Dangerous power line radiation comes from high-voltage networks. Previously, SanPiN standards were approved that established the minimum safe distance from power lines to a residential building, depending on the voltage in the network. Based on this distance, sanitary zones for power lines under high-voltage power lines have been determined and a “burden zone” has been regulated - an area dangerously far from radiation harmful to health. The sale of residential buildings and plots for individual housing construction and SNT in the sanitary zone of power lines in 2021 is strictly prohibited.
Close to residential buildings
Minimum distance from power lines and radiation
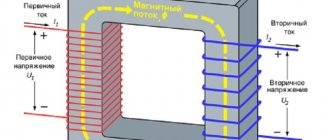
As charged particles move through wires, they create an electromagnetic field. The type of electric current determines the properties of radiation. It can be either constant or variable. Frequent changes in electric current from plus to minus and back contribute to a change in the field value several times more often.
Late at night
It has long been known that exposure to electromagnetic radiation negatively affects a person’s physical condition, just like radiation exposure. Observations on the effects of magnetic radiation on humans and the living environment began to be carried out in the early 80s.
Based on the results of a study in various countries, the WHO - World Health Organization established the maximum permissible radiation standards in hertz per unit of time.
In the Russian Federation and other countries, regulations have been approved prohibiting industrial and civil construction at a close distance from power lines.
People who were in the zone of a powerful field for a long time discovered that they had cancer and heart diseases. Women suffered from infertility. Men developed pathologies of the genitourinary system. Chronic fatigue often appeared. Life expectancy in cities and villages has statistically decreased.
Why is a distance from the fence necessary?
The distance between power lines and the fence in a village or city, required by law, is not just a way to ensure the maintenance and operation of high-voltage lines. The Moscow City Hall plans to transfer such networks to underground ones, because constant exposure to an electromagnetic field is extremely harmful for people living in such conditions.
Not far from the fence
This is not only a danger of headaches and ailments, but also the possibility of developing more serious complications. Even in a village where there are much fewer citizens living on SNT or individual housing construction sites, the state is obliged to ensure compliance with sanitary and protective standards.
| Minimum distance from the fence |
| 10 meters |
They determined not only the security areas in the zone of action of electric fields, but also the distances from the wires to the roadway (at least 6 m from the pedestrian path (starting from 3.5 m) and the height of the branch near the house (starting from 2 m 75 cm)) .
Scientific research has determined the negative impact of electromagnetic fields on reproductive function in men and the possibility of causing miscarriages in women. If rural or urban areas are taken into account, then the distance standards are still aimed at:
- preventing fire in the fence of a residential building or utility room in the event of a probable accident that no one can foresee;
- take the maximum possible precautions regarding the health of people living in an area located in close proximity to power lines (no matter what kind of area it is, even if it is a country house where people do not live permanently);
- to prevent possible consequences from weather conditions that caused a fall, destruction of the structure or release of accumulated charge into the atmosphere.
Read: Distance from the hives to the neighbor’s house and fence: SNiP (SP) and SanPiN norms to the property line
Cheapness of land plots in the sanitary zone
Based on SanPiN norms, construction rules were determined and security zones were created under high-voltage lines. Any child care facilities located at a dangerous distance must be closed. It is prohibited to build residential buildings for permanent and temporary residence closer than the distance indicated to high-voltage lines in SanPiN 2971-84.
At the power plant
Please note that it is not possible to sell a house located in a dangerous zone. Sanitary and fire safety organizations will not approve such a document. When developing individual housing construction sites, you need to take into account the distance to the power lines located nearby.
How dangerous the radiation from high-voltage lines is is shown by land prices. The cost of plots near power lines is low. As you move away it rises every 30 meters. Don't be tempted by the cheap price. First of all, you need to think about the health of your family.
Important points
A person uses electricity all the time, be it at home, in the country or in the office. But few people delve into the fact that power lines not only supply a useful resource, but can also be harmful due to magnetic fields, and in case of failures they become unsafe for humans. It is imperative to adhere to the established rules, which indicate the required distance from the support to the fence of a residential private house for the following reasons:
- To preserve the health of building occupants.
- In order not to suffer from the effects of airborne electromagnetic fields that have a detrimental effect on the human brain.
- In the security zone of power lines, where the voltage level is especially dangerous for humans, the issue of locating residential buildings is especially acute. If the level of danger is off the charts, the area is fenced off with an industrial fence and a ban on construction in this area is put in place.
Power line protection zone diagram
If the security zone is not so dangerous, then fences can be placed at a safe distance with mandatory compliance with the requirements prescribed in SNiP.
- So as not to put loved ones and private buildings at risk, which could catch fire if the power line fails if the fence is at an unsafe distance.
Therefore, SNiP establishes distances from power lines to the fence of a house not just so that people do not receive fines for violations, but for the safety of the population of cities and villages.
Return to contents
Dimensions of the protected area
Let us immediately emphasize that the safe distance from power lines is measured perpendicular to the axis of the overhead line - the high-voltage line. The projection of the outermost wire onto the ground or the outer point of the support structure is taken as the reference point. The width of the sanitary zone depends on the voltage in the wires and is determined by SanPiN 2971-84. Electromagnetic radiation, its background, is measured at a height of 1 m above the soil.
Width of the security zone according to SanPiN standards in 2021
Please note that you cannot build, plant or stay in the sanitary zone for a long time. Land for power transmission lines is prohibited from being sold and used for commercial purposes both in the city and in rural areas, on plots in SNT or individual housing construction.
Preparation and installation
The technological process of constructing an overhead power transmission line consists of preparatory, construction, installation and commissioning work. The first includes the purchase of equipment and materials, reinforced concrete and metal structures, study of the project, route preparation and picketing, development of PPER (electrical installation work plan).
Construction work includes digging pits, installing and assembling supports, distributing reinforcement and grounding kits along the route. The actual installation of overhead power lines begins with rolling out wires and cables and making connections. Then follows lifting them onto the supports, tensioning them, and sighting the sag arrows (the greatest distance between the wire and the straight line connecting the points of its attachment to the supports). Finally, wires and cables are tied to insulators.
In addition to general safety measures, work on overhead power lines requires compliance with the following rules:
- Stop all work when a thunderstorm front approaches.
- Ensuring the protection of personnel from the effects of electrical potentials induced in wires (short-circuiting and grounding).
- Prohibition of work at night (except for the installation of intersections with overpasses, railways), ice, fog, and with wind speeds of more than 15 m/s.
Before commissioning, check the sag and line dimensions, measure the voltage drop in the connectors, and the resistance of the grounding devices.
Safe distance to power lines
The standardized width of the sanitary zone does not correspond to the safe distance standards for housing construction. It is almost 2 times smaller, it is measured not from the outermost wires of the overhead line, but is indicated by one value centered on the axis of the power line. For example, the width of the sanitary zone of a 220 kV line is 25 m. This is approximately 10 m from the support post in one direction. You can build next to power lines no closer than 25 m to the projection of the outermost wire onto the ground.
Sanitary zones of overhead lines
The list shows the safe distance from the house to the power line depending on the voltage in the line:
- 20 kV - 10 m;
- 35 kV - 15 m;
- 110 kV - 20 m;
- 150-220 kV - 25 m;
- 300-750 kV - 30 m;
- 750-1150 kV - 40 m.
Definition. General classification
Electric overhead line (OHL) is a set of devices located in the open air and designed to transmit electricity. The overhead lines include wires, traverses with insulators, and supports. In some cases, the latter may be structural elements of bridges, overpasses, buildings and other structures. During the construction and operation of overhead power lines and networks, various auxiliary fittings (lightning protection, grounding devices), additional and related equipment (high-frequency and fiber-optic communications, intermediate power take-off) and components marking elements are also used.
Based on the type of energy transmitted, overhead lines are divided into AC and DC networks. The latter, due to certain technical difficulties and inefficiency, are not widely used and are used only for power supply to specialized consumers: DC drives, electrolysis shops, city contact networks (electrified transport).
Based on rated voltage, overhead power lines are usually divided into two large classes:
- Low voltage, voltage up to 1 kV. State standards define four nominal values: 40, 220, 380 and 660 V.
- High voltage, over 1 kV. Twelve nominal values are defined here: medium voltage - from 3 to 35 kV, high - from 110 to 220 kV, ultra-high - 330, 500 and 700 kV and ultra-high - over 1 MV.
Note: all figures given correspond to the phase-to-phase (line-to-line) voltage of a three-phase network (six- and twelve-phase systems are not widely used industrially).
Health hazards from power lines
However, a voltage of 10 kV is considered safe for humans. It creates a background density not exceeding 10 μT (measured in microtesla). For comparison, the Earth's magnetic field is 30–50 μT.
Prohibited in the security zone of power lines
It differs from the radiation generated by overhead lines in that it has a constant or smoothly varying value. A current with a frequency of 50 Hz passes through the power line - this means that per second the current changes its direction 50 times, a complete oscillation occurs - an alternating current wave. The magnitude of the emitted magnetic field also changes with this frequency.
Note that the highest value of natural vibrations reaches 40 Hz. When constantly in the zone of magnetic waves with high levels, malfunctions occur in the human body. This is possible not only when standing under power lines for a long time, but also next to household electrical appliances, especially thermal ones. The damage caused by the proximity of overhead lines can be compared with the health damage caused by a hairdryer, refrigerator, washing machine or laptop.
In the European Union countries, it is generally accepted that if the voltage in the power line wires is higher than 35 kV and the apartment is located closer than the standard size of the security zone plus 20 m, then, according to the health standards of the United Europe, such proximity can lead to a number of diseases of the nervous and cardiovascular systems .
Standard distances from supports
The distance from power lines and possible harm to health in such a case are absolutely dependent. Construction of housing in the European Union is permitted at a distance of 20 meters from the sanitary protection zone, if we take its value from Russian PUE standards.
All-Russian standards for the distance to residential buildings are stated above in this article.
Below is a table of European standards.
| Voltage, kV | Security zone according to PUE, m | EU norm for construction, m |
| 35 | 15 | 35 |
| 110 | 20 | 40 |
It is necessary to note that the site for individual housing construction or a dacha may partially be closer to the high-voltage line than the minimum distance to the residential building. In the technical passport this strip is indicated as an encumbrance zone. On this land you can plant a vegetable garden, a garden and put up a fence. You cannot build a house and construct outbuildings. A seating area in the yard should be located away from power lines.
Power lines: purpose and types
A power transmission line is perhaps the most basic component of electrical networks, part of a system of energy equipment and devices, the main purpose of which is the transmission of electrical energy from installations that produce it (power plants), convert and distribute it (electric substations) to consumers. In general cases, this is the name given to all electrical lines located outside the listed electrical structures.
Historical information: the first power transmission line (direct current, voltage 2 kV) was built in Germany according to the design of the French scientist F. Depres in 1882. It had a length of about 57 km and connected the cities of Munich and Miesbach.
According to the method of installation and arrangement, cable and overhead power lines are divided. In recent years, especially for power supply to megacities, gas-insulated lines have been erected. They are used to transmit high powers in very dense buildings to save space occupied by power lines and ensure environmental standards and requirements.
Cable lines are used where the installation of overhead lines is difficult or impossible due to technical or aesthetic parameters. Due to their comparative cheapness, better maintainability (on average, the time to eliminate an accident or malfunction is 12 times less) and high throughput, overhead power lines are most in demand.
Determining power line voltage
When purchasing a plot, it is important to make sure that the distance to the overhead line - high-voltage line - is safe. Information about exactly what voltage is on a nearby power line is not always readily available. You can determine it yourself by the number of wires in the bundle and insulator disks near the pole.
Rules for the location of overhead lines on sites in SNT and individual housing construction
One wire means that the consumer voltage is less than 330 kV with a frequency of 50 Hz. A higher value can be determined by the number of wires in the cable bundle:
- 1 PC. — up to 330 kV;
- 2 pcs. — 330 kV;
- 3 pcs. — 500 kV;
- 4 things. — 750 kV;
- 6-8 pcs. - from 1000 kV.
You should not count the number of cables running between the supports, but the wires in one bundle. You can also navigate by the altitude at which they are stretched: the higher they are located, the greater the tension in them.
If there is one wire in the line, then the voltage is determined by the number of insulators - ceramic disks in one branch hanging from the power line pole. Regulatory figures are given in the list:
- 3-5 insulators - 35 kV.
- 6-8 insulators - 110 kV.
- 15 insulators - 220 kV.
Typical voltage in residential areas
On the streets within residential areas, power lines have a voltage of 6–10 kV, which does not create radiation exceeding a value that is safe for humans. These wires are brought into houses, passing over the fences of the plots.
Options for power line supports depending on voltage
Standards for safe use have also been developed for them. According to SNiP, residential buildings and other buildings must be located no closer than 5 meters from the red line. This is the front boundary of the site. All underground and overhead communications pass through it, including power lines. Only a wire connected directly to the building violates the safe distance.
The insulator on which the wire is attached outside must be located on the wall of the building at a height of 2.75 meters or higher. The entrance to the house should not be located above or next to bedrooms, children's rooms and rooms where the family spends a lot of time. The best option is the wall of a pantry, utility room, or hallway.
The minimum sag of SIP over the pedestrian path is 3.5 meters. The sag of the wire between the overhead line poles must be more than 6 m from the ground above the roadway.
In the countryside
In the private sector, the power line runs along one side of the street - the red line on the plan. The distance from the power line to a private residential building on individual housing construction land must strictly comply with the PUE standards.
Wires to connect the house from the opposite side must only be pulled through additional supports. The height to the insulators exceeds 6.2 meters. The minimum distance from 6 kV power lines to trees is 2 meters horizontally.
Watch a video on this topic.
Wires for overhead power lines
The main requirement for overhead power line wires is high mechanical strength. They are divided into two classes - non-insulated and insulated. They can be made in the form of stranded and single-wire conductors. The latter, consisting of one copper or steel core, are used only for the construction of low-voltage routes.
Stranded wires for overhead power lines can be made of steel, alloys based on aluminum or pure metal, copper (the latter, due to their high cost, are practically not used on long routes). The most common conductors are made of aluminum (the letter “A” is present in the designation) or steel-aluminum alloys (grade AC or ASU (reinforced)). Structurally, they are twisted steel wires, on top of which aluminum conductors are wound. Steel ones are galvanized to protect against corrosion.
The cross-section is selected in accordance with the transmitted power, permissible voltage drop, and mechanical characteristics.
Standard cross-sections of wires produced in Russia are 6, 10, 16, 25, 35, 50, 70, 95, 120 and 240. An idea of the minimum cross-sections of wires used for the construction of overhead lines can be obtained from the table below. Minimum cross-sections of overhead power transmission lines
| Core material | Lines over 1 kV, mm2 | Lines up to 1 kV, mm2 | Branches to inputs (length up to 10 m / over 10 m), mm2 |
| Copper | 25 | 2,5 | |
| Steel | 25 | 25 | 4/4 |
| Aluminum | 356 | 16 | 6 / 10 |
Branches are often made with insulated wires (brands APR, AVT). The products have a weather-resistant insulating coating and a steel support cable. Wire connections in spans are installed in areas not subject to mechanical stress. They are spliced by crimping (using appropriate devices and materials) or welding (with thermite blocks or a special apparatus).
In recent years, self-supporting insulated wires have been increasingly used in the construction of overhead lines. For low voltage overhead power lines, the industry produces grades SIP-1, -2 and -4, and for 10-35 kV lines - SIP-3.
On routes with voltages over 330 kV, to prevent corona discharges, the use of a split phase is practiced - one wire of a large cross-section is replaced by several smaller ones, fastened together. With increasing rated voltage, their number increases from 2 to 8.
Methods of protection against electromagnetic radiation
As you gradually move away from the power line, magnetic radiation decreases. SanPiN indicates the distance when it reaches an acceptable value, but does not disappear completely. Professionals say that a completely safe distance is 10 times the permissible distance.
Layout of poles next to a residential building
Additionally, the house has wires and electrical appliances. During operation, they also emit electromagnetic waves at a distance of up to 2 meters from the compressor and heating elements.
The most dangerous are irons and refrigerators. People receive a large share of radiation from televisions, since they spend a long time in front of them. As a result, all radiation is summed up, and the result is a value that exceeds what is safe for humans.
Residential buildings located closer than 100 meters from household voltage lines and 200 meters from high-voltage lines must be protected from electromagnetic radiation.
Historical reference
One of the first experimental DC power lines with a length of 57 km at a voltage of 1.5–2 kV was built between the cities of Miesbach and Munich in 1882 French. scientist M. Despres. In 1891, for the first time in the world, three-phase alternating current power transmission at a voltage of 8.5 kV was carried out over 170 km from the Lauffen hydroelectric station to Frankfurt am Main, designed and built by M. O. Dolivo-Dobrovolsky. The first cable lines (underground, range 1 km, voltage 2 kV) in Russia appeared at the end. 1870s; the electricity supplied to the cable network was used by ch. arr. for lighting private houses. In 1897, a three-phase power station and a 10 kV power line, 13 km long, were put into operation at the Lena gold mines; in 1914, R. E. Klasson built the power transmission line “Electric Transmission” Bogorodsk - Moscow with a voltage of 70 kV; in 1922, a 110 kV power transmission line was put into operation at the Kashirskaya State District Power Plant - Moscow. In 1927–29, a double-circuit ring network with a voltage of 110 kV was built around Moscow; in 1933, the first power transmission line in the USSR with a voltage of 220 kV was built, Nizhnesvirskaya HPP - Leningrad; in 1950 a pilot plant was put into operation. DC power transmission line Kashira - Moscow with a voltage of 200 kV and a length of 120 km. In 1952, the world's first power transmission line with a voltage of 380 kV and a length of 960 km came into operation in Sweden; in 1956 the South was put into operation. double-circuit power transmission line Kuibyshev (Samara) - Moscow with a voltage of 400 kV and a length of 812 km; in 1959, the world's first power transmission lines with a voltage of 500 kV Kuibyshev - Ural and Volgograd - Moscow were put into operation; in 1964, work on the complete conversion of the Kuibyshev-Moscow power transmission line to a voltage of 500 kV was completed and the formation of a backbone network of 500 kV in Europe began. parts of the country. In 1967, the first pilot plant in the USSR and the second in the world (after Canada) began operating. 750 kV power transmission line Konakovo - Moscow; in 1972–77, construction and phased commissioning of the trans-Ukrainian main line with a voltage of 750 kV Donbass – Dnepr – Vinnitsa – Western Ukraine; in 1975, the Leningrad NPP – Konakovo power transmission line with a voltage of 750 kV and a length of 525 km was put into operation; in 1985–88, phased commissioning of sections of the world's first power transmission line Ekibastuz - Kokchetav - Kostanay with a voltage of 1150 kV, length 900 km, Kostanay - Chelyabinsk (500 kV, 321 km) and Ekibastuz - Barnaul (500 kV, 697 km) was carried out.
In Russia, the total length of operated power lines with a voltage of 35–1150 kV was approx. 3 million km (2010).
Definition of remoteness
The size of sanitary zones along power lines depends on the voltage level. To determine their boundaries, draw a conditional line along the projection of the wires onto the earth's surface. For even greater security, these values should be multiplied by 10.
Power lines against the backdrop of sunset Source elektrovesti.net
A distance of 100 meters from power lines can be considered completely safe for humans. During rainy weather, a large number of oppositely charged ions are released into the atmosphere, which leads to an increase in the area of electric fields and their spread to adjacent areas.
Not only residential and industrial buildings, but also garages, fences and other structures cannot be located on the territory of the sanitary zone. It is also prohibited to plant trees in these areas.
Residential buildings, children's and educational institutions should not be located under the wires. In this case, it is allowed to build production structures of the first and second levels of fire resistance in accordance with fire safety standards.
Wires with birds Source birdsandpowerlines.blogspot.com
The distance from power lines is a conditional value that provides for the safe functioning of people at a sufficient distance from wires and supports. Such a distance cannot guarantee the complete absence of any exposure to the residents of the house.
Underground installation significantly reduces the size of the danger zone, which is no more than 1 meter on each side of the electrical cable. At the same time, moving power lines underground requires investing a significant amount of money. Compared to the air type, the cost of underground installation increases several times. Therefore, this solution is still rarely used in practice.
For large urban settlements, underground cable laying is more typical. In this case, the wires are placed in special trenches, which are laid in blocks or tunnels. The depth of installation is about 1 meter. In this case, it is necessary to organize quick access to the lines during an emergency.
What additional methods of protection are there?
To increase protection from the harmful effects of fields generated by power lines, additional protection options are provided. These include:
- Shielding devices for voltages from 10 kV.
- Roofs made from metal tiles or corrugated sheets should be grounded. The roof is grounded only if the distance from it to the power lines is small.
- The presence of reinforcing mesh - the kind that is laid in reinforced concrete walls.
At present, the harmful effects of power lines on human health have not been officially confirmed. Such studies have not been conducted in Russia. But this does not mean that the problem does not exist.
Possible damage zone in an accident
According to the observations of foreign scientists, a huge number of people who live or work in close proximity to high-voltage structures experience their negative influence, they often feel unwell. In addition, the risk of nervous ailments and the development of cancer increases.
What to pay attention to
People are accustomed to the calm and comfortable use of electricity supplied to our homes - this matter has become so commonplace and proven. However, few people think about the fact that sources of electricity (and, consequently, power lines) are quite dangerous objects:
- electromagnetic fields generated by electrical appliances and sources of electricity are harmful;
- Non-functional, failing electrical appliances or power sources are at increased risk;
- electromagnetic fields affect human brain activity. Their long-term exposure is associated with an increase in blood pressure, an increase in the number of leukocytes in the blood, a change in the rhythm of the heartbeat, and damage to body tissues at the cellular level.
On the Sunset
For these reasons, a number of guidelines have been developed to minimize the risk of injury and damage from potentially hazardous electrical sources.
The reasons why you need to be extra careful when fencing an area with a fence adjacent to a power line are:
- homeowner health protection;
- protection from invisible electromagnetic fields that travel through the air and have a negative impact on human brain activity;
- Since power lines provide the most dangerous voltage for human health, experts are considering a complete ban on the construction of anything in this area, or at least the installation of a fence enclosing the line. In the second case, SNiP standards are raised, according to which the construction of a fence is carried out, regulated by the safety parameters in its official documents;
- The power line should be placed away from the fence, since in case of accidents the fence may catch fire, which is a huge risk to the life and health of people living nearby.
Types of supports
It is for these reasons that rules and regulations (SNiP) were developed, which continue to be improved.