When, back in the 17th century, the French architect Francois Mansara proposed constructing living spaces under the roofs of buildings instead of traditional attics, he most likely did not even imagine how durable and popular his idea would be. Today, almost 400 years later, the construction of houses with mansard roofs is carried out in almost all countries of the world. And this trend is not abating. On the contrary, more and more homeowners are choosing architectural projects with attics. There is a simple logical explanation for this. A do-it-yourself attic roof is original, stylish and profitable.
Mansard roof
Functions and planning solutions
The functional and planning aspect of using the attic floor is determined mainly by the purpose of the building, and the planning features are related to the structure of the building and the rooms below. The attic floor can occupy the entire area of the building, or part of it, but, as a rule, within the limits of the underlying walls of the base building. Architectural and planning solutions can have a wide range, and premises can have any area and configuration.
When designing an attic floor, the choice of a planning option should be based on an analysis of the planning scheme of the base building, determined by studying the social needs of a given residential building and made in accordance with current regulatory requirements.
It is necessary to distinguish between three main types of attic floors:
- attic floor with the formation of a separate floor on one level;
- attic floor with two-level development;
- an attic floor with a spatial organization of a mezzanine floor with a two-level development of the upper floor of the base building.
Video description
In the video you can see an attic under a hip roof:
Half-hipped roofs, of course, look more presentable than all the others. There is room for experimentation in these designs. For example, organize a small balcony as a relaxation area. Or make an open terrace. There are many options, the main thing is to correctly formulate your plan in terms of aesthetic appearance, plus the functionality of the additional part. That is, the balcony should not be just an element of architecture. It should become a full-fledged exploited zone.
Semi-malm mansard roof with balcony Source roomester.ru
Multi-forceps
It is probably difficult to say about the popularity of this type of roofing structure. The roof itself is difficult to construct. It requires a large amount of building materials, and the waste is significant. Especially roofing. But this roof has one big advantage - with its tongs it divides the room into several zones that can be organized for different purposes. And although this is also easy to do with other roofs, multi-gable roofing is easier in this regard.
It should be added that each zone will have its own opening in the form of a door or window. This means there will be no need to install skylights, which are expensive.
Multi-gable roof of a private house with an attic Source remontik.org
Tent
This is another hip roof with an attic. It consists of four identical slopes with the shape of an isosceles triangle. These types of roofs are rare. It's all about the complexity of organizing the space underneath. On all sides, slopes form zones near the ceiling that are practically impossible to use. That is, there is little usable area under such a roof.
But, as practice shows, if it is possible to use the under-roof space for living space, then even under a hip roof it will be organized. After all, the main thing is to insulate the roof structure and create living conditions. One of them is natural light. The photo below shows just such an attic. Notice how well the balcony fits into the architecture of the house, which mainly serves as a window opening.
Hip roof over the attic Source blues-dev.ru
Interior
When designing the interior of the attic floor, you should take into account some characteristic geometric shapes of the premises. We are talking about the placement of stairs, the furnishings of the bathroom and toilet, kitchen, as well as the placement of doors. The free height of staircases in relation to sloping roof surfaces should be taken into account. There are no difficulties when the direction of the stairs is parallel to the slope of the roof or the stairs are placed along the middle axis of the building. Free height is usually not a problem, but the placement of possible parts and components of the roof structure should be taken into account.
The furnishings of the bathroom and toilet should be taken into account the sloping surfaces of the roof, limiting the full height.
Placing doors can be challenging not only because of determining the height of the doorway itself. Here it is also necessary to take into account the unhindered opening of the door, taking into account the sloping wall.
Shed roof with attic
To obtain a simple and spacious attic, pitched roofs are often made. That is, in a room of this type there is one normal wall located vertically, the other wall is an inclined wall, that is, a roof slope.
With a lean-to structure, windows are most often installed on a sloping wall, but windows can be installed in a vertical wall.
A pitched roof is simple to construct, but requires careful calculations.
Fire requirements
Fire safety requirements, especially evacuation routes for the attic floor, depend on the planning structure of the base building: if the functions of the base building and the functions of the attic floor coincide, the staircase-elevator assembly of the building to which the attic is adjacent is used for escape routes; if the functions of the base building and the attic floor do not coincide, creating escape routes requires the installation of special communications, which can be located inside or outside the building and have isolated exits, including between two buildings.
It is allowed that there are no exits to the staircase from each floor of an apartment on two levels, provided that the premises are located no higher than the 6th floor and the apartment is provided with an additional exit. It is allowed to install emergency exits into the common staircase from creative workshops, provided that communication through the vestibule is possible.
When placing offices and offices in the attics of residential buildings with no more than 9 floors, entrances and emergency exits must be isolated from the residential part of the buildings. It is allowed to accept staircases of the residential part of the building as a second emergency exit, while the exit is provided through a vestibule with fire doors. A roof window can serve as a rescue opening through which people from the premises can be evacuated.
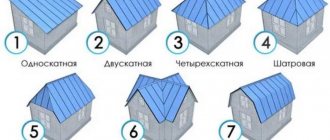
Varieties
All mansard roofs can be classified into 4 categories, each with different designs. Moreover, such attics can be single-level or two-level. It is easier to build a one-level attic. As a rule, this design involves the construction of a conventional gable or sloping roof.
Two-level attics are more difficult to construct. This design involves the construction of 2 rooms at different levels. In this case, the method of combining supports is used.
In the photo of the attic roof you can clearly see the design options for such structures. Additionally, a balcony can be provided. It is constructed by analogy with a window opening.
But this possibility depends on the load-bearing capacity of the walls. If it is not enough, a balcony can be built using additional supports.
Important rules for designing an attic floor
The choice of planning option for the attic should be based on an analysis of the layout of the base building.
A huge role, depending on the level of visual perception, belongs to the lines and shapes determined by the geometry of the roof. An important condition for the placement of attic rooms is their relationship with the communication structure of the building - the foundation.
It is necessary to interact between the designed and existing engineering systems and ensure their collaboration. (In cases where the functions of the attic do not coincide with the functions of the main building, the development of special technical solutions is required).
Of particular importance are the shape and dimensions of the premises, the choice of translucent fencing (vertical or inclined windows), their placement, taking into account the construction of the interior in conjunction with the formation of architecture.
The structural design, material of enclosing structures and attic parts are determined taking into account the unity of the design and architectural forms of the base building (The use of lightweight structures, parts and products is the main requirement).
An attic with a steeply pitched roof requires a special approach to choosing roofing material, providing thermal protection, sealing and waterproofing.
The construction of an attic without relocating the residents of the main building requires a special method for maximum safety of work, limiting the weight of structures and parts, and constructing protection and safety elements.
Useful tips
When choosing an attic design, you should take into account the layout of the house as a whole and the efficiency of using individual rooms and spaces. When erecting an attic roof, it is recommended to follow one simple rule - its boundaries should not extend beyond the walls of the house located below.
Before you decide how you will use the premises and rooms located under the roof, you need to carefully calculate the costs of constructing the attic and its engineering support. And from this, make a decision on the purpose of the attic space.
And the most important point is that when building a roof, it is extremely important to provide it with high-quality hydro- and thermal insulation. They will provide complete protection from leaks and other negative environmental influences.
Did you find this article helpful? Please share it on social networks: Don't forget to bookmark the Nedvio website. We talk about construction, renovation, and country real estate in an interesting, useful and understandable way.
Attic floor structures
The design and geometry of the roof determines the architectural form of the crowning part of the building, and this, in turn, is the need to create unity of structural and architectural solutions in conjunction with the internal space determined by the functional purpose.
The choice of one or another architectural and construction system for the attic floor includes the determination of the load-bearing structure and fencing, as well as the organization of construction work at the site in the built-up part of the city.
For attic floors, it is recommended to choose lightweight structures and materials, since, on the one hand, their transportation to the floor should be as easy as possible, and on the other, the dead weight of the structures should be minimal, taking into account the load that will be transferred to the existing building.
These premises generally indicate that structures should be selected from wood-based materials or thin-walled cold-formed metal profiles. The use of stone and concrete materials to create a load-bearing structure for the attic floor on a building being restored or newly constructed is not recommended.
The roofing covering must meet the same prerequisites, that is, it must be made primarily of lightweight materials in the form of metal sheets, metal tiles, and the like. In cases where this is necessary in order to preserve the environment of an existing building, the covering is made of clay or cement-sand tiles, non-ferrous metal and other materials.
The internal cladding of the attic fence is made mainly of plasterboard sheets. It is advisable to carry out internal partitions by element-by-element assembly with lining with plasterboard sheets on racks made of thin-sheet profiles.
The attic floor is more susceptible to heat loss than the lower floors for the simple reason that there is no “thermal cushion” above it. It has a large total surface of contact with the external environment. Therefore, for reasons of comfort and economy, effective and thorough thermal insulation is necessary. With increased thermal insulation, more stringent requirements are placed on the thermal seal and its implementation. This seal prevents warm air from penetrating through the sealing layer. For thermal insulation, effective insulation should be used, for example, a mineral wool slab, with = 0.004 W/m oC according to calculation. A vapor barrier layer is provided on the inside of the insulation (facing the room), and waterproofing on the outside. It is also important that there is a sufficiently effective ventilation space between the top side of the insulating layer and the underside of the roof covering, which would facilitate ventilation and remove the inevitable flow of moist warm air that will penetrate through the vapor barriers and the insulating layer.
Selection of cross-section and sheathing thickness
The stage begins with choosing the type of sheathing: solid (selected for low slope slopes or low self-supporting abilities of the roofing) or loose (mounted on medium and steep slopes, optimal when working with rigid sheet materials). Next step by step:
- Based on the sum of the loads, the cross-section and thickness of the sheathing lumber is determined.
- The position of the first strip or the bottom edge of the sheet is determined.
- Taking into account the recommendations of roofing manufacturers, roof slope, rafter pitch and SNiP standards, the optimal sheathing pitch is selected.
- The need for strengthening of individual sections (if any) is clarified. Solid flooring or double boards are laid in the upper zone of slopes, under valleys, stairs or heavy objects.
- Manually or using programs, an approximate layout of the planks is calculated.
- A calculation of lumber and fasteners is carried out, the result is rounded up and the margin is increased by 5% (from 10% for a complex attic roof configuration).
Insulation of attics
The attic covering should not only protect the house from precipitation (rain, snow), but also prevent the cooling of the rooms on the upper floor. Warm air always rises, so the air temperature under the ceiling is on average 2°C higher than the middle height of the room. With the same thermal insulation capacity of the walls and roof, heat loss through the latter will always be greater, which is due to the large temperature difference between the outer and inner surfaces of the attic covering. In addition, the moisture content of warm air is usually higher than that of cold air, so condensation on the ceiling of the upper floor can form at higher temperatures than on the inner surface of the wall. Therefore, more stringent requirements are imposed on the thermal protection of roofing coverings than on external walls.
Heat loss through the attic is quite large, so properly insulating its coating can bring a tangible economic effect. When comparing two typical two-story houses with an area of 205 m2 with attics insulated in accordance with previous and new requirements, it was found that the modern level of thermal protection allows reducing heat loss through the coating by more than 3 kW and thereby significantly reducing the power of the heating system and reducing costs heating the house.
Icicles hanging from the roof pose a significant danger to people. In the process of knocking down icicles, there is a high probability of damage to the roof with all the ensuing consequences. One of the reasons for the formation of icicles in winter is insufficient thermal insulation of the roof covering. The snow, heated from below by the heat passing through the poorly insulated covering, begins to melt, and the water flowing from the roof turns into icicles. Only with well-performed thermal insulation will icicles not cause problems in winter.
How to calculate roofing coverage?
Work begins with clarifying the parameters of the slopes (area, method of arranging the eaves overhang, indentation to the gutters) and the usable area of the roof coverings. The latter value is indicated by the manufacturer and varies significantly for sheet materials.
In particular, it is reduced when the slope of the slopes is low and vice versa (consumption for overlap with increased requirements for tightness increases by 20-30%). The calculation itself is carried out according to a simple scheme:
The area of the slopes is divided by the usable area of the sheet or small-piece product.- The found value is rounded up and multiplied by a correction factor of 1.1.
- Using calculators or manually, an approximate layout of materials is drawn up and their quantity is specified.
Design features
The moisture content of warm indoor air is higher than that of cold outdoor air, so the diffusion of water vapor (both through the attic covering and through the outer walls of the building) is directed from the room to the outside. The outer (upper) part of the roofing is a waterproofing layer that does not allow water vapor to pass through easily and promotes the formation of condensation moisture on the inner (lower) side of the roof. The consequences will not be long in coming: despite the well-done waterproofing of the roof, wet spots and mold will appear on the inner surface of the roof covering, the thermal insulation qualities of the insulation will deteriorate, droplets of water will begin to fall from the ceiling (not due to a roof leak, but as a result of condensation of water vapor) .
Considering the negative impact of moisture on the thermal insulation characteristics of materials, the insulation must be protected from moisture by water vapor contained in the air of the room with a layer of vapor barrier material, placing it on the inner (bottom) side of the insulation. To remove moisture that for some reason has entered the heat-insulating material, a ventilated air layer should be provided between the insulation and the outer (waterproofing) layer of the roofing.
Very often, non-residential attic spaces are converted into residential attics, preserving the existing rafter system. At the same time, in an effort to minimize the additional load on the building’s load-bearing structures, lightweight insulation of low density is usually used. Under the influence of wind, low-density insulation is “blown through,” accompanied by heat loss; therefore, in order to maintain the heat-protective characteristics of the structure, a layer of windproof, vapor-permeable material must be laid on the surface of the thermal insulation adjacent to the ventilated layer.
When insulating an attic, you need to remember that heat loss occurs not only through the covering, but also through the end wall. Therefore, the gable of the house also needs to be well insulated in accordance with modern requirements.
Gable roof with attic
A roof with two slopes allows you to create attic spaces with a uniform rise in the ceiling.
In this case, the roof is located at the same angle to the walls, and in the adjacent areas an area with minimal height and functionality is formed.
To get a full-fledged room on the roof, it is enough to build a roof with an angle of 45 degrees. This design is optimal for houses whose width does not exceed 6 meters.
According to many developers, it is believed that a slope of 45 degrees is too much. A slope angle of 40 degrees is considered extremely convenient. This angle allows you to increase the usable area of under-roof spaces and rooms.
Quite often, with a gable structure, an attic is also equipped. Some developers also build a small balcony.
There are several options for creating a balcony on the attic floor. It can be arranged on load-bearing beams that serve as support for the attic. Or build columns on which the balcony slab will rest.
Insulation of attic coverings
Structurally, the attic covering consists of a system of rafters installed in increments of 600...1000 mm. The space between the rafters is filled with heat-insulating material (insulation). It is recommended to use mineral wool slabs based on basalt fiber or fiberglass as an insulating material. Thermal insulation boards or mats can be laid in one or several layers, and the total thickness of the insulation layer depends on the thermal conductivity coefficient of the insulation, the value of which must be indicated in the certificate of conformity.
A ventilated air layer is arranged between the insulation and the roofing. On the inside (bottom) side, the attic covering is protected with a vapor barrier material and finished with plasterboard sheets, lining, etc. If the cross-sectional height of the rafters is less than the required thickness of the insulating layer, wooden blocks are attached to the rafter legs with screws or nails. Insulation boards are placed between them in such a way that there is an air gap between the thermal insulation and the roof. If the cross-sectional height of the rafters is insufficient, horizontally located wooden antiseptic bars can be attached to them. In this case, one layer of insulation is located between the rafters, and the other - between the horizontal bars.
Broken roof
This is one of the types of roofs with two slopes, with the difference that each slope consists of two parts.
This structural subtlety allows you to change the slope of the slope, due to which, accordingly, the height of the wall increases. Obviously, with a broken roof shape, the area of the rooms increases, and the under-roof spaces can be used more rationally.
When deciding to build a broken roof, you must be prepared for the fact that you will also have to build a rather complex rafter system. However, there is also a positive aspect. The load from snow in winter on this type of roof will be much less, since the snow will slide off quite quickly.
Ventilated air layer device
The width of the air gap between the insulation and the roof depends on the profile of the coating material. In the case of using profiled sheets of galvanized steel, tiles, metal tiles and other corrugated sheets, the thickness of the ventilated air gap must be at least 25 mm. When installing a roof made of flat sheets (asbestos-cement sheets, galvanized steel, soft bitumen tiles, rolled materials,...), an air layer of at least 50 mm thick is required. Ventilation of the air gap is carried out through holes in the eaves and in the ridge.
Services for calculating the required parameters
To simplify and verify the calculation, it is recommended to use:
- Professional programs such as Archikad, 3D Max, KZ-Cottage or ArCon (the latter is suitable for people without experience or construction education).
- Google SketchUp, Home Plan Pro, VisiCon and their analogues.
- Construction calculators and online services (stroy-calc.ru, stroysvoimirukami.ru, zhitov.ru, zamer-doma.ru).
Professional programs and applications allow you to create projects in 3-D projection and evaluate the expected appearance of the attic. The time spent on them always pays off - ordinary drawings do not give a full idea of the bulkiness and influence of the attic roof on the design of the house.
Construction calculators require accurate initial data and are most often used when designing power structures and pie, choosing the optimal option and calculating materials.
Video tutorial on how to design a mansard roof in Archicad 16:
Protection of insulation from blowing
On the side of the ventilated air layer, the heat-insulating material must be protected with a windproof, vapor-permeable membrane. The use of vapor-proof materials such as roofing material or polyethylene film as a windproof membrane is completely unacceptable! It should be noted that special membranes perfectly allow water vapor to pass through, but do not, however, allow water in the liquid phase to pass through, and therefore prevent the insulation from getting wet as a result of moisture condensing on the inner surface of the roof covering from the side of the air gap. This property of materials makes it possible to reduce the thickness of the air gap to 25 mm, regardless of the profile of the roofing, which is especially important when insulating an attic along existing rafters: an air gap of small thickness eliminates the need to install additional bars on the inside of the rafter legs. The height of the rafter leg will be sufficient to accommodate insulation of the required thickness and provide a ventilated air gap.
When building a new house, windproof material is laid over the rafters and secured with wooden blocks. When installing an attic in an existing attic, windproof, vapor-permeable material is attached with special slats to the existing rafters. The membrane also protects the insulating layer from moisture from precipitation (rain, snow) entering the air gap during strong winds or through leaks in the coating. The material is laid on the insulation with an overlap of 150...200 mm along the dotted lines marked on the material sheet, and attached to the structure with wooden slats, nails, staples or glue.
Advantages of a semi-attic
The issue of increasing the usable area of the house by arranging an additional upper floor is one of the most pressing in private construction. The construction of a full second (third or more) floor requires serious financial investments and significantly increases the final cost of construction work. The most popular solutions include the construction of an attic roof - this allows you to equip additional living spaces directly under the roof. The walls and roof of the attic floor are roof slopes. If there is a desire to create vertical walls in the attic floor, partitions are installed.
A semi-attic is a fundamentally different approach to arranging an additional floor. A half-attic refers to a living space, the side walls of which are formed by a vertical building structure and a roof slope.
The vertical part of the side outer wall of the attic does not exceed 1.5 meters.
Unlike the attic, in the semi-attic the side vertical walls are load-bearing. The advantages of this design include rational use of internal space and the ability to perform practical vertical glazing.
Significant heat loss occurs through the roof structures of the house, so when building an attic floor, special attention must be paid to the thermal insulation of the roof. It is much easier to insulate a half-attic, since its walls are built from the same material as the entire frame of the house. It should be noted that the final cost of constructing a semi-attic floor is higher than an attic floor. In addition, it is necessary to take into account some features of the arrangement of a semi-attic rafter system.
Designing a semi-attic roof
When developing a project for a semi-attic roof frame, it is important to choose the right angle of inclination of the roof. Due to the architectural features of such a building, the roof is rarely made high, so as not to disturb the proportions of the building. But at the same time, the roof must successfully cope with operational loads, including snow. A semi-attic is usually equipped with a pitched or gable roof. It must be taken into account that the rafter system must be non-thrust so as not to transfer the thrust load to the walls of the attic
.
The prepared diagram of the rafter system should reflect not only the location of the structural elements, but also the principles of their fastening. To prevent the rafters from transmitting thrust to the walls, a roof frame with layered rafters is erected, and the rafter legs must be fastened in a special way, with certain degrees of freedom. The non-thrust system is usually used in the construction of buildings made of stone, brick and other block materials.
The installation of a system with layered rafters requires laying a mauerlat and installing a ridge girder, which must rest on gables or special strictly vertical posts.
In order for the rafter to bend and not transfer thrust to the walls, one of its supports must be fixed, but be able to rotate freely
.
In this case, the second support is movable and freely rotating
.
This installation of rafters can be done in three different ways. Be sure to read: Splicing rafters along the length: the right methods
Installation of non-propelled layered rafters: method No. 1
The lower part of the rafter leg can be hemmed with a support beam, or a tooth can be cut into it to rest against the mauerlat. In this case, in the upper part of the rafters it is necessary to make a horizontal cut with a bevel. The depth of this cut should not exceed a
= 0.25h, and the length of the support area should not be more than
h
- the height of the rafter section.
The bevel of the trim allows you to avoid the spacer load when bending the rafters - a cut without a bevel will rigidly rest against the purlin with its side cheek. The length of the beveled cut must be at least two a
.
If it is not possible to trim the top of the rafter, it must be hemmed with a piece of board of the same section as the rafter leg and secured on both sides with wooden nails or mounting metal plates. The upper ends of the rafter legs are laid freely on the ridge beam. In a gable structure, fastening to the purlin is carried out according to the principle of a sliding support, while the rafter legs are not fastened together. Thus, this version of a gable roof can be considered as a complex of two separate single-pitch structures adjacent to each other.
The hemming of the upper part of the legs of the rafters or the sawing is done horizontally. Installing rafters with a change in the pattern of support of the rafter legs on the purlin leads to the occurrence of thrust loads.
Installation of non-propelled layered rafters: method No. 2 and method No. 3
Installing rafters in this way is the most common option for installing a non-thrust structure when building a gable roof. The lower part of the rafter leg is carried out on a slider, while the top needs to be secured, for this purpose
:
- the rafters rest against the purlin or against each other and are connected using wooden pegs or jagged metal plates;
- the upper parts of the rafter legs are fastened with a bolt or nail connection.
Particular attention is paid to the principle of attaching the lower part of the rafters to the Mauerlat
. It is necessary to secure the rafters in the design position, for which one nail is driven into the side surface at an angle on both sides. Either a single long nail can be driven in from above or a flexible steel plate can be installed. You can also use steel corners - in this case, the rafter is fixed on both sides with corners, and nails are not driven into it. Additionally, these elements of the truss structure are fastened with flexible wire strands - they prevent wind overturning of the roof without interfering with the main fastening to work as a slider.
If you use rigid fasteners with a large number of nails or self-tapping screws, the attachment point for the lower part of the rafter will transfer the spacer load to the power plate.
Features of the third installation method include rigid pinching of the ridge assembly, while in the lower part the rafters are fastened to a slider
. It should be noted that this design provokes the occurrence of a strong bending moment in the ridge unit, which can cause its destruction. In this case, the deflection of the rafters outside the ridge unit is minimal. There are certain difficulties with independently calculating the maximum bending moment of such a ridge unit, so it is recommended to use calculation formulas for beams with two supports (single-span). The device of the nodal connection with rigid pinching of the rafter legs in the upper part makes it possible to construct a rafter system with a certain margin of safety.
Be sure to read: Correct installation of rafters with your own hands
Vapor barrier device
On the inside (bottom) side, the thermal insulation material is protected from moisture by water vapor contained in the air of the room by a layer of vapor barrier - plastic film, glassine, roofing felt or foil vapor barrier material. The material is laid with an overlap of 100 mm and the seams are taped with adhesive tape. The use of adhesive tape not only ensures the tightness of the seams, but also allows you to reduce the amount of overlap to 100 mm (both vertically and horizontally) regardless of the roof slope. The film is attached to the rafters or beams with thin wooden slats. Foil materials are laid with foil towards the room, and it is advisable to leave a small gap between the vapor barrier and the inner lining. In this case, the shiny surface of the aluminum foil will reflect thermal radiation coming from the room to the outside and reduce the amount of heat loss through the attic covering.
From the inside, the attic room is lined with plasterboard sheets, plywood, boards or lining, which are attached to wooden bars or metal profiles installed on the inside of the rafter legs.
Purpose
The rest - furniture, finishing details, accessories - depends on what you plan to use the attic for. It may contain:
- Bedroom . The most obvious solution is that a bedroom in the attic gives a feeling of comfort and security. You can close the hatch, and no one will climb on it, and the low ceiling will not interfere with lying in bed - whether sleeping, reading, or watching videos.
A bedroom in the attic gives a feeling of comfort and security
- Children's room It is inconvenient for a small child - not all attics have stairs that allow you to climb up with a baby in your arms. But for a tomboy of ten years or older, it’s quite enough. Children usually love heights; playing in the attic is interesting, it’s like a tree house, only in the house itself. You just need to make sure that you cannot fall from the stairs, and that the furniture is free of sharp corners.
- Kitchen . Quite an original solution, but if you don’t have enough space on the lower floors, it’s quite possible. Of course, you will have to sweat while conducting the water, and the ceiling must be high for this, but nothing is impossible. The furniture should be light, and so should the refrigerator. The overall design is usually cheerful.
- Living room . If your guests love the exotic, you can create a living room in the attic. A soft sofa, souvenirs and trinkets, a shelf with books on the wall look great in combination with sloping windows and an oddly shaped ceiling.
Choose everything to match the interior style of the room.
Home cinema
- Cabinet . If you don't like to be disturbed while working, an office in the attic is a great solution. Place the table by the window, install electricity and enjoy your privacy - it will be difficult for your family to reach you and they will think ten times before distracting you.
- Home gym . If you have reliable floors and good sound insulation, you can set up a gym in the attic. Hang mirrors on the walls, install a couple of basic exercise machines, or make room for dance training. The main thing is to make sure that jumping in the attic below will not cause the ceiling to swing.
- Library . The attic is the perfect place for it; it will be especially good to read when it’s raining, listening to the sound of drops on the roof. The main thing is that the shelves must be resistant to moisture, otherwise if the roof leaks, you have a chance of losing your entire collection.
Home gym
A billiard room, a home theater, a storage room for supplies - literally anything can be located in the attic, even a greenhouse or a darkroom for photographs.
Advice Before you start furnishing the attic, draw its plan on paper, and then build it in a special program that designers use. If the result satisfies you, you can bring it to life.
Quite an original solution
You can choose any colors for the interior, but cold and light ones are usually recommended - they will make even the lowest ceiling seem higher.
VIDEO: The attic floor is a great place for a cozy pastime
Attic floor design
Ideas for a beautiful interior
Design features and strength
The rafter structure requires sliding and a certain freedom, otherwise all its work will be incorrect. Typically, rafter legs are attached at one end using the sliding support principle, and at the other using a hinged connection. This fastener is the most correct and effective , as it fully supports the entire structure in the correct condition and allows it to work correctly.
The ridge girder must be firmly abutted against the gables to prevent the structure from shifting due to uneven distribution of forces; vertical posts alone will not be enough for this.
To give stability to the entire system, the bottom of the racks that support the purlin are rigidly pinched by cutting into the beam, and also attached to the floors. A horizontal screed is also mounted , securing it to the posts with nails. This contraction is a pre-failure element for the entire structural system and can save the situation if the load on the roof is too great and deformation occurs.
Photos of attic rooms
We offer you a selection of photos of attic rooms for inspiration.
We hope that one of these options will help you build the attic of your dreams.