Sorry for the wait, it's just that weekends are also days off for us.
I decided to answer you today only because there is nothing comforting in the second question.
The fact is that such a scheme from the Internet is not a project, much to our regret. And its viability simply cannot be assessed by the layout of the house. You want to build a fairly complex house. This kind of house cannot be built without a project. You can only build a standard house without a project, and all that you showed are not standard houses. Therefore, either order a project from scratch from a design office, or build a simple house (I already wrote this above), but with our help. We can suggest, recommend, or issue a diagram somewhere (and not a full-fledged drawing), and this is our job. But it won’t work out like that from one plan (with a layout) into something more useful.
I would start over. I would ask a question about the foundations. To answer this question, I need to know:
1. Layer your soils (preferably with layer thicknesses) to a depth of 1.5-2 m.
2. The depth of groundwater (you can look at your neighbors’ wells or just ask your neighbors).
3. Decide on the size and number of floors of the house.
4. Choose material for the walls.
5. Estimate the approximate plan of the house, you can use those previously proposed, but choose a simple gable roof, for example.
6. The attic will be residential or not.
Well, etc. In principle, this would be enough to get started.
Next, you can calculate the thickness of the walls and insulation.
Think about it. We cannot help with that house, since this is not a standard project, the calculation of such a project on our part is like pointing a “finger in the sky” without having heights and design drawings.
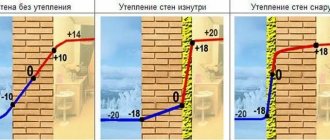
Minimum thickness of a wall made of bricks or blocks
The walls of private houses, cottages and other low-rise buildings are usually made of two or three layers with an insulating layer. The insulation layer is located on the load-bearing part of the wall made of bricks or small-format blocks. Developers often ask the question: “Is it possible to save on wall thickness?”
“Isn’t it possible to make the load-bearing part of the wall of the house thinner than the neighbor’s or than provided for by the project?
On construction sites and in projects, you can see a load-bearing wall made of bricks with a thickness of 250 mm, and from blocks - even 200 mm. has become commonplace.
How to obtain permission for redevelopment
If we talk about the redevelopment of an apartment in general, then regardless of what kind of walls we are talking about, load-bearing or non-load-bearing, it is necessary to obtain permission for redevelopment from the relevant authorities, usually this is the city’s architecture and make adjustments to the project plan, which is what the BTI does and similar authorities.
Without obtaining permission for redevelopment, you should not touch the structures, otherwise you may be asked to pay a fine and return everything as it was. Also, when selling an apartment, difficulties may arise, since reality will not correspond to what is in the project for the apartment.
However, it is also worth saying that getting a redevelopment will not be so easy. Even if we are talking about non-load-bearing structures, you will be faced with the fact that you will need to fill out a bunch of papers and re-draw the project in the BTI, after the technicians have examined your apartment and made all the corrections. In other words, it’s up to you to decide whether it’s worth dealing with it, or whether you can leave everything as it is and just make a beautiful repair. By and large, the layout in many houses is optimal, so it is not always worth turning your fantasies into reality.
Loads and impacts on the walls of the house
Design standards (SNiP II-22-81 “Stone and reinforced masonry structures”), regardless of the calculation results, limit the minimum thickness of load-bearing stone walls for masonry within the range from 1/20 to 1/25 of the floor height.
Thus, with a floor height of 2.5 ... 3 m, the wall thickness in any case should be more than 120 - 150 mm.
A vertical compressive load acts on a load-bearing wall
on the weight of the wall itself and the overlying structures (walls, ceilings, roof, snow, operational load). The design compressive strength of brick and block masonry depends on the grade of brick or class of blocks for compressive strength and the grade of mortar.
For low-rise buildings, as calculations show, the compressive strength of a 200-250 mm thick brick wall is provided with a large margin. For a wall made of blocks, with the appropriate choice of block class, there are usually no problems either.
In addition to vertical loads, horizontal loads act on the wall (wall section),
caused, for example, by wind pressure or transmission of thrust from the roof rafter system.
In addition, torques act on the wall,
who seek to rotate a section of the wall. These points are due to the fact that the load on the wall, for example, from floor slabs or from a layer of insulation and facade cladding, is not applied in the center of the wall, but is shifted to the side faces. The walls themselves have deviations from the vertical and straightness of the masonry, which also leads to additional stresses in the wall material.
Horizontal loads and torques create bending loads in the material at each section of the load-bearing wall.
Stages of work
Since the load-bearing walls are laid on the foundation, it is necessary to waterproof the base before starting work.
Most often, roofing felt or a membrane is used, which covers the base of the building in a single layer, overlapping. The joints are treated with bitumen mastic to prevent moisture from penetrating through the foundation to the walls.
The choice of masonry depends on the average temperature in the region . In the northern and central zones of Russia, options of 2-2.5 bricks are more often used; in the southern regions, 1.5 bricks are acceptable.
There are several methods of dressing, each of them is reliable and is used along the entire length of the wall. Before starting work, masons must have a plan with openings marked on it and points of connection with adjacent walls.
Preparation of the solution
A rigid mortar mass is used for joints so that shrinkage is minimal. How to prepare the joining solution:
- you will need a cement mixture of grade M400 and pure river sand without impurities, the dry components are combined in a ratio of 4:1;
- water is added to the resulting mixture to make it homogeneous and plastic;
- prepare the solution in portions so that it does not have time to harden during the work.
Creating a structure with insulation
Stages of work to create a full load-bearing wall with insulation:
- Form the first row of rough masonry. For example, an option of 2 bricks, lay them dry, taking into account the additional distance at the seams. Before installation, the brick is moistened in water. This is done to prevent the porous and dry material from absorbing water from the solution before it hardens.
- Start rigidly fixing the wall from the corner; further compliance with the horizontality of the walls depends on it. The system for bandaging the corners depends on preference; the physical properties of the wall do not change depending on the choice.
- The corner is initially built in 4 rows. To form the frame of the structure, the press-on masonry technique is used. The mortar mass is placed at a distance of approximately 1 cm from the outer edge of the brick. Stretch the mixture over the surface with a trowel, then place the brick on top, pressing it to the base.
The trowel handle is tapped on the material, horizontal and vertical are checked using a building level. During the process, the solution will be partially squeezed out of the seams; it is used to form new ones.
Between rough masonry and cladding, the house goes through all stages from the appearance of the roof to the laying of communications. Windows and doors are often installed immediately, and the final design of the facade, cladding and insulation of load-bearing walls is the final stage of construction.
How to make walls strong and stable
The strength and stability of walls with a thickness of 200-250 mm or less does not have a large margin for bending loads. Therefore, the stability of walls of the specified thickness for a particular building must be confirmed by calculation.
To build a house with walls of this thickness, it is necessary to choose a ready-made project with the appropriate wall thickness and material. We always entrust the adjustment of the project with other parameters to the selected thickness and material of the walls to specialists.
The practice of designing and building low-rise residential buildings has shown that load-bearing walls are made of bricks or blocks with a thickness of more than 350 - 400 mm. have a good margin of strength and resistance to both compressive and bending loads in the vast majority of building designs.
The walls of the house, external and internal, resting on the foundation, together with the foundation and ceiling, form a single spatial structure (framework), which jointly resists loads and influences.
Creating a durable and economical building frame is an engineering task that requires high qualifications, pedantry and culture from construction participants.
A house with thin walls is more sensitive to deviations from the project, from construction norms and rules.
The developer needs to understand that the strength and stability of walls is reduced if:
- wall thickness decreases;
- the height of the wall increases;
- the area of openings in the wall increases;
- the width of the wall between the openings decreases;
- the length of the free section of the wall, which has no support and interface with the transverse wall, increases;
- channels or niches are installed in the wall;
The strength and stability of walls changes in one direction or another if:
- change the wall material;
- change the type of overlap;
- change the type and size of the foundation;
Possible errors and their consequences
What can go wrong:
The masonry has deviated.
To prevent this from happening, it is necessary to constantly check the angles, horizontal and vertical. If it was not possible to keep track, the wall must be disassembled and rebuilt, since compliance with the geometry is necessary for the strength and stability of the house frame.Small deviations are leveled out later using plaster.
- The dressing was performed incorrectly. The bricks must be laid out so that the load from one of them falls on the two lower ones. The seams should not match, otherwise the strength of the structure is greatly reduced. Those who create masonry for the first time need to familiarize themselves with the technology and dressing options and practice dry.
- Poorly sealed seams significantly reduce the thermal insulation properties and structural strength. The solution should lie smoothly, without gaps. Therefore, they use the principle of pressing, when the mixture under pressure fills the voids.
When creating rough walls, some builders do not pay attention to the cleanliness of the process, are in a hurry, and do not observe the uniform distribution of the solution. Load-bearing walls are the most important element of the structure; you need to pay time and attention to each brick.
Defects that reduce the strength and stability of walls
Violations and deviations from project requirements, construction norms and rules,
which builders allow (in the absence of proper control on the part of the developer),
reducing the strength and stability of the walls:
- wall materials (bricks, blocks, mortar) with reduced strength compared to the requirements of the project are used.
- metal anchoring of the floor (slabs, beams) to the walls is not performed according to the design;
- deviations of the masonry from the vertical, displacement of the wall axis exceed the established technological standards;
- deviations in the straightness of the masonry surface exceed established technological standards;
- The masonry joints are not filled completely enough with mortar. The thickness of the seams exceeds the established standards.
- excessive amounts of brick halves and chipped blocks are used in the masonry;
- insufficient connection of the masonry of internal walls with external ones;
- omissions of mesh reinforcement of masonry;
In all of the above cases of changes in the dimensions or materials of walls and ceilings, the developer must contact professional designers to make changes to the design documentation. Changes to the project must be certified by their signature.
Your foreman’s “let’s make it simpler” suggestions must be agreed upon with a professional designer. Control the quality of construction work done by contractors. When performing work on your own, avoid the above construction defects.
The norms of the rules for the production and acceptance of work (SNiP 3.03.01-87) allow: deviations of walls by displacement of axes (10 mm), deviation by one floor from the vertical (10 mm), displacement of supports of floor slabs in plan (6...8 mm ) etc.
The thinner the walls, the more they are loaded, the less safety margin they have.
The load on the wall multiplied by the “mistakes” of designers and builders may turn out to be excessive (pictured).
The processes of wall destruction do not always appear immediately, but sometimes years after the completion of construction.
Brick laying process
In addition to all the above advantages of this building material, brick has very well-pronounced thermal insulation properties. All this makes brick a real leader among other building materials used in the construction of houses and buildings. There are many types of bricks, which differ from each other in their price and characteristics. With all this, even the most inexpensive brick has fairly high strength characteristics. Next, we will consider in more detail the topic concerning the required thickness of brick walls during the construction of certain objects.
First of all, you have to choose the right type of masonry - this is necessary for the construction of strong and reliable buildings.
At the beginning of the work, it is very important to display a number of factors in the project itself, namely:
- for each building it is necessary to calculate the planned load on the wall itself;
- When performing work, take into account the climatic conditions of the area where it will be carried out (this factor is very important, since it directly affects the strength characteristics of the structure, so the masonry of the load-bearing wall must have good thermal insulation);
- it is important to pay special attention to appearance (the use of artificial stone materials has now become very fashionable).
As a rule, the thickness of the walls is strictly according to state standards. When performing construction work, it is very important to comply with approved GOSTs. Today, the construction of facilities is carried out in accordance with GOST R 55338-2012 and 2 4992-81. According to these GOSTs, the thickness of the walls when laying should be in the range of 0.12-0.64 m:
- One of the thinnest masonry is considered to be one-half brick masonry, namely 0.12 m. This type of masonry is usually used for the construction of small fences, as well as for laying interior partitions.
- The masonry, made in one brick, is 0.25 m thick. This type is used in the construction of fences, fences, sheds, as well as various auxiliary structures. For the southern regions, the most commonly used thickness of brick walls is one and a half layers, i.e. 0.38 m. In those regions where the climate is more severe, the use of two and a half and two bricks is considered the most relevant.
- For a more temperate climate, the thickness of brick walls should be in the range of 0.51-0.64 m. For outbuildings, 0.38 m of masonry is enough. But if the wall is load-bearing, and a residential building is being built, then the thickness should be at least 0.51 m. If the building is multi-story, then according to GOST, a slight reduction in the thickness of the wall of each subsequent floor is permissible.
- Buildings, the height of which will not exceed five floors, must be laid out in two bricks, and if the building is commercial and non-residential, then the thickness is one and a half bricks.
The house is made of blocks with a wall thickness of 180 mm.
The principles of designing a house with minimal wall thickness are clearly visible in the following photos. In house designs with thin walls, elements made of monolithic reinforced concrete are widely used.
The simple architectural form of the house allows the use of commonly available materials for construction and helps optimize construction costs.
The house has 114 m2 of usable area and is designed for a family of 4-5 people. In the attic there are three bedrooms and a bathroom.
On the ground floor along the southern facade with large windows there is a spacious living room combined with a dining room and kitchen. In the other part there is an office, a bathroom and a technical room.
Silicate blocks were used to lay the outer walls of the house. Wall thickness 180 mm. Thin walls increase the usable area of the house.
The house is designed in such a way that there are no internal load-bearing walls. Inside the house there is a load-bearing beam, which is supported by two columns inside and two columns built into the masonry of the external walls. The beam itself and the columns are made of monolithic reinforced concrete. This solution allows for a free layout of the premises on the floor.
To increase the resistance of the walls to loads, there is a monolithic reinforced concrete belt at the floor level of the first floor. The section of the wall with wide, high windows and narrow partitions on the southern facade is also made of monolithic reinforced concrete.
The roof of the house rests on a monolithic reinforced concrete belt on top of the attic walls. Reinforced concrete columns are installed in the attic walls of the attic, on which the roof mauerlat rests. The need for columns in the outer walls is due to the fact that these walls do not have cross connections inside the attic. The absence of transverse walls allows for a free layout of the attic rooms.
Formwork for installing a monolithic column in the outer wall of a house. The column serves as a support for the load-bearing beam inside the house.
Installation of formwork for monolithic columns along the edges of wide window openings.
In the background you can see the formwork for the columns inside the house. The two columns inside are located on the same axis with the columns built into the outer walls.
The floors in the house are prefabricated monolithic, often ribbed, on the same level as the monolithic reinforced concrete wall belt.
The monolithic floor, made integral with the monolithic belt of walls, together with the walls, creates a single and durable spatial structure - the skeleton of the house.
The attic walls of the attic, 1.3 m high, on which the roof mauerlat rests, are reinforced with monolithic columns built into the masonry.
Formwork for the construction of monolithic columns and attic wall belts.
The southern facade of the house with openings for tall large windows. Inside, a monolithic beam is visible, which rests on two columns inside and two columns built into the masonry of the outer walls.
The rafters of each roof slope at the top rest on a truss, the ends of which, in turn, lie on the opposite gable walls of the attic. This solution made it possible to abandon the intermediate posts of the ridge beam. As a result, the space inside the attic is free for planning. The angle of inclination of the roof slopes is 42°.
The foundation of the house is a monolithic reinforced concrete slab 250 mm thick. The foundation slab lies on a layer of insulation. Non-removable formwork made of insulation. Insulation slabs are laid along the perimeter of the foundation, under the blind area. This solution prevents freezing of the soil under the foundation.
Tips for the developer
It is certainly advisable to choose a wall thickness of 200-250 mm made of bricks or blocks for a one-story house or for the top floor of a multi-story house.
The house has two or three floors with a wall thickness of 200-250 mm. build if you have a ready-made project at your disposal, tied to the ground conditions of the construction site, qualified builders, and independent technical supervision of construction.
In other conditions, for the lower floors of two- or three-story houses, walls with a thickness of at least 350 mm are more reliable.
To ensure the strength and stability of a private house with a minimum wall thickness, the installation of a monolithic reinforced concrete belt has become standard. The belt is placed on top of the external and internal load-bearing walls on each floor of the house. Beams and floor slabs, roof slabs must be connected (anchored) with metal ties to a reinforced concrete belt on the walls of the house.
Read about how to make load-bearing walls only 190 mm thick here.
Types of plans for multi-storey residential buildings
High-rise buildings and apartment buildings occupy first place in the practice of housing construction. This is explained by the desire to increase the number of residential premises through dense development on a floor-by-floor basis and reduction of areas for development.
This is the appearance of the facade and the layout of all floors of a residential multi-storey building
The last point is especially important, since otherwise there is a significant increase in the cost of utility networks and an increase in the distance from home to work. The choice of supporting structure and the type of planning of the building in volume affect the efficiency, shape and structure of a multi-storey building.
Houses differ in architectural and planning solutions; the location of the premises is of great importance. There are several types of apartment building plans.
Typical layout of a residential floor of a multi-storey building
The most common is sectional. A good example would be five-story buildings built half a century ago. The house has a landing, to which several apartments adjoin.
The sites themselves can be of different shapes, and the apartments are studio, one-room, 2- and 3-room. This arrangement is characterized by a common exit to the floor and a separate entrance to the room.
3D project and layout of a studio apartment with panoramic windows
This option is economical and has good insulation of apartments. The number of entrances can range from 4 to 12, and in extreme cases - up to 16. Their number depends on:
- customer wishes;
- soil structures;
- area of land for development.
A type of sectional panel housing is considered to be a point arrangement. They are also called a “tower”, which can have the same floor plan as in a sectional building. But there is only one entrance here. For example, if little land has been allocated for construction and the soil has complex topography, such a plan will be a good option.
Layout of a two-room apartment in a panel high-rise building
Houses of the second corridor type are not often found. The difference here is that instead of a landing, there is a long corridor into which all apartments open.
The orientation of the apartments here is one-sided - this is the main disadvantage of this location. Insulation is also not at the highest level. Therefore, this scheme is found mainly in the construction of hotels and hostels.
Gallery-type houses are somewhat similar to the corridor type. Each apartment has access to a gallery located along the longitudinal wall of the structure.
Placement of apartments on the plan in a gallery-type building
Such apartments, even with the smallest area, are well ventilated. Economically, this arrangement is very profitable, since it allows servicing a large number of apartments using a small number of stairs or elevators. However, the technological process of thermal insulation in the local harsh climate is not always characterized by good quality and service life.
Minimum thickness of a wall made of bricks or blocks
The walls of private houses, cottages and other low-rise buildings are usually made of two or three layers with an insulating layer. The insulation layer is located on the load-bearing part of the wall made of bricks or small-format blocks. Developers often ask the question: “Is it possible to save on wall thickness?”
“Isn’t it possible to make the load-bearing part of the wall of the house thinner than the neighbor’s or than provided for by the project?
On construction sites and in projects, you can see a load-bearing wall made of bricks with a thickness of 250 mm, and from blocks - even 200 mm. has become commonplace.
What factors need to be considered when choosing the type of masonry?
When determining how thick a wall should be, it is advisable to focus on the following points:
Estimated load. This is a determining factor, including the number of storeys of the building, as well as its functional purpose. Climatic nuances
The building being constructed must provide comfortable conditions for people, this is especially important for a winter home where people live permanently. The thickness is considered sufficient if the walls do not freeze. Accepted Standards
When calculating the thickness of walls, it is important to focus on the standards prescribed in the current GOST. Only under this condition will the house be safe to live in. External attractiveness. The aesthetic component is very important for an external wall, so it cannot be ignored either. Thin masonry looks most preferable, but is not always acceptable.
Loads and impacts on the walls of the house
Design standards (SNiP II-22-81 “Stone and reinforced masonry structures”), regardless of the calculation results, limit the minimum thickness of load-bearing stone walls for masonry within the range from 1/20 to 1/25 of the floor height.
Thus, with a floor height of 2.5 ... 3 m, the wall thickness in any case should be more than 120 - 150 mm.
A vertical compressive load acts on a load-bearing wall
on the weight of the wall itself and the overlying structures (walls, ceilings, roof, snow, operational load). The design compressive strength of brick and block masonry depends on the grade of brick or class of blocks for compressive strength and the grade of mortar.
For low-rise buildings, as calculations show, the compressive strength of a 200-250 mm thick brick wall is provided with a large margin. For a wall made of blocks, with the appropriate choice of block class, there are usually no problems either.
In addition to vertical loads, horizontal loads act on the wall (wall section),
caused, for example, by wind pressure or transmission of thrust from the roof rafter system.
In addition, torques act on the wall,
who seek to rotate a section of the wall. These points are due to the fact that the load on the wall, for example, from floor slabs or from a layer of insulation and facade cladding, is not applied in the center of the wall, but is shifted to the side faces. The walls themselves have deviations from the vertical and straightness of the masonry, which also leads to additional stresses in the wall material.
Horizontal loads and torques create bending loads in the material at each section of the load-bearing wall.
Selection of material
Today, bricks such as single, one-and-a-half and double are produced. A standard brick has a size of 0.25 × 0.12 × 0.65 m. This standard was approved back in 1925. A little later, standards were approved for one-and-a-half and double bricks, respectively, 0.25 × 0.12 × 0.88 m and 0.25 × 0.12 × 0.138 m. It is believed that the latter types of brick are considered more economical.
Related article: Do-it-yourself poured walls
As practice shows, for a load-bearing type structure it is more profitable to use 2.5 bricks. In this case, the cladding should be done using a single method, as it looks more aesthetically pleasing. If you use only a single brick with this type of masonry, the cost of such material will be thirty percent more.
One of the most important characteristics of brick is its thermal conductivity. Although brick is considered to be quite thermally conductive, it is inferior in this indicator to materials such as wood and foam concrete.
This important characteristic can be significantly improved by using hollow materials for cladding. It is very important to know that such materials cannot be completely used for the construction of load-bearing structures, since its strength is significantly less than that of a solid one.
In addition, this type of material absolutely cannot be used in the construction of foundations and foundations of buildings.
How to make walls strong and stable
The strength and stability of walls with a thickness of 200-250 mm or less does not have a large margin for bending loads. Therefore, the stability of walls of the specified thickness for a particular building must be confirmed by calculation.
To build a house with walls of this thickness, it is necessary to choose a ready-made project with the appropriate wall thickness and material. We always entrust the adjustment of the project with other parameters to the selected thickness and material of the walls to specialists.
The practice of designing and building low-rise residential buildings has shown that load-bearing walls are made of bricks or blocks with a thickness of more than 350 - 400 mm. have a good margin of strength and resistance to both compressive and bending loads in the vast majority of building designs.
The walls of the house, external and internal, resting on the foundation, together with the foundation and ceiling, form a single spatial structure (framework), which jointly resists loads and influences.
Creating a durable and economical building frame is an engineering task that requires high qualifications, pedantry and culture from construction participants.
A house with thin walls is more sensitive to deviations from the project, from construction norms and rules.
The developer needs to understand that the strength and stability of walls is reduced if:
- wall thickness decreases;
- the height of the wall increases;
- the area of openings in the wall increases;
- the width of the wall between the openings decreases;
- the length of the free section of the wall, which has no support and interface with the transverse wall, increases;
- channels or niches are installed in the wall;
The strength and stability of walls changes in one direction or another if:
- change the wall material;
- change the type of overlap;
- change the type and size of the foundation;
Safety precautions
When performing work on the construction of external and internal load-bearing walls and partitions, strict compliance with the requirements of labor safety measures set out in SNiP 12-04-2002 (section 9) and SNiP 12-03-2001 Labor safety in construction is necessary. Part 1. General requirements.
Lifting building materials and products to the floor, moving them to workplaces must be carried out using lifting means and packaging means to prevent them from falling and being damaged.
Workers receiving loads at masons' workplaces must be trained and have a slinger's certificate. A stable radiotelephone connection must be established between the workers and the tower crane operator.
Before installing carpentry, all window and door openings in the external walls being constructed must be fenced or closed with safety shields (grids).
Prohibited
when laying masonry, stand on it with your feet or lean on it.
The flooring used must be of stock production only. It is prohibited
to use pallets, boxes, containers, as well as other objects not intended for these purposes as scaffolding .
The gap between the wall (partition) being erected and the working floor should not exceed 50 mm. The flooring of working scaffolds must be regularly (at least 2 times per shift) cleared of debris. Protective canopies with a plan size of at least 2 x 2 m must be installed over the working entrances to the section. The suspended scaffolds used must be of an inventory type only and subject to periodic inspection.
In areas of masonry of external walls, external inventory protective canopies must be installed in the form of flooring on brackets. The brackets are hung on steel clamp hooks attached to the wall being built along the course of its laying. The first row of protective canopies is installed at around 3.300, and is maintained until the completion of the construction of the external walls. The second row of protective canopies is installed on the external walls and is rearranged along the course of the masonry every 6 m. It is allowed to use the second row of flooring made of mesh materials with a cell size of no more than 50 x 50 mm.
All construction waste generated during the work must be collected in a special container (garbage container) and, as it accumulates, removed from the floor by tower crane for removal off the construction site. Removing construction and household waste by throwing it down through window or door openings or from balcony slabs is prohibited.
Quality control of brickwork work
— acceptance of previously completed installation work preceding brickwork
— quality control of building materials and products used for masonry and mounted lintels
— control of production operations related to the production of stone works and laying of lintels over openings
— acceptance control of completed stone work with execution of inspection reports for hidden work.
Acceptance of previously completed work prior to the construction of external and internal load-bearing walls and partitions should be carried out in accordance with the requirements of Section 2, paragraphs 2.111...2.113 of SNiP 3.03.01-87 and working drawings of the project.
Control of production operations is carried out according to the scheme of operational quality control of stone work and work on the installation of lintels over window and door openings of walls and partitions.
Defects that reduce the strength and stability of walls
Violations and deviations from project requirements, construction norms and rules,
which builders allow (in the absence of proper control on the part of the developer),
reducing the strength and stability of the walls:
- wall materials (bricks, blocks, mortar) with reduced strength compared to the requirements of the project are used.
- metal anchoring of the floor (slabs, beams) to the walls is not performed according to the design;
- deviations of the masonry from the vertical, displacement of the wall axis exceed the established technological standards;
- deviations in the straightness of the masonry surface exceed established technological standards;
- The masonry joints are not filled completely enough with mortar. The thickness of the seams exceeds the established standards.
- excessive amounts of brick halves and chipped blocks are used in the masonry;
- insufficient connection of the masonry of internal walls with external ones;
- omissions of mesh reinforcement of masonry;
In all of the above cases of changes in the dimensions or materials of walls and ceilings, the developer must contact professional designers to make changes to the design documentation. Changes to the project must be certified by their signature.
Your foreman’s “let’s make it simpler” suggestions must be agreed upon with a professional designer. Control the quality of construction work done by contractors. When performing work on your own, avoid the above construction defects.
The norms of the rules for the production and acceptance of work (SNiP 3.03.01-87) allow: deviations of walls by displacement of axes (10 mm), deviation by one floor from the vertical (10 mm), displacement of supports of floor slabs in plan (6...8 mm ) etc.
The thinner the walls, the more they are loaded, the less safety margin they have.
The load on the wall multiplied by the “mistakes” of designers and builders may turn out to be excessive (pictured).
The processes of wall destruction do not always appear immediately, but sometimes years after the completion of construction.
What should be the thickness of brick walls and partitions according to GOST
When carrying out work on laying brick walls, each builder must know exactly how thick the walls should be according to GOST. Brick is most often used in construction work on the construction of houses and buildings of various types. The thickness of brick walls depends directly on its purpose. As a rule, walls are laid with a thickness of two bricks, since this material itself is very reliable and has a high level of stability. In addition, brick walls are not particularly picky about the choice of foundation, so it does not have to be very powerful and massive.
The house is made of blocks with a wall thickness of 180 mm.
The principles of designing a house with minimal wall thickness are clearly visible in the following photos. In house designs with thin walls, elements made of monolithic reinforced concrete are widely used.
The simple architectural form of the house allows the use of commonly available materials for construction and helps optimize construction costs.
The house has 114 m2 of usable area and is designed for a family of 4-5 people. In the attic there are three bedrooms and a bathroom.
On the ground floor along the southern facade with large windows there is a spacious living room combined with a dining room and kitchen. In the other part there is an office, a bathroom and a technical room.
Silicate blocks were used to lay the outer walls of the house. Wall thickness 180 mm. Thin walls increase the usable area of the house.
The house is designed in such a way that there are no internal load-bearing walls. Inside the house there is a load-bearing beam, which is supported by two columns inside and two columns built into the masonry of the external walls. The beam itself and the columns are made of monolithic reinforced concrete. This solution allows for a free layout of the premises on the floor.
To increase the resistance of the walls to loads, there is a monolithic reinforced concrete belt at the floor level of the first floor. The section of the wall with wide, high windows and narrow partitions on the southern facade is also made of monolithic reinforced concrete.
The roof of the house rests on a monolithic reinforced concrete belt on top of the attic walls. Reinforced concrete columns are installed in the attic walls of the attic, on which the roof mauerlat rests. The need for columns in the outer walls is due to the fact that these walls do not have cross connections inside the attic. The absence of transverse walls allows for a free layout of the attic rooms.
Formwork for installing a monolithic column in the outer wall of a house. The column serves as a support for the load-bearing beam inside the house.
Installation of formwork for monolithic columns along the edges of wide window openings.
In the background you can see the formwork for the columns inside the house. The two columns inside are located on the same axis with the columns built into the outer walls.
The floors in the house are prefabricated monolithic, often ribbed, on the same level as the monolithic reinforced concrete wall belt.
The monolithic floor, made integral with the monolithic belt of walls, together with the walls, creates a single and durable spatial structure - the skeleton of the house.
The attic walls of the attic, 1.3 m high, on which the roof mauerlat rests, are reinforced with monolithic columns built into the masonry.
Formwork for the construction of monolithic columns and attic wall belts. The southern facade of the house with openings for tall large windows. Inside, a monolithic beam is visible, which rests on two columns inside and two columns built into the masonry of the outer walls.
The rafters of each roof slope at the top rest on a truss, the ends of which, in turn, lie on the opposite gable walls of the attic. This solution made it possible to abandon the intermediate posts of the ridge beam. As a result, the space inside the attic is free for planning. The angle of inclination of the roof slopes is 42°.
The foundation of the house is a monolithic reinforced concrete slab 250 mm thick. The foundation slab lies on a layer of insulation. Non-removable formwork made of insulation. Insulation slabs are laid along the perimeter of the foundation, under the blind area. This solution prevents freezing of the soil under the foundation.
Tips for the developer
It is certainly advisable to choose a wall thickness of 200-250 mm made of bricks or blocks for a one-story house or for the top floor of a multi-story house.
The house has two or three floors with a wall thickness of 200-250 mm. build if you have a ready-made project at your disposal, tied to the ground conditions of the construction site, qualified builders, and independent technical supervision of construction.
In other conditions, for the lower floors of two- or three-story houses, walls with a thickness of at least 350 mm are more reliable.
To ensure the strength and stability of a private house with a minimum wall thickness, the installation of a monolithic reinforced concrete belt has become standard. The belt is placed on top of the external and internal load-bearing walls on each floor of the house. Beams and floor slabs, roof slabs must be connected (anchored) with metal ties to a reinforced concrete belt on the walls of the house.
Read about how to make load-bearing walls only 190 mm thick here.
Schemes of a residential building with layout
Before choosing an example project for building a cottage on a site, you need to decide how many floors there will be in the building. The budget and area will depend on this. The purpose of the premises also plays an important role.
Sometimes a small building area is a good argument for building a one-story building.
Project of a one-story house 8 by 8
Buildings with such an area are in demand in suburban construction, in dense urban areas. This is due to their affordable price. The plan of a one-story house may vary depending on the presence of an attic floor, garage, and basement.
Layout with dimensions of a one-story cottage 8 by 8 meters with a terrace
If necessary, this includes the basement floor.
Country house plan 9 by 9
The limited land resource makes it possible to place quite large cottages with dimensions of 9 x 9 m. The design of such buildings is complete and can accommodate all the necessary premises according to an individual plan. Construction materials and technology may vary.
When planning, take into account the rules of layout with an attic floor or garage compartment.
10 x 10 house layout
This cottage is suitable for small families. Before you start planning, you need to take into account how the building will be located on the site, how many residents will live here. It is important to take into account the types of heating and water supply, as well as the possibility of adding a terrace or garage space.
Layout and layout of the premises of a two-story building 10 by 10 meters
Lovers of spacious rooms will appreciate the plan. Large rectangular rooms meet all the parameters of private individual construction.
Watch the video for an overview of the layout of a 10 by 10 house.
Two-story house plan
The development of a project for a two-story house of large dimensions is entrusted to architects. Reasonable placement of rooms will make the building comfortable. It is necessary to discuss in advance the location of the staircase, the location of the premises relative to the cardinal directions. The kitchen windows should face south. The living room is set to the west, and the bedrooms will always be light if they are placed with windows facing east. It would be nice to put the stairs on the north side.
The location of the cottage relative to the streets must also be taken into account. For example, bedrooms and lounges should be located away from noisy highways. All details can be discussed with the designer.
How to determine a load-bearing wall: the question is both complex and simple
Not all owners of their own house or apartment are satisfied with the appearance of all the rooms. And then, when undertaking a major renovation, they begin to think about transforming the premises. The most drastic way that comes to mind is redevelopment. If for owners of suburban real estate there are no too great difficulties, then owners of apartments in multi-storey buildings immediately face a big problem. This is a limitation of work when it comes to loaded structures that bear the weight of the upper floors. Failure to comply with these requirements will inevitably endanger everyone in the building. Therefore, the question of how to determine a load-bearing wall becomes a priority.
How to draw a house plan yourself
To begin building a mansion, it is necessary to design the location of internal rooms and partitions. The plan drawing must correspond to the technological process:
An example of making a building drawing yourself
- determination of all required dimensions;
- designation of the middle of the axis of the main walls;
- drawing of internal partitions of all rooms;
- location marks for window and door openings.
Then the functional structures are drawn:
The boundaries of non-residential rooms are indicated by dotted lines.
The height of the premises and number of storeys are indicated separately. Next, each individual object is assigned a number, and a table is created based on all the data. Further actions are carried out directly by the architectural department.
What is a load-bearing wall?
This is a partition that serves as a support for floor slabs. The load-bearing wall is installed perpendicular to them. The short side of the slab rests on this partition, which takes on a significant part of the mass and then transfers pressure to the foundation.
Typically, load-bearing (main) structures are external walls and those located between apartments or blocks. Partitions located in the apartments themselves, as a rule, do not carry much load. More often, redevelopment involves the demolition of interior partitions, but not everyone and not everywhere can determine what cannot be touched.
If, during a major renovation, the owners incorrectly identify the load-bearing wall and then begin to get rid of it, cracks will most likely appear in the building. The worst consequence is the collapse of the ceiling. Therefore, without firm confidence in one’s correctness, confirmed by the relevant authorities, no work can be carried out.
Pros and cons of using building materials
Advantages:
- strong and durable material that retains its properties for centuries, maintaining decent appearance and quality for a long time;
- brick is a frost-resistant material, does not react to wind, prevents the penetration of moisture, it does not rot, and is not susceptible to attack by insects and rodents;
- withstands high temperatures, fireproof;
- high sound insulation properties;
- environmentally friendly, maintains a favorable climate inside the building.
Flaws:
- heavy - for load-bearing walls you will need a lot of bricks, which need to be transported by several machines, this is expensive, there is also a large load on the foundation, which will need to be given maximum attention and strengthened, which also requires financial investments;
- each brick requires laying by hand, the load-bearing walls are the thickest, it will take a lot of time to install;
- It is not recommended to work with them in winter, otherwise the solution will not retain its properties and cracks will appear in the walls later;
- There may be problems with the passage of radio waves into the room, which affects the operation of some devices.
How to detect load-bearing walls?
In some cases, identifying such a load-bearing wall in a residential area does not cause any particular difficulties, but in other apartments this operation is not so simple. The easiest way out of the situation is to read the construction documentation - the technical passport, which all owners of privatized apartments have. However, not everyone will be able to understand the drawings, since at least minimal construction experience is required, as well as the ability to understand such documentation.
Sometimes the task is simplified, since it is possible to determine the load-bearing wall by its location. All external partitions of the building are considered as such, as well as those that open onto the landing. The walls bordering neighboring apartments are, in most cases, load-bearing structures.
Thickness and material will help determine what you are looking for. If it is a brick, then the thickness of the load-bearing wall must be at least 380 mm, for a reinforced concrete structure - 140-200 mm, for monolithic walls - from 200 or more. The location of the floor slabs can also answer the question, since all partitions located perpendicular to them are load-bearing by definition. However, this rule also has exceptions. These include, for example, buildings built in the Czech Republic.
These are just the basics, they can tell you where you can find such structures, but for a detailed examination it is better to go on a trip to all types of multi-story buildings.
Thermal conductivity of aerated concrete
When constructing residential buildings, their reliability and durability come first. The next parameter is their ability to withstand environmental influences, heat and cold. If aerated concrete is chosen for external load-bearing structures, the thickness of the building walls determines the stability of the internal microclimate in the premises.
Thermal conductivity refers to the ability of blocks to transfer heat throughout their volume from the outer edge to the inner one. To calculate the indicators, the amount of heat in watts passing through 1 m³ of substance in 1 hour is taken. The lower this number, the better the insulating qualities of the material.
The average value for porous blocks is 0.10-0.15 W/(m×°C), and for bricks - 0.40-0.50 W/(m×°C). It has been experimentally established that 1 cm of gas silicate material neutralizes 1 °C of cold.
So, in order to calculate how thick aerated concrete walls should be, you should take as a basis the following correspondences of the thickness of the blocks in cm and their thermal conductivity indicators:
- 12 — 1,15;
- 18 — 0,75;
- 20 — 0,70;
- 24 — 0,57;
- 30 — 0,45;
- 36 — 0,39;
- 40 — 0,35;
- 48 — 0,29;
- 60 — 0,22;
- 72 — 0,19.
Large sizes are rarely used and are used only in industrial construction for the construction of outbuildings, where it is necessary to maintain a constant and stable temperature.
Brick buildings
The thickness of the walls in such buildings depends on the brickwork. The width of the standard product is 120 mm. Laying in two rows with a distance of 10 mm between them (at the seam) gives a wall thickness of 250 mm. A three-row dressing system will give 380 mm, further - more.
The easiest way is to measure the thickness of a wall whose purpose is unknown. If the values obtained are 80, 120 or 250 mm, then such a partition is actually just a partition. When the thickness is 380, 520 or more, then the load-bearing wall has been found, however, with any measurements it is necessary to make corrections - for layers of finishing material.
Not the most popular and widespread solution - wooden floors in brick houses - makes its own adjustments to the thickness of the load-bearing walls. In this case, the loaded structures may be slightly thinner.
Recommendations from experts
Recently, many land owners prefer to build houses themselves, as this allows them to significantly save money. In order for the building to be durable and last for decades, it is necessary not only to draw up the project correctly, use high-quality building materials, but also to accurately calculate the thickness of the external and internal floors.
The following expert advice will help beginners with this.
The thickness of the walls consists of an inner, middle and outer part. Therefore, in order to correctly lay out the partitions, you need to pay special attention to the corners. To do this, a main point is selected and beacons are placed from it. The brick must be laid with dressing, using a certain pattern. After each laid row, the walls should be checked for verticality. If this is not done, then curvature may appear in the plane and the thickness will be unequal. It is recommended to calculate the width of the supporting structures based on the characteristics of the climatic zone in which the house is planned to be located. However, it cannot be less than 38 cm. In the northern regions, the thickness of the floors must be increased to 64 cm. To save material and obtain optimal wall thickness, it is necessary to lay out the blocks in a “well”. The result will be two partitions spaced apart from each other with a width of 140 to 270 cm. The space between them can be filled with sawdust, lightweight concrete or slag. Since the internal walls are made thinner than the external ones and do not require additional thermal insulation, they must be laid out to a thickness of at least 25 cm. In order for the loads on such structures to be distributed evenly, the joints of the internal and external walls should be reinforced with a special mesh or reinforcement every five rows of masonry. As for the walls, their thickness can be 51 cm and they are also reinforced. When laying 1.5 bricks, additional supports with a cross section of 38x38 cm are placed. For interior partitions that are not load-bearing and only zone the space, you can select any thickness. For example, between rooms and in the bathroom you can make masonry of 0.5 bricks, and for the pantry and other auxiliary rooms, “rib” masonry with a thickness of 65 mm is suitable. Such structures should be reinforced with wire every 2-3 rows of masonry. If you increase the thickness of the masonry, the room will acquire higher heat and sound insulation, but at the same time the cost of purchasing the material will increase. If external walls are erected “for jointing”, then their aesthetic appearance will depend on the composition and quality of the cement mortar. The thickness of all seams in this case should be the same, so the solution must be evenly filled with all voids and cavities
Since such structures are not very thick, insulating material and good finishing using facing slabs will help increase their thermal stability. When building walls, it is also important to remember that any deviation in their thickness can provoke unpredictable consequences. Therefore, during masonry it is impossible to allow changes in their height, as well as to reduce the distances between openings or increase their number.
You will learn about bricklaying a corner in one brick from the video below.
Panel houses
Conventional interior partitions in such houses have a thickness of 80-100 mm; they can be constructed of gypsum concrete. Standard load-bearing walls in panel buildings are 140 mm, 180 or 200 mm. If during the measurement the owners received less than 120 mm, then this is also a partition that is not a supporting structure.
The layer of plaster present in such buildings must also be taken into account when measuring, but it is usually 50 mm, no more, and this figure will not have a big impact. If possible, it is better to take correct values that completely exclude the thickness of finishing materials.
Frame partitions:
With a wooden frame covered with boards and shingles
They are a prefabricated structure. The thickness of such a partition depends on the thickness of the frame and, taking into account the plaster layer, is 10-15 cm. As a rule, such partitions were made quite a long time ago in brick, block, stone and private adobe houses. Most often, such partitions are found in “Stalin” buildings and private houses.
Panel partitions made of boards
They are a prefabricated structure. Found only in wooden houses. If the boards are planed, they are not plastered.
With a wooden frame covered with plasterboard sheets
Oddly enough, plasterboard partitions were made by Soviet builders long before perestroika, although not very often. The thickness of such a partition depends on the thickness of the frame.
With a metal frame covered with plasterboard sheets
Modern partitions are not found in houses and apartments built before 1990. The thickness of such a partition, taking into account the thickness of the drywall, is 7.5, 10, 12.5 and 15 cm.
With a wooden frame covered with chipboard or plywood
Homemade partitions. Found in apartments and houses that have undergone redevelopment.
With a wooden or metal frame covered with plastic or MDF wall panels
Modern homemade partitions.
Khrushchev, Stalin, Brezhnev
The structural design of the first two buildings is unchanged; it does not depend on the specific layout of the apartments. In these cases, all longitudinal walls of houses are load-bearing, and transverse structures are simple partitions. The exception is the walls adjacent to the flight of stairs. They are also designed for installation of floor slabs.
Brezhnevki, which became the prototype for new buildings, have a good layout, so the owners are unlikely to decide to destroy something that already looks almost perfect. In any case, this is unlikely to be done: redevelopment is limited, since in these apartments the load-bearing structures are most of the walls.
Why do you need a layout with dimensions?
The layout of the house includes several important points. Before understanding the architectural intricacies, you need to understand the difference between a house project and a layout. The main specifics of a country building project are characteristics, calculations, descriptions of the future structure. It includes accounting for building materials and house subsystems:
- Description of architectural elements: building drawing, layout of residential and utility rooms, designation of windows and doors.
- Calculation of the structure of the foundation, frame, roof, schematic representation of drawings with markings.
- Electrical equipment with a detailed plan for connecting the house to the power grid and a wiring diagram for sockets.
- Engineering communications: ventilation, gas, septic tank, water supply, heating.
As shown above, the structure of the diagram includes a plan of a house with an attic, which indicates the area, internal arrangement of the premises of the main building, with doors, partitions, stairs and windows marked on the diagram.
Drawing and layout of all floors of the building with an attic
It turns out that by refusing the services of an architect, the entire component of the project documentation falls on the home owner. After all, the layout of apartments cannot exist separately from the planned calculation. However, under the guidance of a designer, the owner of the property can draw the plan himself.
Monolithic house
These buildings are the largest originals, the layout of which can be completely unexpected. The thickness of the walls also varies. A partition with a thickness of only 200 mm is often classified as non-load bearing. Large values - 250, 300, 350 mm - cannot guarantee that the owners have a load-bearing wall in front of them.
Trying to find out anything in such apartments is very problematic. The surest way is to search for project documentation or consult with a representative of the developer’s company. The simple reason for these “very strange things” is the use of foam blocks of different thicknesses for the construction of partitions.
What can you do and what can’t you do?
The question of how to determine a load-bearing wall arises only for those who are planning to improve something in the apartment - to destroy it, in order to then gain more space for creative activity.
Therefore, it is better to immediately write that complete dismantling of the partition, on which a serious load is placed, is impossible. The likely outcome is the destruction of the building. Any independent redevelopment requires permission from higher authorities. If it comes to the demolition (relocation) of a load-bearing wall, then in the event of uncoordinated actions to restore it, extreme owners will pay out of their own pockets. Most likely, there will be a fine. Other possible consequences are a summons to court, confiscation of an apartment.
If no drastic actions are planned, and we are just talking about an opening, then such actions are quite acceptable. But only if the redevelopment is approved, and an architect bureau will take on the creation of the project.
Chasing of load-bearing walls is prohibited, so it will not be possible to hide communications in such partitions. Wiring communications (ventilation, water supply, sewerage) through main walls, on the contrary, is possible.
What kind of walls are there in a building?
Characteristics do not affect the distribution of walls into groups
The location of the element and its role in the arrangement of the building are important. These points are studied before the installation of floors begins.
Technical data sheets confirm the presence of the following varieties:
- Partitions. Vertical structures inside, for fencing. With support in the form of ceilings, to separate adjacent rooms. The simplest definition.
- Curtain walls. Usually they become external if the floor does not reach 6 meters in height, allowing support on floors within the same structure. Protects the building from environmental influences.
- Self-supporting walls. With fencing function, also in a vertical position. The weight is completely transferred to the side of the foundation. Serve for protection from the environment, only in the case of interior spaces. This is the main difference.
- Bearing wall. Towards a vertical plane, with the main functions of a load-bearing and enclosing nature. The foundation will not only become a support for it, it will transfer the entire load to it with its own weight and ceilings. Provides separation of adjacent buildings along with protection. Curtain walls are elements that differ from this group.
The location of the element and its role in the arrangement of the building are important
Load-bearing, self-supporting and load-bearing walls - what's the difference?
Self-supporting walls are small in thickness compared to their analogues. Thanks to this, the construction of the structure requires less material. The standard range is from 50 to 380 mm, depending on the source material for construction. The panel house is no exception.
Non-load-bearing enclosing structures can also be erected when it comes to the construction of different types of buildings. Elements with a lower location do not transfer the load to the structures. Such products are also called hinged. For them, construction always takes place within one floor. But structures become self-supporting if the floor height exceeds 6 meters. At the same time, approaches to design and actual construction are changing.
If the wall is self-supporting, it is a fence located outside. Provides additional protection by being adjacent to the building from the main frame. The fastening goes from the side, along the entire perimeter of the floor. Self-supporting enclosing structures can consist of one layer or several layers at once. When placed inside buildings, the main purpose becomes the function of partitions. For self-supporting walls it is the same, only with some adjustments.
Self-supporting walls are small in thickness compared to their analogues.
What is needed to demolish walls?
This is the approval of a redevelopment project. Such issues are resolved by the Bureau of Technical Inventory (BTI). The list of required documents includes:
- a plan developed by representatives of the BTI, separately for each specific case;
- a technical report has been drawn up allowing the demolition of the partition;
- approval of actions by the housing inspection.
It will take a considerable amount of time to collect documents and obtain permission for redevelopment, which apartment owners need to remember.
What are the job requirements?
The answer to the question is complex and simple at the same time, since there are several ways to determine a load-bearing wall, but not in every multi-story building even this process can be easily accomplished. However, before contemplating such a “rearrangement”, it is better to think carefully, because for reconstruction you will have to coordinate all future actions with municipal authorities and architectural departments.
All work related to load-bearing walls requires a separate permit, even if they are carried out by a professional team. Any partial dismantling, which is permitted extremely rarely, involves the installation of temporary columns that will bear the weight of the floor slab. Calculating the dimensions of such structures and monitoring the entire process is the responsibility of engineers licensed for this type of activity.
Unauthorized actions in a multi-storey building threaten to refuse to register changes, which means that any real estate transactions (sale, donation, etc.) will become impossible, and it does not matter whether serious structural elements were affected.
You can learn how to determine load-bearing structures in a drawing by watching this video:
Small prefabricated partitions
Brick partitions laid out in half or quarter brick
The brick can be either fired clay (red) or silicate (white). The thickness of a brick partition, depending on the method of laying and the thickness of the plaster layer, is 10-18 cm. As a rule, brick partitions were made only in brick, block, stone and private adobe houses. But even in brick and block houses, partitions may not be made of brick. It is not recommended to make new brick partitions in multi-storey buildings with a thickness of half a brick. The load on floor slabs from such partitions is approaching critical.
Partitions made of tongue-and-groove and simple blocks of gypsum or foam concrete
The thickness of a partition made of blocks, taking into account the plaster layer, is 8-12 cm. As a rule, block partitions were made in brick and block houses.
Partitions made of cinder blocks, ceramic or natural stone
The heaviest type of partitions. They are practically never found in Soviet apartments. It is highly not recommended to make partitions in multi-storey buildings from such materials - the floor slabs may not withstand such a load.
Glass block partitions
They are practically never found in Soviet apartments. But now, with the advent of a large selection of colored and embossed glass blocks, they are gradually conquering their sector.