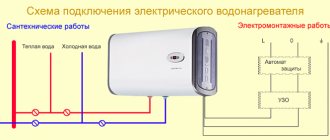
The heating system of a multi-story building is of particular interest; it can be considered using the example of a standard five-story building. It is necessary to find out how heating and hot water supply function in such a house.
Heating diagram for a two-story house.
In a five-story house, central heating is assumed, the house has a heating main inlet, there are water valves, and there may be several heating units.
In most houses, the heating unit is locked, which is done to achieve safety. Despite the fact that all this may seem very complicated, the heating system can be described in simple words. The easiest way is to take a five-story building as an example.
The heating scheme for the house is as follows. After the water valves there are mud traps (there can be only one mud trap). If the heating system is open, then after the mud traps through the inserts there are valves that are located from processing and supply. The heating system is designed in such a way that water, depending on the circumstances, cannot be taken from the back of the house or from the supply. The thing is that the central heating system of an apartment building operates on water that is superheated, the water is supplied from a boiler room or from a thermal power plant, its pressure ranges from 6 to 10 kgf, and the water temperature reaches 1500°C. Water is in a liquid state even in very cold weather due to increased pressure, so it does not boil in the pipeline to form steam.
When the temperature is so high, the hot water supply is turned on from the back of the building, where the water temperature does not exceed 700°C. If the temperature of the coolant is low (this happens in spring and autumn), then for the normal functioning of the hot water supply this temperature cannot be sufficient, then the water for the hot water supply comes from the supply to the building.
Now you can disassemble the open heating system of such a house (this is called an open water intake), this scheme is one of the most common.
Related article: How to hang a ceiling cornice with your own hands
Heating standards for apartment buildings heated centrally
These norms are the most “ancient”.
They were calculated at a time when they did not save on fuel for heating the coolant, the batteries were hot. But houses were built mainly from materials that were “cold” in terms of heat-saving qualities, that is, from concrete panels. Times have changed, but the norms remain the same. According to the current GOST R 52617-2000, the air temperature in residential premises should not be lower than 18°C (for corner rooms - at least 20°C). At the same time, the organization that supplies thermal energy has the right to reduce the air temperature at night (0-5 hours) by no more than 3°C. Heating standards are set separately for different rooms of the apartment: for example, in the bathroom it should be at least 25°C, and in the corridor - at least 16°C.
Society has been fighting for a long time, and at times not unsuccessfully, to change the procedure for determining heating standards, tying them not to the air temperature in the premises, but to the average temperature of the coolant. This indicator is much more objective for consumers, although it is unprofitable for the heat energy supplier. Judge for yourself: the temperature in residential premises often depends not only on the operating system, but on the nature of a person’s life activity and living conditions.
For example, the thermal conductivity of brick is much lower than that of concrete, so in a brick house at the same temperature you will have to spend less thermal energy. In rooms such as the kitchen, the process of cooking food does not generate much less heat than from radiators.
Much also depends on the design features of the heating devices themselves. For example, panel heating systems will have a higher heat transfer rate than cast iron radiators at the same air temperature. Thus, heating standards tied to air temperature are not entirely fair. This method takes into account the outside air temperature below 8°C. If such a value is recorded for three days in a row, the heat generating organization must unconditionally supply heat to consumers.
For the middle zone, the calculated values of the coolant temperature depending on the external air temperature have the following values (for the convenience of using these values using household thermometers, temperature indicators are rounded):
Outside air temperature, °C
Temperature of network water in the supply pipeline, °C
Using the table above, you can easily determine the water temperature in a panel heating system (or any other) by using a regular thermometer at the time of draining part of the coolant from the system. For the forward branch, use the data in columns 5 and 6, and for the return branch, use the data in column 7. Note that the first three columns establish the release temperature of the water, that is, without taking into account losses in the transmission main pipelines.
If the actual coolant temperature does not correspond to the standard temperature, this is the basis for a proportional reduction in the payment for the central heating services provided.
There is also an option to install heat meters, but it only works when all apartments in the building are served by a centralized heating system. In addition, such meters are subject to annual mandatory inspection.
Combined heating piping layout
Often there is not just one heating device installed in a room, but several. It is irrational to connect a separate two-pipe loop-branch to each radiator during collector-beam wiring. It is better to lay a separate branch to each room, which will bypass several heating devices inside the room, implementing a dead-end or parallel circuit.
Scheme of combined heating system wiring.
Such a system is calculated as a beam system. Branches that supply several radiators with coolant are subject to a separate calculation as dead-end or passing. In modern systems, radiators are equipped with thermal valves (temperature regulators), which can be adjusted by users to different temperatures, based on the current requirements for comfort in the room. It becomes difficult to maintain temperature stability in the room.
It turns out that you can get rid of instability while simultaneously reducing the cost of connecting radiators by connecting them according to the so-called. "pass-through scheme".
“Walk-through” radiator connection diagram.
The thermal valve is installed only on the first radiator in the circuit, regulating the coolant flow through all heating devices connected in series. They are perceived as one radiator. Balancing difficulties will arise with multi-section devices (10 or more sections).
Good old stoves
Potbelly stove stove
A potbelly stove is a portable metal stove that is suitable not only for heating, but also for cooking. And due to the material used in their manufacture, such stoves warm up the room almost immediately. At the same time, the main drawback of potbelly stoves is also associated with this - the temperature begins to drop immediately after you stop heating. A modern modernized version of potbelly stoves are the stoves of Professor Butakov, which we have already written about on our website.
Today, such devices are in many ways superior to their competitors and are widely used in garages and domestic premises, in country houses, but they can also be used at home. Indeed, at minimal cost you can heat the room in record time. The main thing here is to properly organize the removal of smoke from the room.
The average cost of a potbelly stove is 3000-3500 rubles.
Radiant heating system
- Radiant heating system - the optimal solution
- Radiant heating: a simple scheme of actions
- Editing like aerobatics
- You can’t do without a circulation pump
Heating systems require a dilemma, especially when it is necessary to include both the personal preferences of the owners and the individuality of the structure that needs heating. Those who live in apartment buildings are familiar with the pattern: the higher the floor, the less heat there will be, which means the degree of comfort will decrease and the health of the families living there will worsen. The reason is the sequential combination of heat exchangers to one, passing through and connecting the riser together. The consumption of purchased pipes allows you to save on them, but it is impossible to achieve a uniform temperature in all apartments. The temperature will also vary in the rooms that make up the living space.
It is recommended to combine pipe lines made of polypropylene and copper materials by welding.
Time shows that a radiant heating system is most suitable for balanced temperature control. To designate it, the synonym collector is used. This modern heating system has proven itself with its performance criteria and safe characteristics for residents.
Types of beam wiring
Method 1. With forced water circulation
Previously, a radiant heating scheme equipped with pumps that pump water was not very popular due to the high cost of parts. But now the price of equipment has dropped significantly, and more and more people are choosing it.
The main difference from the gravitational scheme is that liquid (water or antifreeze) flows from the boiler to the batteries and back not due to the difference in temperature and pressure, but with the help of pumps.
This results in the following benefits:
- there are no restrictions on the geometry and number of rooms in housing construction;
- heating can be installed in rooms of any size;
- To connect radiators and collectors, you can use pipes of any length, laid without a slope.
One of the elements of a radiant heating system with forced circulation is a pump
Advice! Despite the fact that the circulation pump can be installed at any point in the system, it is advisable to do this on the return manifold before supplying coolant to the boiler. There the liquid temperature is the lowest, which has a positive effect on the service life of the equipment.
Method 2. With natural water circulation
In this case, the coolant moves due to gravity: the heated water becomes less dense and lighter, therefore it is displaced to the upper point of the system, after which, as it cools, it flows through the collectors and radiators, and then returns to the heater.
The gravity beam heating system has the following features:
- During installation, an open expansion tank is required, installed at the highest point. It compensates for the thermal expansion of the coolant and prevents an increase in internal pressure in the pipelines.
- A radiant heating network with natural circulation does not require the installation of expensive electrical equipment, which significantly reduces the estimated cost of work.
- Heating with natural circulation is completely energy independent. Even if there is a power outage, which often happens in summer cottages or in rural areas, you will not be left without heat.
The gravity heating system does not use pumps
Carpets and crevices
It is worth noting that we ourselves, even at night while sleeping, produce a fairly large amount of heat. In order to heat a room exclusively on your own, it is necessary to minimize heat loss.
Primarily they occur due to the presence of cracks. If you do not have plastic windows, you will have to glue their perimeter with a special insulation, which will not allow cold air to penetrate into the apartment through the cracks, and warm air to seep out. The same applies to the front door - its perimeter should also be sealed with special insulation.
Cool surfaces also have a big impact on the temperature in the room. First of all, this concerns the floor and glass on the windows. To prevent the air in the entire room from being cooled by the window glass, it is better to curtain the windows at night with thick curtains that will cover almost the entire space from the eaves to the floor. This will allow some of the cool air to remain between the window and the curtains, preventing it from leaking into the rest of the room. All this is due to the low degree of thermal conductivity. Thanks to the same property of dense fabric, you can keep the heat in the room by covering the floor with any carpet.
Design features of the heating circuit
In the heating circuit behind the elevator unit there are various valves. Their role cannot be underestimated, since they make it possible to regulate heating in individual entrances or in the whole house. Most often, the valves are adjusted manually by employees of the heat supply company, if the need arises.
Modern buildings often use additional elements, such as collectors, heat meters for batteries and other equipment. In recent years, almost every heating system in high-rise buildings has been equipped with automation to minimize human intervention in the operation of the structure (read: “Weather-dependent automation of heating systems - about automation and controllers for boilers using examples”). All the described details allow you to achieve better performance, increase efficiency and make it possible to more evenly distribute thermal energy throughout all apartments.
Hot water supply in heating systems
DHW in multi-storey buildings is usually centralized, with water heated in boiler rooms. Hot water supply is connected from heating circuits, both single-pipe and double-pipe. The temperature in the hot water tap in the morning can be warm or cold, depending on the number of main pipes. If there is a single-pipe heating supply to an apartment building with a height of 5 floors, then when you open a hot tap, cold water will flow out of it first within half a minute.
The reason lies in the fact that at night, rarely do any residents turn on the hot water tap, and the coolant in the pipes cools down. As a result, there is an overconsumption of unnecessary cooled water, since it is drained directly into the sewer.
Unlike a single-pipe system, in a two-pipe version, hot water circulates continuously, so the above-described problem with hot water does not arise there. True, in some houses, a riser with pipes is looped through the hot water supply system - heated towel rails, which are hot even in the summer heat.
In the summer, the entire system that provides central heating in an apartment building is tested. Utility services carry out routine and major repairs on the heating main, while disconnecting certain sections of it. On the eve of the upcoming heating season, the repaired heating main is re-tested (for more details: “Rules for preparing a residential building for the heating season”).
Features of heat supply in an apartment building, details in the video:
Why do residents refuse central heating?
There are a number of reasons for this:
- unjustified heating costs;
- poor-quality heating of the apartment during the cold period;
- improper heat distribution (especially for corner apartments and rooms located on the ground floor);
- dependence on the established timing of the heating season (cold in autumn and hot in spring);
- inability to maintain the desired temperature at any time.
Judging by the reviews, those who abandoned the central heating system and spent money on installing a “autonomous system” quickly return the invested funds, saving on utility bills.
Pressure drop
In order for the heating system to perform its functions normally, the pressure drop, which is the difference between its values at the supply and return, must be of a certain and constant value. In numerical terms, it should be in the range from 0.1 to 0.2 MPa.
A downward deviation of the parameter indicates a failure in the circulation of the coolant through the pipes. A fluctuation in the direction of increasing the indicator indicates airing of the heating system.
In any case, you need to look for the reason for the change, otherwise individual elements may fail.
If the pressure has dropped, then check for leaks: turn off the pump and observe changes in static pressure. If it continues to decrease, then they look for the location of the damage by sequentially removing different sections from the diagram.
If the static pressure does not change, the reason lies in equipment malfunction.
The stability of the operating pressure drop initially depends on the designers, on the hydraulic calculations they performed, and then on the correct installation of the line. The heating of a high-rise building functions normally, the installation of which takes into account the following points:
- The supply pipeline, with rare exceptions, is located at the top, the return pipeline at the bottom.
- Spills are made of pipes with a cross-section from 50 to 80 mm, and risers and inlets to batteries - from 20 to 25 mm.
- In the heating system, regulators are built into the bypass line of the pump or the jumper connecting the supply and return, ensuring that even with sudden changes in pressure, airing will not occur.
- The heat supply circuit contains shut-off valves.
There are no ideal operating conditions for a heating system. There are always losses that reduce pressure indicators, but still they should not go beyond the limits regulated by the Construction Norms and Rules of the Russian Federation SNiP 41-01-2003.
The concept of heating standards can be completely different for two situations: when the apartment is heated centrally, and when autonomous heating is installed and functioning in the house.
Central heating in the apartment
How to choose a boiler?
Having decided on the power of the boiler, proceed to choosing its type . The boiler can be single-circuit (i.e., intended only for heating) or double-circuit (in addition to heating, the boiler heats water).
Next you need to decide on the type of fuel. Boilers are single-fuel (gas boilers or electric boilers) and combined type, that is, they can operate on different types of fuel (for example, gas + electricity or gas + liquid fuel + electricity).
It is also worth considering when choosing a boiler - the material of manufacture; This factor affects the lifespan of the equipment. Boilers made of steel or cast iron are quite heavy and more difficult to install, but they last a long time.
A gas boiler
Autonomous gas heating is the most relevant today, since gas is considered the cheapest type of fuel.
A closed-type gas wall-mounted boiler with a combustion chamber, according to experts, is the best option for home heating today. It has a horizontal smoke exhaust system, due to which carbon monoxide escapes to the street.
Advantages of a gas boiler:
- silent operation;
- multi-level security system;
- maintaining the required temperature in the apartment, regardless of gas pressure;
- acceptable price.
Electric boiler
Electric heating can be the main or additional heating option. The system is easy to use, easy to install, and takes up little space.
Electric boilers can be wall-mounted or floor-mounted . Both options are effective, silent, and functional.
Electric heating is less in demand than gas heating, but in the future, perhaps, this type of fuel will become more relevant.
Features of heating an apartment in a multi-storey building
By carefully reading the instructions for the heating scheme of a multi-storey building, you can make sure that all norms and requirements must be observed.
Any apartment must have adequate heating, raising the air temperature to 22 degrees and maintaining indoor humidity within 40%.
The layout of the heating system of an apartment building provides for its proper installation, thanks to which it is possible to achieve such temperatures and humidity.
In the process of designing such a heating scheme, you should invite highly qualified specialists who will be able to accurately calculate all the necessary aspects for the work. They must ensure that uniform coolant pressure is maintained in the pipes. This pressure should be the same on both the first and last floors.
The main feature of a modern heating system for a multi-storey building is that it operates on superheated water. This coolant comes from the thermal power plant and has a very high temperature - 150C with a pressure of up to 10 atmospheres. Steam is generated in the pipes due to the fact that the pressure in them increases greatly, which also contributes to the transfer of heated water to the last houses of the high-rise building. Also, the heating scheme of a panel house assumes a considerable return temperature of 70C. During warm and cold seasons, water temperatures can vary greatly, so the exact values will depend solely on the characteristics of the environment.
As you know, the temperature of the coolant in pipes installed in a multi-story building reaches 130C. But such hot batteries simply do not exist in modern apartments, and all because there is a supply line through which heated water passes, and the line is connected to the return line using a special jumper called an “elevator unit.”
The heating system of a multi-storey building, which is the most efficient, in any case should include the presence of an elevator unit.
This scheme has many features, since such a node is designed to perform certain functions. The high-temperature coolant must enter the elevator unit, which performs the main function of heat exchange. The water reaches a high temperature and, using high pressure, passes through the elevator to inject coolant from the return. In parallel, water from the pipeline is also supplied to recirculation, which occurs in the heating system.
This heating scheme for a 5-storey building is the most effective, therefore it is actively installed in modern multi-storey buildings.
This is what heating looks like in an apartment building, the scheme of which provides for the presence of an elevator unit. On it you can see many valves, which play an important role in heating and uniform heat supply.
As a rule, such valves can be adjusted manually without any problems. But valve adjustment, as a rule, is carried out only by highly qualified specialists who work in government services.
When installing heating in an apartment building, the scheme should also provide for the presence of such valves at all possible points so that in the event of an emergency it is possible to shut off the flow of hot water or reduce the pressure. This is also facilitated by various collectors and other equipment that operates automatically. Therefore, this technique provides greater heating performance and efficiency of its supply to the top floors.
A large number of multi-storey buildings have single-pipe heating systems that require bottom wiring. It is worth noting that the design of the high-rise building itself and many other aspects that may affect the heating scheme are also taken into account.
Depending on these aspects, the coolant can be supplied either from top to bottom or from bottom to top. Some houses have special risers that act as a supplier of hot water up and cold water down. Therefore, in many apartments, cast iron batteries are installed, which are very resistant to temperature changes.
Purpose and principle of operation of the elevator unit
It was said above that the water in the heating system of a multi-story building heats up to 130 degrees. But consumers do not need such a temperature, and heating the batteries to such a value is absolutely pointless, regardless of the number of floors: the heating system of a nine-story building in this case will not be different from any other. Everything is explained quite simply: the heating supply in multi-storey buildings is completed by a device that turns into a return circuit, which is called an elevator unit. What is the meaning of this node, and what functions are assigned to it?
The coolant heated to a high temperature enters the elevator unit, which, in its principle of operation, is similar to a dosing injector. It is after this process that the liquid carries out heat exchange. Coming out through the elevator nozzle, the coolant under high pressure exits through the return line.
In addition, through the same channel, the liquid is recirculated into the heating system. All these processes together make it possible to mix the coolant, bringing it to the optimal temperature, which is sufficient to heat all apartments. The use of an elevator unit in the scheme makes it possible to provide the highest quality heating in high-rise buildings, regardless of the number of floors.
Features of the heating system of apartment buildings
When installing heating in multi-storey buildings, it is imperative to comply with the requirements established by regulatory documentation, which include SNiP and GOST. These documents indicate that the heating structure must ensure a constant temperature in the apartments within 20-22 degrees, and humidity must vary from 30 to 45 percent.
Despite the existence of standards, many houses, especially older ones, do not meet these indicators. If this is the case, then first of all you need to install thermal insulation and change heating devices, and only then contact the heat supply company. The heating of a three-story house, the diagram of which is shown in the photo, can be cited as an example of a good heating scheme. To achieve the required parameters, a complex design is used, requiring high-quality equipment. When creating a project for the heating system of an apartment building, specialists use all their knowledge to achieve uniform heat distribution in all sections of the heating main and create comparable pressure on each tier of the building. One of the integral elements of the operation of such a design is operation on a superheated coolant, which provides for the heating scheme of a three-story building or other high-rise buildings.
How it works? The water comes directly from the thermal power plant and is heated to 130-150 degrees. In addition, the pressure is increased to 6-10 atmospheres, so the formation of steam is impossible - high pressure will drive water through all floors of the house without loss. The temperature of the liquid in the return pipeline in this case can reach 60-70 degrees. Of course, at different times of the year the temperature regime may change, since it is directly related to the ambient temperature.
Pipe selection
To save your own time and money, it is recommended that even when coordinating the project with the housing office, you think in advance which pipes will be used. Referring to the advice of experienced specialists, it is advisable to take pipes made of plastic or metal-plastic.
Copper, like steel, pipes are far from the best option for amateur beginners. They will require special handling, additional skills and, of course, special tools to be able to weld and cut parts.
- Plastic pipes are good because deposits do not appear inside them due to the quality of the water used.
- Low thermal conductivity allows you to provide rooms with heat for a long time.
- Pipes made from polypropylene can be called the best, based on the ratio of their price and quality.
Connecting them does not require any particularly complex skills, and it will not take much time to master the soldering iron needed to work with them.
Providing heat to apartment buildings with a centralized heating system
As is known, the provision of heat to a significant portion of the housing stock is carried out centrally. And, despite the fact that in recent years more modern heat supply schemes have appeared and are being implemented, central heating remains in demand, if not among owners, then among developers of multi-apartment housing. However, it should be noted that many years of foreign and domestic experience in using this heating option have proven its effectiveness and right to exist in the future, subject to trouble-free and high-quality operation of all elements.
A distinctive feature of this scheme is the generation of heat outside the heated buildings, the delivery of which from the heat source is carried out through pipelines. In other words, centralized heating is a complex engineering system distributed over a large area, providing heat to a large number of objects at the same time.
Electric heater
The most common way to warm up in a cold room with the central heating turned off is to turn on an electric heater.
The two most common types of electric heaters for us are the fan heater and the oil heater. The first one, however, is not suitable for night time: it is too noisy and not designed for long-term use. The second operates on the principle of a regular radiator, only it heats up not water, but special oil. It takes quite a long time to warm up the room, but modern oil heaters are completely safe to leave overnight.
Recently, humanity has invented several more types of electric heaters. The first of them is an electric convector: cold air, passing through a heating coil, heats up and exits from the top of the device. But such heaters also have disadvantages - they are quite bulky, like oil heaters, by the way, and relatively expensive.
The most modern heaters are infrared and carbon. They work on the same principle - a lamp emitting infrared rays heats people and objects without heating the air. But such a heater is also unlikely to be suitable for night vigils - a lamp, even an IR lamp, even a carbon one, emits a fairly strong glow and will interfere with falling asleep.
Rescue from the cold: causes of heat leaks and ways to eliminate them
More details
Pressure in the heating system of a multi-storey building
The actual pressure value is influenced by the following factors:
- Condition and power of equipment supplying coolant.
- The diameter of the pipes through which the coolant circulates in the apartment. It happens that, wanting to increase temperature indicators, the owners themselves change their diameter upward, reducing the overall pressure value.
- Location of a specific apartment. Ideally, this should not matter, but in reality there is a dependence on the floor, and on the distance from the riser.
- Degree of wear of pipelines and heating devices. If you have old batteries and pipes, you should not expect pressure readings to remain normal. It is better to prevent the occurrence of emergency situations by replacing worn-out heating equipment.
How pressure changes with temperature
The working pressure in a high-rise building is checked using tubular deformation pressure gauges. If, when designing the system, the designers included automatic pressure regulation and control, then they additionally install sensors of various types. In accordance with the requirements specified in regulatory documents, control is carried out in the most critical areas:
- at the coolant supply from the source and at the outlet;
- before the pump, filters, pressure regulators, mud traps and after these elements;
- at the outlet of the pipeline from the boiler room or thermal power plant, as well as at its entry into the house.
Please note: a 10% difference between the standard operating pressure on the 1st and 9th floor is normal
Direction of coolant movement
Depending on the movement of the coolant, the wiring can be with bottom or top supply. With top supply, hot water from the boiler is first supplied through a vertical riser to the very top of the heating system, and then descends down the risers and is sent back to the boiler.
With a bottom supply, water enters the heating devices from below, passes (presses) through them, and at the highest point of the heating system is collected in the return pipeline, through which it flows into the boiler.
Both types of supply can be used in both single-pipe and two-pipe heating systems. However, practical experience shows that for a two-pipe system, top supply is more acceptable, while for a one-pipe heating system this does not matter.
About the centralized heating system and schemes for its implementation
The central heating system of a multi-storey building has never been particularly efficient - up to 30% of the heat is still lost on the way to the consumer, which is paid for by the consumer. Therefore, many apartment owners abandon the central heating system in favor of an autonomous system due to its greater efficiency and cost-effectiveness. But how does centralized heating of apartments work, and can it be improved?
The system for distributing pipes around the house is schematically very complex, plus the supply of pipes to a residential building, and the distribution of heat across areas. In just one individual house, the circuit includes hundreds of valves, taps, drains, fittings, distributors and flanges that work on the central equipment - the elevator unit, which regulates the distribution of heat throughout the house.
Schemes for supplying coolant to a separate apartment from an elevator unit are different. Thus, the bottom-spill scheme uses the principle of supplying coolant in the direction from bottom to top. Those who live in “Brezhnevka”, “Khrushchev” and “Stalinka” buildings know how it works.
In a multi-storey building with such a coolant supply scheme, the supply and return pipes are installed around the perimeter of the house, starting from the basement, and act as jumpers between the heating mains. This scheme is a closed cycle with the beginning and ending in the basement of the house. The highest point of this piping is the highest apartment(s) in the building.
General house heat metering unit
- The main drawback that this heating system in an apartment building has not gotten rid of is the mandatory bleeding of air at the highest point of the wiring when starting the system. For this purpose, Mayevsky taps or conventional valves are used. If the air is not vented, then the air lock will definitely shut off the system at some arbitrary point, cutting off heating to the entire house.
- Another disadvantage of the bottom-spill scheme is that half of the house is heated by hotter radiators (from the coolant supply pipe), and the other half of the residents receive a slightly cooled coolant (mostly from the return), and nothing can be done about it. The temperature difference is especially noticeable on the lower floors of the house.
Heating scheme with bottom spill
Important: For those who are still connected to the central heating system and live on the top floor, do not move the Mayevsky tap to the attic so that there are no questions, including financial ones, from your housing and communal services. Moreover, the attic is not heated, and the pipes can simply shrink and break
Top pouring is used for taller buildings, starting with nine-story buildings. The coolant supply pipe does not go into the apartments, but is led to the technical floor - the top one, immediately after the last residential one. On this floor there is an expansion tank, an air valve and valves, with the help of which the necessary risers are turned off in case of need - repair or accident. When organizing a top-dispensing scheme, the heat is distributed more evenly among the apartments, and the distribution does not depend on which floor or entrance the apartment is located on. Such a heating system in an apartment building, the diagram of which is shown in the figure below, is optimal for high-rise buildings.
There is only one drawback of the scheme: after transportation through all floors of an apartment building, the coolant reaches the last heat distribution branch cooled down, and the heat transfer in the apartment can only be increased by increasing the number of sections in the radiators throughout the apartment.
Heating scheme with bottom spill
The regulations for the provision of central heating services in an apartment building stipulate the temperature limits in the apartment: during the heating season, the temperature in residential premises should not be less than +20 0 C, and in the bathroom or combined bathroom +25 0 C. For the kitchen, the temperature threshold is lower - up to +18 0 C, since it is almost always additionally heated - with a stove (gas or electric) for cooking.
Important: all temperature requirements apply to apartments in the center of the house. For corner and side apartments the temperature should be 3 -5 0 C higher
Experts working in this field argue that central heating in an apartment building is becoming obsolete, and the era of mini-boiler houses and autonomous heating systems is coming. But until this happens, you have to choose.
Electric heating pads
In the second half of September in the evening in your own unheated apartment, another electrical device will help you warm up - a heating pad. Typically, heating pads have a medical function and are used to warm up some part of the body that requires heat therapy. But they can also be used for purposes other than their intended purpose, if the situation forces it.
Most modern electric heating pads, which are available on pharmacy shelves, have a special temperature regulator. By setting it to the minimum value, you can create a completely comfortable atmosphere in your bed, which will allow you not to freeze on a September night.
Do not despair if even the minimum setting in the electric heating pad turns out to be too hot for you. The heating pad can be placed not in its traditional place under the sheet, but on top, on the blanket. In this case, it will give you less heat, which will partially escape into the atmosphere, and you will not experience overheating.
Article on the topic
Carpet and fan. 10 ways to make your apartment warmer
General requirements for installation of beam distribution
When using collector-beam wiring, a common method is to lay pipes in the floor in a screed, the thickness of which is 50-80 mm. Plywood is laid on top, covered with a finishing floor covering (parquet, linoleum). This thickness of the screed is quite sufficient for free “monolithization” of the intra-apartment (intra-house) radial wiring of the heating system. It is possible to lay pipes externally along the walls under decorative skirting boards, which entails an inevitable increase in the length of the pipelines. There are known options for laying radial distribution pipes in the space of a suspended (suspended) ceiling, in grooves.
Connecting radiators with a collector-beam circuit.
Metal-plastic or cross-linked polyethylene pipes (PEX pipes) are used, laid in a corrugated pipe or in thermal insulation. PEX pipes have an undoubted advantage here. According to SNiP, only unbreakable connections can be “mortared” into concrete. PEX pipes are connected using tension fittings, which are permanent connections. Metal-plastic pipes use compression fittings with union nuts. “Monoliquing” them means violating SNiP. Each detachable pipe connection must be accessible for maintenance (tightening).
Even without fittings, not every metal-plastic pipe is uniquely suitable for laying in a floor screed. Manufacturers' products suffer from a serious defect: layers of aluminum and polyethylene delaminate under the influence of repeatedly changing coolant temperature. After all, metal and plastic have different coefficients of volumetric expansion. Therefore, the glue connecting them should be:
- internally strong (cohesive);
- adhesive to aluminum and polyethylene;
- flexible;
- elastic;
- heat resistant.
These requirements are not met by all adhesive compositions even from well-known European manufacturers of metal-plastic pipes, which delaminate over time; the inner layer of polyethylene in such a pipe “collapses,” reducing its cross-section. The normal operation of the system is disrupted, and the location of the malfunction is almost impossible to find - usually the “sin” is due to malfunctions of thermostats, pumps and other products with moving parts.
In light of the above, we recommend that readers pay attention to metal-plastic pipes from VALTEC, which uses American adhesive from the DSM concern, which ensures the strength of the metal/plastic connection, adhesion and the complete absence of delamination
Radiant heating - a simple scheme of actions
Heating manifold diagram.
This type of radiant heating system is especially suitable for permanent people who prefer stability in everything. They definitely do not neglect correct regulation of the temperature component. Pursuing this goal, they install a pair of collectors with their own hands. They will be adjacent to the required number of heating appliances and heated floors. Their main functions will be to collect water and divide this coolant through the created heating system. A pair of collectors is securely fixed in the cabinet.
This radiant heating system involves its own individual style of connecting the pipeline - loops. Every radiator is connected to the distribution manifold of the house. It is better to hide the pipelines emanating from it to all fixed heating devices in a reliable floor or in the walls, hiding them under the baseboards.
It is gratifying that this system is universal to a certain extent. If you need to replace not all, but only part of the heating devices, then this can be easily done with your own hands. There is no need to turn off the entire system for this.
Dead-end and associated wiring
Dead-end wiring is a wiring in which the coolant enters and exits the heating device from the same side. In this case, the flow of water seems to reach a dead end, changes its movement and then leaves the heating device.
With associated wiring, the coolant flow enters the heating device from one side and exits from the opposite side, that is, it moves in parallel with the general flow of water from the boiler to the return pipeline.
It is believed that passing wiring is more effective. Indeed, it is precisely when it is used in a heating device that the formation of stagnation zones, in which the intensity of heat transfer is minimal, is least likely. With dead-end wiring, on the contrary, the formation of zones in the heating device is inevitable in which the speed of water movement is minimal, and therefore the process of heat transfer is minimal.
Automatic collector-beam system
The supply of coolant to radiators connected via radial wiring can be made automatically adjustable. In this case, instead of a plastic manual control cover (position 4 in the figure “Complete manifold block”), a small-sized electromechanical servo drive is installed on the thermal valves of the return manifold (position 2 in the figure “Complete manifold block”), connected by a cable to an analog thermostat or controller. Radiators are connected to heating pipes without any fittings at all (ball valves can be installed).
Dimensions of the thermal valve servo drive.
Such a scheme has increased capital costs, while simultaneously providing an increased level of comfort. The user-desired air temperature can be set from the control panel of the room thermostat, the signals of which are processed by servo drives on the thermal valves of the return manifold. The system can be controlled by a so-called chronothermostat, which provides the user with the ability to set a temperature control program for a week, differentiated by day of the week and time of day.