The ventilation system of a private house should ensure a flow of fresh air into all rooms of the house and stimulate its renewal. The air duct system and openings for air flow are called supply air. Air ducts and exhaust openings are exhaust. Everything seems to be simple.
But in practice, the question of the most efficient design of a ventilation system is one of the most controversial. One of the most controversial issues is whether ventilation can be vented into the attic. It may be better to dispose of waste and contaminated air mass directly, i.e. through the wall?
In the article we presented, all aspects of constructing a ventilation system for a country house are discussed. We will introduce you to the regulatory requirements and nuances of the organization. Our recommendations will help you decide on the most practical option.
What is attic ventilation
Free air exchange between the under-roof space and the street is carried out through gaps and holes.
Holes in the ridges and under the roof overhang work most effectively. Positioned in this way, they use the pressure of wind and heat emanating from the ceiling of the house. If the ventilation of a cold attic in a private house is equipped correctly, in one hour the air goes around the entire roof twice from the inside. The movement of flows is directed from below from the vents under the eaves upwards to the ridge plates with special holes. If the roof is insulated, a gap of up to 5 cm wide is left between the roofing material and the insulation for the free passage of air.
The best exhaust is ensured by a combination of vents in the ridge and pitched elements mounted near the ridge. For tiled roofs, tiles are made with vents for air exchange.
And another way to ventilate attics in private homes is to install deflectors (turbines for ventilation) that provide mechanical draft. The method is good for ventilating an insulated attic above the attic.
The slight slope of the roof must also be taken into account when planning the ventilation of a cold attic. Vents in the ridge can be covered with snow, so they are replaced with pipes, the height of which should be higher than the snow cover.
The most ancient method of ventilation is a ventilation window in the attic. To ensure excellent air exchange in a cold attic, a combination of vents under the eaves, in the ridge and dormer windows is quite sufficient.
Ventilation of the cold attic of houses with a hip roof is different in that the house does not have gables. Therefore, there is nowhere to install ventilation windows in the attic. Thus, cold attics under hip roofs are ventilated using ridge and eaves vents.
It is more difficult to arrange the ventilation of the attic above the attic. Here, ventilation is provided by cracks in the roofing pie and mechanical means of traction. The ventilation outlet to the attic is hidden in the columns.
Functions of attic ventilation
A residential attic cannot exist without good air exchange.
A ventilation system during a particularly hot period eliminates stuffiness, but in winter it effectively prevents cold and moisture from entering the room. That is why an important point is the correct installation of the ventilation system with your own hands, because:
- the system eliminates moisture and prevents the formation of dampness in the insulating material - it is thanks to ventilation that the heat insulator maintains its functionality for many years, preventing the penetration of heat and cold;
- with properly created ventilation, the formation of fungus and mold is minimized, thereby eliminating the possibility of premature destruction of wooden roof elements;
- in extreme heat, it prevents hot air from entering the house;
- prevents the accumulation of moisture, thereby preventing corrosion that negatively affects metal tiles;
- eliminates the formation of icicles under the eaves in severe frosts;
- saves energy resources, thereby reducing the costs required to heat a residential attic in winter.
Main functions
The process of air exchange in a room consists of regulating heat exchange processes and maintaining optimal environmental indicators - temperature, humidity level, speed of movement of air masses.
The engineering system, equipped in accordance with established technical requirements, ensures the free flow of air and its movement in space due to installed dormer windows, vents, aeration devices of various designs and other openings.
The device of normally functioning ventilation is necessary especially if equipment for a supply and exhaust ventilation system or ducted air conditioner is located within the non-residential space. If the condensate that settles on it is not drained in a timely manner, repairs will have to be done very often.
The functional purpose of the system is the regular supply of the required volume of air and its subsequent removal, which contributes to:
- reducing moisture in the room;
- providing the necessary microclimate;
- preventing the formation of condensation and the development of fungus;
- creating continuous air exchange;
- preventing deformation of rafters in the building.
The organization of ventilation should be carried out both in a warm and in an uninsulated attic. In the summer, the roof surface heats up to high temperatures, transferring most of the heat to the lower part of the house.
In the presence of ventilation devices, the temperature inside the entire building decreases, which reduces the load on the air conditioning system, if present.
High humidity in the autumn-winter period affects the microclimate of the attic. At the same time, the thermal insulation qualities of the structure will be significantly reduced, because the water contained in the insulation and materials will contribute to heat loss. Therefore, an air exchange system is equipped to remove excess moisture.
Due to the large temperature difference inside and outside the room, condensation forms, walls, floors, floor beams, rafters, mauerlat, and vertical posts become wet. All this leads to rotting of the wooden components of the roof and the appearance of dampness.
Due to the difference between the temperature outside the roof and within the attic space, condensation forms on the inner surface of the roof or in the insulation. It must be removed through ventilation
To effectively ventilate the room throughout the year, without loss of heat in the house, the following technical standards are provided: for every 500 m2 of room, 1 m2 of ventilation openings is required.
In addition, in order to prevent the formation of water droplets on the beams of the structure, insulation measures should be taken - installing steam and waterproofing.
Ventilation system installation
Before installing an attic ventilation system, you need to make a project and calculate all the necessary parameters.
At the same time, at the design stage, you should carefully measure the entire attic of a residential building and write down all the important dimensions and parameters required for the calculation and installation of the ventilation system.
If the choice falls on a forced-type system, it is important to choose a fan that is appropriate in power. During installation, you should follow a certain procedure:
During installation, you should follow a certain procedure:
Based on the diagram, mark all ventilation elements, including valves and exhaust pipe. Make holes in the roof using a special tool. For supply valves, through holes must be made in the cornice or pediment
It is important to consider that the supply valves are located below the exhaust valves. Install the required valves. The cracks must be sealed. A pipe cover is installed on the roof and firmly secured.
Before installing the pipe itself, you need to make sure that all joints are securely sealed. The pipe must be installed strictly in a vertical position, taking into account all required distances. A fan is mounted on the pipe inside the room, and a deflector is mounted outside. After this, the system can be used.
A test for air exchange in the room is carried out over several days.
Correct installation of ventilation will ensure the most efficient supply of fresh air and optimal removal of exhaust air. Any violations during installation of the structure will significantly reduce the efficiency.
Basic SNiP requirements for ventilation systems
The requirements of SNiP can be considered redundant, but they still need to be fulfilled. They clearly prescribe not only the minimum required air exchange for each room, but also regulate the characteristics of each of the system elements - air ducts, connecting elements, valves.
The required air exchange is:
- for the basement - 5 cubic meters per hour;
- for living rooms - 40 cubic meters per hour;
- for the bathroom - 60 cubic meters per hour (plus a separate air duct);
- for a kitchen with an electric stove - 60 cubic meters per hour (plus a separate air duct);
- for a kitchen with a gas stove - 80 cubic meters per hour with one working burner (plus a separate air duct).
It is logical to equip the bathroom and kitchen with a forced ventilation system, even if natural ventilation is sufficient for the rest of the house. Exhausting air from the basement to avoid the concentration of carbon dioxide, which is heavier than air, is also often provided by a separate air duct.
The air circulation diagram in the house, made in the style of infographics, gives an idea of the flow of air flows. It is very important to check the functionality of the system after installing the duct system
Homeowners who are not ready to turn the roof of their house into a palisade of air ducts often think about how best to arrange ventilation communications within the attic. After all, I would like the design not to be too bulky.
Forced, with exhaust fan
Considering the relatively small area of the vast majority of attics, they do not need forced inflow. In approximately 95-99% of cases, installing a forced exhaust system will be sufficient.
How to make an influx depends on a number of circumstances, but in most cases the classic scheme is suitable. In the classical scheme, the supply system is organized through gaps, windows (through micro-ventilation or simply opening a window, through a comb), window valves, or through the air duct system, if there is one.
The exhaust system is organized as an isolated/separate one directly to the street (a pipe with a fan that blows air from the attic to the street), or through an air duct system. The second option is relevant if the building has an exhaust air duct - a separate line is extended to the attic.
Types of ventilation systems
Ideally, a non-residential attic should be cool in summer and dry in winter, and a residential attic should be comfortable for people at any time of the year. And this is precisely the goal that is pursued when choosing the desired ventilation option.
The classic type of attic ventilation in a private house is natural. Such ventilation is always based on physical laws: warm air rises and easily exits through the roof ridge. For this purpose, special ventilation holes are thought out in advance in the ridge.
Another way to provide natural ventilation is to install perforated soffits. We are talking about a special lining for cornices, designed not only to provide a spectacular look to the roof and its completeness, although many people think so. Where it is necessary to provide only an aesthetic appearance, but ventilation is not needed, solid soffits are installed. It is good to hide lighting wiring and other communications under them.
Perforated soffit is also used to cover the ceiling on a porch or veranda. Such roofing elements are made from plastic, copper, aluminum and steel. In the latter case, the soffits are covered with an anti-corrosion layer and a polymer coating. Perforated soffits allow air to pass through, but trap small birds and debris:
But if ecowool or sawdust was used as insulation, then they should be protected from blowing away:
Natural ventilation is also provided by vents. These are very simple designs for which a minimum of material is used. There are only two types of them: cornice and ridge:
All this can be complicated by turning the ventilation system into one single network. Then aerators and roof vents will come into use. Also, experts often recommend organizing the exit of ventilation pipes into one shaft, which will save a cold attic with a metal roof from condensation.
Forced ventilation is more expensive. Its task is to ensure that a special device controls air masses. Devices such as deflectors do a good job of ventilation. They are especially valued abroad, although in Russia they can increasingly be seen on the roofs of country houses. The essence of their work is simple: the device uses wind energy to increase traction in the pipe. A classic deflector usually has two parts: a stationary one, which is attached to the ventilation pipe, and a rotating one. The movable nozzle is a ball with vertical blades. A special bearing allows rotation along its internal central axis. Deflectors and weather vanes are installed, as a rule, on the ridge or closer to the ridge with a distance between elements of no more than 8 meters:
Please note that ventilation pipes must be routed above the roof of the house, and in no case should they be left in the under-roof space. Otherwise, warm, humid air from living rooms will begin to accumulate in the room, and condensation will quickly form on the roofing. All this threatens moisture getting into the insulation and onto the wooden rafters, which will not end well.
In voluminous roofs of complex shape, as an option, you can install a supply and exhaust system with a recuperator. True, it most often requires a constant power source - this should be taken into account. And if we talk about a residential attic, it generally needs its own ventilation system, separate from the whole house.
Calculation of metal roof ventilation
To choose the right ventilation equipment for a metal roof, you need to take into account the following parameters:
- roof area;
- roof shape;
- slope angle;
- aerator performance.
It is believed that metal roofing is the most vulnerable to moisture and needs maximum protection from vapors rising from the building. Therefore, such a roof is equipped with the maximum number of devices, including forced ventilation systems. Every builder knows that there are no restrictions on ventilation. Ideally, the air temperature both outside and inside the roof should be the same, and this can only be achieved through active ventilation.
There are no state standards for installing aerators for pitched roofs, so disagreements often arise regarding the frequency of their location. Some believe that it is necessary to install deflectors at the rate of one device per 40 m2 of roof, others argue that this is not enough and it is necessary to double their density. Some people prefer to install devices dotted at intervals of 0.5–0.6 m; there are even experts who advise embedding a valve into almost every sheet. Perhaps their opinion is dictated by the desire to protect the roof, but one can also assume that this is simply an attempt to increase the cost of the goods and services provided.
The main regulatory document regulating the construction of roofing is SP 17.13330.2011. Appendix “B” provides several examples of calculating the number of ventilation devices (aerators). Complex mathematical calculations that take into account many factors (climatic conditions and properties of materials) given in the document are for informational and advisory purposes only. All calculations are given for flat roofs. Regarding pitched metal roofing, it is noted that the ratio of the area of ventilation ducts to the area of the horizontal projection of the roof should be 1/300, and a table is given of the recommended height of the ventilation duct depending on the angle of inclination of the roof.
Cold attic: is ventilation needed?
In cold attic spaces there is a constant change in temperature, so the ventilation system must be adjustable. When building a house with your own hands on the roof, the lattice and rafters may not be completely closed, or lining is used, which has open intervals for air circulation.
And also the need for ventilation will depend on the outer cover of the roof. If slate or ondulin is used and a film is installed to provide vapor barrier or windproofing functions, then designing ventilation is not required.
Air circulation will occur naturally. After all, this roof is capable of allowing air to pass through. And also additional ventilation passages will be obtained during installation of the material. The resulting seams and skates allow air to pass through well.
When using metal tiles, there is one factor to consider. Even when installing the film under this material, condensation will still form, so it is necessary to provide ventilation.
If the house has a gable roof, then ventilation outlets are made in the gables of the openings. For air circulation, you can leave gaps of the same dimensions when sewing fronts and wind overhangs.
Some buildings have stone gables. In this case, you make small holes in the wall through certain areas with your own hands. This procedure avoids the appearance of stagnant air. This attic ventilation in a private home requires periodic adjustment.
To do this, it is necessary to provide for closing the holes made, as well as installing a grill on them so that foreign objects or small insects do not penetrate into it.
Cold attic ventilation design
Ventilating a cold attic is a fairly lightweight design that you can do yourself without any problems. To design and create a system, you need to know the basic aspects of the theory and have basic skills.
Creating a ventilation system in a cold attic in a private home is an easy task. It works due to the large volume of air and the absence of any obstacles to its normal circulation. The described ventilation method can be created by ensuring ventilation of the attic using several structures: eaves overhang, gable windows, grilles, roof ridge and ridge, etc.
For rooms with a gable roof, the best option would be to choose gable windows or eaves overhangs. They are best suited for designing an attic ventilation system with this type of roof.
If your cash reserves are quite meager, then as a budget alternative, you can use the option of using conventional grilles. Usually, they are installed in the amount of two pieces, where one can be adjusted, and the second is static, but at the same time the vents face downwards. As an additional accessory, a mosquito net can be attached to them, which will block access to insects.
The hip roof structure does not have gables. Therefore, to create a ventilation system, only cornice overhangs can be installed on them. In this case, the air is exhausted through the roof ridge.
The most difficult situation arises when working with valleys. Due to their specific design, it is quite difficult to ensure ventilation when working with them. However, this can be done using spot cornice aerators.
Features of warm attic ventilation
Modern heating systems very rarely use a natural air circulation system. Therefore, when converting an attic space into an attic, it is necessary to ensure absolute ventilation.
For a roof made of sheet metal and flexible tiles, it is necessary to sew counter battens, rafters and sheathing. Ventilation of a warm attic, the roof of which is made only of metal, is carried out using specialized windproof films - geosynthetics.
For roofs covered with slate, the use of counter battens is not necessary, since the attic will be ventilated in the same way as in other rooms.
Ventilation in the attic with attic
Ventilation of a warm attic in a private house is more difficult to arrange. Air movement in the under-roof space is only possible between the rafters. Therefore, it is necessary to resolve the issue of ventilation at the stage of attic construction. A space of 2-3 cm should be left between the layer of waterproofing and thermal insulation. Which additional layers of roofing cake should be used depends on the material with which the warm attic is sheathed. Ventilation under flexible tiles requires the installation of a counter batten. The metal sheathing must be supplemented with a layer of windproof film.
Ventilation of the attic above the attic is provided according to a similar principle: inlets - soffits - on the overhang, outlets on ridges.
The openings on the ridges and eaves must be located along the entire length in order to ventilate the entire roof, preventing stagnation of air and steam in individual spaces.
The attic itself is ventilated in the same way as any other living space. Air from the street enters through a window or supply valve and exits through the ventilation pipe along with excess moisture.
Design and principle of operation of attic ventilation
The arrangement of air exchange in the attic is carried out according to the general principles of installing ventilation in the house, residential and warm rooms. This can be a natural or forced air circulation system.
The simplest type of attic ventilation is the installation of hatches or windows directly in the roof. By opening them, the necessary circulation of air masses is ensured. But such ventilation is inconvenient and not always effective.
Disadvantages of natural ventilation through hatches:
- Creating drafts.
- High heat loss in winter.
- Overheating of air in hot summer weather.
It is better to take care of the arrangement of more complex supply and exhaust ventilation.
Hatches or windows are perfect for creating a supply line. To ensure inflow, special valves are suitable. The required number of valves is calculated according to established standards.
Exhaust ducts are discharged through the pediment (a triangular, pentagonal or rounded wall, depending on the shape of the slopes, covering the side space of the attic, between two roof slopes) or the roof ridge. Plastic pipes are suitable for exhaust hoods. They are mounted vertically into the roof slope. The lower end of the pipe is placed as high as possible.
Plastic pipes are suitable for arranging a hood in the attic. The upper end of the pipe, according to standards, should rise above the ridge by at least 50 cm. In case of typical heavy snowfalls in the area where the house is located, the pipe rises another 10-20 centimeters so that it is not covered with snow . It is placed in a special plastic box and insulated. A deflector is installed at its street end. It will increase circulation and protect the pipe from dust, snow, rain and leaves. It is better to install the exhaust pipe on the opposite side of the room relative to the location of the supply elements. To increase efficiency, it is recommended to install a standard fan on the hood. It will allow you to control the flow of fresh air.
Natural ventilation with access to the attic
Gravitational ventilation, also known as natural ventilation, ensures air circulation according to the principle familiar from school: warm air is lighter than cold air. Warm air rises through exhaust ducts located as high as possible. Cooler air from the supply ducts enters the house.
Ventilation ducts in a one- and two-story private house can be combined into one system only if there is a good ventilation system in the attic itself. This reduces the number of air ducts on the roof
If effective under-roof ventilation is properly arranged in the attic and in the roof pie, then the exhaust air exhaust systems can be fully or partially combined.
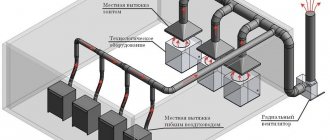
The circulation and removal of contaminated air mass within the attic will be ensured by:
- fan risers;
- aerators (an air duct with access to the street, which forcibly ensures constant air circulation in the attic);
- proper installation of a roofing pie (the simplest is ventilation using two gaps under the roof and above the rafters);
- roof vents that cut directly into the roof system.
If a natural ventilation system is organized within an unheated attic, a rational solution is to combine all the ventilation pipes in the attic to be discharged through a common ventilation shaft.
A single riser vent can solve condensation problems in your attic. The natural ventilation system closes on it
If the attic is sufficiently ventilated, condensation will not accumulate in it. Unfortunately, roof vents or attic gaps do not always provide it fully.
Ventilation of the cold triangle of an unheated gable roof (called a gable or gable) is carried out by installing ventilation windows or openings with access to the street. This ensures there is sufficient air circulation in the attic
Dormers and attic vents that can be closed and opened should provide more air circulation than other methods of natural attic ventilation. For example, supply and exhaust openings drilled in the gables.
Natural ventilation in the attic: general principles
The natural ventilation system directly depends on the correct installation of insulating materials. A prerequisite for laying insulation is the presence of ventilation spaces between the layers of the material used and under the roof surface. Natural ventilation is based on the creation of natural draft, thanks to which there is a constant flow of air masses. The total area of the ventilation ducts should be 0.2% of the total area of the attic. The simplest installation option is to route the channels through the gables. This technology can be applied to non-stone roofing elements.
The size of the gap for free air exchange depends on the roofing material used for the roof:
- when using metal tiles, tiles, metal profiles, the gap should be more than 25 mm;
- when using soft materials and flat products, the space for air flow should be more than 50 mm;
- when installing waterproofing and insulation, the space between them should be from 20 to 30 mm.
Important! To create high-quality natural ventilation above the attic space, it is necessary to create a hermetically sealed separation of the ventilation cavities, due to which the natural ventilation of the attic floor will be carried out evenly, without the formation of “dead” zones.
Installation of natural ventilation
A natural ventilation system is created during roof installation. To implement air exchange, you will need to install special elements responsible for air exchange under the roof. For air flow, soffits are used, which are installed around the perimeter of the building. The perforated surface allows air to enter the attic. To remove exhaust air, point or continuous aerators are used, which are installed on the slope of the roof.
Special aerators are mounted on the ridge. It is thanks to ridge aerators that the efficiency of all natural ventilation increases, because the area of the outlet surfaces of the elements is much larger than that of conventional ones. The number of aerators is calculated individually and depends on the total roof area. For 100 m2 of area to be ventilated, 2 aerators are installed.
Important! Natural ventilation functions flawlessly only in the cold season, since air exchange requires a difference in temperature outside and inside the room. That is why ventilation of the attic roof requires the installation of a forced air exchange system.
System of dormer windows and vents
One of the common measures for arranging attic ventilation in a private house is air exchange carried out by dormer windows. In this case, you don’t need to use a system of holes, vents and gaps. According to experts, this method is not extremely effective, but condensation does not accumulate in the room. The rules are as follows:
- The size of such windows should be at least 60x80 centimeters.
- Windows are installed on opposite gables.
- The windows are placed at an even distance from the cornice, the sides of the building and the ridge.
- The distance between two adjacent windows is at least one meter.
- The window can be installed directly into the ventilation grille in the attic.
This method of air exchange is popular in the construction of dachas and country houses. But there is also a disadvantage of such a system: air can stagnate under the dormer window and above it. But if you choose high-quality building materials and carry out the installation correctly, condensation will not accumulate in the attic space. Another, simpler way is to place vents. So how to create ventilation yourself, without resorting to the help of specialists?
In a private house, you can do the ventilation of a cold attic yourself. Evidence that condensation has accumulated is the appearance of an unpleasant smell of mustiness and dampness. Violation of comfort prompts many to immediately take up tools and begin fixing problems. In order for the ventilation system to ensure optimal air exchange, condensation does not accumulate and heat loss does not occur, it is important to pre-design all elements. If the roof is gable, the arrangement will not raise questions or problems. After the planning stage, you can start working:
- Vents are made in the gables.
- Wind slopes are covered on the sides of the roof with wood.
- All cracks are made uniformly, creating airflow over the entire surface of the attic.
Important! If the gables are made of stone, then there can be no gaps, and, armed with a tool, you need to make a couple of dormers in the surface.
Doors and hatches to the upper attic floor
At the entrance from the stairs to the attic and to all upper floors, it is advantageous to install an entrance door that blocks the flow of air from the lower floors and divides and isolates the air space of the floors into independent blocks.
Ventilation on the floor will work more efficiently if you choose a door with a good seal and install a door closer that constantly returns the door to the closed position.
The topmost step of the stairs, directly in front of the door, must have a tread width of at least 60 cm.
For the purpose of dividing the air space of floors, doors can also be installed on the lower floor, at the entrance to the stairs upward.
The hatch acts as a door to the country attic. Approaches to the hatch opening must be fenced on three sides. The height of the fence is at least 0.9 m.
The hatch opens easily and smoothly thanks to gas springs (gas lifts) or an electric drive. In addition, the hatch must have a locking device in the open position. The hatch can be ordered from a hatch manufacturer, or you can make it yourself.
When making it yourself, experts recommend reducing the weight of the manhole cover and installing two gas elevators (you can choose automobile ones). Gas elevators must be installed with the rod down, and the cylinders must be attached to the hatch flap.
Gas springs - lifts are selected according to the location on the finished lid. Measure the force in kg. to lift the finished sash, convert to Newtons (kg x 10 = N), add 30% to the resulting value and determine the total power of the gas springs. Next, purchase a set (2 pieces) of gas elevators in the store with a capacity within the calculated values.
Common myths about ventilation
Some people have doubts about the need for ventilation. Therefore, disagreements arise. Let's try to figure out whether it is possible to do without this system:
- Heat escapes through ventilation in winter. This is the most common opinion. If it takes a long time to heat the house, and cooling occurs very quickly, then air exchange does not affect this problem in any way. This is due to shortcomings when installing insulation materials. But if the insulation is of poor quality, it can release moist air into the attic. As a result, condensation appears and wooden floors begin to rot.
- Ventilation of a hip or hip roof is only necessary in summer. In fact, if air exchange is disrupted in winter, icicles will grow and mold and mildew will appear.
- It doesn't matter how much area the ventilation hole will occupy. This opinion is erroneous and it is not recommended to place holes by eye. Such ventilation will cause poor air circulation. It is worth adhering to a certain scheme: for every 500 m2 there is 1 m2 of ventilation.
How to make accurate calculations?
The optimal climate in the attic is maintained if the air in it is completely replaced twice a day. This avoids excess moisture and protects the insulation from dampness.
Let's do the math. For example, installing windows on gables or louvered grilles ensures air replacement at a rate of 1/2 per hour. If you install a more complex forced ventilation scheme, the air exchange rate will increase to 5 per hour. However, increased ventilation to a certain extent increases heat loss. Therefore, it is important not to go too far and the most appropriate amount of air exchange in the attic is still considered 1/2 per hour.
If we talk about more accurate calculations, roofing manufacturers usually indicate 0.32 square meters of ventilating surface per 100 square meters. This formula achieves an ideal balance between air inflow and outflow. But if the situation is atypical and such ventilation is not enough, then the ratio is 0.32 square meters of ventilation for every 50 square meters of floor.
And to implement proper ventilation you will need the following elements:
A few final tips
- pay attention to the strength of the ventilation, it must withstand any weather fluctuations;
- you can put continuous soffits under eaves with fine screening mesh. To prevent corrosion, the holes should be made of aluminum or plastic;
- to prevent the formation of frost in the attic, install vents inside the room between the rafters and make holes so that they cannot become clogged with debris;
- You can install a fan on the roof for better air extraction. The distance between it and the supply system must be at least 8 m;
- the air supply unit should be placed in the cleanest place in the attic;
- install a recuperator that can cool or heat the air, thereby preventing condensation from forming in a cold attic;
- equip ventilation pipes with grilles or diffusers;
At first glance, there is nothing complicated in arranging ventilation, but in fact it is better to take this issue seriously and consult with specialists. After all, the microclimate in the house and your health, as well as the durability of the building itself, depend on its quality.
Ventilation of problem areas
In addition to the ridge, the need for increased ventilation arises in areas where moisture accumulates on the roof: valleys, drainage funnels, drips, this is especially felt on roofs with long slopes. It is strictly not recommended to drill through rafters; this will not lead to the desired effect and will only reduce their load-bearing capacity.
On roofs with a large slope (above 45°), special point aerators are installed along the valley; on flatter roofs this method is not suitable. In this case, it is recommended to organize forced ventilation (as for all roofs with complex shapes).
Regardless of location, all ventilation openings are protected with special elements from debris and are periodically checked.
Roof and its assembly
The roof on the attic floor is ventilated by the movement of air flows located under the roofing material. These flows rise upward, that is, to the ridge of the roof. Sometimes proper roof assembly is enough for good ventilation, but at times it is necessary to use additional devices.
Overhang with vent in the attic
Proper ventilation of the roofing pie is ensured by the creation of ventilation gaps. In addition, the location of the layers is also important. If we consider the roofing pie from the inside of the attic, then it should be designed like this:
- Ceiling trim;
- Vapor barrier, which is necessary to retain warm air inside the attic, also prevents moisture from entering the insulation. It is important to leave about 5 cm between the sheathing and the vapor barrier film, but the film should be closely adjacent to the insulation itself;
- Insulation, which is most often made of mineral wool, which is laid between the rafters;
- Layers consisting of counter-lattice and sheathing. They form the gap necessary for the unhindered passage of air flow. If the rafters are not thick enough, the space between them is increased using additional bars.
- Waterproofing film. Such a film is capable of transmitting evaporation coming from inside the room into the space under the roof, but at the same time retaining moisture coming from outside. This happens due to the special structure of the film; it is microperforated.
- The final layer is the roofing material itself. A gap is also left between it and the previous layer, which is necessary for ventilation of the roof.
It is very important to leave a small outlet for air flow. It is located at the ridge of the roof. This is done with the help of additional roofing accessories.
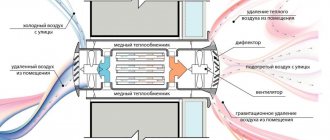
Hybrid type
On the attic floor it is possible to install hybrid ventilation. It provides natural suction. The system is maintained at low pressure. Cold air rises.
Scheme of natural ventilation in a private house and attic
The channels are installed in such a way as to ensure natural air draft. A special feature of hybrid ventilation is flow control. A mechanical regulator or a remote control unit is used.
According to environmental friendliness there is a division into classes:
- economy;
- standard;
- eco.
Hybrid ventilation uses filters to remove dust and allergens.
Attic space: the need for ventilation
The design of the ventilation system is the most important part of the design.
Ventilation is involved in the heat exchange processes of the entire residential building. During the hot season, the roof can heat up over one hundred degrees, and heated hot air enters the house, aggravating the heat in it. In cold weather, other problems may arise. Cooled air forms drops of condensation on insulated floors: this moisture negatively affects wooden elements.
Even basic ventilation can prevent premature damage to the rafters.
Attic ventilation ensures mixing and equalizing the temperatures of the roof structure and the external environment. It prevents the formation of ice during the melting of the snow cover, avalanches and the appearance of large icicles. Setting up a high-quality air exchange system is actually extremely important.
Well-designed attic roof
In modern construction, they try to provide all structures with maximum thermal insulation and seal them in order to reduce heat loss. This concerns structures enclosing the attic, perhaps most of all. After all, it is through the roofing system that the greatest amount of heat can escape.
If the layers of hydro-, steam- and thermal insulation in the roofing pie are folded without ventilation gaps, the insulation system will practically not work. Moisture that falls out in the form of condensation due to temperature differences, household fumes, and rainwater that has penetrated under the roof will not have the opportunity to escape outside.
Water is an excellent conductor; due to its content in the insulation, heat waves will freely pass outside. In addition, it provokes rotting of the wood from which the rafter frame is made, and often the cladding of the attic.
Draining the roofing pie is perhaps a separate extensive topic. However, its effectiveness significantly affects the microclimate of the attic, especially in the summer heat, when the top layer of the roof warms up to +1000C. Therefore, we will briefly talk about how this should be arranged.
With proper organization of the roofing pie, with the installation of ventilation ducts of the required cross-section, the insulated slopes are regularly washed by air currents. As a result, the dried roof does not allow heat waves to pass through, and building structures do not get wet or fail.
The purpose of any roof ventilation devices is to ensure air movement from the overhangs to the ridge. The easiest way to do this is under a roof made of slate or ondulin: under the waves of roofing material, the air freely rises to the ridge; in this case, the overhangs are not tightly hemmed.
The situation with metal tiles and corrugated sheets is almost the same, but it is advisable to provide their eaves with ventilation grilles or cover them with an air-permeable seal. The relief roof must be separated from the waterproofing by a spacer bar - it forms a ventilation gap required to remove fumes and atmospheric water accumulated under the coating.
Other materials, in particular soft tiles or sheet metal, require the artificial creation of 1 or even 2 ventilation layers of 3–5 cm, separating the vapor barrier from the insulation, and the waterproofing film from the coating.
For the inflow and exit of air flows into the roofing system, openings must be made to allow the flow to move freely
For this purpose, ventilation ducts are arranged by laying sheathing and counter-lattice. Air will rise between the slats. If the thickness of the rafters is not enough to lay all layers of the roofing pie and provide ventilation gaps, the rafter legs are extended with bars.
For inflow into the roof overhangs, perforated inserts are used - soffits or ventilation grilles, at regular intervals along the entire length of the overhang. For exhaust, a special ridge with aeration or point aerators are installed.
The total cross-sectional area of all openings for ventilation of the under-roof space should be 1 m2 for every 300 - 500 m2 of roof slope area.
Both the under-roof space and the gable sheathing can be ventilated through point aerators if the organization of long aerators or slots is impossible
Ventilation of the gables is carried out between the sheathing and the façade cladding material. If the sheathing is installed horizontally, then the sheathing supports are vertical, and they do not interfere with natural ventilation.
If the frame slats need to be fixed horizontally, there are several solutions for gable ventilation:
- Fasten small sections of slats horizontally in a checkerboard pattern. It's economical and efficient, but it can be difficult to get everything level.
- Install long slats, but make holes in them in a checkerboard pattern.
- Construct a vertical counter lathing. Ventilation in this case will be most effective, but the most material will be required.
If the sheathing is diagonal, preference should be given to the vertical arrangement of the slats.
DIY installation
Before you start arranging the attic ventilation with your own hands, you need to create its design, carefully consider the layout of its components, and write down on paper the sequence of work. During the preparation process, it is imperative to inspect all areas of the attic space, take the necessary measurements, and note the design features of the attic. When performing forced ventilation, it is necessary to select an exhaust fan with the appropriate technical characteristics. Sequence of installation work:
- In the diagram, according to the established designations, the fixation points of the valves and the area for laying the exhaust pipe are marked.
- You need to drill holes in the roof using a drill or hammer drill. These works are carried out very carefully so as not to damage the layers of the roofing cake, the design of which includes roofing, sheathing, waterproofing, insulation and vapor barrier layers. Holes for supply valves are made in the cornice or pediment. You should definitely take into account the placement of supply and exhaust ducts. The first ones are equipped below.
- Valves are being installed in the wall. A tube is inserted into a pre-drilled hole, which is covered with a grille on the street side. A filter is installed on the inside and the valve body is attached. All these elements are included in the valve delivery kit. The gaps between the structural elements and the wall surface are carefully sealed.
- On the roof surface where the hole for the pipe is drilled, the lining is securely fixed, and the quality of sealing of the connecting sections is checked. Next, the pipe is installed strictly vertically. It is imperative to maintain all calculated distances.
- A fan is mounted to the pipe on the inside of the building, and a deflector is mounted on the outside. The ventilation system is ready for operation. The effectiveness of its work is tested over the course of several days.
It is important to understand that properly equipped attic roof ventilation is one of the conditions for comfortable living in a country house. When arranging it with your own hands, it is imperative to comply with established building standards, design it together with the structure of the house and equip it at the stage of erecting the roof of the building.. https://www.youtube.com/embed/VGCQE8ZgaSE
Device
With a cold roof
This is the simplest case of solving the problem, since the attic space allows large volumes of air to move freely. Vents located under the eaves, under the ridge strip, in the gables allow air masses to circulate due to natural convection:
- cold air is drawn into the attic from the outside through the eaves vents;
- warm air rises from the ceiling of the living room up under the roof and exits through ridge vents.
Of course, in this way it is impossible to completely level out the temperature difference between the roof surface from the outside and inside, however, it is usually not enough for condensation to form on the inside of the attic.
As a rule, the number of vents located at the top and bottom of the slope of pitched roofs of a simple configuration is the same. The only condition under which normal air circulation is ensured is that the total area of the vents should be about 0.33% or ⅟300 of the area of the slope.
For a warm roof
Attic ventilation is somewhat more complicated. In such a structure, air cannot circulate freely, since it is almost entirely occupied by attic spaces.
Air circulation in the residential attic, located in the under-roof space, is ensured by a convective flow directed from the eaves towards the ridge. In order for it to pass this path unhindered, additional space is created in the roofing pie between the layers of heat and waterproofing using counter-lattice and sheathing. The gap must be at least 5 cm high.
Then a ventilated circuit is formed in the space under the roof, that is, they provide air flow, as well as its exit with vapor:
- tributary: eaves overhang along the bottom of the roof, then attic windows (above them), valley or others where the contour is interrupted;
- exit: ridge, attic windows (under them), junction points, that is, where they need to be made specially.
Attention! It is important to ensure continuity of the circuit to eliminate the formation of “stagnant zones”, places where condensation may accumulate
attic ventilation
Purpose of roof ventilation
Roof ventilation is designed to remove moisture from the space located between the external moisture-proof material: tiles, corrugated sheets, slate, and internal roof structures.
The main functions it performs:
- preventing the accumulation of unventilated air under the roof. This is especially true for houses with residential attics,
- preventing the formation of frost and ice in roof cavities,
- timely removal of moisture and dampness from the attic space.
The need to install roof ventilation systems is determined by fluctuations in daily air temperatures, as a result of which condensation forms on the inside of the roof: in the winter in the form of frost, and in the summer - dampness.
This problem can be partially solved thanks to the construction of a so-called “roofing pie”, which includes a layer of vapor barrier. However, waterproofing layers cannot always and not everywhere prevent the accumulation of dampness under the roof.
The moisture formed inside the “roofing pie” leads to a sharp drop in the efficiency of its operation. Since mineral wool slabs are usually used as insulation, under the influence of dampness they become compacted and lose their thermal insulation properties. In winter, moisture accumulating under the roof turns into ice and, expanding, gradually destroys the attic structures. In the warm season, dampness leads to the formation of fungus and mold, which can spread throughout the entire building.
Roof ventilation can eliminate all these problems.