- Brick
- Stainless steel kit elements
- Video about the importance of correct chimney installation
The outlet duct is one of the key elements of a room heating system. Through it, waste combustion products are discharged into the street. It can be made from different materials. We will look at what type of chimney is best for a solid fuel boiler, so that you understand how to organize the most reliable, efficient and safe design.
The correct design of the sleeve affects the stability of the draft and the efficiency of the heating device. An unsuitable pipe (too small a cross-section, with a rough internal surface) and improper installation lead to excessive soot clogging, and subsequently overheating, which leads to destruction and the release of harmful chemical compounds. The duration of operation without repair or replacement of individual elements is also very important. Therefore, already at the design stage it is necessary to clearly understand what to give preference to: stainless steel, ceramics or brick.
MATERIAL FOR BOILERS
As stated earlier, steam boilers with a pressure of up to 0.7 atm and hot water boilers with a heated water temperature of up to 115° can be made from cast iron or steel of any grade.
The rules issued by the State Boiler Inspectorate of the USSR Ministry of Power Plants and mandatory for all ministries and departments exclude these boilers from consideration. However, in order to ensure the durability of boilers and trouble-free operation, it is necessary to set some, at least minimal, requirements for the manufacture of this group of boilers. The Boiler Supervision Authority of the Ministry of Public Utilities of the RSFSR issued rules relating to steam boilers with a pressure of up to 0.7 ati and hot water boilers when heating water to 115°.
The following requirements apply to the materials used for the manufacture of low-pressure boilers.
Cast iron can be used no lower than grades SCh 15-32.
The boiler operating pressure is allowed to be equal to half the test hydraulic pressure at which it is tested when leaving the factory. The latter should be within the range of 6-10 ati for hot water boilers and 3 ati for steam boilers.
For the manufacture of steel boilers, carbon steel of any grade can be used.
For parts of the boiler located within the furnace, for example, for fire tubes, carbon steel of a quality not lower than MSt grades is required. 2 and MSt. 3.
Pipes that are the heating surfaces of boilers are allowed only seamlessly drawn.
When installing pipes for welding without the use of rolling, pipes welded with an overlap are allowed.
Welders who have passed tests and are approved for responsible welding work are allowed to perform welding work. The calculated tensile strength of the metal is taken to be equal to the minimum value of the tensile strength for steel of the accepted grade. If there is no information about the steel grade or its mechanical properties, then the calculated tensile strength is taken to be 32 kg/mm2.
Test hydraulic pressure for steel steam boilers is 3 atm, for steel hot water boilers - operating pressure plus 3 atm, but not less than 6 atm.
When making a boiler using riveting, the seam overlays and rivets should be of approximately the same quality as the base sheet material.
By choosing one or another type of seam and knowing how much weakening the sheet produces, the designer can accurately calculate the boiler based on the tensile strength values and specifying the corresponding reliability coefficient. Subsequently, the tightness of the rivet joints made is checked by a hydraulic test.
It is somewhat more difficult to obtain guarantees regarding the safety margin when manufacturing boilers using welding. A welding seam, in contrast to a riveted seam, consists not only of rolled material (which received its quality characteristics on samples cut from sheets), but also of cast material, and the casting itself is carried out by the welder during the process of making the seam. The quality of this cast material strongly depends on the source electrode metal (usually electric arc welding is used), on the skill and conscientiousness of the welder, on electrical equipment, etc. It is very difficult to check the quality of the deposited cast metal, since even with partial destruction of the weld, cutting out the corresponding samples, there will be no guarantee that the adjacent seam has the same quality indicators. Obtaining a high-quality weld is of significant interest. The design of the seam according to 244, with the quality of the cast material not exceeding the limits allowed for the base sheet material, makes it possible to bring the degree of weakening introduced by the seam to unity and, thus, obtain maximum metal savings. In this case, the walls of the drum will be stressed equally both within the seam and in the whole place. In a boiler with riveted seams, the wall thickness is taken based on the metal stresses in the longitudinal seam, weakened by the rivet holes, and therefore the stresses in the whole place are always slightly reduced, as a result of which material is overused.
Currently, rules have been developed for the use of welding in the manufacture of steam boilers with pressures above 0.7 ati. According to these rules, the electrode wire and the deposited metal (both separately) must be subjected to tensile and elongation tests, as well as impact strength .
The tensile strength in the deposited metal samples must be no less than the lower tensile limit for the base metal (welded sheets), the relative elongation must be no less than 18%. When testing for impact strength, the latter must be at least 8 kgm/cm2.
Such requirements for the weld allow, when calculating welded products, to accept for butt welds of the type shown in 244 a weld weakening coefficient equal to cp = 0.95.
High quality welds can only be achieved with proper organization of the technological process for manufacturing a welded boiler at a factory with a staff of highly qualified welders, using electrodes with a special thick coating that protects the cast metal from the harmful effects of air.
It is difficult to check the quality of the weld in a completed product. The most dangerous defect is lack of penetration - voids hidden inside the seam. To ensure complete reliability of the seam in such a critical structure as a steam boiler, it is planned to scan part of the seams using an X-ray machine or rays of radioactive substances.
Installation Requirements
A properly constructed chimney should eliminate the possibility of fire and ensure 100% smoke removal from the boiler to a place where carbon monoxide poisoning is excluded. This is the meaning of all the requirements:
- A heavy brick structure must stand on a strong foundation or a solid reinforced concrete floor.
- It is imperative to insert a sleeve into the channel located in the load-bearing wall.
- It is recommended to build a boiler room next to the house or use an external chimney for a gas boiler.
- The pipe must be built vertically, the permitted deviation is no more than 0.1°.
- Horizontal channels should be made with a slope of at least 0.01°, they should not exceed 3 m in total, each length should not exceed 1 m.
- A cleaning hatch is installed in the place of the knee.
- Part of the pipe outside the house should be insulated.
What kind of steel is used to make boilers?
A steam boiler operates under significant pressure, therefore it is a very responsible unit and must ensure reliable operation.
The higher the operating pressure and temperature at which the boiler operates, the more difficult the conditions are for the metal from which the boiler is made.
Basic requirements for boiler metal: 1) high heat resistance - the ability of the metal to maintain strength under conditions of high temperature and high stress; 2) high viscosity - the ability of a metal to maintain its mechanical properties under changing or repeated loads; 3) reduced susceptibility to aging - the ability of a metal to maintain its mechanical properties for a long time; 4) metal resistance against corrosion - under the influence of water and steam; 5) structural stability - the stability of the metal against structural changes that reduce its mechanical properties; 6) density, homogeneity of the metal structure, the absence of internal defects in it: caps, cracks and foreign inclusions.
Promotional offers based on your interests:
Therefore, boiler elements under pressure are made exclusively of steel (GOST 5520-62). This steel, in addition to high requirements regarding its chemical composition, is subject to more careful control and additional tests for impact strength and sensitivity to aging.
Sheet steel grades St. 2 and Art. 3 is intended for boilers and vessels operating at temperatures not exceeding 120°C. For boilers operating at higher temperatures, steel grades 15K and 20K are used.
Boiler parts that are not directly under pressure can be made from ordinary quality carbon steel (GOST 380-60) or high-quality structural carbon steel (GOST B 1050-60).
Advantages of a brick chimney
A chimney made of bricks is most often mounted on a stove, taking into account its advantages such as:
- the ability of the material to resist fire;
- duration of operation;
- ease of brick laying;
- no need for specialized maintenance;
- easy repair.
A brick chimney can withstand high temperatures, but relatively often gets clogged.
A brick chimney can also be characterized on the negative side: it is rough inside and therefore quickly becomes contaminated with soot, the accumulation of which negatively affects the draft force. The disadvantages of a brick chimney also include its heavy weight, which often requires placing the stove on a separate base.
Ꙭ Metals of boiler units - steel and cast iron - ikotel.info
The main metals used for the manufacture of boiler units are steel and cast iron.
Steel is used both relatively cheap - carbon steel, and more expensive - alloyed, i.e., one in which other metals are added in some quantity to improve the mechanical and physico-chemical properties. There are low-alloy steel, in which additives are contained in small quantities, not exceeding 0.5-1.0%, and high-alloy steel, in which a significantly larger amount of additives is added. Low-alloy boiler steel belongs to the class of pearlitic, and high-alloy boiler steel belongs to the class of austenitic steel.
Carbon steel is widely used in boiler making. The carbon content of this steel should not exceed 0.3% to avoid deterioration in the quality of welded joints due to air hardening during welding. The content of sulfur and phosphorus should not exceed 0.045% for each of these elements. The maximum temperature at which carbon steel can operate reliably and for a long time is 500 °C; exceeding it leads to a sharp intensification of scaling on the metal.
Alloying of boiler steel is intended to increase its strength and scale resistance at high temperatures. Chromium, molybdenum, nickel, vanadium, titanium, tungsten, niobium, manganese and boron are used as alloying additives, which are introduced in various combinations. Chromium is introduced into steel to increase its heat resistance, i.e., the ability to resist corrosion (scale formation) at high temperatures; the presence of 12-14% chromium in steel makes it stainless. Molybdenum is added to increase heat resistance, that is, to increase the tensile strength and yield strength of steel at high temperatures, as well as to improve its technological properties (weldability) and simplify heat treatment. Nickel increases the toughness of steel, its heat resistance and aging resistance. To increase creep resistance, i.e., reduce the yield strength of steel as a result of prolonged operation at high temperatures, vanadium and niobium are added to low-alloy chromium-molybdenum steel, and titanium and tungsten are added to high-alloy steel. The presence of manganese in steel in the range of 0.3-0.8% is determined by the technological requirements of the smelting process, and increasing the manganese content in steel to 0.9-1.5% aims to increase its strength. Alloying elements in steel grades are designated by letters of the Russian alphabet: B - niobium; B - tungsten; G - manganese M - molybdenum; N - nickel; P - boron; C—silicon; T - titanium; F - vanadium; X - chrome.
In the designation of high-alloy steel grades, numbers are placed behind the letters, which indicate the content of these elements in the steel as a percentage. The numbers before the letter designation indicate the carbon content of the steel in hundredths of a percent for low-alloy steel and tenths of a percent for high-alloy steel. If in high-alloy steel the amount of carbon is not limited by a lower limit with an upper limit of 0.09% or higher, numbers are not placed before the letter designation.
Design dimensions
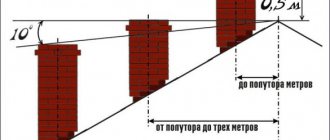
The installation of the chimney is carried out taking into account the requirements of Gorgaz or Oblgaz for its height and cross-section:
- The chimney should rise above the ridge of the roof of the house by 0.5 m, if it is closer to it than 1.5 m. If the offset is from 1.5 m to 3 m, their height is the same. When the distance is even greater, the chimney height line is on a straight line extending from the ridge at 10° downwards.
- The dimensions of the chimney for a gas boiler are determined after purchasing the product. The usable space inside the brick well (sectional area multiplied by the height) must exceed the volume of the combustion chamber. Information can be obtained from the technical data sheet.
- The side of the channel is made a multiple of the size of the brick, taking into account the seams. Often 20×20 cm (¾×¾ stone) is chosen so that, if necessary, sleeving can be easily carried out.
Selection of boiler material
Chapter 6. MATERIALS AND BASICS OF CALCULATION OF STRENGTH OF STEAM BOILERS
Reliability of operation of a ship's steam boiler must be ensured at the design stage. It is known that its accident leads not only to the loss of ship speed, a decrease in electricity generation, but also to the creation of dangerous conditions for operating personnel caused by the filling of the engine room with hot gases and steam. Losses associated with a boiler failure far exceed its cost. Therefore, when designing boilers, strength calculations of heat-stressed parts and assemblies are performed.
The basis for the calculations is the science of strength - the strength of materials.
Under the influence of external forces, the boiler parts change their shape - they become deformed. During deformation, internal elastic forces arise in the material, acting between the particles and resisting external loads, that is, the stressed state of the material appears. The intensity of internal elastic forces is called stress. The strength of boiler parts depends on the magnitude of stresses arising during deformation, as well as on external conditions: temperature conditions; presence of corrosive media (water, steam, fuel combustion products); repeated, sometimes alternating loads that arise during starts, stops and changes in the steam output of boilers; vibration loads due to combustion pulsation and certain modes of movement of the steam-water mixture in pipes.
The reliability of the boiler is largely determined by the reliability of those parts that are under the influence of internal pressure. Therefore, the Rules of the USSR Register regulate the calculation of the strength of these particular boiler elements: collectors, bottoms, bottoms, heating surface pipes.
The USSR Register determines the grades, chemical composition, strength and ductility characteristics of steels from which ship boiler parts can be made.
The strength and ductility characteristics of steels include: tensile strength
, yield strength, elongation, contraction, impact strength.
All these characteristics for each steel grade depend significantly on temperature. For example, for carbon steel (Fig. 6.1), an increase in temperature above 350–400°C leads to a sharp decrease in and. It has been experimentally established that the strength characteristics of carbon steel at > 350°C not only decrease, but also become unstable. They decrease with increasing load holding time (Fig. 6.2). The loss of strength in this case is associated with the accumulation of internal microscopic cracks in the metal, or its creep
.
The creep process is characterized by the relative creep rate of the metal
Creep limit and long-term strength limit are used as criteria that determine the strength of steel at high temperatures and stress.
Creep limit
is called the voltage at which the creep rate is equal to a given one. For boiler parts, the creep rate does not exceed 2.75∙10 –11 s –1, which corresponds to a deformation of 1% for 10 5 hours of operation.
Long-term strength limit
is the stress that, at a given temperature, causes a metal to fracture after a certain period of time.
Since the stresses occurring in the boiler parts are mainly influenced by external load and temperature conditions, the determining condition for the selection of materials is the parameters of the steam produced by the boiler - pressure and temperature.
Other factors that also influence the choice of material only complement the requirements that must be met by the quality of the material used for individual boiler elements. Such additional properties that characterize the quality of boiler steels include heat resistance, endurance, heat resistance, corrosion resistance, the tendency of steel to relax stress and structural changes during long-term operation under conditions of high temperatures and external loads, and weldability.
Heat resistance
steel is characterized by the value of the long-term strength limit
at a given temperature; endurance,
or resistance of steel to destruction under the influence of repeated repeated loading, is the fatigue limit.
Metal fatigue is associated with the formation of microcracks in it and, as a consequence, brittle fracture of the part at stresses significantly lower than the tensile strength or even the yield strength. Usually . scaling,
can occur .
Heat resistance
is the ability of steel to resist oxidation in a high-temperature gas environment. It is expressed quantitatively by the temperature at which intense oxidation of steel begins – the temperature of scaling. For example, for carbon steel this temperature is 500°C.
Materials used in boiler construction must have high corrosion resistance
both in gas and steam environments, and in boiler water. The assessment of this material quality is determined by the corrosion rate measured in millimeters per year (mm/year).
, stress relaxation is possible in metals
, that is, a spontaneous drop in time in the stress of a deformed metal as a result of the transition of elastic deformation to plastic. Steels prone to relaxation are not used for the manufacture of boilers, since relaxation leads to a loss of strength and density of the rolling joints of pipes in the walls of the collectors.
Long-term operation of steel at high temperatures can cause significant structural changes in it: spheroidization and graphitization, which contribute to the softening of steel. Spheroidization is associated with a change in the shape of pearlite grains (lamellar pearlite in the steel structure takes a spherical shape), graphitization is associated with the decomposition of carbides into metal and graphite. Steels subject to softening at high temperatures are not recommended for use in heat-stressed boiler parts.
How to build a brick chimney
Pros and cons of the design System elements Features of calculations Choice of material Process technology Pipe lining
The efficiency, and most importantly, the safety of the operation of a solid fuel boiler or stove largely depends on the smoke exhaust system. Therefore, it should be given special attention. On sale you can find many modern steel models that are produced industrially. They just need to be installed correctly. However, not everyone likes the high cost and lack of durability. Many people decide to build a brick chimney with their own hands. Let's look at all the stages of this process.
Metal boilers
The metal of steam boilers operates under very difficult conditions, as it is affected by the pressure and temperature of water and steam (steam-water mixture), the own weight of the lining and the uneven expansion of parts of the boiler unit.
The wall thickness of drums, collectors and pipes, dimensions of frame parts, etc. determined depending on the magnitude of the total load and the required safety margin, ensuring long-term performance of the parts. In addition to strength, the metal must have ductility (no brittleness), resist corrosion and have good weldability. Therefore, for the production of parts of boiler units (especially those that operate under pressure), high-quality steels are used.
All grades of boiler steel contain small, strictly limited amounts of carbon, manganese and silicon, as well as incompletely removed harmful impurities - sulfur and phosphorus. Steel containing only these elements is called carbon steel.
Carbon steel is used to make water economizers, screens and drums of boiler units operating at temperatures up to 450 °C. At temperatures above 450 °C, the strength of carbon steel decreases sharply. Therefore, for the manufacture of parts operating at higher temperatures, special heat-resistant steel is used, into which a small amount of molybdenum, chromium, nickel and other chemical elements is added to impart certain properties to the metal. This type of steel is called low alloy steel.
Low-alloy steel grades 12Х1МФ and 15Х1МФ are usually used to make radiation heating surfaces of direct-flow boiler units and steam superheaters (except for the outlet part), operating at temperatures up to 540 °C.
Both carbon and low-alloy steels are pearlitic steels, characterized by a dark surface.
The greatest heat resistance is possessed by chromium-nickel steel of the X18N12T austenitic class, also called stainless steel, in which the alloying additives of nickel and chromium reach 30% of the metal mass. Pipes of the outlet part of steam superheaters of high-pressure boiler units are made from this steel, the metal of which is exposed at a temperature of 570-660 °C. In addition to nickel and chromium, steel contains a small amount of titanium, which stabilizes the steel structure at high temperatures. This steel has a light, shiny surface. The main advantages of austenitic steel are its high heat resistance and ability to resist corrosion at high temperatures due to the high content of chromium (18%) and nickel (12%); hence the name - stainless steel. Austenitic steel is many times more expensive than pearlitic steel.
Let's see how individual elements of the chemical composition of steel affect its properties.
Conclusion
A solid fuel boiler needs a properly installed chimney. In this case, it will be able to work as efficiently as possible - burning all the fuel and transferring the required thermal energy to the coolant.
Often, homeowners choose a brick chimney, although its laying requires a lot of effort and time, but it fully copes with its task for a long time. The video in the article will help you find additional information on this topic.
Did you like the article? Subscribe to our Yandex.Zen channel
Carbon influence.
As the carbon content of steel increases, it becomes stronger and less ductile. An excessively high carbon content is harmful, since steel that is too hard and has low plasticity is less resistant to various mechanical deformations that occur, for example, when screen pipes are pinched when firing a boiler, and the weldability of steel also deteriorates.
For the manufacture of heating surfaces of boiler units operating at steam temperatures up to 450 °C, carbon steel grade 20 with a carbon content of up to 0.25% is widely used, and for the manufacture of boiler frames, carbon steel grade St. 3. Low-alloy steel contains even less carbon. For example, in steel grade 12Х1МФ used for the manufacture of steam superheaters of modern boiler units, the carbon content should not exceed 0.15%.
Comments
June 06, 2016
Author: Vasya
I read your article and was very interested in a stainless steel chimney with insulation, the so-called sandwich pipe. I would like to see more information about this design. I found some installation tricks at kamin-maker.ru/dymokhody/dymohod-iz-sendvich-truby -sobiraem-i-uteplyaem-sam/ It turns out that despite the fact that there is insulation inside the pipe, condensation still appears and it needs to be additionally insulated from the outside. And another very important fact, such a chimney must be at least 5 meters, it is important to take this into account when selecting this device.
Answer
Skirting radiators
This is a newfangled option when small radiators are installed around the perimeter of the apartment, at the level of the baseboard and disguised as worthless.
The main disadvantage will be this very plinth, it is wider and higher than ordinary plinths, and therefore there will be a small side around the perimeter of the room, which will not allow the bedside table or bed to be pushed completely against the wall. Agree, it’s very inconvenient when all the objects in the room stand 3-5 centimeters from the walls.
The advantage will be a more uniform heat distribution compared to radiator batteries. There will be no warm or cold corners in the rooms and it will be more pleasant to be in such a house.
Budget wood-burning autoclave
Nowadays, one of the popular and cheapest types of boilers for making at home is solid fuel. They are made for cottages or private homes.
But how to make a wood-burning boiler yourself?
You should start by preparing the necessary elements. First of all, take a thick-walled tube with the height of the heating chamber and weld the bolt.
Next, from a sheet of metal, make a circle slightly larger than the cross-section of the pipe. Then drill a slot in it for the required bolt. Connect the tube and screw and tighten the nut tightly.
At the same time, not forgetting that the air duct can be easily covered with metal, so that it is possible to change the size of the connector and adjust the combustion power of the fuel.
The second stage is the manufacture of the body. The top of the gas cylinder is removed and a cylinder of metal sheets is attached. A 15 cm pipe is attached to the side - this is a chimney.
At another stage, a disk is made that dissipates heat. Cut out a smaller circle from sheet metal and attach a handle to the body. Then you need to combine the boiler and casing. At the last stage, steel legs are welded for better air circulation.