.
In contrast to this advantage, there is a nuance - this is a decrease in the variety of wall decor, that is, the insulation is less durable and fastening some structures can be difficult. It is logical that the construction of an additional layer on the walls leads to an overall reduction in the area of the house.
IMPORTANT!
When using the method of internal wall insulation, be sure to pay attention to the environmental friendliness of the material. It is highly not recommended to use polystyrene foam and its derivatives due to the synthetic origin of the material and the increased risk of fire
When burned, it releases toxins. We recommend paying attention to eco-insulation materials
It is highly not recommended to use polystyrene foam and its derivatives due to the synthetic origin of the material and the increased risk of fire. Releases toxins when burned
We recommend paying attention to eco-insulation materials
External insulation is a more standard and safer way to retain heat. This type of insulation has the following advantages:
- The walls are protected from destruction and are less susceptible to weather conditions;
- Does not take up space in the room;
- Lower requirements for the environmental component of insulation;
This is interesting: How to insulate a house with foam insulation
Disadvantages of polystyrene foam
To make the right decision, in addition to all the positive things, it will be very useful to know some of the negative aspects inherent in polystyrene foam. There are several of them.
Foam plastic is a flammable material
No matter what the manufacturer writes on the packaging, polystyrene foam burns and melts when in contact with fire. Therefore, you need to make sure that the fire does not get close to it. The consequences can be very dire.
This is why polystyrene foam cannot be used on a ventilated façade. Direct contact with air and the void between the insulation and the surface of the facade create all the conditions for good combustion. Emptiness, by the way, works as an additional air draft.
Polystyrene foam releases hazardous substances
During the process of natural aging - destruction, polystyrene foam releases styrene monomer. Its smell can be clearly heard if you put a pack of foam sheets in a closed room. After a while, a characteristic unpleasant odor will appear in the room. That is why you cannot use foam insulation inside residential premises. But, unfortunately, few people know about this.
By the way, this is why you need to insulate a bathhouse with polystyrene foam carefully and carefully. When heated to 90 degrees Celsius, the release of volatile compounds hazardous to human health becomes very large.
Polystyrene foam is hygroscopic
That is, it attracts moisture.
No matter what they say, he does it, although not quickly, but confidently. Therefore, insulating a damp, cold basement with ordinary polystyrene foam would be a very bad idea. It is better to use extruded polystyrene foam for these purposes. It has a different internal structure due to which it does not attract moisture. To test this statement, you can put a piece of regular and extruded foam in water. After a while you will get two materials with different moisture content. One will be heavy and wet, and the second will be dry and light.
Polystyrene foam works as a vapor barrier
This is another serious disadvantage that few people think about at the design and construction stage. It manifests itself especially well in houses that are built entirely from polystyrene foam blocks.
During breathing, a person exhales warm water vapor with the air. This steam must escape from the room. The main direction of steam movement is up and to the sides. The ceiling and walls act as a kind of steam outlet; they “breathe”. A building insulated with polystyrene foam must have good forced ventilation. Otherwise, in winter it will be possible to collect water on the windows with buckets, and the room will be very humid.
Benefits of mineral wool
Mineral insulation
Composition and characteristics of mineral wool
Mineral wool brand Izorok
Minvata Technofas
Why has mineral wool become such a popular insulation material for private construction? The answer to this question is simple - due to the totality of its advantages, this material is superior to other insulation materials in certain characteristics.
- Mineral wool does not burn. It can only melt, and only at very high temperatures. Therefore, this insulation is better suited for buildings made of wooden beams or logs than combustible foam.
- Mineral wool is easy to handle - it does not require the use of special equipment, like ecowool. The installation process is simple - take it out of the package, cut it (if necessary), lay it, and secure it with dowels or glue.
- Mineral wool does not shrink over time and is not attractive to rodents, insects, fungus and mold. In addition, it is able to retain its properties for several decades.
- And like any good insulation, mineral wool has extremely low thermal conductivity values - 0.03-0.047 W/(m*K) depending on the type of material and the outside temperature.
About mineral wool brands
conclusions
In the article we talked about the key points for using stone wool aspiration. Let's summarize what has been said. So, the advantages of mineral wool crumbs:
Disadvantages of insulation obtained from stone wool production waste:
We recommend a topic that describes in detail the use of mineral wool aspiration - Decagon, or the path from the sphere to the coaxial yurt.
Source
Additional insulation of a frame house
When building a frame house, thermal insulation materials are placed between the frame posts and then covered with slabs inside and out. If this insulation is not enough, you can additionally install external thermal insulation.
When insulating the outside with mineral wool, a vapor barrier membrane is attached from the inside, which protects the thermal insulation from condensation, that is, air vapor from the room.
For this, aluminum foil, polyethylene film or a special vapor barrier film with a ventilation function is used. The last option is more expensive than others, but from a technical point of view it is the best solution.
To protect the insulation from blowing, a windproof layer is attached to the outside. OSB, chipboard or plywood can be used as internal cladding. The outer cladding is made of eurolining, siding and other materials.
The walls of a frame house can be insulated from the inside. This method of thermal insulation has many serious disadvantages. When insulating walls from the inside, condensation forms in the structure. The dew point for internal insulation will be in the supporting frame structure. If you cannot do without internal insulation, you can perform thermal insulation using liquid foam insulation.
Which one to choose, which one is better, manufacturers
Manufacturers (especially large ones) offer a wide selection of basalt-based insulating materials for insulating various structural elements of buildings:
The Danish company ROCKWOOL offers product lines for facades, roofs, sound insulation, private house construction, in particular for baths and saunas, frame walls, attics, walls for plastering and others.
The Russian company Technonikol produces materials for walls, floors, pitched and flat roofs, for plastering and ventilated facades, etc.
Basalt insulation ISOVER Frame house. photo source here
Under the Isover brand (France) , materials are produced that cover all structures that require heat and sound insulation, in particular, roofs, walls, including frames, floors and more.
Popular lines and leading industry representatives are analyzed in a separate publication.
Some manufacturers' websites provide a calculator for easy and quick calculation of the required amount of materials . By selecting all the initial data: climatic region, building type, insulation element, temperature and humidity in the room, and others, the program provides the optimal insulation option, its characteristics, recommended insulation layer thickness and cost. These capabilities and available recommendations will allow you to select a material with optimal properties for solving specific problems and perform high-quality thermal insulation.
Results
The density of mineral wool for walls and roofs must be at least 55 kg/m. cube, and for horizontal floors 35 kg/m is enough. cube For work, you can use both stone wool and glass wool. In any case, the insulation is protected by films. The first, main task is to prevent steam from entering the mineral wool. For this purpose, a vapor barrier is laid between the warm room and the insulation. The second, no less important task is to allow the steam that has leaked out to leave the insulation pie. To do this, the walls are covered with a wind barrier, and the roof, floor and ceiling are covered with a diffusion membrane. The use of membranes on horizontal floors (except the roof) is more of a recommended measure than a mandatory one.
What does the mineral wool cover on the wall, how and why should it be attached?
In fact, stone fiber is attached to the walls not to block any elements from view. The purpose of the event is to isolate the vertical surface from the external environment.
Fibrous mineral wool with air perfectly inhibits heat transfer, and the chaotic arrangement of threads can absorb a lot of acoustic noise. But fixing a slab or several products will not solve the issue; a balanced and comprehensive approach is needed. The main task is to select basalt insulation with the appropriate properties, but this is not enough. You need to know exactly how to attach the insulating material and the installation sequence of the entire thermal insulation system.