NAVIGATION
1. Gas. 2. Solid fuel. 2.1. Firewood 2.2. Euro firewood (briquettes) 2.3. Fuel granules (pellets) 2.4. Sawdust and wood chips 2.5. Coal 2.6. Peat 3. Liquid fuel 3.1. Diesel fuel (diesel fuel) 3.2. Fuel oil 3.3. Biofuel 3.4. Waste oil 4. Electricity
Due to the nature of the production of the following types of fuels, their combustion rate and the amount of heat generated (i.e. calorific value or specific heat of combustion) can vary greatly from each other. For example, differences in the calorific value of birch and spruce firewood can be more than 30%.
Therefore, the “pros and cons” given below in the text are presented solely as a comparative example and cannot reliably reflect the effectiveness of a particular type of fuel. We ask you to pay special attention to this and before making a final decision, study this or that type of fuel more carefully yourself.
We would also like to note that calculations of the cost of heating costs are provided for informational purposes only. In all modern boilers, the technical documentation indicates the features and fuel consumption, which are close to the most reliable and it is on them that you should rely when making the final decision.
So, let's start, as a rule, in practice it is customary to use the following types of fuels:
GAS
Natural gas is a mixture of gases that are formed underground during the decomposition of organic matter, which is why it is a mineral.
At 101.325 kPa and 20 °C, natural gas acquires a gaseous state, which is why, as a rule, natural gas underground is in a gaseous state, i.e. in the form of separate accumulations, gas deposits. But it is also found in the form of gas caps in oil and gas fields or in a dissolved state, for example, in oil or water. 92-98% of natural gas is methane (CH4), while its composition may also include heavier hydrocarbons, such as ethane (C2H6), propane (C3H8), butane (C4H10) and other non-hydrocarbon substances such as hydrogen (H2), hydrogen sulfide (H2S), carbon dioxide (CO2), nitrogen (N2), helium (He).
It is worth mentioning that natural gas, in its pure form, has no odor or color, which increases the risk of poisoning if it leaks. In order to determine the source of the gas leak, experts began adding special substances to it - odorants, for example, ethyl mercaptan, which has a strong unpleasant odor of rotten cabbage, rotten hay and rotten eggs.
ADVANTAGES
ENVIRONMENTAL SAFETY
Low amount of emissions of harmful substances into the atmosphere during combustion.
Low cost
Compared to other types of fuel, gas is the cheapest type of fuel, taking into account the costs of transportation, storage and associated labor costs.
High calorific value
High calorific value compared to other types of fuels.
Neutral:
Autonomy
If you have a gas main, when gas pipes are already connected to your house from the street, you just have to connect them to the boiler and no longer worry about replenishing fuel. But in the absence of a gas main, you will be forced to purchase gas using gas cylinders (gas holders) of 50 liters, which in turn will need to be changed every 1-2 days.
Labor costs
If there is a gas main, labor costs are minimal. If there is no gas line, you will have to take care of transportation, storage and replacement of gas cylinders.
Warehouse space
If there is no gas main, you will have to allocate premises for storing gas cylinders. To create an autonomous heating system, reduce labor costs and eliminate a separate storage room, large-volume gas tanks should be installed underground and filled before the start of the heating season.
Chimney
If the boiler has an open combustion chamber, then the installation of a full-fledged chimney system will be required to remove the exhaust gases, and if the combustion chamber is closed, then a coaxial chimney will be sufficient.
Danger to others
If gas boilers have an open combustion chamber, then a certain amount of exhaust gases can enter the room in which the boiler is located, which can lead to carbon monoxide poisoning in surrounding people. In contrast to gas boilers with a closed chamber, where the likelihood of exhaust gases entering is minimal.
Energy independence
All gas boilers with a closed combustion chamber require constant power supply, unlike gas boilers with an open combustion chamber.
Cons
Explosion hazard
High probability of explosion if safety precautions, operation, installation and maintenance are violated.
Difficulty of installation
Due to the high risk of explosion, the installation of a heating system requires appropriate permits and qualified personnel.
Separate space
The room in which the gas boiler will be located increases the level of fire and explosion hazard, which imposes certain restrictions on the design of the house.
Noise
Compared to electric boilers, gas boilers create noise when operating.
Installation cost
High installation cost for creating an autonomous heating system in the absence of a gas main.
Fuel briquettes
In its composition, this type of fuel is similar to pellets, but looks somewhat different: briquettes are larger and can be not only cylindrical, but also of any other regular shape. The starting raw materials are the same wood chips, sawdust, and shavings. Organic residues of plant crops grown in agriculture are also widely used.
Some types of fuel briquettes are made exclusively from dry pine needles. Perhaps this is the only option for their useful use
Fuel briquettes have the same advantages and disadvantages as pellets. The main difference still comes from the size: briquettes are not suitable for automatic loading, so they are placed in the firebox manually. Products with an aesthetic appearance have gained popularity among owners of fireplaces and decorative stoves due to the almost complete absence of smoke during combustion.
Fuel briquettes are produced in various standards:
Pini-kay
Although the company with a similar name has already closed, the introduced technology is thriving. The briquettes are dark in color and have a hexagonal shape with a central channel. Pressure during molding – up to 1100 bar + exposure to high temperature. Best characteristics and high price.
RUF
Popularly known as “bricks”. These briquettes are indeed made in the form of small parallelepipeds. Formed at pressures up to 300 bar.
Cylindrical shape
Sometimes with a longitudinal hole. Working pressure – up to 600 bar.
CALCULATION OF THE COST OF GAS COSTS
To calculate gas consumption for heating, you must use the following formula:
V = Q / (n/100 x q)
- Q is the heat load for heating (kW/h), for example, let’s take 24 kW/h.
- q is the calorific value of the gas (kW/m³), which depends on the brand of gas supplied. To find out exactly what brand of gas is used in your home or area, we recommend contacting your gas supply company directly.
- n – coefficient of performance (efficiency) of a gas boiler, expressed as a percentage. It is indicated in the boiler passport.
For example, let’s choose a boiler - Lemax Premium 35 V. This boiler was chosen due to its technical power indicators, its value is very close to the thermal load value for a house with 300 m3, namely 24 kW/h. It is also worth noting the high efficiency rate of 90%. To ensure that the boiler power is enough to heat the house even in the most severe frosts, it is recommended to use a reserve of 30%. For the purpose of calculation, we take G20 gas with low calorific value, namely Hi = 9.5 kWh/m.
Now we substitute all the values into the formula and calculate:
V = 24 / (90.0 / 100 × 9.5) = 2.5 m³/h.
Thus, to heat 300 m3 per day you will need 60 m3 of gas. And for the heating season, it turns out to be 183 days (from October 15 to April 15), taking into account temperature fluctuations, you will need:
(60 m3 (daily gas consumption) x 183 days (heating season)) / 2 (taking into account temperature fluctuations) = 5490 m3
Minimum required power
An accurate calculation of the boiler's heating output is carried out by a heating engineer based on SNiP 2.04.01-85. However, in domestic conditions, for an average uninsulated or weakly insulated house with a masonry of 2 bricks and a ceiling height of 2.7 m, the minimum required power is calculated from the rule of 1 kW per 10 m2, we also recommend laying a 20% reserve.
For example, for the house described above with an area of 150 m2, the minimum required power of an oil-fuel boiler will be (150/10) * 1.2 = 18 kW.
SOLID FUEL
Solid fuels are combustible substances, which are predominantly composed of carbon. These include substances that have the properties of a granular body, allowing them to be extracted, stored and moved using well-known mechanical systems and transport devices.
Solid fuel can be natural, i.e. natural, for example, wood, peat, slate, etc., as well as artificial, for example, charcoal, coke, semi-coke, etc.
2.1 FIREWOOD
Firewood is one of the most affordable types of solid fuel. There are a huge number of tree species that can be used for heating purposes.
ADVANTAGES
High calorific value
High calorific value compared to other types of fuels.
Environmental Safety
Low amount of emissions of harmful substances into the atmosphere during combustion.
Low ash and no sulfur
Unlike other types of fuels.
Independence from main communications
Unlike gas.
No explosion hazard
Unlike gas.
Cheap and easy installation of a heating system
No permitting documents are required, unlike gas, and qualified employees.
Energy independence
No power connection required.
Neutral:
High labor costs
Before firewood is used for heating, it must be sawed, split, and allowed to dry for a year or two in an appropriate room. An alternative option is to buy ready-made firewood, which in turn will increase their cost.
Price
Purchasing untreated firewood can significantly reduce costs, while increasing labor costs for subsequent processing.
Cons
Lack of autonomy
It is necessary to constantly manually replenish the boiler with fuel, as well as periodically service it, cleaning it from ash, etc.
Danger to others
For boilers with an open combustion chamber, there is a risk of exhaust gases entering the room in which the boiler is located, which can lead to carbon monoxide poisoning in surrounding people. Unlike boilers with a closed chamber, where the likelihood of exhaust gases entering is minimized.
High requirements for fuel storage
If stored improperly, firewood may become wet, which will reduce its calorific value; therefore, a room protected from precipitation is required.
Warehouse space
Depending on the needs and volumes of heating, there may be a need for a spacious room for storing firewood for the winter.
Complete smoke exhaust system
Chimney installation required.
2.2 EUROWOOD
Euro firewood (briquettes) is waste from wood processing, food industry or agriculture pressed into the form of logs or bricks, where a natural polymer, lignin, is used as an adhesive.
ADVANTAGES
High calorific value
High calorific value compared to other types of fuels.
Environmental Safety
Low amount of emissions of harmful substances into the atmosphere during combustion.
Low ash and no sulfur
Unlike other types of fuels.
Independence from main communications
Unlike gas.
No explosion hazard
Unlike gas.
Cheap and easy installation of a heating system
No permitting documents are required, unlike gas, and qualified employees.
Energy independence
No power connection required.
Low labor costs
Unlike traditional firewood, Eurowood does not need to be sawed, split, or allowed to dry for a year or two in an appropriate room. On the contrary, the fresher the fuel, the better, because Over time, they can accumulate excess moisture, which will negatively affect the heating value.
Neutral:
Lack of autonomy
It is necessary to constantly manually replenish the boiler with fuel. An alternative option is to install an additional automatic fuel supply system to the boiler, but in this case the cost and complexity of installation will increase. Also, do not forget about the need for periodic maintenance, cleaning from ash, etc.
Cons
Danger to others
For boilers with an open combustion chamber, there is a risk of exhaust gases entering the room in which the boiler is located, which can lead to carbon monoxide poisoning in surrounding people. Unlike boilers with a closed chamber, where the likelihood of exhaust gases entering is minimized.
High requirements for fuel storage
If stored improperly, the fuel may become wet, which will reduce the calorific value; therefore, a room protected from exposure to precipitation is required.
Warehouse space
Depending on the needs and volumes of heating, there may be a need for a spacious room for storing fuel for the winter.
Complete smoke exhaust system
Chimney installation required.
2.3 FUEL GRANULLES (PELLETS)
Fuel granules (pellets) are waste from wood processing, food industry or agriculture pressed into granules. A distinctive feature of pellets is their higher density and lower humidity compared to standard firewood and Euro firewood, while the heat transfer remains at the same level.
The pros and cons are the same as those of Euro-firewood, except for the lack of autonomy. If desired and available funds, it is possible to install an autonomous heating system, when the fuel will flow into the boiler automatically as it burns.
2.4 SAWDUST AND CHIPS
Sawdust and wood chips are crushed waste from wood processing, food industry or agriculture. Unlike Euro firewood and pellets, they have not undergone any processing; accordingly, they have low density and high humidity. But the lack of processing significantly reduces their cost.
The pros and cons are the same as those of edrov and fuel pellets, except for the lack of autonomy. If you wish and have the funds, it is possible to install an autonomous heating system, where the fuel will flow into the boiler automatically as it burns.
2.5 COAL
Coal is a sedimentary rock of plant origin, consisting of combustible carbon and other chemical elements. The “older” the rock, the less moisture it contains and the greater its calorific value.
ADVANTAGES
Independence from main communications
Unlike gas.
No explosion hazard
Unlike gas.
Cheap and easy installation of a heating system
No permitting documents are required, unlike gas, and qualified employees.
Energy independence
No power connection required.
Low cost
Unlike other types of fuels.
Cons
Low calorific value
Compared to liquid fuel and gas.
Huge harm to the environment
Compared to other types of fuels.
Presence of coal dust
Polluting the room.
Complete smoke exhaust system
Chimney installation required.
Presence of sulfur
Destroying the cauldron.
Warehouse space
Depending on the needs and volumes of heating, as well as the presence of coal dust, a spacious room is required to store fuel for the winter.
Danger to others.
For boilers with an open combustion chamber, there is a risk of exhaust gases entering the room in which the boiler is located, which can lead to carbon monoxide poisoning in surrounding people. Unlike boilers with a closed chamber, where the likelihood of exhaust gases entering is minimized.
Lack of autonomy.
It is necessary to constantly replenish the boiler with fuel manually. Also, do not forget about the need for periodic maintenance, cleaning from ash, etc.
2.6 PEAT
Peat is a natural material that forms in swampy areas. Therefore, it contains quite a high percentage of water and needs to be dried. After drying, dry peat crumbles extremely easily, making it inconvenient to use. Therefore, it is mixed with sawdust and pressed into various shapes.
ADVANTAGES
Environmental safety
Low emissions of harmful substances into the atmosphere during combustion
Low cost
Unlike other types of fuels.
Independence from main communications
Unlike gas.
No explosion hazard
Unlike gas.
Cheap and easy installation of a heating system
No permitting documents are required, unlike gas, and qualified employees.
Energy independence
No power connection required.
Cons
Lack of autonomy
It is necessary to constantly manually replenish the boiler with fuel. Also, do not forget about the need for periodic maintenance, cleaning from ash, etc.
Low calorific value
Compared to liquid fuel and gas.
Danger to others
For boilers with an open combustion chamber, there is a risk of exhaust gases entering the room in which the boiler is located, which can lead to carbon monoxide poisoning in surrounding people. Unlike boilers with a closed chamber, where the likelihood of exhaust gases entering is minimized.
High requirements for fuel storage
Fuel may catch fire if not stored properly.
Warehouse space
Depending on the needs and volumes of heating, there may be a need for a spacious room for storing fuel for the winter.
Complete smoke exhaust system
Chimney installation required.
Alternative heating
The least common type of energy for heating in Russia is alternative sources. The technical units that implement the selection of free energy are quite original and progressive. Here heat is generated by 3 types of devices:
- Solar panels;
- Electric heat generators;
- Heat pumps.
The use of these devices has many features - you can read about it in detail here.
In addition to single-fuel boilers, there is a separate type of equipment - universal (combined) boilers. They differ structurally from their classic counterparts and can use several types of fuel (in different combinations). You can read about these heating units here.
Another option for using fuel types is to combine heat generators - installing two boilers operating on different energy sources. In this case, the total costs of purchasing equipment increase; the use of high-quality schemes for joint piping of boilers is required. Hint content
The type of fuel is a fundamental criterion when choosing a method of heating premises - not only a private house and cottage, but in some cases also an apartment. It affects the type of equipment used, which differs in cost, installation algorithm, and level of comfort provided. And of course, the most important thing is that the amount of heating costs in the cold months depends on the type of energy used.
(138, 1 today)
CALCULATION OF THE COST OF EXPENSES FOR SOLID FUEL
As an example of calculating costs for solid fuel, let’s take firewood from wood, whose calorific value is 2716. The calculation will be carried out using a simplified formula:
V = 24 * Q / (q * 0.01efficiency)
- 24 – number of hours per day;
- V – amount of fuel per day;
- Q – heat load (kilowatt-hour) required for heating 300 m2;
- q is the calorific value of 1 cubic meter of wood (kW/m3), in our case 2716;
- Efficiency is the efficiency factor (%) of the boiler; for example, let’s take 80%.
V = 24*24/(2716*0.8) = 0.26 m3
Thus, to heat 300 m3 per day you will need 0.26 m3 of wood. For the heating season, which is 183 days (from October 15 to April 15), taking into account temperature fluctuations, you will need:
(0.26 m3 (daily gas consumption) x 183 days (heating season)) / 2 (taking into account temperature fluctuations) = 24 m3.
Brown coal
Brown coal has always belonged to the lower class of solid fuel. It is used quite rarely in industry due to its low calorific value. It is usually less than that of dry wood and approximately corresponds to 3.5 kWh/kg. The main trump card of brown coal remains its low price. However, even under this condition, the choice of brown coal as a fuel for the boiler is justified only in those places where the corresponding deposits and processing plants are located.
LIQUID FUEL
Liquid fuel is a mixture of various hydrocarbons, the molecules of which are connected in very long chains; thanks to this connection, the fuel acquires a liquid state of aggregation. To achieve maximum combustion efficiency, it is recommended to spray liquid fuel in the form of tiny particles in the combustion chamber and only then mix it with air. The main disadvantage of liquid fuel is the threat of low temperatures; it must be stored at a positive temperature.
3.1 DIESEL FUEL
Diesel fuel (diesel fuel) is a petroleum product consisting of a mixture of hydrocarbons that are obtained by distillation and selection of certain fractions from them. Nowadays diesel fuel is widely used as fuel for internal combustion engines of agricultural and construction vehicles, diesel locomotives, ships, and passenger cars.
ADVANTAGES
High calorific value
High calorific value compared to solid fuel.
Independence from main communications
Unlike gas.
Cheap and easy installation of a heating system
No permitting documents are required, unlike gas, and qualified employees.
Neutral:
Autonomy
If desired and available funds, it is possible to install an autonomous heating system, when the fuel will flow into the boiler automatically as it burns.
Danger to others
For boilers with an open combustion chamber, there is a risk of exhaust gases entering the room in which the boiler is located, which can lead to carbon monoxide poisoning in surrounding people. Unlike boilers with a closed chamber, where the likelihood of exhaust gases entering is minimized.
Cons
Environmental harm
High amount of emissions of harmful substances into the atmosphere during combustion.
High requirements for fuel storage
Fuel may catch fire if not stored properly.
Warehouse space
Depending on the needs and volumes of heating, there may be a need for a spacious room for storing fuel for the winter.
High price
Compared to other types of fuels.
Presence of odor and operating noise
Compared to other types of fuels.
3.2 MAZUT
Fuel oil is a relatively inexpensive type of fuel, which is obtained from the products of oil refining and gas condensate raw materials, or as a result of secondary processes of their processing. Fuel oil consists of hydrocarbons (with a molecular weight of 400 to 1000 g/mol), petroleum resins (with a molecular weight of 500–3000 or more g/mol), asphaltenes, carbenes, carboids and organic compounds containing metals (V, Ni, Fe , Mg, Na, Ca).
ADVANTAGES
High calorific value
High calorific value compared to solid fuel.
Independence from main communications
Unlike gas.
Low ash content
Around 0.3-0.5%.
Neutral:
Autonomy
If desired and available funds, it is possible to install an autonomous heating system, when the fuel will flow into the boiler automatically as it burns.
Danger to others
For boilers with an open combustion chamber, there is a risk of exhaust gases entering the room in which the boiler is located, which can lead to carbon monoxide poisoning in surrounding people. Unlike boilers with a closed chamber, where the likelihood of exhaust gases entering is minimized.
Cons
Unstable composition of fuel oil
From close to oil to highly viscous cracking residues, which leads to coking and prolongation of the combustion process.
Environmental harm
High amount of emissions of harmful substances into the atmosphere during combustion.
Warehouse space
Depending on the needs and volumes of heating, there may be a need for a spacious room for storing fuel for the winter.
High price
Compared to other types of fuels.
Presence of odor and operating noise
Compared to other types of fuels.
High sulfur content
Around 3.5%.
High pour point
Around +(25-30 °C).
3.3 FUEL
Biofuel is a combustible mixture created from plant or animal raw materials, such as soybean seeds, sugar cane, and various organic wastes. Biofuels include bioethanol, biomethanol, biobutanol, demethyl ether, and biodiesel.
ADVANTAGES
High calorific value
High calorific value compared to solid fuel.
Independence from main communications
Unlike gas.
Environmental Safety
Low amount of emissions of harmful substances into the atmosphere during combustion.
Cheap and easy installation of a heating system
No permitting documents are required, unlike gas, and qualified employees.
Neutral:
Autonomy
If desired and available funds, it is possible to install an autonomous heating system, when the fuel will flow into the boiler automatically as it burns.
Danger to others
For boilers with an open combustion chamber, there is a risk of exhaust gases entering the room in which the boiler is located, which can lead to carbon monoxide poisoning in surrounding people. Unlike boilers with a closed chamber, where the likelihood of exhaust gases entering is minimized.
Cons
High cost
Compared to other types of fuels.
High fuel storage requirements
If stored improperly, the stove may catch fire.
Warehouse space
Depending on the needs and volumes of heating, there may be a need for a spacious room for storing fuel for the winter.
3.4 USED OIL
Waste oil is hydraulic, transmission, transformer oil, as well as vegetable oil, used for its intended purpose.
ADVANTAGES
High calorific value
High calorific value compared to solid fuel.
Independence from main communications
Unlike gas.
No explosion hazard
Unlike gas.
Cheap and easy installation of a heating system
No permitting documents are required, unlike gas, and qualified employees.
Neutral:
Autonomy
If desired and available funds, it is possible to install an autonomous heating system, when the fuel will flow into the boiler automatically as it burns.
Danger to others
For boilers with an open combustion chamber, there is a risk of exhaust gases entering the room in which the boiler is located, which can lead to carbon monoxide poisoning in surrounding people. Unlike boilers with a closed chamber, where the likelihood of exhaust gases entering is minimized.
Cons
Additional costs
For filtration before use and for converting the boiler to waste oil
High fuel storage requirements
If stored improperly, the stove may catch fire.
Warehouse space
Depending on the needs and volumes of heating, there may be a need for a spacious room for storing fuel for the winter.
High fuel cost
Compared to other types of fuels.
Prices: summary table
| Model | Available power, kW | Number of circuits | Efficiency, % | Cost, rub. |
| Kiturami Turbo 13R | 13, 17, 21, 30 | double-circuit | 86 | 43 000 |
| Ferroli ATLAS 32 | 32, 47, 62, 78, 95 | single-circuit | 64,3 | 63 000 |
| ACV N3 | 16, 25, 30, 51 | single-circuit | 90 | 93 000 |
| NORTEC B70 (WB 40) | 40, 59, 147, 197 | single-circuit | — | 159 000 |
DieselLiquid fuel BoilersWaste oil
CALCULATION OF LIQUID FUEL COSTS
As an example of calculating heating costs, let’s take diesel fuel (diesel fuel). The approximate consumption of diesel fuel per hour of boiler operation can be found by multiplying 0.1 by the boiler power according to the passport. For example, if we chose a 25 kW boiler to heat 300 m3, then it will consume 0.1 * 25 = 2.5 liters of diesel fuel per hour.
Thus, to heat 300 m3 per day you will need:
2.5 liters (consumption per hour) * 24 (hours in a day) = 60 liters of diesel fuel.
For the heating season, which is 183 days (from October 15 to April 15), taking into account temperature fluctuations, you will need:
(60 liters (daily consumption of diesel fuel) x 183 days (heating season)) / 2 (taking into account temperature fluctuations) = 5490 liters.
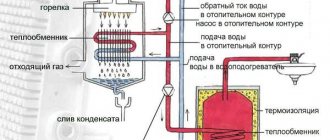
Oil burner
For liquid fuel heating units, fan (pressurized) burners are used. They atomize liquid fuel entering the burner under pressure with the required atomization ratio. Air is also forced into the burner, which is correctly called forced air.
The fuel mixture is ignited by electrodes. Further operation of the boiler is ensured by built-in automation.
Here it’s time to note that the design of boilers contains a lot of electronics and equipment powered by electricity (fans, pumps). This makes diesel boilers electrically dependent and this must be taken into account when purchasing and installing. If your home has frequent electrical problems, then you need to take care of a backup power supply.
Automation (control)
According to its characteristics, fuel can be supplied to the boiler independently; it does not need to be thrown in like firewood. Therefore, in boilers of this type, maximum attention is paid to automatic control, which minimizes the presence of a person in the operation of the boiler.
Using the example of the Kiturami boilers I came across, let’s see what is included in the boiler automation. On the body we see sensors for fuel level, temperature, and overheating. Yes, electronic remote control unit. Boiler indicators allow you to monitor the temperature of the coolant in the heat exchanger, circulation pump, burner, and power supply. Tricky buttons “Sleep”, “Shower”, also elements of universal automation. That's a plus.
Safe Operation
Liquid fuel boilers are considered high-risk objects. Improper operation of such units not only leads to a violation of thermal conditions, but can cause a boiler explosion or create a fire. Persons over 18 years of age who are certified to know the rules of safe operation are allowed to operate industrial liquid fuel units.
In domestic furnaces installed in residential buildings, the owner of such housing construction bears responsibility for safe operation. Therefore, he is obliged to follow all factory instructions for operating the installed boiler. This applies to the procedures for turning on, turning off, setting the operating mode and operating the fuel facility.
The manufacturer specifies the frequency and types of maintenance work for the unit. It is usually carried out annually before the unit is put into operation. This includes cleaning the external and internal surfaces of the boiler and smoke ventilation systems. Checking the condition of convective heating surfaces, pipelines, shut-off and control valves and primary sensors of the safety system.
conclusions
If in your area there are problems with gasification, and you cannot get additional power for an electric boiler, but you need heating in the house and you need hot water, then liquid fuel boilers are what you need.
©Obotoplenii.ru
More articles
- Kiturami liquid fuel boilers: descriptions of popular models
- Wissmann liquid fuel boilers: description, features, models
- Liquid fuel boilers Protherm review, advantages, assembly, installation
- Liquid fuel boiler, design and operation
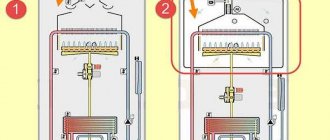
Design and principle of operation of the boiler
Liquid fuel units operate on the same principle as gas units. The main difference is the use of a fan burner (nozzle). The type of device largely determines the efficiency and economy of the boiler.
Our compatriots are considering installing a liquid fuel unit as an alternative heating method in the absence of a centralized gas supply line
Main operating units of the heat generator
Structural elements of a liquid fuel boiler:
- burner;
- the combustion chamber;
- heat exchanger;
- chimney;
- Control block;
- frame.
The liquid fuel heating installation is equipped with a line with a pump that supplies fuel and a tank for storing fuel.
To increase the performance and efficiency of the device, manufacturing companies are improving models by adding different heat exchange plates and chimney tubes to the device.
The main module of the installation, which is responsible for preparing the fuel-air mixture and transmitting it in the amount necessary to maintain the operation of the heat generator.
The liquid fuel burner is fan driven. Fuel is supplied and injected into the combustion chamber under pressure - forced air injection is performed
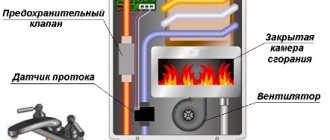
Standard burner equipment for an oil-fuel boiler:
- Ignition transformer. Generates a spark that ignites the fuel.
- Control block. Determines the start-up phases, performs control and stops the burner. The connection of a photocell, an ignition transformer and an emergency shutdown sensor is provided.
- Solenoid valve. Corrects the supply of fuel to the combustion chamber.
- Air regulator with filter. The device normalizes the air supply, preventing the ingress of solid particles.
- Preheater. Changes the state of the fuel, reducing its viscosity. The more liquid the fuel enters the nozzle hole, the more economically it is consumed.
- Fuel overflow pipe. It is connected to the tank where the fuel is heated.
- Flame pipe. Through the main line, thermal energy is supplied to the place where the coolant is heated, which then circulates in the heating system.
What to look for when choosing
When choosing a liquid fuel unit, in addition to the thermal power, which must provide all the heat losses of the building and the load on the hot water supply, it is important to pay attention to the types of acceptable fuel.
It is necessary that, according to GOST, it corresponds to the one that the owner plans to use and which is available in sufficient quantities in the area of residence to eliminate high transportation costs.
Liquid fuel heating devices work with a fuel system; it is important that the automation unit is consistent with its operation. For example, if in an emergency the heating boiler suddenly turns off, after the shut-off valve is cut off, the fuel must be returned back to the storage container.
Typically, the fuel system is not included in the delivery of the unit, so you will have to install it yourself. Some models are equipped with a fuel heater in front of the injector; attention must also be paid to this in order to take into account the fuel parameters at the outlet of the fuel supply system.