In this article:
- Concept of gas supply system design
- Requirements and regulatory documents for gas supply design
- Where does the design of gas supply and gas distribution systems begin?
- Gas supply network design process
- Nuances of designing gas supply for residential buildings and industrial enterprises
- Design features and methods of installing an external gas pipeline
- Requirements for designing an external gas pipeline
- Selecting an organization engaged in the design of gas supply facilities
- Ways to save on gas supply design
Gas supply design is complex engineering work that includes not only design activities, but also the preparation of documentation, studying the requirements, features of the gasified facility/territory, and the conditions for laying a gas pipeline.
Such research cannot be carried out independently, since a certain level of clearance and qualifications are required to carry out this work. You will learn about the stages and important nuances of designing gas supply systems from our material.
Concept of gas supply system design
A facility gasification project is a scheme for installing energy equipment. When developing this document, the client’s wishes and all current legislation are taken into account.
The project consists of indicators and calculations of the energy efficiency of the gasified facility, justification for a particular decision on the installation of a gas pipeline (underground or above-ground), detailed specifications for the materials used and supply devices.
The project is not a single document, but a collection of various documentation, specifically:
- layout diagrams of underground and above-ground gas pipelines;
- diagrams of chimneys and ventilation ducts;
- technical conditions for gas supply;
- inspection reports for each smoke and ventilation duct;
- all required by law executive documentation for the gas main to which the facility will be connected;
- passports and certificates for each installed gas device;
- explanatory note.
The laws of the Russian Federation do not allow the construction of new gas supply lines, their reconstruction or the installation of gas equipment without preliminary preparation of the project.
At the design stage of a gas supply, gas distribution or gas consumption system, suitable equipment is selected, an estimate is drawn up for installation work and the purchase of all materials. The project helps to correctly select and prepare the premises where gas supply devices will be installed, and coordinate construction or repair activities with government agencies.
What should be included in the project
Drawing up gasification projects begins with initial data. Design work is carried out using water and gas supply technology.
A specialist goes to the site, collects the necessary information, and takes distance measurements:
- from the gas supply source to the walls of the house;
- between structures, outbuildings that are located on the property of the owners and neighbors.
Design includes preparation of the following technical documentation:
- gasification plan for the site, it is possible to lay the pipe above ground and underground before entering the house;
- diagrams with fuel connection points, placement of equipment with the floor plan of the house, including the basement floor, where boiler rooms are often located;
- fire safety regulations indicating valve locations, pressure at the inlet and outlet of the frequency flue in MPa.
The house plan indicates gasified areas, gas equipment connection points, taking into account the wishes of the customer and compliance with the requirements for the facility to ensure fire safety.
Read more: Gasification of a dacha and What to do if the gas is turned off
Requirements and regulatory documents for gas supply design
As a rule, industrial and residential facilities are gasified, but public buildings and business centers usually do not require gas consumption and gas supply systems. Either the decision on gasification is made by the owner, or it is carried out within the framework of a municipal or state program (if we are talking about housing stock).
Why is gas supply design necessary during construction or renovation of buildings? This is required by the NPB and SP:
- Unimpeded access must be provided to any section of the gas supply line. This also applies to gas equipment. It is unacceptable to sew it into a wall or hide it behind temporary or permanent structures.
- Control conductors must be provided on the pipelines, with the help of which you can check the gas contamination of the basement or underground floor if there is no other way to get to these rooms.
- Gas pipelines are not laid in living rooms.
- Project documentation must be agreed upon with the gas distribution organization.
Gasification of a non-residential building or premises is subject to an even greater number of rules and regulations, since production processes cause additional risks when operating gas equipment. Working and design documentation are drawn up in strict accordance with these standards.
In order to begin construction or renovation, the project must undergo an examination, be approved by the State Regional Development Organization and verified by the state construction supervision authorities that issue permits. If the standards are violated somewhere, the experts will refuse a positive conclusion and will not issue a building permit.
The building's gas consumption system includes gas-using and technical devices, an internal network and a gas pipeline. Gas is used to heat public buildings and residential buildings, cook food, and heat water. To comply with all requirements when connecting gas or carrying out other work on the gas supply system, consider:
- Technical conditions imposed by the gas distribution company: entry points, number of connected devices, maximum consumption volumes.
- NPB and SP requirements regulating repair, reconstruction and construction.
- Will the participation of employees of the gas supply organization be necessary to connect and launch the gas supply system?
- Safety standards regarding technical devices, their installation and use.
The main role in the design and installation of gas pipelines, as well as gas supply systems, is played by the experience and professionalism of the performers - the designer and those who will install the equipment. At the design stage, you need to think through everything: the layout of internal pipelines, connection points, installation of the necessary equipment and metering devices.
The main document on which developers of OCS reconstruction and construction projects rely is the Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation No. 87, which classifies the subsection describing the gas supply system as a key part of the project. The textual and visual content of this subsection is determined by the type of object (residential, industrial, etc.) and its functional characteristics.
But there are other regulatory documents governing the design of gas supply:
- Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation No. 1314 (rules for the technological connection of buildings to gas distribution networks);
- SP 118.13330.2012 (gasification of public buildings);
- SP 54.13330.2016 (gasification of apartment buildings);
- SP 56.13330.2011 (gasification of production facilities);
- SP 402.1325800.2018 (design of gas supply in a residential building).
In addition to building regulations, it is also necessary to comply with fire safety standards and sanitary and hygienic requirements. Selected building materials and gas equipment must have declarations and certificates in the UAIS system.
If you do not have to build a gas distribution system from scratch, but repair an existing one or replace its individual components, you can entrust the design of gas supply to a design or expert firm. The main thing is that the contractor is a member of the SRO. In addition to the technical connection conditions, the working and design documentation must take into account the schemes for separating responsibilities between the GRO (gas supplier) and the owner of the building.
Where does the design of gas supply and gas distribution systems begin?
It should be remembered that before starting the design of any gas system, it is necessary to agree on and obtain technical specifications for gas supply.
Such documents can only be issued by gas distribution organizations. Having received the specifications, the owner of a plot of land or building can order a gasification project. But until he has the technical specifications in hand, it is too early to start developing the project - it is simply impossible.
To obtain technical conditions, the owner sends a package of documents to the regional gas service, consisting of:
- Applications for technical specifications. Its author can only be the homeowner himself or the owner of the site where construction is planned.
- Photocopies of a document confirming the identity of the author (a copy of the passport is sufficient).
- Documents confirming the ownership of the building and the legality of the construction: a contract for the sale and purchase of a house, an act of acceptance, a technical passport from the BTI. All documents are in originals only.
- When submitting an application at the stage of building a house - documents certifying ownership of the land: land purchase and sale agreement, certificate of ownership.
- Explications of the building on the ground.
This is interesting!
“Utility networks: internal and external communications”
More details
You may be allowed to connect your house to the gas main only if your area is included in the gasification plan.
And, of course, there must be a technical possibility of connecting to the main line (that is, it has a sufficient volume of gas to provide another point of consumption).
Specifications are prepared within a month. Connection to the gas pipeline route is carried out in compliance with a number of requirements (in particular, the requirement that the house be removed from the gas pipeline by a maximum of 200 m).
Gas consumers are divided into groups. Buildings with a design area of up to 250 m2 belong to the first group. They can be gasified, but the rate of energy consumption for them is limited to 5 m3 per hour.
Larger buildings are also connected, but it is much more difficult to obtain technical specifications for them: first you have to agree on the transfer of this consumer to the first group.
Technical conditions can also be obtained by contacting a special company, but this will entail additional costs. It will be cheaper and more rational to prepare the necessary documentation yourself.
Gas supply network design process
The first stage of gas supply design is the calculation of all indicators according to established rules. It is necessary to calculate the volume of gas that will be required to uninterruptedly supply all gas-consuming devices. Then, with the numbers in hand, you can begin to think through the trajectory of the future highway.
At this stage of designing a gas supply system, it is necessary to take into account all current building codes and requirements. The pipeline is the path from the gas pipeline to the underground reservoir. At the point of insertion, a valve must be installed that blocks the flow of energy resources, and at the point of entry into the building - a device for metering gas consumption.
After this, they begin to select equipment for gas supply, and this is also the task of the engineer (of course, taking into account the wishes of the client). Only a qualified specialist can select those models of equipment that, in terms of their functionality, are suitable for the operation of the pipeline being built.
All this equipment is purchased in specialized stores. They sell only certified products, so you don’t have to worry about the quality of the product.
All devices used in the gas supply system must have technical passports and certificates containing all the necessary marks. These documents will soon be transferred to the gas service employee, whose authority includes issuing permits to launch the system.
The designer prepares a plan for the placement of all equipment and a diagram for the distribution of pipes in the building. After this, it is necessary to carry out hydraulic calculations for the designed gas pipeline.
This is necessary to accurately determine the diameters of the pipes on each section of the pipeline and predict pressure losses in the gas pipeline, as well as ensure the operability of the network being created. And only after this they begin to draw up a specification.
As a result, the customer receives:
- A diagram of the entire gas distribution system - from the insertion point to the places where the equipment is connected.
- Sections of the house and plans of each floor, where wiring diagrams are drawn and equipment placement points are marked.
- Detailed diagrams of mounting units, equipped with installation tips and necessary explanations.
- Specification of building materials and equipment.
- Description of measures to protect the system from external harm.
- Tips for maintaining and operating the future gas network.
The design of a gas supply system ends with the submission of documentation for approval to the service that issued the technical specifications (its technical department). Gas service workers, having carefully checked the project and assessed it from the point of view of safety and compliance with rules and regulations, make a decision on whether to approve the project or return it for revision.
If the decision is positive, you can begin laying pipes and installing devices according to the project. Any changes that arise during the construction or repair process must also be agreed upon with the technical department of the gas service, otherwise the gas pipeline will not be allowed to be put into operation.
Remember that all documents documenting the completion of work are stored in the archives of the State Regional Office where you submitted them. This means that arbitrary changes to the project are illegal and construction must be carried out in strict accordance with it.
Gas saving
The cost of blue fuel is steadily increasing every year. Many owners achieve savings using the following methods:
- to save hot water, you need to use a shower rather than a bath - this will reduce heating costs (less liquid is required);
- installation of a double-circuit boiler;
- thermal insulation – by maintaining heat in the house, you will not need to spend a lot of fuel;
- installing double-glazed windows - this will reduce heat escaping from the room;
- it is important to pay attention to pipe routing - if done correctly, it will reduce consumption by 10-15%;
- installation of controlled heating - manual temperature adjustment;
- installation of the meter.
The correct selection of heating equipment affects not only safety. But also on the consumption of blue fuel. If you install a low-power boiler, the consumption will decrease. At the same time, it will be impossible to maintain a comfortable temperature. If the boiler is too powerful, the consumption will increase. It is important to approach the design correctly. Therefore, it is important that a competent employee does this. Incorrectly designed heating pipes and incorrectly selected equipment lead to serious losses.
Nuances of designing gas supply for residential buildings and industrial enterprises
1. Design of gas supply systems for residential buildings
Intra-house gas communications consist of:
- input;
- basement gas pipeline;
- common risers;
- apartment wiring;
- gas appliances.
Keep in mind that the gas pressure in the pipes inside a residential building should not exceed 0.003 MPa. For this reason, internal gas pipelines are also called low-pressure systems.
When designing internal gas supply, energy consumption by consumers - residents of the house - is calculated according to SNiP No. 2.04.08-87:
- If there is a gas stove in the apartment and a central hot water supply, the annual gas consumption rate per person is 2800 MJ (for natural gas) and 2540 MJ (for liquefied petroleum gas).
- If you have only a gas stove and a gas water heater, but without hot water supply, this norm increases to 8000 MJ for natural gas and to 7300 MJ for LPG.
- If the only appliance that consumes gas in the apartment is a stove, then the standards are average: 4600 MJ and 4240 MJ, respectively.
2. Design of gas supply systems for industrial facilities
The task of designing gas supply at an industrial facility is more difficult to complete than designing gasification for a residential building. The specificity is determined by the purpose of a particular industrial enterprise and individual building. An engineer needs even greater accuracy and attentiveness.
Industrial gas systems consist of:
- entry into the territory of the organization;
- intershop pipelines;
- intra-shop pipelines;
- GRP, GRU;
- PIRG (points for measuring gas flow);
- piping installations, which also consume gas.
At industrial facilities, the gas pipeline operates according to the following principle: gas enters the internal network through an inlet and is then distributed throughout the plant. A GOU is installed at the entry point - the main shutdown device, which is serviced by the city gas services (in this regard, it is advisable to place the device outside the territory of the facility).
As a rule, for industrial enterprises a dead-end branched gas pipeline with a single input is designed. However, in large industries, where it is strictly forbidden to stop the gas supply (at thermal and hydroelectric power plants, for example), ring networks are installed, sometimes even with several inputs.
This is interesting!
“Two-stage design: from development of technical specifications to designer’s supervision”
More details
Gas pressure in the city gas distribution system also plays an important role. When designing a gas supply network, the engineer calculates the optimal pressure level of the energy resource at the points where it enters the gas burners, taking into account the configuration of the workshops where gas is used and their location on the plant territory.
Design features, methods of installing an external gas pipeline
Gas supply systems are either underground or aboveground by design. Let's look at each type in detail.
Underground installation is the best option for locating gas communications. The pipes are laid in trenches of the appropriate depth (which must be calculated at the gas supply design stage in accordance with SNiP). However, this proven method is already becoming a thing of the past, giving way to the more modern trenchless installation.
Trenchless construction of a gas pipeline costs two to three times less, so it is often chosen. In addition to savings, it has other significant advantages. For example, the speed of laying gas pipes.
This is the most gentle method: it allows you to preserve the natural objects encountered along the way, the road surface, and buildings.
Pipes are laid using very simple technology. First of all, a pilot well is dug, after which, using directional puncture or horizontal drilling, a trunk is created in which the communications will lie. The internal surfaces of the excavation are strengthened with a casing pipe or the surrounding soil is stabilized with a solution.
When the solution has set, gas pipes are placed inside the well, sometimes in special protective cases. Without a casing, gas supply pipes are at risk of mechanical damage or problems due to stray currents.
This is a typical danger for gas lines in places where water pipes or heating networks cross them. Laying gas communications under the road also promises a lot of trouble if you do not protect them with a case. In addition, at the points where the pipe enters the building and exits the ground, it is also placed in a case (usually a steel pipe).
Both options for underground installation of gas pipelines are reliable, but even trenchless installation is quite expensive. Above-ground installation is much, sometimes up to 60%, more economical, but an open pipeline is much more vulnerable than an underground one. The pipes are placed on supports that follow the laying path.
Aboveground gas pipelines should be protected from all risks: mechanical stress and damage, rust, temperature changes. Such pipelines have to be protected so that they are not deliberately damaged by vandals or someone makes an unauthorized connection.
This imposes special requirements on the location of the open pipeline, which should be taken into account when designing and installing gas pipelines and gas supply systems: pipes are laid where unauthorized people will not have access to them, or they are placed at a certain height. In any case, the specific solution for the project is chosen by the design engineer. The customer's wishes are taken into account, if possible, but do not determine the result.
Before this, the engineer analyzes all the collected data on the local climate and landscape features, groundwater locations, soil chemical composition, etc.
Sometimes projects for combined laying of communications are developed: some sections of the route pass above the ground, others are hidden in the ground. At intersections with the roadway, gas pipes are laid strictly underground, but throughout the rest of the length they can be installed above ground. Be that as it may, only the designer can decide where and how best to lay the gas main pipes.
Requirements for designing an external gas pipeline
Clause 26 of the technical regulations includes the following rules that must be observed when designing external gas pipelines:
The type and method of laying , as well as the distance, vertical and horizontal, to the nearest object (natural or artificial - building, structure, etc.) are determined:
- pressure in the pipeline;
- density of area development;
- levels of responsibility of surrounding buildings.
All this must be taken into account to ensure that natural gas transportation is safe and does not create additional risks for nearby facilities.
If the project includes an underground part of the gas pipeline, then its installation depth depends on:
- climate, geological and hydrological conditions in the area;
- external influences on the gas main.
If the gas pipeline is crossed by power lines whose voltage exceeds 1 kW, then the gas supply system must include:
- devices and structures that protect gas pipes from falling electrical wires in the event of their break;
- devices and structures that protect pipes from power line supports falling on them.
The gas pipeline must also include appropriate protective devices and coatings, in accordance with clause 27 of the technical regulations, in places:
- the pipe enters the ground and exits outside (if there is an underground part of the gas pipeline);
- intersections of tunnels, canals, underground collectors (to protect them from gas from the underground section of the gas pipeline);
- passing through the wall of a gas well;
- passing through the building structure of the house;
- detachable metal-polyethylene connections in the underground part, if any;
- intersections with an oil pipeline or heating main.
pp. 28-300 of the technical regulations prohibit the design of high-pressure gas supply systems in the following places:
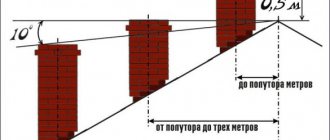
- In premises of categories A and P of explosion and fire hazard, unless it is a gas metering point or a gas distribution center building. Gas pipes in them cannot be laid either above or below the room, or along its walls.
- On automobile and pedestrian overpasses built from flammable materials of groups G1-G4 or from non-combustible materials.
- In the territories of warehouses intended for storing flammable materials of the above groups.
- In industrial buildings built from combustible materials of the above groups.
- In public buildings and structures - above the roof and along the walls.
Important! The design of an external gas pipeline must contain shut-off valves that allow you to disconnect a particular section of the gas pipeline, a technical device (the types of locking devices, their number and placement points should be described). This function is used when you need:
- localize or eliminate an emergency in the gas supply system;
- carry out repairs and restore communications after an accident;
- liquidate, mothball the gas pipeline.
How much does a private home gasification project cost?
The estimate for gasification of a private house includes all installation costs and payment for designers. The price is affected by:
- How standard is the procedure (we have to take into account the terrain features);
- distance from utility networks to the wall of the house;
- type of selected metering devices;
- method of laying the pipeline;
- connection costs, regional prices apply, benefits are determined at the level of constituent entities of the Federation or municipalities;
- cost of materials used;
- soil feature (for underground installation).
The cost of a gasification project for a private home depends on the level of infrastructure development and distance from the center. In the Moscow region it fluctuates around 40 thousand rubles. In the Leningrad region, the suburbs of St. Petersburg - up to 30, in Kazan from 18 to 40, the largest spread, Saratov and regional areas from 8 to 16 thousand rubles.
Selecting an organization engaged in the design of gas supply facilities
Even if you want to develop a housing gas supply system project on your own, you will not succeed. There are also few opportunities to save money on this type of work. This document is mandatory for construction, reconstruction and repair, and in order to develop it correctly, you need to take into account a lot of rules and regulations. They are contained not only in state standards, but also in codes of rules. You will also have to study reference books and technical literature.
Professional designers know and can do all this, which is why you should contact them. Choose dedicated design departments, not just freelancers offering design services.
In almost any city there are several companies that provide gas supply design services in residential buildings, and the most reliable of them, as a rule, are members of self-regulatory organizations.
These are the ones that it is advisable to choose if you want to be sure of timely, professional and high-quality execution of your order.
Membership in an SRO opens up additional opportunities for companies to select clients, receive expensive orders and participate in tenders (companies offering gas supply design and not included in any SRO are deprived of all this). For them, a poorly executed project is a blow to their reputation and financial losses.
The SRO only accepts firms that meet a certain set of requirements - for example, having at least two professional design engineers on staff.
These organizations undergo regular inspections every three years to confirm their knowledge and skills. Checks are carried out by a special commission, which issues a certificate to those who have demonstrated the required level of training.
To carry out orders in the field of gas supply design, a SRO member company must have a license for this type of activity. Be sure to check whether the contractor has a license before signing an agreement with him to develop a gasification project for a building.
The contractor must not only draw up the project itself, but also undertake to coordinate and approve it, and undertake all the work of taking measurements on site and visiting gas services. Include this clause in the contract to minimize your design hassle.
Safety precautions
The gas sector has been and remains one of the most vulnerable areas of the energy supply system. Usually, Gorgaz employees, when carrying out design and installation work on gasification of buildings, warn future owners about the most important points of compliance with safety regulations.
The greatest threat is posed by excavation work in the area of underground gas communications and attempts to unauthorizedly connect home gasification systems to the network. Very often, plastic pipes are used to supply gas, which can be easily damaged even with a shovel, especially since you should not lay gas supply systems and water or electrical lines in the same trench at the same time.