When building houses on a strip foundation, free space remains under the floor (between the first floor ceiling and the ground). This is the underground (or underground).
Usually this space is either not used at all, or communications are laid in it. Less often in the underground they make a place to store something.
Since this space is closed (ground below, house floor on top, walls on the sides), it is necessary to organize its ventilation. This point is often forgotten when it comes to small buildings: a dacha, a garage, a bathhouse, an outbuilding. And in vain: stagnant air under the joists will lead to problems. What exactly, and how to avoid them, will be discussed below.
Why is ventilation needed?
Ventilation of a wooden floor in a private house must be organized for many good reasons. If the building was built without a ventilation device for the underground volume, it is necessary to correct this by independently installing ventilation holes and ducts (depending on the structural and operational features of the house).
The main reason that encourages you to take a responsible approach to the issue of ventilation of the underground space is dampness. It is necessarily present to one degree or another under the floor of every private house, no matter how dry the soil may seem.
Moisture evaporation from the ground rises upward and settles on load-bearing, wooden, and concrete structures, slowly but constantly causing damage to underground structures. Concrete elements deteriorate over time, metal elements gradually corrode.
Wooden lintels and structures rot and collapse when exposed to moisture. In addition, during decay, rotting wood provides a breeding ground for mold and mildew. Invisible spores penetrate upstairs, into the rooms of the house, having a depressing effect on the microclimate of the premises.
Gradually, over time, a private building will collapse at its foundation; it is not possible to correct this after a certain critical level. Warming up the house from the inside does not affect the drainage of the underground space, since modern hydro- and heat-insulating floor materials do their job well.
Briefly about the main thing
Ventilation is as important a part of the cellar arrangement as hydro- and thermal insulation. A poorly designed ventilation system will not cope with the job, which will result in spoilage of supplies. Air circulation for underground ventilation is organized in two ways: natural and forced (mechanical).
The choice of a suitable system (pipe diameter) largely depends on the area of the room. You should not install one pipe in a spacious cellar (or basement); two channels will provide the required level of air circulation. If natural circulation is weak, it is made combined or completely forced, installing one or two fans.
Ratings 0
Principles of proper ventilation
- Ventilation of the finished floor is carried out due to the air gap between the decorative covering (floor board, fiberboard flooring, plywood with laid parquet, laminate, etc.) and insulation. It is approximately 1.5-5 cm.
- The underground space is ventilated using vents installed in the base according to a specific pattern based on the structural features, soil characteristics, and the prevailing wind direction.
- The ventilation opening is located at least 30 cm from the ground level.
- If the house is located in a lowland, the ventilation should be 1.5 times larger, reducing the distance between them.
- The foundation of the intermediate walls is also equipped with openings for ventilation based on the general calculation scheme.
- When natural draft is not enough, for effective ventilation of the underground space, especially for large houses, ventilation openings are equipped with forced mechanisms.
- Ventilation is necessary all year round, including in winter.
Selection of materials
If the cellar or basement has a small area, then installing one two-channel pipe would be optimal. For a free-standing cellar, you can use boards carefully matched to each other.
For manufacturing, lumber with a thickness of 3-4 cm and a width sufficient to build a box with a side of 18 cm is selected. A diagonal partition is installed inside, and a control valve is made for each channel. It is important to understand that the gaps between the boards significantly reduce the efficiency of air exchange. Therefore, it is necessary to take care of the tightness: coat the joining lines of the boards with molten bitumen.
Plastic ventilation pipe Source ytimg.com
To organize ventilation in the basement or cellar (including two-pipe), round or square pipes made of the following materials are used:
- Asbestos-cement . Asbestos-cement pipes are convenient because they are long enough, and you don’t have to think about how to connect them correctly. The material has additional advantages: relatively light weight and affordable cost. The products are resistant to corrosion, are not afraid of frost and humidity fluctuations, and have a long service life.
- Plastic . They are made from different types of polymers and are suitable for installing hoods due to their low cost and light weight. Polymer pipes are chemically inert, do not rust, do not require cleaning, and are durable in use.
- Galvanized (metal) . Cast iron and steel pipes are galvanized, and it is preferable to use the second option, as it is lighter. Galvanization enhances corrosion resistance; The products themselves are relatively cheap and easy to install. During installation, it is important not to damage the galvanized layer, this will reduce the service life of the product.
Metal pipes for ventilation Source gidroguru.com
Organization of ventilation of a wooden floor
Buildings whose floor is not based directly on the ground are equipped with a system for ventilating the air volume between the ceiling and the ground. As a rule, natural ventilation with self-draft, organized by forcing wind through vents, circulation of warm flow from the interior through ventilation holes in the floor, and baseboards, is sufficient.
For large houses, natural draft may not be enough. In this case, a forced ventilation system based on a stationary one is thought out.
When laying the foundation, ventilation under the floor is planned in accordance with the rules and regulations, and the layout of the vents inside the base is calculated. There are several principles for organizing underground ventilation to effectively remove excess moisture:
- Plug ventilation holes when pouring the foundation.
- The height of the ventilation openings inside the base (vent) is not lower than 30 cm above the soil level on the outside.
- The distance between holes is up to 3 m.
- Vents are installed along the entire perimeter of the base without exception.
- Ventilation holes are made from the inner corner at a distance of 1 m.
- If the internal walls have their own foundation, openings are also built inside these structures, but more often 1.5 times than along the base.
- The circumference of the ventilation opening is 120-150 mm, the rectangular side is from 100 mm.
- Place the holes opposite each other.
- When a private house is built without organized ventilation of the underground space, and there are wall plinths, ventilation holes are made inside the main plinth 1.5-2 times more often.
- Ventilation outlets must be closed with decorative grilles and diffusers to prevent rodents from entering. It is recommended to purchase grilles with adjustable blinds to limit access of small animals under the floor of the building during autumn migration periods.
How to make perfumes with your own hands?
To create a round vent, when pouring the foundation, a plastic pipe is built into the formwork.
At the construction stage, there should be no problems with this. It is enough to lay wooden beams wrapped in roofing felt or polyethylene in certain places while pouring the foundation. After the concrete has set, the inserts are removed and holes are left for ventilation. Instead of bars, especially along the outer perimeter, you can immediately lay metal or plastic sections of pipes of the appropriate diameter, selecting deflectors for them or equipping them with gratings (so that rodents do not enter the underground from the outside).
Important! To protect the ventilation ducts from the penetration of rodents (if there is such a tendency), special grilles in the form of blinds are used, with the help of which the existing gaps can be adjusted. During the period of rodent migration, the gaps are reduced, but cannot be completely closed.
If a private house was built, but the ventilation system was not taken care of in time, you will have to do the ventilation yourself using a powerful hammer drill with a cylindrical nozzle equipped with diamond or pobedit cutters. The reinforcement in the foundation can interfere with this process, which is likely to get in the way of drilling the hole. A welding machine will help here, with the help of which the steel rods blocking the path are removed.
Floor ventilation in a wooden house
Undoubtedly, ventilation of the basement space is of paramount importance for the safety of the wooden floor. However, the wooden floor itself needs direct ventilation. As a standard, this is done using wall ventilation grilles and ventilation baseboards.
In a decorative covering with a final wooden flooring, openings are made near the walls, at the joint between two boards, so as not to violate their strength characteristics. They are closed with special grilles.
Openings are calculated in each individual case separately, taking into account the pattern of air flow in the rooms and the location of heating equipment. When properly organized, air circulates in the space between the floor insulation and the decorative covering.
Ventilation grilles must not be closed or blocked by pieces of furniture. The air flow must always flow freely for effective ventilation.
You can increase the ventilation of a wooden floor by using special ventilation skirting boards. The air flow penetrates through holes in them with a diameter of 10-15 mm. They are installed on opposite sides of the floor covering, ensuring uninterrupted air circulation.
In some cases, such a plinth is installed only against one of the walls. On the opposite side, the floor fits tightly against the wall, the joint is covered with a regular plinth. To ensure circulation under the floor covering, a pipe is installed that vents air outside. The outlet outlet is installed at a distance of one and a half meters, which ensures a large pressure drop. This increases the draft several times, making ventilation more efficient.
The wooden floor in the apartment is ventilated according to the same scheme, using ventilation grilles and baseboards.
How to install air ducts correctly
In the case of a large room, you will need to install two air ducts. Regardless of whether you are going to arrange ventilation for the basement of a private house, or a separate cellar, you must adhere to the following recommendations:
- Air exchange will be uniform if the pipes have the same cross-section. If you want the air to be exhausted faster, choose an exhaust pipe with a slightly larger diameter (the total cross-section should not change).
- The pipes are installed at the maximum distance from each other, that is, on opposite walls. The greater the distance, the better the room is ventilated. It is important for the process that the pipes have no bends or turns.
- The exhaust pipe is installed so that its lower edge is located under the ceiling (not lower than 1.5 m from the floor). Then all the warm air will be forced out without stagnation.
Pipe insulation with mineral wool Source ytimg.com
Winter ventilation issue
In an effort to avoid cooling the floor covering, owners of private houses close the vents inside the basement during the winter cold. At the same time, the soil under the house does not freeze, maintaining a positive temperature. Moisture continues to evaporate, albeit not in such quantities.
When the ventilation openings are closed, condensation collects in the underground space, settling on the supporting structures. It should be remembered that you need to keep the floor warm by properly insulating it. Closed ventilation holes will not save the floor in the house from cooling, while ventilating the floor even in winter will not significantly affect heat loss. In this case, the moisture released by the earth will be effectively removed.
Is it necessary to close vents in the foundation for the winter?
To preserve heat under the floor in winter, some homeowners seal the holes with rags, insulation, wooden plugs, or seal them with clay. This should not be done for the following reason. Melted snow causes an increase in relative humidity in the underground. Dampness increases, supporting beams mold and rot. When the vents are buried, condensation provokes the growth of fungi and rot. The floor can be kept warm if you lay on it high-quality thermal insulation material with a thickness of at least 20 mm.
Ventilation in a wooden house: rules for providing a log house with an air exchange system
In low-rise construction, houses made of timber or logs are now leading. Wood attracts with its affordability and environmental friendliness. Its disadvantages quite rightly include sensitivity to condensation and household moisture, but well-organized ventilation in a wooden house will help minimize their harmful effects.
We will tell you how to create stable air exchange in structures made of lumber. An optimal microclimate in your home is the key to health. In addition, in a wooden building, ventilation will help protect structures from damage by fungus and premature failure.
Types of organization of air exchange in the subfloor of a house
From the above we can conclude: due to the described features, air exchange in the basement of a wooden house needs appropriate adjustment.
In addition, it would be useful to ventilate the floor in a private house. For this purpose, the floor structure is usually chosen to be floating.
Forced ventilation is more expensive, but also more effective. Its distinctive feature can be considered the use of special electrical appliances to increase the speed of air flow in the basement.
Typically, a forced ventilation system works in conjunction with natural ventilation.
The choice of ventilation scheme is carried out at the design stage of a wooden house. Its installation and installation must be carried out simultaneously with its construction.
This significantly reduces labor costs, because during construction, pipes for the required number of inlet and outlet channels can be immediately laid.
Then, after finishing the laying, drilling large-diameter holes in the concrete foundation is an extremely thankless task.
Features of natural air circulation
After the future ventilation scheme for the subfloor of a wooden house has been selected at the design stage, you can begin to implement the design solution. In any case, it is necessary to make mortgages for natural ventilation.
They are scraps, usually of plastic sewer pipes with a cross-section of 120 mm in diameter or can be square in shape. The length of these elements is equal to the thickness of the foundation walls.
Wooden houses are most often built:
- on a strip foundation: its walls are located under all the walls of the house. During pouring, the elements mentioned above are inserted into the foundation body to organize air passages in the foundation;
- on a columnar foundation: piles or pillars, for example, made of brick, are connected to each other along the perimeter of the house. The subfloor is supported in the same way on individual pillars. In this case, gaps are left between the rough and finished floors and between the floor and the walls, which serve for natural ventilation. Mortgages for supply channels are made in the outer plinth belt;
- on a solid concrete slab: in this case, ventilation ducts for the subfloor are installed in the baseboards of wall structures.
As a matter of fact, the channels that serve to pass air form the main part of the natural ventilation system of the underground space. From the material presented above, it becomes clear how to ventilate the basement.
You can do the work yourself. The easiest way to do this is at the stage of pouring the foundation and construction.
Arguments in favor of a ventilation device
Is a specially organized air exchange system needed in a wooden building as such? The opinion that wooden houses “breathe” does not provide grounds for completely abandoning systems that remove excess moisture and exhaust air from premises.
Just as in the construction of buildings made of concrete and brick, the construction of houses made of lumber uses technologies that reduce heat loss. It’s just that instead of synthetic materials, natural seals made of jute, flax, and felt are used in the inter-crown joints. Mineral wool is placed in the ceilings.
Insulated wooden building structures do not allow air masses to circulate naturally. In addition, builders and owners began to actively replace the usual window and door frames with sealed plastic analogues.
As a result, fresh air does not enter inside, and exhaust air does not exit outside. The inhabitants are not supplied with the required amount of oxygen for breathing. Mold fungus settles on undried wooden structures, destroying buildings with amazing speed.
In addition, wood perfectly absorbs moisture! If you do not deal with humidity, heat loss will at least double. After all, water is an ideal conductor for heat waves.
The tree does “breathe,” but not so much that air exchange occurs in full without a specially organized ventilation system. Walls made of wood will not be able to fully remove household fumes. They will not provide the opportunity to remove dust suspended in the air with microorganisms.
Organizing ventilation in a house made of timber or logs will eliminate the influence of the listed negative circumstances on the organisms of residents and building structures. It is simply necessary to create a natural scheme, but you can also build an artificial one. And if the supply and exhaust system is also equipped with a recuperator, then the exhaust air can be used to heat a fresh portion from the street.
Heating and finishing the basement
In theory, the heating system in these rooms can be absolutely anything. But for safety reasons, gas boilers are not installed there, since if the quality of air exchange is poor, in the event of a gas leak, the entire house is exposed to great danger.
Types of heating devices for underground spaces
At the moment, the heating systems market can offer a huge selection of electric heating systems, but even those with unusually low energy consumption thoroughly dry out the air in the room.
For comfortable use of the basement, it is recommended to install a split system that works to cool the air in winter (due to the increased work of heating systems), and in summer to ventilate and heat the room.
One of the heating options is UFO, which heats not air masses, but all objects located nearby. All systems, both UFO and split, will dry out the air very much, but this is exactly what is needed, because there is a fairly high level of humidity there.
To avoid this, you can install ionizers and humidifiers, special equipment that will not be unnecessarily expensive to purchase. After such arrangement, the basement is ready for use for any purpose.
The choice of heating system is calculated depending on the purpose. If this is a technical room, then there is no additional need to heat such a room.
If the basement area is large, you can make a cut into the central heating pipe and distribute the pipes evenly around the perimeter. But, as with other heating systems, this method will only work well in winter.
Regulatory requirements for air exchange
The presence of ventilation must be provided for at the design stage of the house itself. The study of building codes (SNiP) is recommended for both independent builders and customers of construction crews.
Not all migrant workers can be trusted; most have to be carefully monitored.
SNiP number 41-01-2003, which regulates the rules for the design of ventilation and heating systems, sets standards for air circulation speed both in the building itself and in its individual rooms:
- for living rooms, living rooms, bedrooms, the norm is 30 m 3 / hour;
- for kitchens and bathrooms where humidity is high, the norm is from 50 to 70 m 3 /hour;
- for utility rooms the norm is 15 m 3 /hour.
Regardless of the type of ventilation system, it must provide the required volume.
The designer's task is to select the type that suits the needs. You also need to immediately decide on the equipment and calculate the area of the air ducts if they are planned for use.
Organization of air exchange in a building under construction
Floor ventilation in a private house with a strip base is formed during the pouring of the foundation. This can be done by laying asbestos-cement pipes in the base.
- Using a grinder with a circle on a stone, the pipe is cut into small cylindrical fragments with a length equal to the thickness of the base.
- Metal parts are laid in the ground at a depth of 0.15 m (at least) and, rising above it, by 0.5 m. Such a depth is necessary so that the snow crust does not reach the ventilation holes and melt water does not flood them. In this case, the central point of the air duct should be at a height of approximately 0.3 m from the ground.
- Ventilation ducts are mounted opposite each other on different walls on the leeward side and on the opposite side.
- The cross-section of the installed shells can be rectangular or round (0.15 m).
If, for example, you need to arrange ventilation in a house with an area of 6x6 square meters, then you will need at least 8 holes located in 2m increments. Start of installation - corner of the house. To ensure that all zones are well ventilated, a distance of no more than 0.9 m is maintained from the corner to the nearest hole. For large areas, there should be at least 3 air holes covered with decorative grilles on each side.
Remove debris, debris and wet materials. This is necessary to simplify the drying process. Now that the space is clear, remove any standing water. Depending on how much water you have, you may need to use a sump pump to collect the water.
If any mold is present, it is very important that you clean it before using any airflow equipment such as a dehumidifier. This will just spread the mold and also contaminate the equipment.
The United States Environmental Protection Agency provides a quick guide to mold, moisture, and your home. It contains some basic information about mold, cleaning guides, and prevention and control tips. Since mold can be harmful to your health, it is best to educate yourself about the proper cleaning procedures.
Types of ventilation systems
Ventilation systems are divided into groups according to the methods of stimulating air movement and the type of action. The optimal option is selected depending on the tasks being solved, the area and number of floors of the building. To a large extent, the choice is influenced by the financial capabilities of the future owner.
Classification by method of motivation
For wooden houses and log cabins, the following types of ventilation are most often used:
- Natural (gravity). Provides for the presence of ventilation vents (vents) and an exhaust duct that form air flow circulation based on the laws of physics. It should be taken into account that the rate of natural air exchange depends on weather factors, because movement is possible only if the air density outside the window is higher than inside.
- Artificial (mechanical). In it, the movement of air flows is stimulated by fans installed either in the supply components or in the exhaust components. Its undeniable advantage is the stability of operation in any weather. The mechanical system is absolutely independent of the physical parameters of the air mass outside and inside the house.
- Mixed (combined). In essence, it is a modernized version of the natural type of ventilation. To organize it, either the exhaust or the supply is mechanized with a fan. If an exhaust fan is installed, then the influx is carried out naturally. And vice versa: supply with a fan, exhaust - natural.
Kinds
All types of ventilation are divided into several types, depending on its purpose, complexity of arrangement and principle of operation. But the principle of operation of any of them will be based on the laws of physics on the movement of air masses. Cold air goes down and warm air rises.
Natural supply ventilation
The simplest, vent system in the foundation or basement. It is installed during the construction of a house and consists of small holes in the upper part of the basement.
If the basement is located below ground level, then the hood is equipped with plastic or asbestos-cement pipes with a diameter of 10-15 cm. They are brought above the surface to a height of 30 cm and covered with grates to prevent debris and rodents. This method is natural and depends on fluctuations in street temperature, wind strength, and humidity.
When calculating its throughput, 1/400 of the total area of the basement is taken - this way we get the total area of all vents.
The holes should be located on the leeward side, least susceptible to precipitation. Houses with a complex foundation shape and located in low-lying areas can have up to one hole every 3-4 meters. We close the vents with gratings on the outside.
This inexpensive option is well suited for ventilation of garages and non-residential basements or as an additional means to the main ventilation system.
Natural exhaust ventilation
Supply and exhaust type. For proper operation, you will need to install two pipes for ventilation, and the supply and exhaust ventilation device looks like this.
- The first pipe is located under the very ceiling of the basement and is intended for the outflow of warm air. We place the exhaust pipe as high as possible, preferably at the level of the roof ridge. This is necessary to ensure good traction. The part of the pipe that is located in the open air must be insulated to prevent freezing in winter and covered with a canopy from precipitation.
- The second pipe for the supply of fresh air is located at a height of 30-40 centimeters from the floor level, and its entrance is located on the street a meter above the ground and covered with a grill. Convection will occur due to the temperature difference between the street and basement air. Such a system will work most effectively when the supply channels are spaced on different sides of the basement.
All natural exhaust ventilation systems have one drawback - their dependence on weather conditions and prevailing winds. It will not work if the temperature in the basement and outside are equal.
Forced
It is used if natural supply ventilation cannot cope or there is no physical opportunity to use it. Typically used in the following cases:
- The basement area is from 40 m2 or has several rooms isolated from each other;
- High room humidity, when condensate in the exhaust duct freezes in winter and impairs the permeability of air masses;
- The architecture of the house does not provide for high ventilation pipes;
- A sauna, cafe, gym, workshop or other source of unpleasant odors is installed in the basement.
The forced supply and exhaust ventilation device has a system of channels and fans that circulate air.
The main condition is to force the air to constantly circulate, which is ensured by the synchronous operation of exhaust and supply fans. Their number is calculated depending on the volume of the cellar or basement and the throughput of the air ducts.
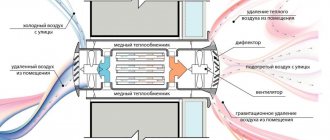
Supply and exhaust ventilation with heat recovery
For a basement floor in which permanent residence is planned, it is not enough to simply install a forced ventilation system. The room must be insulated and waterproofed. The issue of heating and heating is also resolved.
Increasingly, supply and exhaust with heat recovery is being built into such schemes.
Well-heated air enters the exhaust pipe, and in order not to release ready-made calories into the atmosphere, the air is passed through a special ceramic recuperator. When heated, it gives off heat to fresh air. The air flows do not intersect. The efficiency of such a device is 50-90% depending on the design of the heat exchanger. All heat recuperators are very reliable, do not require additional maintenance and can last for decades.
Equipped with moisture traps, dust filters, sensors that monitor humidity and air temperature. For a residential premises, these indicators lie in the range of 50-65% relative humidity and 18-220C. Such systems are most often found in “smart homes”, and their installation is complex and should only be carried out by professionals.
Ventilated floor installation
An important component of organizing air exchange in a log house is the ventilation of the floor, foundation and lower crowns of the log house. The system will dry the lumber of the base of the house, which means it will protect the entire building from rot and fungus.
Basic principles and rules for base ventilation:
- Installation of vent holes (diameter - 10 cm) on the windy and opposite side of the log house base. The distance from the ground to the center of these holes should be at least 33 cm.
- Construction of the floor using a floating scheme with gaps around the perimeter of the premises. The gaps are loosely covered with a plinth, so that the air entering the vents can freely escape.
- Formation of ventilation holes in the floor structure that communicate with the underground. They are covered with gratings, suitable if the floor covering was not natural floorboards, but linoleum, carpet, laminate and similar material that does not allow air to pass through.
During the frosty period, the vents selected in the base or foundation are closed with dampers, which significantly reduce air exchange, and in the summer, grilles are placed on them.
The distance between the vents themselves is about 2 meters if the house is located in a lowland. If the log house stands high, then this distance should be increased, since the strength of the wind increases, and therefore the intensity of the blowing.
Particular attention should be paid to the air exchange system of attics and attics, on which the condition and durability of the roof largely depends. Ventilation of the attic and attic will increase the total amount of vents to 500th share of the total area of the entire house.
To organize natural air exchange in the attic or attic, pediment ventilation and dormer windows are installed. The type of ventilation structure is selected based on the shape of the roof. It is clear that in pitched versions it is easier to create an opening in the pediment; hip and hipped ones are equipped with dormer windows.
To remove the exhaust air mass, ventilation shafts will be required. They are most often planned in the center of the building, closer to the ridge. In summer, ventilation shafts can be equipped with fans, so the operation of the entire system on hot, windless days will be ensured.
Roof ventilation requires careful attention to the following nuances:
- Between the insulating layers, insulation and roofing it is necessary to leave gaps of 3-5 cm.
- The specified distance is ensured by the installation of lathing and counter-lattice.
- Thermal insulation from the inside must be protected by a layer of vapor barrier.
- The insulation layer in the roofing pie must be protected from the outside by waterproofing, separated from the roofing by a ventilation gap.
Compliance with established norms and rules is necessary to develop a competent ventilation project in a private home. Knowledge of building regulations and pre-prepared drawings will help you do without designers, and at the same time achieve your goal - to keep a wooden house in a condition suitable for living.
Operation of the underground throughout the year
Perhaps, a detailed examination of the temperature and humidity conditions inside and outside the basement space of the house does not apply to houses with a special underground ventilation device through air intakes located under the baseboards. This is a complex system of holes of different sizes, through which air exchange should occur between the rooms and the underground space. The advantage of this design is that the ground under the house does not freeze, and the foundation of the house does not freeze either.
If the builders made do with a simpler design, when open windows (so-called “vents”) from the underground to the street serve as air intakes, then homeowners should pay attention to the following information:
- These ventilation holes are made mainly on the leeward side and on the opposite side in order to create natural draft. To do this, it is necessary to know which wind direction is dominant in a given area.
- It is imperative to ensure that in the summer the ventilation openings are free - not cluttered with things from the inside and not overgrown with weeds from the outside.
- If ventilation is not good enough, it should be increased. This can be done by cutting holes in the base using diamond drilling or by increasing traction in existing ones. For this purpose, a tin pipe is connected to the hole, protected from precipitation and the penetration of rodents. The higher you make it, the better it will perform its function.
- An option to increase the draft of the underground ventilation holes: insert into them on one side of the house several forced-action fans connected to electricity and turn them on several times a day for 20-30 minutes.
- In winter, however, the ventilation holes should be closed, otherwise the frosty air will cool not only the floor, which is uncomfortable for household members, but also the ground and wooden structures. And such a sharp change in temperature can subsequently lead to moisture condensation in the room when it gets warmer.
- When it gets cold, broods of small rodents (mice and rats) look for a warm shelter, and the subfloor of the house just meets their needs. Since mice are destroyers of wooden structures and carriers of diseases, their presence is dangerous for the residents of the house. Therefore, it is necessary to protect the basement space of the house from them. To do this, either hollow bricks are inserted into the windows, which will need to be “sewn up” for the winter, or gratings with 5x5 mm cells are installed on them, and for the winter they are replaced with special plugs made of wood or clay.
- If the ventilation holes are left open during the winter, care should be taken to ensure that melt water does not penetrate into the subfloor through them in the spring or during a thaw. A melting snowdrift located at the window level poses a danger to the underground space, since the presence of moisture is detrimental to the entire structure of the house. To prevent this from happening, snow must be thrown 1.5 meters from the house.
- After the snow melts and the thaw sets in, the plugs from the vents will need to be removed and the underground ventilated.
Air conditioners against natural air exchange
Can air conditioners replace the natural circulation of air masses in a room?
Any, even the most expensive, climate systems are significantly inferior to simple ventilation. Want to think fast to keep you productive? Ventilate the room more often, and even better, do not skimp on the ventilation system, since, for example, in winter it is not always possible to open the window for a long time.
All split systems have two blocks that operate synchronously:
- External is a compressor that condenses the refrigerant;
- The internal one is a radiator that heats the air that circulates around it forcibly.
The air, which will subsequently be cooled, is also taken indoors. This means that the split system cools and passes through the same air masses.
How to prevent mold from reoccurring
If mold has taken place, then nothing will prevent it from appearing again. You need to create conditions under which it will be uncomfortable for her to reproduce and live in your house and basement.
- First of all, this is to ensure good and constant ventilation of the room.
- The walls should not be filled with furniture or littered with rubbish. The air should circulate well in the room.
- Check to see if rainwater is getting into the underground and if there are any traces of groundwater.
- If you notice that your neighbors have mold and the buildings are located quite close to your home, then preventive treatment with an antiseptic against mold can be carried out twice a year.
Mold spores are constantly in the air, and we live in friendly neighborhoods with them, but whether we allow mold to break into our space is another matter. The main thing to remember here is that everything is in our hands, the rules for preventing mold are very simple!
Conclusions and useful video on the topic
The conclusion suggests itself, the ventilation system is an integral part of wooden houses:
If you figure out in advance how to properly make ventilation in a log house and organize it correctly, the building will last for many years without the slightest problem.
Tell us about how you installed a stable air exchange system in your own house, built from timber or logs. Share technological nuances that may be useful to site visitors. Please leave comments in the block form below, post photographs related to the topic of the article, and ask questions.
Installation of combined and forced ventilation
Combined ventilation is arranged according to the same principle as natural ventilation, using a supply and exhaust pipe. The difference is that a fan is additionally installed in the exhaust duct. It will help remove stagnant air, and clean air from the street will be supplied automatically.
If the room has a large area, the fan is also installed in the supply duct. Such forced ventilation in the basement does a good job of quickly drying the room, but at the same time increases energy consumption.
Fans with a power of up to 100 W are chosen for installation. Since the basement is a place with high humidity levels, it is better to use low voltage for power supply. Two types of devices are suitable for installation:
- Duct . Such fans are economical in operation; they are mounted at any point in the pipe.
- Axial . They require much more energy, but they are more powerful and move air more efficiently. It is recommended to install an axial fan in combination with a check valve that blocks the flow of air from the street.
Air throttle valve for round air ducts Source panoramavent.com
Ventilation of the floor base is a real necessity
Floors in private residential buildings are often fixed in a rigid pattern to wall surfaces. But in most cases they are made to float. This design involves linking the perimeter of the house into a single structure and erecting floors on a separate foundation. The latter is most often made from intermediate walls and columns.
Even in situations where the building has a grillage, the floors resting on it are not rigidly fixed. This is done precisely so that it is possible to arrange high-quality underground ventilation. In particular, through the gaps located under the baseboards (between the wall surfaces and the floor base). Any home craftsman knows that natural wood in use proves to be a very capricious and finicky material, which is characterized by increased susceptibility to moisture.
High-quality underground ventilation
If you do not build floor ventilation in the house, atmospheric influences will cause fungus to appear on the wood and its subsequent destruction (and, believe me, quite quickly). Microorganisms that settle on wooden floor elements in a private home not only have a detrimental effect on the structure, but also negatively affect human health. The fungus releases spores into the air. They enter the body of the residents of the house, affecting the kidneys, liver, and lungs. This leads to the occurrence of pathological phenomena in the human body and the development of serious illnesses.
Considering all that has been said, we conclude that floor ventilation in a private wooden dwelling must be equipped without fail. Otherwise, instead of a comfortable life, you will get a bunch of diseases and constant problems.
Why is it necessary to provide underground ventilation? (+video)
Normal ventilation for this space is necessary to prevent high humidity. It can occur from autumn to spring due to:
- groundwater;
- melting wall, rain;
- condensate
If the subfloor is not ventilated, high humidity in it leads to the following problems:
- The appearance of mold.
- Dampness on the first floor.
- Acceleration of destruction of wooden elements (beams, joists).
A common situation: the house was built well, insulated, with a good heating system. But in winter the floor is damp for some reason. This happens precisely because the underground floor of the cottage is not ventilated, the humidity in it rises, and the floor boards become saturated with moisture - which is why it is already felt in the living quarters.
This situation is especially dangerous for a wooden house - because wood is most “afraid” of moisture, and most quickly deteriorates because of it.
Floor ventilation - what options exist?
Ventilation of the underground space of a private house can be: natural, forced. In the first case, free circulation of air masses underground is assumed. This is achieved by installing special holes in the foundation of the building. They are called products. Such holes are usually sufficient for effective ventilation. Therefore, there is no special need for the installation of additional ventilation devices and hoods.
It is very simple to create natural ventilation, as well as to monitor it. You will not have any problems with such a system if you take into account the following important recommendations for arranging and operating vents:
- You need to decide which wind direction most often blows in the area where your residential building is located. This is required so that you can make holes for ventilation on the leeward side and on the opposite side to it.
- If there is insufficient draft in the vents, a small-diameter tin pipe should be connected to them and raised as high as possible. Such a simple measure is guaranteed to increase the efficiency of natural ventilation. There is another way to increase traction - cutting small holes in the basement of the house using diamond drilling technology.
- In winter (during severe frosts), it is recommended to close the vents in a wooden house with clay or wooden plugs (they must fit tightly into the ventilation holes). If you leave them open, the wood and soil under the residential building will freeze. With spring warming, this will lead to the appearance of condensation on the floor base and in the underground.
- In summer, outlets must always be open. Make sure that the openings of the ventilation system are not overgrown with plants outside the house or blocked by objects inside.
Arrangement of vents in the field
Forced floor ventilation is used less frequently. This is due to the fact that during operation it creates quite a loud noise. Of course, you can turn it off. But for this you will have to buy additional special mufflers. They are not cheap - some models of such devices are more expensive than the entire exhaust ventilation system.
In addition, not every home craftsman will be able to correctly install forced floor ventilation or select the right elements for it. Therefore, the vast majority of owners of private homes prefer to equip air vents. We will tell you in more detail later how this is done.
Natural or forced: tips for choosing
Designing and arranging proper ventilation in the cellar begins with choosing the type of ventilation, and here several points must be taken into account. Many cellars and basements simply do not need a forced system due to their relatively small size. If you provide them with excessive ventilation, the result can only be a worsening of the microclimate and storage conditions.
In large rooms, installing a forced ventilation system is a must if you want humidity and temperature to remain at the desired level. If you are in doubt which option to choose, a combined air exchange system can be the golden mean.
A large room needs forced ventilation Source comfortclub.ru
See also: Catalog of companies that specialize in engineering systems (heating, water supply, sewerage and others) and related work
It is important to understand that the functioning of natural ventilation is significantly influenced by external conditions: the climate characteristic of a given region, the duration of winter and summer, and the outside temperature.
It works best in winter, when the difference between outside and inside temperatures increases. The greater the difference, the better the air exchange, but it is important that it does not become excessive. When frosty air enters too actively, the cellar and all its contents can freeze. To prevent a catastrophe from occurring, it is necessary to monitor temperature fluctuations and, if it drops significantly, temporarily block the air supply.
In summer, the temperature difference becomes minimal, which leads to the cessation of air circulation. Therefore, a natural supply and exhaust ventilation system is not recommended for southern regions with hot and long summer periods. Here the optimal choice (even for a small cellar) would be a combined ventilation device.
The cellar may have a common ventilation system with the garage. Source garazhov.ru
If the room is small, it is permissible to limit yourself to one pipe, but divide it into two channels vertically, and provide a valve on each. Then it will simultaneously work for inflow and exhaust, and it will be possible to regulate the intensity of the flow using valves. To check the presence and strength of air flow, you can attach a sheet of paper to the opening of each channel.