To install a heating system, you will need a source of thermal energy. This can be main or liquefied gas, firewood, electricity or liquid fuel. The most profitable option is gas. But not all settlements have mains gas. In this case, use its liquefied version. If you decide to use a gas cylinder for heating, you need to familiarize yourself in advance with the advantages and disadvantages of such systems, as well as understand the nuances of their design.
Gas... and other gas
Blue fuel has been the most popular and cheapest energy source for many years. Most often, two types of gas are used for heating and, accordingly, two connection methods:
- Magistralny . This is methane purified from impurities with the addition of a tiny amount of fragrance to facilitate leak detection. Such gas is transported through gas transportation systems to consumers.
- A liquefied mixture of propane and butane, which is pumped into a gas holder and provides autonomous heating. When this liquid transforms into a gaseous state, the pressure in the tank increases. Under high pressure, the gas mixture rises through pipes to the point of consumption.
Both types have their pros and cons:
- When connecting to a main line, there is always a danger of pipeline breakage and a decrease in pressure in it. The gas tank provides complete autonomy; you only need to monitor the availability of gas;
- gas tank equipment and its maintenance are expensive . But this is the only possibility of gas heating if there is no mains in the accessible vicinity;
- To calculate the gas consumption for heating a house of 100 sq. m, a comparison is made of the calorie content of the fuel from the main line and the liquefied mixture in the cylinder. The calorie content of a propane-butane mixture is three times greater than that of methane: the combustion of 1 m3 of the mixture produces 28 kW, and the combustion of the same amount of methane produces 9 kW. Accordingly, different amounts will be spent on heating the same area.
The liquefied mixture is often pumped into small containers for autonomous heating.
For autonomous heating, liquefied gas in cylinders is also used Source blog.mybacharach.com
See also: Catalog of companies that specialize in home insulation services.
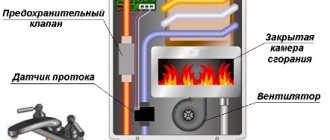
Requirements for boilers
On the left - convection (traditional), on the right - condensation Source otivent.com
Before buying a heater to operate on LPG, you should remember that a gas boiler using gas cylinders will only function if the unit is capable of operating at a reduced pressure from 0.003 to 0.004 bar or from 2.96 to 3.94 atm. Otherwise, no fundamental changes to the equipment will be required. If this is the case, then in the technical passport of the boiler from the manufacturer there is always a section that indicates the operating conditions for liquefied gas.
Important: even if you thoroughly understand the settings and convert the unit yourself, you should not put it into operation! Before start-up, contact a nearby public or private enterprise so that the reconfiguration of the equipment can be inspected by a licensed specialist.
Selecting a boiler for conversion to LPG
Heaters differ in mounting methods Source otivent.com
Manufacturers of any gas boilers set themselves the task of increasing the efficiency of the unit as much as possible, and this, first of all, depends on the complete combustion of fuel in the system. Despite the difference in the state of methane and liquefied hydrocarbons, the principle of their combustion is no different from each other, but there are some nuances that will have to be taken into account. It should be remembered that it will not be possible to use both energy carriers (LPG and methane) at the same time, since the reconfiguration process involves partial disassembly of the boiler with the replacement and reconfiguration of some components and parts.
To select and purchase a gas boiler, you need to consider the following:
- Power. For every 10 m of residential premises with ceilings no higher than 2.7 m, 1 kW will be needed, but if the rooms are higher, then you need to calculate by volume: for every 10 m3 - 0.41 kW. Then the resulting power must be multiplied by a factor of 1.2 - this is the simplest and most reliable method of calculation.
- If the house does not have a chimney, or rather, there is no way to use it for your heater, then choose a suspended model with a closed combustion chamber. There, combustion products exit through a coaxial pipe, which is discharged through the wall directly next to the boiler.
- If your house still has a chimney, but you don’t have a lot of money, without any doubt, take a model with atmospheric draft (open combustion chamber). Such a unit will be cheaper and without losing the efficiency of heating the house.
- If you choose a double-circuit boiler, make sure that the heat exchanger is separate (one for heating, the other for DHW). This option is more convenient to maintain and more reliable in operation. Also, for a budget option, you can buy a parapet boiler - there is a coaxial pipe with the combustion chamber open, but the most powerful of them is no more than 12 kW.
What increases gas consumption
Gas consumption for heating, in addition to its type, depends on the following factors :
- Climatic features of the area. The calculation is carried out for the lowest temperature indicators characteristic of these geographical coordinates;
- The area of the entire building, its number of floors, the height of the rooms;
- Type and presence of insulation of the roof, walls, floor;
- Type of building (brick, wood, stone, etc.);
- The type of profile on the windows, the presence of double-glazed windows;
- Organization of ventilation ;
- Power in the limit values of heating equipment.
The year the house was built and the location of the heating radiators are also important.
Calculation of main gas flow
The calculation of the required power is carried out on the assumption that the height of the rooms does not exceed 3 m, its area is 150 m2, the condition of the building is satisfactory, and there is insulation. Then, to heat 10 m2 of area, an average of 1 kW of energy is consumed at a temperature lower than –10 0C. Since this temperature on average lasts only half of the heating season, you can take the base value as 50 W*m/hour.
Depending on the thickness of the wall insulation, gas consumption is significantly reduced Source m-strana.ru
Gas consumption for heating a house of 150 m2 will be determined by the ratio
A = Q / q * ɳ
- Q in the selected example is calculated as 150 * 50 = 7.5 kW and is the required power needed to heat a given room.
- q is responsible for the type of gas and exerts specific heat. For example, q = 9.45 kW (G 20 gas).
- ɳ shows the efficiency of the boiler, expressed in relation to unity. If efficiency = 95%, then ɳ = 0.95.
Let's carry out the calculations and find that the gas consumption for a house with an area of 150 m2 will be equal to 0.836 m3 per hour, for a house measuring 100 m2 - 0.57 m3 per hour. To obtain the average daily quantity, the result obtained is multiplied by 24, for the monthly average - multiplied by another 30.
If you change the boiler efficiency to 85%, 0.93 m3 will be consumed per hour.
Calculation of the amount of liquefied gas
The formula A = Q / q * ɳ can be used to determine the amount of various fuels. Since liquefied gas is either in a gas tank or in cylinders, the volume of their capacity is measured in m3, therefore the consumption of liquefied fuel is calculated in these units.
The table shows the cost of autonomous gasification Source m-strana.ru
When calculating the consumption of liquefied gas for heating a house of 200 m2, the following indicators :
- density of a mixture of propane and butane. For example, for type G 30 ρ = 0.524 kg/l;
- specific heat of combustion . For G 30 it is equal to 45.2 MJ/kg (23.68 MJ/l) or 6.58 kW/l.
Average values can be taken from the first example, given that Q = 200*50 = 10 kW
A = 10 / (6.58 * 0.95) = 1.6 l/hour
Average daily consumption will be 1.6 * 24 = 38.4 (l)
Provided that a cylinder with a capacity of 50 liters is used, but filled for safety reasons to 42 liters, it can be argued that it will last for approximately a little more than a day.
Average monthly gas consumption will be 38.4 * 30 = 1152 liters. And this is already 27.5 cylinders (1152/42 = 27.5).
Similar calculations can be carried out in order to determine the gas consumption for heating a 100 m2 house from a gas holder. Its quantity will also be determined in liters.
A = 5 / (6.58 * 0.95) = 0.8 l/hour
In a day, the gas tank will be empty by 19.2 liters, and in a month - by 576 liters, over a heating season of 7 months - by 4032 liters. This must be taken into account in order to replenish the capacity in a timely manner.
The gas tank is refilled using special machines Source pinterest.cl
How much does heating cost?
The amount of heating depends on the amount of gas consumed and the price per 1 m3 in a given region. By simply multiplying two numbers, you can determine costs per day, per month or for the entire heating season.
In terms of absolute price per m3 (kg), main methane is 3-4 times cheaper than propane-butane mixture. However, when comparing the heating consumption of a building of 100 m2, methane requires an average of about 3000 m3, and only 1000 m3 of liquefied mixture. Therefore, it can be argued that how much liquefied gas costs for heating a house is the same price for main gas, due to higher consumption.
Gas cylinders
Connecting cylinders
A special reducer is used to regulate the pressure Source stroyinstal.ru
Connecting liquefied propane-butane is carried out in exactly the same way as connecting natural methane, but given the fact that the LPG pressure is higher, there should be a reducer at the outlet of the manifold from the cylinders. Only it’s not the same as what you’re used to seeing when connecting a gas stove at the dacha, although the essence is the same - it’s adjusting the pressure. In our situation, it is a device with a regulator and a pressure gauge.
How to pay less
Since you won’t be able to significantly win in price by installing autonomous heating, you need to turn to energy-saving technologies.
- Carry out thorough insulation of not only the walls of the building, but also the roof, floor, foundation, even the basement, if there is one.
- Replace double-glazed windows with energy-saving ones, the profile is frost-proof.
- Install a boiler with maximum efficiency and an electronic thermostat.
- Check the condition of the house's thermal insulation using a thermal imager to identify cold spots and eliminate them.
- Change the ventilation and air conditioning system. Just an open vent or a window set for ventilation takes in more heat than a window opened for 5-7 minutes and a complete change of air in the room.
- Install heated floors , especially in hallways and hallways.
- Install electronic sensors to block heating above the set temperature.
It is very effective to use the smart home system, which will reduce gas consumption by at least 25%. If you follow all the tips, your home will be warm and cozy, and your gas bills won’t be terrible.
The smart home system is easier and more comfortable to control using a remote control Source archidom.ru
Safe Operation
It is prohibited to use heaters, electric heaters, heating cables, etc. as a means of heating heating cylinders.
Tanks with fuel reserves can only be stored inside separate cabinets, the top of which is drilled to form ventilation. It is recommended to insulate the structure from the inside on the sides and below with polystyrene foam, without covering the ventilation holes. It is not allowed to insulate the cylinders themselves by heating them from the outside, even if they are partially covered with frost.
Frozen cylinders
It is important to follow the rules for filling tanks so that equipment does not explode at home.
Immediately after assembling the heating unit, it is necessary to check for leaks.
Gas pipes must have walls 2 mm or more thick, and in places where they pass through the wall, before pulling the pipeline, a special case with soft filling or a piece of pipe of a slightly larger diameter is placed. In the latter case, the voids are filled with construction foam.