Backdraft in the combustion chamber, which occurs during gusts of wind, is a fairly common problem. A gas boiler constantly goes out during strong gusts of wind, which impairs its efficiency; due to frequent clocking, it reduces its service life, and models with manual ignition have to be constantly ignited even in the middle of the night.
The problem can arise both in floor-mounted atmospheric boilers with an open combustion chamber and a vertical chimney, and in boilers with a closed combustion chamber and a coaxial chimney. However, correcting the situation in more than 90% of cases is not difficult.
Why does a chimney need a deflector?
Why is reverse thrust bad? The fact is that the difference in air temperature in the house and outside sometimes plays a negative role. If there is insufficient draft, not only does the firewood burn poorly, but smoke and soot also enter the room. Especially when the weather is changeable. In addition to the unpleasant odor, this is fraught with dangerous air compounds for people living inside the house.
It was in order to solve the problem of air blowing in that special deflectors for the chimney pipe were created. And absolutely all types of deflectors have only one principle of operation: they increase the draft in the chimney on the channel by deflecting air flows.
The whole secret is that air flows, when they encounter an obstacle in the form of deflectors, form a zone with low pressure, and the pressure difference in the channel increases. Thanks to this, the air draft in the chimney becomes 20% more effective.
Today, to ensure forced draft, the following deflectors are installed all over the world:
A standard chimney pipe deflector consists of the following main parts:
- external cylinder , which is used as a ceramic, metal, asbestos-cement pipe;
- top glass or diffuser. Its shape expands towards the bottom, just so that it can be conveniently attached to the lower cylinder using special brackets;
- umbrella - a special cone-shaped cap that is installed on top of the diffuser;
- the bottom glass , on which everything rests.
By the way, some deflectors have a small flaw in their design. So, if the wind creates a vortex right in the hood, it will interfere with the exit of smoke from the chimney. For this purpose, an additional reverse cone is specially installed in the umbrella, which reflects such air flows and cuts them at the stage of exiting.
This roofing element is installed so that the wind cannot prevent fuel combustion products from leaving the chimney, but, on the contrary, pulls them out of the chimney, while simultaneously maintaining high-quality combustion of wood in the fireplace or stove. Deflectors are usually installed on the chimneys of heating boilers that burn solid fuel.
They do not need to be installed on gas boilers, in accordance with SNiP “Installation of smoke and ventilation ducts.” The only exception is that a turbo deflector is installed on gas pipes if the temperature of the exhaust gases does not exceed the maximum (200-500 degrees Celsius). In this case, for safety reasons, it is advisable to use special high-temperature nozzles.
Reasons for attenuation
Before looking for a problem and a way to solve it, you need to find out the type of boiler installed:
- volatile - the design of the device operates solely on power supply;
- non-volatile - its automation does not interact with electricity.
Having understood what type of unit it is, you can begin to search for the cause of the boiler failure:
- lack of electricity supply;
- power supply with fluctuations and surges;
- incorrect factory settings data;
- remote control.
These reasons come to mind for anyone who is faced with the problem of flame extinguishing in a burner. After checking each point, you should start thinking more globally.
You can, of course, immediately call a specialist, but the reason for turning off the heating can be a real trifle, which anyone can handle:
- a gas-based boiler goes out due to the low gas supply pressure of the central pipe;
- the breakdown may be hidden in some problems with the chimney pipe;
- The cause of the breakdown may be a failure of the device’s automation;
- weather conditions, strong wind blows out the igniter;
- unstable operation of the electronic system of the device, where every detail will need to be checked.
To determine a likely problem in the operation of the AOGV system, you need to pay attention to the type of unit:
- open type heating boiler;
- closed heating boiler;
- electric gas equipment.
Open type equipment
This type of boiler is equipped with an automatic valve that can stop and resume the gas supply.
There are many causes of malfunctions in open boilers, but each of them can be solved.
- There may be a loss of draft in the chimney.
- The gas pressure in the central pipe decreased, causing the boiler to stop working.
- Lack of the required amount of air.
- Strong winds can negatively affect the operation of the heating unit. When there is a draft, the flame breaks off and the device goes out.
- System failure, such as a faulty thermocouple sensor.
With closed camera
A boiler equipped with a closed combustion chamber is in higher demand. The appearance of the device resembles a miniature boiler room, which is equipped with an additional degree of protection.
It is this protection that stops the gas supply if there are compelling reasons:
- the movement of coolant in the heating system has stopped;
- the air flow has decreased or stopped altogether;
- power surges occur in the electrical network;
- a banal power outage.
Electrogas technology
Devices that additionally connect to the network may also disconnect for unknown reasons
The most important thing is to check the electricity supply. If there is current in the socket, the cause of the breakdown should be sought on a larger scale
The main signs of malfunction of electric gas equipment:
- the device shows no signs of life, the indicators do not light up, there is no sound from the unit;
- the indicators light up, the device display shows that work is in progress, but ignition does not occur in the network;
- The unit works without errors, but when ignited, the burner goes out immediately.
Blows out the gas boiler or reverse draft
If you don’t have a problem with your gas boiler or water heater blowing out in a strong wind, you are a happy person. Agree, it’s not very pleasant to wake up in winter in a bitter frost from the cold in the house and then spend half the night heating the room or soaping up under hot water, and rinsing off the soap under ice cold water. This problem was the cause of poor sleep and spoiled my mood for a long time.
Most often, the boiler goes out due to the so-called reverse draft. This means that instead of the flue gases escaping into the chimney, under the pressure of the wind they are directed into the firebox and knock down the flame.
I would like to share my experience in combating this negative phenomenon using the example of a gas water heater.
Having purchased and installed my first gas water heater in the house, I encountered an unpleasant phenomenon. In certain wind directions or gusty winds the flame went out. Moreover, in particularly severe frosts, cold air entered the heater through the chimney and, in the end, the coil was defrosted. Home repairs did not work. The gas water heater had to be replaced. After this, we had to close the chimney at night, just in case.
What do they advise on the Internet to combat backdraft?
- The first advice that is present everywhere is to increase the length of the chimney
- The second tip is to install a deflector (deflecto - deflect) at the end of the pipe to increase traction.
- The third tip is to try to avoid sharp turns in the chimney flue.
- Other tips, in my opinion, are less interesting.
How I dealt with the water heater and boiler blowing out
- Extended the chimneys by about 1 meter. The result is zero.
- I installed fungi at the ends of the pipes. Did not help.
- I installed 2 types of deflectors on the chimney of the water heater. The result is negative.
The boiler no longer blows. No backdraft
A positive result for the boiler was obtained after installing a Grigorovich deflector on the chimney. Now, in any wind, reverse draft does not occur.
Grigorovich deflector on the boiler chimney (right)
For the water heater, the problem turned out to be more interesting. I installed, in my opinion, a very good homemade traction amplifier of the Wind-Voodoo type. It works like a weather vane, turning its “back” to the wind. By the way, crows began to fly around my yard because... The traction amplifier is made in the shape of an eagle.
Deflector traction booster type Wind-Voodoo
Adding my eagle, unexpectedly for me, had no effect.
Replacing the flexible aluminum pipe from the heater to the chimney hole in the wall from a diameter of 120 to 100 helped to completely get rid of reverse draft. The fact is that my first water heater made in the USSR had an “exhaust” diameter slightly larger than the diameter of the pipe, the new “Oasis” has an outlet 100 mm. Because of this, the pipe was simply put on top of it with large gaps. I also made the transition from the heater to the chimney smoother. In aesthetic terms, it lost, but the flue gases turned out to move easier, with less resistance.
Connection of the water heater with the smoke duct
These modifications have been tested throughout the winter and we can confidently say that the boiler and water heater no longer blow out. There is no backdraft effect.
The reverse draft is blowing out of the gas boiler. What to do if the gas boiler or water heater is blowing out. How to deal with the backdraft effect. The role of the deflector to increase draft in the chimney.
Reasons for blowing
Before you ask what to do if the wind blows out your gas boiler, you need to determine the cause of the problem. According to experts, the boiler blows out for several reasons. One of them is the appearance of an ice build-up on the installation head.
With this phenomenon, there is no need to rush to knock off the ice, as this can lead to damage to important elements of the heating system. If an ice edge appears on the head and inside the boiler, and the oxygen flow no longer enters the installation, it means that it will stop working. In this case, you should slowly defrost the head by removing it and moving it into the house.
While the tip is thawing, it is necessary to stop the gas supply, and after igniting the igniter, slowly open the tap. After waiting for flames to appear in the main burner, you need to warm up the device. This will allow the structure to operate at minimal gas pressure. With a stable temperature increase, the pressure can be increased.
When trying to understand why a gas boiler blows out in the wind, it is important to know about all the design aspects and structure of the system. Correct and timely measures will avoid many troubles and protect the installation from damage.
The burner flame has blown out - we solve the problem with the chimney
If your autonomous gas boiler constantly blows out, first look for problems in the chimney design. Pressure drops in a gas pipe occur extremely rarely, and the pressure drop is insignificant. A technical malfunction of a gas boiler, due to the simplicity of the design of heating equipment and the high degree of reliability of modern models, is also unlikely.
The most common situations encountered related to the chimney:
- ice crust covering the ventilation duct of the heating device - the formation of an ice cap inside the chimney prevents air circulation, putting the gas boiler in a state of oxygen starvation (along with combustion products, water vapor enters the chimney duct, condensing and freezing on the walls of the chimney);
- reverse draft that occurs when the wind increases or changes direction (a strong air flow, entering the chimney, reaches the combustion chamber and extinguishes the flame in the boiler).
Troubleshooting
It is very important to detect malfunctions in the operation of a gas boiler in time and eliminate them in time to avoid accidents. The main sign of a gas boiler malfunction is very weak combustion of the burner or its complete absence
There can be many reasons for this manifestation.
Malfunction of the internal mechanism of the gas boiler
Another sign is that the burner is difficult or impossible to light. This manifestation can occur due to filter clogging, broken electronic contacts, or violation of the electrode gap. If the filter can be cleaned yourself, then if other problems arise, a professional approach is required.
Other signs of a gas boiler breakdown include noise and spontaneous shutdown of the device, nozzle whistling, and others.
How to deal with backdraft. Basic mistakes and misconceptions
It was previously said that backdraft can be combated by increasing the length of the chimney. The solution to the problem is quite simple, but such a solution does not always give positive results.
The second solution to the problem in such a situation is to install a deflector on the upper edge of the chimney, the task of which is to increase the draft in the chimney.
The third option is to reduce the number of bends and sharp turns of the chimney, which increase cavitation (vortex) of the flow of hot air with smoke as it passes through the pipe.
In both the first and second cases, the situation will not change radically. Extending the pipe by 1 meter will not give the expected effect. Installing a deflector on the chimney also does not completely solve the problem. If the weather worsens significantly, the wind will still blow out the unprotected gas boiler, and the heating will fail again. What to do? What is the optimal solution?
A specially designed deflector is a solution to the problem
An effective method that can solve the problem of reverse draft once and for all is to install an aerodynamic device on the chimney - a deflector of a special design.
In a conventional deflector, air flows act on its outer part. As a result of the interaction of the air mass with the surface of the deflector, a rarefied atmosphere is created, which increases the draft in the chimney. The phenomenon is called the Bernoulli effect, the concept of which came to us from aviation. In other words, when air encounters an obstacle and bends around it, a rarefaction zone is created around the obstacle, enhancing the lifting effect of the wing.
For reference: a deflector of even a conventional design increases the efficiency of any chimney by 15-20%, not to mention devices with a more complex design.
If a conventional deflector is not able to eliminate wind blowing of a gas boiler, a device of a more complex design is installed. Today there are several types of deflectors with complex configurations. Among the most popular products, the following types should be highlighted:
- “Smoke tooth” type deflector;
- Grigorovich deflector;
- "Voller" type deflector;
- spherical and rotating deflectors.
Two types of devices are considered the most popular in our country: the Grigorovich deflector and “smoke tooth” devices.
The Grigorovich deflector is a device in the design of which all contours and elements are directly related to aerodynamics. Unlike the usual umbrella-shaped deflectors we are used to, standing on pipes in private homes, this device has two cones, direct and reverse. The interaction of the two cones ensures the necessary movement of air flows, thereby creating a zone of low pressure around the chimney. Due to the temperature difference between the cold and hot flows, the draft in the pipe increases several times, preventing any penetration of outside air inside.
Note: deflectors of complex design, on the contrary, use the force of the wind to increase draft in the chimney, that is, when there are gusts of wind at an angle, from above or below, air, penetrating under the lower cone of the deflector, sucks in the air masses entering the chimney.
With the correct location and design of a chimney equipped with a deflector, backdraft will not threaten you - any gusts of wind will not be a problem for a working boiler.
Another point worth noting is when the wind blows out the gas boiler and the heating system does not start. We are talking about an insufficiently heated chimney. During long shutdowns of the heating system, which is typical for country houses and cottages, when the boiler is first started, the burner flame often quickly extinguishes. The explanation for this behavior of gas heating equipment is quite simple - it is difficult for waste combustion products to rise up a cold chimney, and any gusts of wind only hinder the heating of the channel.
To get out of this situation, it is enough to warm up the chimney at low boiler operating modes, gradually increasing the power of the device to optimal parameters, and the hot combustion products in the heated chimney will rush upward naturally.
How to make water heated floors with your own hands?
Today, the most common option for warm water floors is concrete water flooring. Since in this design the pipes are completely covered with a screed, there is no need to install any additional heat separators. You can learn how to make a heated floor on the ground.
Installation of concrete water floors takes place in several stages:
- The entire room must be divided into equal sections, their area should not exceed 40 square meters.
- The rough surface of the floor must be covered with insulation materials.
- Next, you should lay the reinforcing mesh and install the pipe contours.
- The heating system needs to be tested.
- Pour the concrete screed.
- After all the above steps, you can proceed to finishing work.
Marking the room is necessary in order to avoid cracks in the concrete screed due to temperature changes. The ratio of plots should be 1:2.
Concrete floors should be cleaned and then insulated with insulating material.
This is done to ensure that there is no heat loss in the room. A variety of materials used for these purposes in construction can be used as a thermal insulation layer. A layer of polyethylene must be laid on top of the thermal insulation material.
The reinforcing mesh should be laid in cells, the size of which should be 150 by 150. The cross-section of the mesh rods should vary between 4-6 mm. Sometimes a second layer of reinforcing mesh is laid on top of the installed pipes. Pipes should be placed on top of the mesh. This is done taking into account design features. Typically the distance between pipes is from 70 to 300 mm. Plastic clamps help secure pipes and reinforcement mesh. Sometimes special wire is used for these purposes. The pipes should not be rigidly fixed to the fittings, so that later when the temperature changes, deformation of the screed does not occur. We recommend reading the article “Electric floor - comfort and warmth of your beloved home.”
There are many ways to lay pipes, for example:
- spiral,
- double snake,
- snake
However, it is worth considering that when installing pipes in internal walls, you need to take as small a step as possible. At one end the pipe must always be attached to the supply manifold, and at the other - according to the design diagram.
When the pipes are laid, you should proceed to crimping. This procedure is carried out under working pressure. Pressure testing is necessary to avoid mechanical damage. After this operation, you can proceed to pouring the screed. Before this, the system should stand for a couple of days with a pressure of 3-4b. An article about the “warm baseboard” heating system will also be interesting.
At the end you can carry out finishing work. The final layer of the floor covering must be selected taking into account its temperature resistance. We recommend reading the article about laying solid boards on different types of flooring.
Making a deflector
The simplest version of a deflector such as a Volpert-Grigorovich device is quite easy to make with your own hands.
Required tools and materials
- Marker or felt-tip pen.
- Ruler.
- Iron scissors.
- Mallet.
- Wooden beam for stand.
- Riveting device.
- Drill, metal drills (or drill-tip screws).
- Galvanized iron sheet 0.3–0.5 mm thick (aluminum sheet or thin stainless steel is suitable).
- Metal parts that are available: corner, studs, thick wire and the like.
Size calculation and diagram
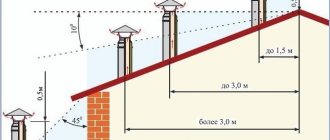
Since the quality of the deflector depends on the accuracy of manufacturing, drawing up the correct drawing is the most important step in the entire process. The dimensions were verified by scientists in a wind tunnel, and they must be followed. The parameter to start from is the diameter of the chimney channel D.
The dimensions of all parts of the deflector are set in proportion to its diameter
Table: dimensions of deflector parts relative to its diameter
| Index | Coefficient in relation to diameter |
| Lower diffuser diameter | 2 |
| Upper diffuser diameter | 1,5 |
| Diffuser height | 1,5 |
| Recessing the pipe inside the diffuser | 0,15 |
| cone height | 0,25 |
| umbrella height | 0,25 |
| reverse cone height | 0,25 |
| Gap between umbrella and diffuser | 0,25 |
Instructions for making a deflector with your own hands
- We transfer the drawn details onto cardboard and make a cardboard mock-up. We check that the parts match each other.
- Let's open the layout back up. We trace this cardboard pattern, placed on a galvanized sheet, with a marker.
- We cut out all the details with iron scissors.
- We roll up the casing and drill holes in its edges.
- We fasten the casing with rivets (or we don’t drill or fasten it, but use drill-tip screws).
- In the same way, we fasten the lower and upper cone plates in turn.
- The top plate is larger, so we cut 6 tabs in its edge to attach to the bottom plate.
- We attach studs to the bottom plate to connect to the casing.
- We use them to attach the umbrella to the casing.
- To secure the finished deflector to the chimney, it is better to separate the top part of the pipe and connect it to the deflector on the ground. The strength of this connection is extremely important. The wind load at altitude will be great and can interfere.
The deflector may not be very beautiful, but you will immediately feel its usefulness: the draft will increase by a quarter, the roof will be protected from sparks. The pipe with it can be one and a half to two meters lower.
Pouring technology
Forming a concrete floor on the ground is a rather complex procedure that requires compliance with the following sequence of actions:
First of all, a rough foundation is prepared. To do this, the top layer of soil is removed, and in its place is placed dense soil, which was obtained after digging a hole for the foundation. Try to completely remove soil containing organic matter, as it will rot and sag over time. After leveling, this layer must be compacted with a vibrating plate.
Please note that the bottom of the wire should not come into contact with the insulation. Therefore, the entire mesh is raised above the surface using special plastic bosses
If it is planned to form a warm floor inside the room, then all its elements must be placed directly on the fittings.
When everything is ready, fill the floor from scratch
It is important here to do everything at once in order to form a monolithic structure. Alignment of the screed occurs according to previously installed beacons or relative to marks on the walls
Before pouring, be sure to secure damper tape along all walls. It can be purchased at any hardware store or made from small pieces of polystyrene foam.
Finishing the floor occurs only after the concrete has completely dried. This period can last from 1 to 2 months depending on the thickness of the screed.
Effect of altitude
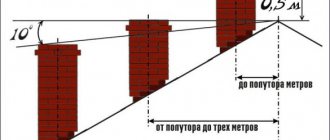
As for the height of the chimney, the higher it is, the better the speed of smoke movement . However, there are also limitations here. A chimney that is too high creates a lot of resistance to smoke movement, resulting in worse draft. That is, it decreases.
The correct chimney height is five meters. The starting point is considered to be the level of the grate. This height is quite enough for any weather. However, experts advise making calculations based on a specific case, because it may be that this height will create excessive thrust. The consequence of this is an increase in the need for firewood. If such a height is planned without taking into account specific features, then you will have to use means by which the draft in the chimney can become less.
There is also one more nuance. Chimney channels can be horizontal. This increases the length of the chimney, which also affects the speed of smoke movement. It decreases because smoke turbulence . Soot always accumulates in these places. It also reduces the diameter of the passage , as a result of which the thrust weakens. To ensure optimal speed, increase the height of the chimney by an amount equal to the length of the horizontal sections.
Checking and determining traction
These two processes are necessary for those people who want to optimize the heat transfer from burning wood and minimize heat loss. Such owners must use special devices.
Also, the speed of movement of carbon monoxide can be calculated by making an assessment of the flame. So, you can check whether the craving is normal or very strong.
In addition to these methods, there are folk ones. They involve the use of a sheet of paper or a match. The first one is brought to the chimney. The position of the paper should be perpendicular to the channel. If the sheet begins to deviate from its original position, then air moves through the chimney. The amount of deviation depends on the speed of air movement. The calculation will not be very accurate, however, it will be sufficient for making further decisions.
The match is lit and blown out. Next, they quickly move it into the firebox and observe the direction of movement of the smoke . This check is very simple.
Ways to reduce
It involves using a special regulator. This device has a mechanism for regulating the pressure in the pipe and a special sensor that analyzes the current draft. It can create a pressure of 10-35 Pa. Works automatically. Such a regulator is the best solution, since it can both reduce and increase thrust. Thanks to it, there will be no backflow of smoke.
The blower is also very effective. It affects the supply of fresh air to the firebox. If you close it completely, then a minimum of air will enter the firebox and the draft will immediately decrease.
How to reduce draft in a cast iron stove-fireplace
It is not easy to answer the question, since its motives are completely unclear. It is difficult to imagine a situation in which there might be a need to radically reduce cravings. And it’s even more difficult to understand what kind of stove design we are talking about. Cast iron stove-fireplace is a very broad and loose term that combines various systems. It is very difficult to give recommendations at random, without understanding what kind of stove we are talking about. Therefore, let's try to consider several possible options.
Modern wood-burning stove-fireplace. Combustion is regulated by a blower. It is advisable to place a large open section of pipe at the beginning of the circuit - it heats up intensely, but deliberately participates in heat exchange. Such a stove is more decorative than utilitarian; there is no need to do anything with its draft - it will cost you more
Let's start with something simple. How is traction generally adjusted? In theory there are two options:
- change the cross-section of the chimney (regulated by a valve);
- change the amount of oxygen entering the combustion zone (regulated by the blower).
In practice, it is impossible to regulate draft by pipe cross-section - it is dangerous, because Carbon monoxide may enter the room. You can and should regulate the blower, but there are some nuances here too.
Too much oxygen - heat will simply go into the pipe, reducing efficiency. Too little oxygen and it will get worse. The fuel will not burn completely and the (very intense) deposition of soot and stove condensate (creosote) will begin on the inner walls of the stove and chimneys. Such deposits disrupt heat transfer - soot is a good heat insulator. Even more dangerous is that soot is 90% carbon, and therefore terribly flammable. At some point it may catch fire. The process can be explosive or chain in nature. In any case, soot burning is a very intense process, and the temperature develops extremely high - 1100 degrees (600 degrees during normal wood combustion). Not every pipe can withstand this temperature.
Therefore, it is important to select the desired degree of combustion. This is very easy to do based on the color of the flame:
- Burns with a white flame - a clear excess of oxygen. We cover the vent (door or valve - depends on the specific design).
- If the color of the flame is reddish, there is a clear lack of oxygen and intensive soot deposition is taking place. We open the vent.
- The normal flame color is straw yellow. Some “experts” advise “smothering” combustion by increasing its duration and reducing its intensity. Indeed, initially the heat transfer of the furnace increases noticeably, but this effect is short-lived. Very soon, the harm from such a combustion regime many times overpowers the very illusory and controversial savings.
External factors
Why is there poor draft in the stove if it is built correctly and the chimneys have recently been cleaned?
In addition to the above reasons, stove draft depends on external environmental factors and weather. The most common of them:
- improper ventilation in the house,
- fluctuations in temperature and humidity outside,
- wind and other climatic factors.
Let us consider in more detail what we have to do in these cases.
Ventilation failure
The influx of fresh air helps to establish the required pressure difference in the stove and chimney. If the house is cold and the stove has not been fired for a long time, this difference is minimal. And the lack of air in the combustion room can create a temporary vacuum in the room and provoke reverse draft. On the other hand, excessive drafts are also unfavorable, since vortex air flows can disrupt the air flow into the firebox and disrupt proper draft.
This is often observed in the summer, and also if the windows are located above the firebox level, in this case it will be easier for the hot air to change direction towards the exhaust through the window. You need to be especially careful with gas stoves; there is a danger of not only changing the direction of draft, but also extinguishing the burner and filling the room with gas.
Before the first attempts to light the stove, it is necessary to check not only the draft in the firebox, but also the air movement in the room, and when using the stove, constantly monitor the ventilation. This is also necessary to prevent carbon monoxide poisoning.
Strong wind
Gusts of strong wind may temporarily prevent smoke from escaping from the chimney. With such a disruption of the flow of hot gas, the thrust may work in the opposite direction. This happens more often with chimneys connected directly to the firebox without passing through heating wells.
The situation in the wind is also worsened by the horizontal location of the pipe exit, which is often used in the utility rooms of the lower floors of the house (exit through the wall).
Protection from the prevailing winds in a given area is provided with the help of pipe caps, “smoke chambers” or “wind vanes”. They also prevent getting wet during rain and snow. The humidity of the outside air is another obstacle to good traction.
Installing a chimney will solve the problem
High humidity
This factor is indirect, but no less unpleasant. High humidity in the external air can form due to low atmospheric pressure, which already reduces draft. The increased density of the humid surrounding atmosphere reduces rarefaction and impairs the movement of smoke.
It is easy to notice that during rain and snow, smoke reluctantly comes out of the chimney, spreads along the roof, and with every gust of wind escapes through the stove door into the room. And vice versa, in clear dry weather the draft is excellent and the smoke rises to the sky. Finally, with high humidity in winter, a dense coating of frost forms in the pipe, which sharply reduces the cross-section and prevents the normal release of gases.
In this situation, you will have to clean the chimney frequently.
What type of gas boiler to choose so that the flame does not blow out
The minimum speed of flue gases at which the flame will not be blown out is 6-8 m/s. Flows of heated air entering the chimney move in a spiral. The vortices gradually increase in speed, which reaches maximum intensity at the exit from the chimney.
There are boilers in which the natural movement of flue gases is replaced by forced one. The design of turbocharged models with a closed combustion chamber includes two blower fans. The first one supplies air to the firebox, the second one removes combustion products. It is impossible to blow out a turbocharged unit with wind. Attenuation indicates that one of the failed fans needs to be replaced.
The wick burns weakly
Gas boiler wick
The wick burns weakly for two reasons: either it is clogged and needs to be cleaned, or you have weak inlet pressure. If you have a home controller, be sure to check its settings. You may need to increase the inlet pressure, as it constantly fluctuates due to the fact that gas consumption is different in different periods.
Accordingly, during the heating season, when gas boilers are operating, gas consumption is higher and the inlet pressure also drops. And the regulator, as far as you know, maintains a certain differential between the inlet pressure and the outlet pressure. Accordingly, this differential also drops, because of this your wick may burn weaker. Check the regulator setting and also clean the wick.
Solving the problem for different types of boilers
Equipment with a closed burner is called turbocharged and requires electricity to operate. To prevent damage to the control board during power failures, a voltage stabilizer is installed when installing boilers.
Boiler units with an open combustion chamber are called atmospheric . They are independent of the power supply system.
Thus, atmospheric and turbocharged boilers have different designs. Therefore, the principles for solving the problem of their attenuation will also differ.
Atmospheric boilers are energy independent. But in a turbocharged engine, the cause of burner extinguishing may be a problem in the electronic part, and not just blowing wind
In atmospheric boilers the draft is natural. The device does not receive the set volume of air if it is insufficient or there is insufficient air flow. It is necessary to artificially increase the volume of oxygen taken in by installing additional supply ventilation and a regular hole in the door with a grill.
You can also use one of the following methods:
- reducing the diameter of the chimney by installing an internal pipe, which will speed up heating and eliminate the effect of excessive dilution of gas with air;
- installation of a deflector;
- increasing the length of the chimney.
Turbocharged boilers are more stable in operation, but only if they are installed on the leeward side.
In the opposite situation, installing a deflector or reconstructing the chimney by creating a “draft break” - constructing a zone inside the chimney that prevents the reverse movement of combustion products.
We make sure that the burner goes out due to the wind
In order not to waste efforts in vain, which sometimes happens in practice, it is worthwhile to accurately determine the reasons for the burner extinguishing, since this could be an automatic error, low gas pressure, or difficulties with the removal of combustion products. Characteristic signs of wind blowing are:
- visual changes in the shape and direction of the flame caused by the wind;
- characteristic sound of a vortex in the combustion chamber;
- the burner does not turn off without reason in calm weather, be sure to check this item!
A common cause of fading is low gas pressure in the line or incorrect flame height. At low gas pressure, the flame decreases and drops critically low to the burner. To prevent it from burning out, the automation turns off the burner and the boiler goes out. The normal flame height is considered to be 2-4 cm. If the burner flame height is less, it is necessary to adjust it, but we do not recommend doing this yourself; for this it is better to call the gas service.
It is also necessary to check the tightness of the connections and the entire chimney structure. First of all, if there is an inspection hole in the chimney, pay attention to it: it must be closed and hermetically sealed. If this is not possible, it is worth purchasing a modern sealed plug.